Reasons for the appearance of “fog, ambiguity” in the head
Do you always feel a little drunk or drugged? This condition makes it difficult to concentrate, perform usual work, and may be accompanied by recurring headaches. To get rid of discomfort, it is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence and try to eliminate it.
Cerebral circulatory disorders
Insufficient supply of oxygen to brain cells leads to the fact that it issues inadequate commands to the nerve centers. A person may feel dizzy, feel nauseous, and have dark vision. If a patient experiences fog in the head along with a headache, the causes of discomfort may lie in the following:
- A person suffers from an infectious disease that affects the brain structures.
- The patient develops an inflammatory process, causing a significant increase in temperature.
- The patient experienced extensive intoxication of the body.
- A severe allergic reaction develops.
- Respiratory failure caused by bronchial asthma and chronic rhinitis is observed.
- Ear damage: destruction of the eardrum, vestibular neuronitis, Meniere's disease.
A feeling of brain fog due to poor circulation can also occur after a head or neck injury. Bruises, blows, and whiplash injuries lead to a concussion, displacement of brain structures, and a significant deterioration in the blood supply to the tissues of the head.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
Most often, office workers, doctors, teachers, and people of intellectual work complain of strange sensations in their heads. Fuzzy head syndrome is a relatively new disease that has already become quite common. It is classified as a mental disorder caused by mental and emotional fatigue and lack of sleep. Main symptoms:
- Feeling of fog in the head, vagueness, heaviness, confusion in consciousness.
- Sleep disturbance – insomnia at night and drowsiness while awake.
- Violation of the emotional background - irritability, hot temper, suspiciousness.
- Constant feeling of anxiety.
- Expectation of failure, unreasonable fear.
- Feeling tired, apathetic.
The disease develops gradually, at first there is general weakness in the morning, slight irritability in case of minor problems. Then the patient begins to get angry for any reason, the head becomes “woolly,” and pressing headaches may occur, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the skull. Over time, the symptoms include chest pain, periodic tachycardia, and a feeling of severe weakness throughout the day.
If a person says that his head has been in a fog for days, the reasons should be sought in his lifestyle. Constant stress, pressure at work, hyper-responsibility, stable refusal of normal sleep, prolonged nervous excitement lead to disruption of the nervous system and the development of asthenic syndrome. In addition, poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency, frequent colds, and bad habits aggravate the condition.
Possible reasons
One of the reasons for distracted attention and weakness is lack of sleep
One of the common causes of brain fog and confusion is lack of sleep. A person only needs 8 hours of sleep a day for the body to work at full strength. For some, less time allotted for rest is enough: only 4-5 hours. At the same time, they feel full of strength and vitality.
With a constant lack of sleep and staying on your feet for a long time, there is a negative effect on the structures of the cerebral region:
- narrowing of peripheral vision;
- distraction;
- decreased psychomotor reactions;
- deterioration of coordination and perception of light.
Numerous studies have proven that a lack of proper rest and sleep causes a malfunction in the interaction between neurons in the brain, and this is a direct path to general weakness and the development of various diseases.
The second cause of illness is chronic fatigue syndrome or astheno-neurotic syndrome. In addition to brain fog, memory and level of intelligence are impaired, and psychomotor reactions slow down. The clinical picture is caused by the accumulation of cytokines in the spinal cord cavity, which are similar to eotaxin, present in the body of people suffering from multiple sclerosis.
A third possible cause of confusion is therapy with certain medications, especially those taken on an empty stomach. The symptom is complemented by nausea. When overdosing on nootropic drugs, concentration is disrupted and the person becomes distracted. Similar effects are observed with the abuse of analgesics.
Some mental disorders are accompanied by similar symptoms. For example, this often happens with depression, when energy is lost, vitality decreases, and a person’s thoughts and consciousness become vague. This also includes panic attacks and bipolar disorder, which occur with disruption of normal consciousness.
When a neck injury occurs, blood flow to the brain is disrupted.
If a person is injured in the next 24 hours, for example, as a result of an unsuccessful fall, a sharp turn of the body, a car accident, and damages the neck, local pain occurs and the mobility of the region is limited. Due to impaired blood circulation in the damaged area, blood flow in the cerebral region also fails, which is characterized by confusion of consciousness, memory impairment, and concentration.
The appearance of brain fog periodically occurs in women during menopause and pregnancy. At such a time, the body undergoes hormonal changes and the balance of sex hormones is disrupted. All this occurs with increased sweating, hot flashes, confusion, and abnormal heart rhythm.
If the volume of oxygen entering the cerebral region is insufficient, a person’s consciousness becomes clouded. Compression of cerebral vessels causes hypoxia and disruption of its nutrition. Other symptoms include:
- decreased ability to work;
- dizziness and weakness;
- impaired memory and concentration;
- fast fatiguability.
If left untreated, cells that do not receive enough oxygen and other nutrients gradually die, causing serious and sometimes irreversible consequences.
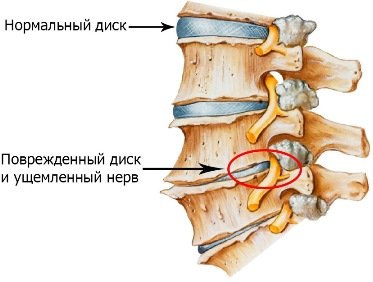
With osteochondrosis of the neck, compression of the arteries occurs and the brain experiences oxygen starvation
Another possible cause of brain fog is degenerative processes in the cervical spine. This may be osteochondrosis, which, in addition to confusion of consciousness, occurs with the following symptoms:
- pain in the neck, which radiates to the arm, shoulder, shoulder blade, head;
- dizziness;
- impaired sensitivity of the skin in the area with pathology;
- restriction of department mobility.
Confusion and dizziness are a consequence of insufficient blood supply to the brain, which is caused by compression of the vertebral artery.
Comprehensive diagnostics
If a person experiences a feeling of foggy consciousness, often has a unclear head, or headaches, it is necessary to visit a neurologist. It is this specialist who, after examining the patient and listening to his complaints, suggests undergoing additional examination or refers him to a specialist. Possible diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
- CT and MRI of the head, cervical spine.
If the development of astheno-neurasthenic syndrome is suspected, the person will be referred to see a psychotherapist. If circulatory disorders are caused by neurasthenia, the patient may additionally be advised to undergo rheoencephalography.
Diagnostics
If fogginess in the head appears constantly, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Therapists, neurologists, and psychotherapists deal with this issue.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must interview the patient and find out what additional symptoms he has, as well as conduct a diagnosis. Here is a list of mandatory tests needed to find out why fuzzy head syndrome occurs:
- General analysis of urine and blood. Exclude the presence of inflammatory reactions and infectious processes.
- Ultrasound of blood vessels in the cervical spine.
- CT or MRI of the spine and brain. An MRI and CT scan will allow you to exclude malignant processes, determine the condition of blood vessels, identify the presence of chronic diseases of the nervous system, etc.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
The patient may also need to consult other specialists.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
If there is no clarity in the head, then this may indicate astheno-neurotic syndrome. This pathology, in addition to constant fog in the head, is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Problems falling asleep.
- Superficial sleep.
- Suspiciousness, irritability, hot temper.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Unreasonable anxiety.
- Daytime sleepiness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Memory problems.
- Stiffness of movements.
- Dizziness.
- Constrictive headaches.
- Tremor of the limbs.
In most cases, this syndrome affects people who are mentally stressed. In addition, this pathology often affects those who have an unstable psyche.
Symptoms
Typically, patients present the following set of complaints:
- the feeling that there is fog in the head, the head is cloudy, all in a haze;
- it’s difficult to think and hard to concentrate, sometimes you can’t formulate a thought;
- confusion and illusory thinking;
- it is difficult to remember what you know well;
- problems with short-term memory (sometimes even in the process of some action a person forgets what he is doing and why, or, having started a phrase, cannot finish it because he has forgotten what he wanted to say);
- ordinary intellectual tasks that were previously easily solved now become too difficult;
- You get distracted very quickly, but you can’t concentrate;
- the feeling that there are so many thoughts in your head that it is impossible to choose just one.
All these symptoms can appear at the same time, or they can come one at a time. They can be constant or occur only at certain hours and days. They can be extremely strong or barely noticeable.
They can arise in a clear connection with some stressful event, or they can come as if from nowhere.
They may be the only sign of chronic anxiety, or they may complement other anxiety symptoms.
Brain fog has many causes. And some of them are far from nervous, but indicate serious physical illness. Therefore, before you believe that your fog is nervous, you need to undergo a medical examination.
Prevention
Cloudiness in your head will no longer bother you if you follow preventive measures. First of all, this symptom manifests itself in people in case of an incorrect lifestyle. If you eat poorly, don't get enough outdoor exercise, smoke, drink alcohol, don't exercise, take drugs, don't sleep well, or are constantly stressed, then you shouldn't even think about feeling good.
That is why, in order to improve the condition, experts recommend normalizing your rest and sleep patterns, and sleeping at least 8 hours every day. It will be very important to avoid frequent stressful situations. In addition, experts recommend increasing physical activity and exercising regularly. The best option would be swimming, cycling or jogging. In parallel with all this, you will have to adhere to the correct diet and nutrition regimen, as well as give up bad habits.
Now you know how to deal with brain fog. If you completely change your life, you can not only get rid of brain fog, but also strengthen your immune system and improve your overall health.
Causes
The causes of heaviness in the head are often associated with physical and mental fatigue. In this case, the discomfort goes away spontaneously after a long, complete rest.
Cloudiness in the head occurs due to an unhealthy lifestyle (abuse of alcohol, drugs, physical activity at night, irregular diet) or due to a pathological process.
Common causes of development:
- Lack of sleep, sleep disorder. Often, a feeling of vagueness inside the skull appears after prolonged sleep, which is usually associated with poor rest hygiene or venous stagnation. To prevent discomfort, it is necessary to ventilate the room before going to bed and choose comfortable bedding (pillow, mattress).
- Poor nutrition. A deficiency of important nutrients - vitamins, microelements, protein, healthy fat (olive oil, avocado, sea fish) leads to the feeling that the head is plagued. Disturbances can be triggered by the consumption of foods that cause an allergic reaction.
- Chronic stress. Regular exposure to stress has a negative impact on health, leading to the development of depression, insomnia and discomfort in the skull area.
- Taking pharmaceutical drugs and nutritional supplements. Some medications (anticonvulsants, painkillers, statins, antidepressants, sleeping pills and sedatives, acetylsalicylic acid) provoke the development of fuzzy head syndrome.
- Increased blood pressure levels. Any deviations in blood pressure values from the norm can provoke a feeling that there is cotton wool inside the skull.
- Meniere's disease, vestibular disorders. Pathologies of the vestibular system are one of the likely causes of the feeling of a cloudy head.
- Thyroid dysfunction. Excess and lack of hormones lead to an unpleasant feeling inside the skull.
- Concussion, brain contusion. Suffered TBIs cause a condition where the head is dizzy, there is pressure on the ears and there is a pressing pain in the area of the skull. Disturbances occur in the acute period and can be observed much later than the episode of TBI, transforming into post-traumatic syndrome.
The feeling of a heavy head can occur against the background of inflammatory processes occurring in the respiratory, visual and hearing organs. Pathologies of the heart and vascular system can provoke the appearance of symptoms. Damages to the joints and other structures of the musculoskeletal system are often accompanied by a condition where clouding occurs in the head.
Folk remedies for getting rid of headaches and pain in the eyes
In alternative medicine there are special methods that allow you to relieve unpleasant sensations of a pressing nature. Warmed milk or a herbal decoction of chamomile or mint with the addition of a spoon of honey helps a lot: this drink will calm your nerves and relax. Valerian root tea helps relieve tension and relieve mild pressing pain. To prepare it, one tablespoon of crushed root is poured with boiling water and steamed in a water bath for half an hour. The decoction is consumed before meals.
Self-massage is recommended to relieve pain. Manipulations help relieve tension and normalize local blood flow. A warm bath with the addition of chamomile decoction and essential oils improves the condition of the skin, relieves dizziness and eliminates pain in the eyes. The use of medicinal compresses helps to get rid of bursting pain. Bandages made of cabbage leaves, potatoes and onions are applied to the temples and forehead. An ordinary cold compress will also help relieve discomfort.
Methods for treating heaviness in the head
As already mentioned, heaviness in the head in itself is not a disease. This is only a symptom, and it is the root cause of the condition that needs to be treated.
Treatment of the underlying disease is specific, selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, and entirely depends on the identified disorders.
However, symptomatic treatment of heaviness in the head and similar accompanying symptoms is also possible. Most often, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, antispasmodics and other drugs are used in therapy to relieve discomfort. In some cases, they resort to blockades.
However, we should not forget that long-term drug treatment is addictive, and the drugs lose their effectiveness over time. So this approach to treatment can be truly justified only in a situation where heaviness in the head is caused by serious organic lesions. In other cases, if possible, it is recommended to solve the problem through safer therapeutic methods without the use of “chemistry”.
Thus, heaviness in the head can be easily eliminated with the help of self-massage of the biologically active zones of the back of the neck, the back of the head, the temporal region, and the crown. Impact on these areas not only relieves tension from the neck muscles, but also stimulates the flow of fresh blood, which helps improve well-being and restore performance.
In addition, you should pay attention to a number of treatment methods that have proven effective in improving blood flow in the cervical spine and normalizing blood supply to the brain. These primarily include manual therapy and all kinds of physiotherapeutic procedures.
In addition, regular performance of even simple exercises allows you to strengthen the muscle corset and, accordingly, reduce the load on the spinal column itself and protect it from the development of destructive processes.
Exercise can also give good results in the fight against heaviness in the head, drowsiness, fatigue and other associated symptoms. Physical activity helps saturate the blood and tissues with oxygen. In addition, regular performance of even simple exercises allows you to strengthen the muscle corset and, accordingly, reduce the load on the spinal column itself and protect it from the development of destructive processes.
Main syndromes of clouded consciousness
Several syndromes of clouded consciousness have been identified - amentia, stupor, delirium, oneiroid, twilight stupor.
Stun
– a pathological condition characterized by the fact that a person seems to be in a dream, has difficulty answering standard and simple questions, gives unclear answers, becomes inactive, often silent and indifferent. But he does not exhibit hallucinations, as well as affective disorders or delusional states.
Oneiric obscuration
- dream-like, delusional-fantastic cloudiness. Fantastic dreams grow in a person’s head, which can be partially combined with the surrounding environment, then the patient can react to people nearby. A person with this type of clouding of consciousness usually has a frozen expression on his face; he may be silent, inactive, and practically motionless. The gaze alternates between amazement or delight, detachment or fear.
Should I be worried about brain fog?
Malfunctions in the functioning of human vital systems do not always manifest themselves in the form of pain and other striking symptoms. Sometimes they take the form of uncomfortable sensations. Brain fog is one of the common warning signs that many people simply ignore.
Its one-time appearance against the background of intense physical or mental stress should not be a cause for alarm.
If a person does not have clarity of thought and there is a decrease in the quality of vision for no apparent reason and on a regular basis, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor for advice.
Symptoms of a fuzzy head
Depending on the cause, the pathological manifestation may occur once a week or less, or become a constant companion.
Clouding of consciousness can be mild and annoying, but sometimes its severity prevents you from doing your usual activities. An attack can last from 2-3 minutes to several hours.
The condition when the head is in a fog is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness and a feeling of lethargy, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the head;
- fatigue and weakness that are not associated with any type of activity or rest;
- a feeling of futility and dullness of consciousness - as if there is a vacuum in the head after drinking alcohol or drugs;
- headache, increased heart rate, and changes in blood pressure may be present. Often a person does not think well and cannot even move due to the fact that the muscles “do not work.”
You will learn about the effect of high blood pressure on the occurrence of cephalgia here.
This vague state usually develops in response to external factors. This could be a change in weather, increased mental activity, or unusual physical activity. In complex cases, the clinical picture appears on its own, without any provoking factors.
Causes of a heavy head
Under certain conditions, fuzzy head syndrome can develop in a healthy person.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, which can cause fogginess of consciousness, forgetfulness, weakness and capricious mood.
The same picture is sometimes observed during menopause, but it is not as pronounced. Lack of sleep, disruption of work and rest patterns, and drug abuse are also common causes of this unpleasant condition.
Oxygen starvation
Compression or blockage of the channels through which oxygen enters the brain leads to a deficiency of the substance in the tissues. This causes a decrease in the functionality of the organ and a deterioration in the person’s well-being.
The patient develops confusion, fog in the eyes, and severe weakness. The head feels very heavy, and cephalalgia may develop. In advanced cases, loss of consciousness is possible.
In the supine position the condition improves slightly.
Oxygen deficiency in the brain is caused by the following factors:
- consumption of alcohol and drugs;
- smoking tobacco and various mixtures;
- pathologically high or low blood pressure;
- diseases of the spine, due to which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted;
- past traumatic brain injuries;
- refusal to walk in the fresh air, physical activity, or ventilate rooms;
- swelling of the nasal passages due to a cold or allergic rhinitis.
Refusal to treat oxygen starvation can lead to the development of ischemia. Brain tissues deficient in the chemical compound gradually lose their functionality.
At first, the structures surrounding the affected area take over its responsibilities, but gradually a stage of decompensation develops. Entire areas of the brain cease to fulfill their purpose, which negatively affects the entire body.
How to diagnose?
The only and sure way to determine the cause of poor health is to consult a doctor. As a rule, the patient is referred for examinations:
- taking tests;
- X-ray, CT, MRI;
- consultation of specialized specialists.
The prescription of other measures depends on the severity and frequency of symptoms. In most cases, the diagnosed cause of pressure, wooliness and head fog is damage to the cervical vertebrae.
Diagnostic methods
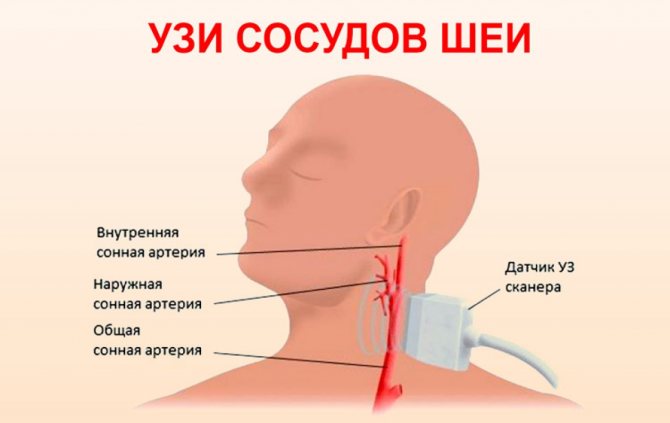
First of all, an ultrasound scan of the neck vessels is performed.
On the first visit, the patient is asked about disturbing symptoms, how long ago they occurred, frequency of occurrence, and intensity. They examine the anamnesis, finding out what chronic processes are present in the body, whether there are injuries and surgical interventions.
Next, laboratory tests (analysis, tests, other diagnostic procedures) are prescribed, the results of which determine the general state of health. Tests for blood sugar levels, hemoglobin, and oxygen volume are required.
The patient is referred for consultation to a specialized specialist depending on the accompanying manifestations: to a vertebrologist, neurologist, otoneurologist, otolaryngologist, audiologist, or others.
A specialized doctor prescribes instrumental diagnostics. For dizziness and confusion, these are studies of the cervical spine and head:
- X-ray analysis;
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
Additional diagnostics may be required, for example, electrocardiography, angiography, posturography, etc.
Lack of oxygen
If the human brain begins to lack oxygen, this can trigger a feeling of brain fog. For this reason, hypoxia develops due to compression of the vessels through which the blood must carry oxygen, as well as all the necessary substances to nourish the organ. In addition to fogginess, a person experiences other symptoms:
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Heaviness in the head.
- Bad memory.
- Unclear consciousness.
- Slow reaction.
- Problems with information perception.
- Fatigue, severe weakness.
If you do not start treating this pathology, the brain cells that experience oxygen starvation will gradually lose their functionality, which will lead to serious complications.
Features of manifestation
Dizziness, cloudiness, heaviness can accompany people constantly or appear periodically. If your head is in a fog, this will not always indicate the development of some kind of disease.
For example, if a person felt very good a minute ago, then almost in an instant he begins to experience discomfort, dizziness, fogginess, dullness of consciousness and blurred vision.
The whole problem with feeling like your head is in a fog is that the symptom can manifest itself while performing some important task or at the workplace. For this reason, the patient is deprived of the opportunity to carry out his usual activities. Dizziness and foggy head may be accompanied by other symptoms, for example:
- Low or high blood pressure.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness during the day and sleep disturbances at night.
- Headache.
- Palpitations.
- Excessive sweating.
Quite often, such a picture is accompanied by unreasonable fear, a feeling of lack of air, and also the formation of ringing in the head. There are many different causes of brain fog. A list of them will be described below.
Heaviness in the head, dizziness, weakness and a feeling of lethargy can occur either once a week or several times a day. Often this is facilitated by the influence of something:
- weather;
- physical activity;
- mental activity.
But sometimes this condition can arise, as they say, “out of nowhere.” Those. Just a minute ago, a person feeling in good shape suddenly experiences incomprehensible sensations.
His head seems to become heavy and stretches towards the floor, his eyes become foggy, and his consciousness becomes dull, making it impossible to carry out any activity.
The condition is as if the person instantly became drunk.
Feelings of “wooliness” may be accompanied by headache, dizziness, weakness, rapid heartbeat, and increased/decreased blood pressure. Often the patient experiences weakness throughout the body.
This condition can manifest itself either partially or completely, depriving a person of the ability to move normally. The duration of the attack is several minutes, but can last for a longer time.
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome
This disease can be cured using psychotherapeutic methods. However, provoking factors should also be excluded at the initial stage of therapy: lack of sleep, stress, mental stress and excessive physical activity. If you do not reduce the influence of these factors, then drug treatment and psychotherapy will not have the desired effect and will not eliminate the unpleasant symptom.
Medicines are used in severe cases. The most effective are sleeping pills, restoratives, antipsychotics, antidepressants and tranquilizers.
Treatment for fuzzy head
The principles of therapy depend on the cause that provokes the condition. Eliminating the underlying disease will relieve the unpleasant symptom. In this case, medications are taken only with the permission of the doctor after the diagnosis has been established. During treatment, the patient's physical activity should be limited and rest should be ensured.

To quickly and independently get rid of brain fog, you can try the following approaches:
- try to sleep in a dark, ventilated and quiet room;
- perform a light massage of the collar area to restore blood circulation and breathe fresh air;
- if you have high blood pressure, take an antihypertensive drug or drink a diuretic tea (bearberry, lingonberry leaves);
- if you have low blood pressure, drink coffee or strong black tea;
- if fog in the head is combined with cephalgia, you can take a one-time drug from the NSAID group - Ibuprofen or Citramon.
You will learn about possible methods of treating headaches without medications from this article.
In cases where the appearance of fog in the head is associated with the peculiarities of the regime or work, it is worth thinking about changing the type of activity or adjusting the schedule. People in responsible positions are helped by relaxation techniques and hobbies. The systematic use of traditional medicine gives a good effect. Ginseng and Eleutherococcus will have a general strengthening effect on the body. Melissa, chamomile and mint will help relieve tension.
A cloudy head indicates disruptions in the course of biochemical reactions in the brain. Such a sign cannot be ignored if it appears systematically. Timely diagnosis will allow you to identify the problem at an early stage of development and eliminate it without harm to the body.
Materials used in the article:
https://house.jofo.me/373051.html
https://insultinform.ru/bolezni/golovnye-boli/tuman-v-golove-prichiny
https://sostavkrovi.ru/sosudy/mozga/sindrom-deficita-vnimaniya-sdvg.html
Post Views: 114
Pathological causes of blurred vision and dizziness
The above symptoms may indicate a serious illness. They are included in the symptoms of the following diseases:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anemia;
- hypoglycemia;
- vascular diseases;
- migraine;
- atherosclerosis;
- stroke;
- diseases of the spine;
- intracranial tumors;
- head injuries.
Foggy vision often occurs in people with glaucoma. This is an ophthalmopathology in which intraocular pressure increases. During an attack of glaucoma, dizziness may also occur.
Causes of foggy eyes
A hazy image may appear during the development of ophthalmological diseases, mild or severe visual deviations. Sometimes nebula is a symptom of other ailments or systemic diseases in a person.
| White haze in some cases is recorded in one eye, but more often there is bilateral blurred vision. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle often complain of similar symptoms. |
After working for a long time at the monitor, a person seems to see a fog in front of him (computer syndrome), a symptom may appear after instilling some drops into the eyes (in this case, the duration of the symptoms is insignificant, a good image appears after the composition of the tear film is normalized).
Sometimes a person notices fog in the eyes while visiting a bathhouse or sauna. This is due to the influence of hot and humid air on the visual organs. After some time, the protective film is restored and the symptoms disappear.
What to do if clouding of consciousness occurs
When clouded consciousness appears, it is necessary to identify its cause, which can be either psychological in nature or associated with a physiological disease. Since the person is in an altered state, it is necessary to call for medical help immediately.
In case of acute psychological changes in consciousness, it is important to take the patient to a psychiatric clinic, accompanied by a doctor or nurse. When aggression occurs, doctors use appropriate psychotropic medications.
Clouding of consciousness: first symptoms
Symptoms of a disorder such as clouding of consciousness may appear gradually over a long period of time or occur unexpectedly. The main symptoms of clouding of consciousness are:
- disorientation;
- hallucinations, as well as psychomotor hyperactivity;
- inability to think clearly;
- unexpected confusion or embarrassment;
- apathy and withdrawal (see also - what is apathy and how to get rid of it);
- memory deterioration or partial sudden loss;
- inability to distinguish between negative and good actions;
- inability to act independently and make simple decisions.
A person in a clouded state is not aware of his personality, as well as his social affiliation. Sometimes only one or more of the symptoms described above appear. Prolonged clouding of consciousness leads to dementia and loss of personal qualities.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
At the moment, treatment of vertebral artery syndrome is a difficult task to solve, as evidenced by the many different treatment methods from different clinics and the lack of a single generally accepted treatment regimen. Here are the main directions in the treatment of vertebral artery syndrome:
- Anti-inflammatory and decongestant treatment.
- The use of drugs that normalize blood circulation in the brain. The use of neuroprotectors and metabolic therapy to protect brain nerve cells under conditions of oxygen starvation.
- In case of severe impairment of cerebral circulation, surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is used to eliminate the causes of compression of the vertebral artery.
- Rehabilitation treatment, involving physical therapy, massage, acupuncture.
Severe headaches with cervical osteochondrosis are somewhat alleviated by painkillers, but this symptom can only be completely eliminated by eliminating osteochondrosis.
Diseases that cause blurred vision
If the problem affects both eyes, the cause may be ophthalmological diseases:
- Cloudiness in the structure of the eye caused by the onset of cataracts or formed as a result of corneal edema. A person notices a gradual decline in the quality of vision, sees objects as if through “foggy glass.” When the cornea edema, the image is not only distorted, but also symptoms such as pain and photophobia, and changes in the shade of the cornea appear.
- Various pathologies of the optic nerve (partial deformation, ischemic neuropathy, atrophy, etc.) Patients complain of impaired color vision, problems with visual fields.
- Inflammation in the structure of the eye, in which patients experience pain and burning, there is a change in the color of the conjunctiva, the sclera becomes red, and the eyes water.
- Bleeding in the visual organs, in which symptoms depend on the location of the problem and may include blurred vision, pain, a red color to the damaged area, and a feeling of pressure.
- Glaucoma, in which patients complain of severe headaches, pounding in the temples and nausea.
- Retinal pathologies (uveitis, retinopathy, AMD), manifested in the form of a veil in the affected areas, which over time covers the entire field of vision. The patient sees poorly in the twilight, speaks of “sparks and lightning in the eyes,” but there is no pain.
- Deviations of refraction, in which the symptoms depend on the type of disease (farsightedness, myopia, etc.)
A person sees poorly if he has other diseases:
- Deviations in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
- Kidney ailments.
- Diabetes.
- Poisoning with chemicals and all kinds of toxic substances (ethyl alcohol, mercury, lead, arsenic, nicotine, etc.)
- Heavy bleeding.
- Hypertension and associated retinal vasospasm.
- Eclampsia that occurs during pregnancy.
- Damage to the central nervous system.
- Anemia.
- Traumatic brain injury, mechanical damage to the visual organs.
- Pathologies in the brain (atherosclerosis, micro-strokes, circulatory disorders in the veins, encephalopathy as a result of hypoxia, etc.)
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
This disease is associated with an emotional, functional disorder of the nervous system. With the syndrome, people feel constant fatigue, followed by irritation. Astheno-neurotic syndrome is the result of overwork, heavy mental work, and stress. Patients experience increased emotionality, sensitivity, and a predisposition to depression. Neurasthenia is accompanied by:
- loss of appetite;
- sleep problems;
- fog in the head;
- weakness.
Phobias and nervous breakdowns develop against the background of the disease. Giving up bad habits, proper rest, and moderate physical activity will help cope with the causes of the syndrome.
- Cloudiness in the structure of the eye caused by the onset of cataracts or formed as a result of corneal edema. A person notices a gradual decline in the quality of vision, sees objects as if through “foggy glass.” When the cornea edema, the image is not only distorted, but also symptoms such as pain and photophobia, and changes in the shade of the cornea appear.
- Various pathologies of the optic nerve (partial deformation, ischemic neuropathy, atrophy, etc.) Patients complain of impaired color vision, problems with visual fields.
- Inflammation in the structure of the eye, in which patients experience pain and burning, there is a change in the color of the conjunctiva, the sclera becomes red, and the eyes water.
- Bleeding in the visual organs, in which symptoms depend on the location of the problem and may include blurred vision, pain, a red color to the damaged area, and a feeling of pressure.
- Glaucoma, in which patients complain of severe headaches, pounding in the temples and nausea.
- Retinal pathologies (uveitis, retinopathy, AMD), manifested in the form of a veil in the affected areas, which over time covers the entire field of vision. The patient sees poorly in the twilight, speaks of “sparks and lightning in the eyes,” but there is no pain.
- Deviations of refraction, in which the symptoms depend on the type of disease (farsightedness, myopia, etc.)
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
So, we figured out that the head is in a fog - this can be a symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia. To eliminate it, you need to seek help from a doctor. To relieve symptoms, various medications are used: sleeping pills, sedatives, drugs for dizziness, as well as medications to normalize blood pressure. In addition to drug treatment, experts also recommend adjusting your lifestyle: eating right, doing light sports, walking more often, eliminating stressful situations, waking up and going to bed at the same time, and giving up bad habits.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you experience fog in your eyes or a feeling of “foggy head,” you should consult a physician or ophthalmologist. Collecting complaints, data on risk factors and concomitant diseases can guide the doctor to the correct diagnosis. To confirm it, both general clinical studies and special ophthalmological studies are carried out.
The first include a general and biochemical blood test, a general urine test. These methods make it possible to identify the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, assess the level of glucose in the blood to exclude diabetes mellitus, and assess the general condition of the patient.
One of the key methods in making the correct diagnosis is to perform biomicroscopy with a special ophthalmological microscope or slit lamp. If inflammation occurs in the superficial membranes of the eye, then hyperemia and swelling of these layers will be clearly visible. With uveitis (inflammation of the choroid), leukocytes and lymphocytes, inflammatory cells, appear in the middle membranes of the eye. In addition to them, there are cellular aggregates, inflammatory fluid, and in the long-term, adhesions.
Assessing the transparency of the vitreous allows one to detect pathological changes. In addition, all patients with this symptom must have their intraocular pressure measured, since glaucoma very often manifests itself as transient visual impairment. If pathological processes in the brain are suspected, patients are referred for an MRI or CT scan.