January 15, 2020 Admin Home page » MRI and CT scan of the brain Views: 6044
First, it is necessary to consider the general indications for which an MRI of the child’s brain may be prescribed. Magnetic resonance imaging is a study that can most accurately detect diseases of the brain, as well as cranial nerves and blood vessels in the early stages. This study has the highest degree of visualization and, accordingly, high diagnostic accuracy when it is necessary to detect the presence of tumors and many other brain injuries.
The doctor prescribes an MRI of the child’s brain when he experiences:
- frequent dizziness for no apparent reason and headaches;
- fainting;
- there is a decrease in the quality of vision and deterioration of hearing for unknown reasons;
- convulsions (even one-time);
- delayed development of psychomotor skills and speech;
- mood swings and causeless changes in behavior;
- brain concussion.
Is it possible to do MRI for children?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a painless and safe examination method. There is no need to be afraid of this diagnosis, because during its implementation there is no effect of radiation and x-rays on the body.
In the images obtained as a result of the examination, you can see organs and tissues that are not visible during other types of diagnostics. The magnetic fields used are harmless, so MRIs can be performed on children.
At what age can an MRI be done?
Some clinics agree to only accept children over 5 years old for examination. But if necessary, pediatric MRI is performed even on newborns.
Age restrictions are due to the fact that the child must lie still for 15-40 minutes during the procedure. If this does not work, the device will produce unclear images that are of no diagnostic value.
It is difficult for children to withstand so much time in a motionless position inside a confined space. The situation is complicated by the fact that MRI machines make noise during operation. To perform an MRI on a newborn or a child under 5-6 years old, light anesthesia is often used.
Indications and contraindications
Tomography is prescribed for children with various diseases. An examination is required if a small patient:
- pathology of the brain and spinal cord;
- skeletal diseases;
- diseases of the abdominal, thoracic, and pelvic organs;
- problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system, eyes, ears;
- tumors (for example, Wilms tumor, which appears in children aged 1-3 years).
Using the procedure, you can identify diseases of internal organs, structural defects of soft tissues, see cysts, hematomas. We recommend periodic preventive examinations for children who engage in active sports if there is a high risk of injury. The results of impacts may not appear immediately, but with the help of MRI, their negative consequences can be detected and treatment can begin.
MRI is not performed if the child has internal metal implants. They can distort the results of the examination. But they are extremely rare in children. If a child under 5 years of age cannot be given anesthesia, the procedure may be denied.
MRI of the brain
How are MRIs done for children? Is it dangerous to do an MRI of the head if the child is 2 years old? The impact of the magnetic field on the body is so small that it is not recorded as dangerous. After the procedure there are no complications on the nervous system or decreased immunity.
The tomograph scans the brain in longitudinal and transverse sections every 5 mm, then a computer program creates a three-dimensional image on the display. The doctor can monitor the condition of the organ and identify pathology even in its infancy.
In what cases do pediatricians prescribe brain MRI for children? The doctor will refer you for examination if the baby has disorders of the central nervous system, which is responsible for correct reflexes. This can be determined by the following condition:
- developmental delay;
- decreased vision/hearing;
- tendency to seizures;
- dizziness, fainting;
- other deviations in behavior.
The work of the brain coordinates all physiological processes in the body. If a pathology is detected, the child is urgently examined. It is necessary to examine the baby even after the first seizure appears - they can occur with an increase in body temperature. This condition may not be dangerous, or it may indicate a serious illness.
Causes of pathological abnormalities:
- birth injuries;
- intrauterine pathologies;
- penetration of infection;
- toxic effects;
- head injuries.
Children can be the victim of an accident - a fall or a strong blow. Parents are required to show their child to a doctor if this happens. Fainting and headaches can clearly indicate a concussion, especially if they are accompanied by vomiting. Children under 3 years old cannot tell anything, so mothers should be vigilant and immediately take their child to an appointment with a pediatrician.
How is MRI performed?
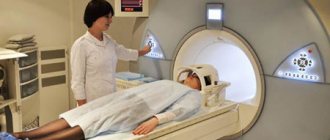
The child is placed in the desired position on a special table of the device, fastened and brought inside the tomograph. To diagnose some diseases, a study performed with contrast is required. A special substance is injected into the body, with the help of which the vessels are contrasted during the examination.
The procedure is painless, so even a child can have an MRI without pain relief (anesthesia). Depending on the requirements of the clinic, parents are asked to remain in the reception area or are allowed to monitor the progress of the diagnosis with the laboratory assistant.
To prevent the child from being frightened by noise, he may be offered earplugs or headphones through which music can be heard. If the baby was given a sedative or anesthesia, then his condition is monitored using devices. An MRI is performed on a child without anesthesia if there is no doubt that he will lie quietly during the examination.
Under anesthesia
For young children, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. After all, it is necessary that they lie still during the diagnosis. If the child is conscious, he may be afraid of closed spaces (except for cases when open MRI machines are used) and noises.
Anesthesiologist administers anesthesia. Sedatives are administered on an empty stomach. The fasting period for infants should be 2-4 hours. Children over 1 year of age should not be given food for 4 hours before anesthesia is administered.
It is necessary to remain in the clinic until the child fully regains consciousness. After anesthesia, the baby is allowed to go home no earlier than a few hours later. Sometimes it is recommended to stay under medical supervision overnight.
How long does it take?
The standard duration of the examination is 20-30 minutes. Sometimes it lasts longer. For example, scanning the abdomen takes longer than scanning the brain.
How often can a child have an MRI?
If it is necessary to monitor changes in the child’s condition, the doctor may periodically prescribe repeated tomographs. Electromagnetic waves do not affect the condition of the body, so diagnostics can be carried out as often as required to monitor the condition and select effective treatment.
The frequency of examination of young children is determined by how often they can be given anesthesia.
Risk of MRI for a child
MRI scanning has no risk for the child, since the parts of the device do not touch the body of the small patient, and he does not feel pain during the scan.
The patient's body is not exposed to x-rays, which makes it possible to perform several procedures in 1 day or a short period of time. Side effects may occur after administration of a contrast agent or anesthesia. In the first case, reactions manifest themselves from the gastrointestinal tract, in the second - from the nervous system.
Negative actions after MRI with contrast and anesthesia are most often associated with patients’ failure to comply with preparation rules and ignoring contraindications.
In addition to MRI, young patients may be offered other types of examinations - X-rays, ultrasound or CT. The latter type of diagnosis is not inferior in information content to MRI, so people ask the question: what is best for the child? The answer depends on the type of disease. For example, pathologies of bone tissue are better visualized using a computed tomograph. Some of the advantages of MRI over CT include:
- Better visualization of soft tissues.
- Possibility of controlling the development of cancer tumors.
- Clear visualization of vessels and small capillaries.
Possible risks
The MRI diagnostic procedure is safe. There is no harm from electromagnetic waves.
If tomography is performed on young patients, then it is necessary to assess the risk of anesthesia. Before the planned administration of sedatives (hypnotics), parents should talk with an anesthesiologist. The doctor will find out all the information about the child, including information about possible allergies. The decision on the advisability and admissibility of administering anesthesia is made after a conversation with the child’s representatives.
For children with kidney failure, CT scans with contrast can be done after a doctor has assessed the condition.
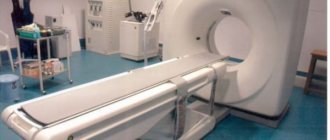
How are MRIs and CT scans performed on newborns and older children?
The CT and MRI procedures are painless. A tomograph is an installation with a retractable table, which is surrounded by special magnets or emitters. The child is placed on a flat surface, and when contrast is administered, his hand is immobilized with special fasteners. Devices are attached around the patient's head that transmit and receive signals from the installation.
During the examination, the device may make booming sounds that frighten the baby. Because of this, many children under the age of 7 are given anesthesia. To diagnose certain diseases, the patient is asked questions during the procedure. This type of research is most often used for children over 10 years of age.
It is considered safer to perform a spiral CT scan of the brain (SCT) for children. With SCT, the X-ray tube rotates around a table, which speeds up the procedure, reduces the amount of radiation and produces images in three dimensions. The specialist who conducts the diagnostics is located in a separate room. He controls the process of the procedure and records the indicators of the computer study.
For infants, CT or MRI is performed only under general anesthesia. If necessary, the patient's head is secured with special belts. Parents can stay next to the child or in the room with a specialist and watch the procedure on monitors.
In the video you can see how an MRI of the brain is performed on a small child. The procedure does not require special preparation. However, when administering anesthesia or contrast, the following requirements must be observed:
- last feeding – 4 hours before tomography (for infants – 2 hours);
- presence of a cardiogram;
- testing for sensitivity to the drug.
conclusions
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe and painless diagnostic method. With its help, the doctor can assess the condition of internal organs, bones, joints, and soft tissues. Even newborn babies are allowed to undergo tomography.
MRI in children allows us to detect diseases at the earliest stages. In the images taken during tomography, you can see tumors, cysts, pathologies of the development of organs, bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues. It is carried out in the presence of various diseases of internal organs, skeleton, deterioration of vision, hearing, lack of speech, impaired mental and physical development.
For young children who may be frightened by the noise of the tomograph and cannot lie still for a long time, the procedure is performed under anesthesia. The anesthesiologist administers a short-term sleeping pill to the baby.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Another question that worries parents is: “How to prepare a child, especially a preschooler, for an MRI of the brain and other parts of the body?” First of all, you should stop eating before the procedure. For infants - at least a couple of hours; for older babies, the period increases to 4-5 hours. Why is it important? The fact is that anxiety - and it is inevitable - in some cases provokes vomiting. If an MRI is planned under anesthesia, the child should not eat since the evening of the previous day.
Is it possible to do MRI on babies?
MRI is prescribed to children in rare cases when other studies do not accurately diagnose or differentiate the disease.
The magnetic field does not have a negative effect on the growing body, however, during the procedure the child must lie still for 30-40 minutes, which is impossible for a baby. For this reason, an MRI of a child under 1 year of age is performed under anesthesia. To perform an MRI, a baby only needs “medicated sleep” (short-term intravenous sedation). Full general anesthesia is not necessary. However, “medicated sleep” also has contraindications and limitations, so before using it you should consult your pediatrician.
“Medicine sleep” is used regardless of the age of children, if the rules of behavior inside the tomograph cannot be explained to them. It should be taken into account that during diagnostics the device makes quite loud sounds that can frighten a child.
Possible side effects
To the question whether it is possible to do an MRI on young children, the answer can only be positive - the diagnosis is harmless even for newborns. However, in rare cases, this diagnostic procedure may lead to side effects, namely:
- allergic reaction to a medication;
- weakness, loss of appetite and nausea after examination with the use of anesthetics.
No other side effects are observed if the examination is carried out correctly.