Sometimes it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based only on the patient’s words, and additional procedures cannot be avoided.
During the examination, computed tomography of the head is often used - the most informative method of diagnosis. X-rays can be used to obtain images of a patient's organs.
This method allows you to diagnose hematomas, injuries, other brain pathologies, as well as problems with the spine and spinal cord. Data processing falls on the shoulders of the radiologist, and then the neurologist, who makes the final diagnosis.
Operating principle
Computed tomography is based on X-rays, which provide data to visualize a specific area. The analysis of this data is performed by the program. A standard X-ray has a point-by-point principle of operation, and a CT scan of the head involves a smooth movement of the beam along the patient’s body. The result is a series of layer-by-layer horizontal and vertical images of the necessary organs (up to 320 per zone).
The most advanced examination method is the use of a multislice tomograph. With this method, not only the beam moves, but also the table on which the patient lies.
Does an MRI cause pain or discomfort?
MRI does not cause pain or other discomfort to the person during the examination. The body may sometimes feel a slight warmth or tingling sensation, although most often people physically feel nothing at all. The administration of contrast is well tolerated in most cases. True, sometimes there are cases of individual hypersensitivity or allergies.
The main discomfort associated with MRI is the psychological stress that some people experience due to the cramped space. There is enough air in the device, and the design is made in such a way that part of the patient’s body is outside. To calm down, the patient needs to understand that during the study he is being monitored by a doctor, and the whole process is completely under control.
Indications
Computed tomography of the brain is considered the most effective diagnostic method for traumatic brain injuries, tumors, the presence of cysts in the pineal gland and hemorrhages. It can also be prescribed in the following cases:
- stroke;
- inflammation of the brain;
- neoplasm;
- blockage of a vessel by a thrombus, embolism;
- hydrocephalus;
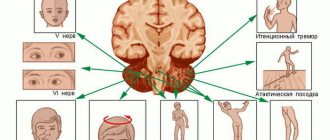
- blurred vision;
- sensory disturbance;
- clouding of consciousness;
- frequent pain;
- examination before operations;
- contraindications to MRI;
- violation of facial symmetry.
In addition, head tomography can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment procedures. With this technique it is much easier to monitor the condition of blood vessels, skull bones and brain.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to prescribe tomography for children under 14 years of age.
The method is strictly prohibited for pregnant women, since X-rays can cause pathologies in the fetus, and for nursing women if a CT scan with contrast is planned. An exception is made in situations where the baby is not allowed to breastfeed for at least two days.
For kidney disease, a procedure with contrast is not recommended, as it may worsen the patient's condition.
It is not advisable to perform tomography in cases of severe pain, when the patient cannot remain calm and is constantly moving, since the procedure requires a person to remain motionless.
For some blood diseases and allergic reactions, CT with contrast is contraindicated.
In case of claustrophobia, tomography is possible only under anesthesia.
Excess weight (more than 130 kg) may cause refusal to carry out the procedure if the body dimensions are larger than the camera of the device.
In the case of a bone marrow tumor or any problems with the thyroid gland, even minor radiation exposure is especially dangerous.
When is MRI of the brain with contrast contraindicated?
The decision that a diagnostic procedure cannot be performed is made by the doctor. People who have metal implants or a pacemaker in their bodies are subject to an absolute ban. If the patient has claustrophobia or epilepsy, the session is possible under the supervision of a specialist.
Contraindications for MRI with contrast:
- allergy to the solution used for intravenous administration;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding – you will have to abstain from lactation for at least a day after administration of the drug;
- bronchial asthma;
- severe damage to the kidneys, heart and blood vessels;
- exhaustion or dehydration of the body;
- taking beta blockers.
If the patient is significantly obese, the use of a tunnel MRI machine is not always possible. In this case, the procedure is carried out using an open version of the equipment or another diagnostic option is selected.
Harm from the procedure
A one-time diagnosis results in an X-ray load of 1-2 mSv, while the available maximum for 1 year is 150 mSv. However, when prescribing a tomography, the doctor must take into account all the characteristics of the patient, from age to the number of examinations already performed. Sometimes, if a person’s life depends on the procedure, when prescribing a CT scan of the head, the maximum dose is not taken into account.
Preliminary measures before the procedure
As such, there are no special requirements for the patient before undergoing tomography, with the exception of the contrast method, when it is necessary to conduct the study on an empty stomach. Therefore, it is enough to remove all metal objects and change into comfortable clothes.
However, the following documents are usually required:
- direction;
- disease history;
- results of previous diagnostics;
- other papers related to this case.
If the patient has diabetes, then a CT scan of the brain requires certain preparation - refusal of glucose-lowering drugs.
How to prepare for an MRI?
Before an MRI with contrast, the patient must fast from food and water for 2 hours before the procedure. This is due to the introduction of medication into the body (during normal diagnostics, you can eat and drink). Before the examination, a person needs to remove all metal items (rings, earrings, clothes with fasteners).
An important point is psychological preparation for the diagnostic procedure. Considering that during the study you need to be in a practically confined space for 20-30 minutes, without moving or talking, the right attitude is important. During an MRI of the brain with contrast, the machine makes noise and different sounds. Therefore, to protect the ears, a person wears special headphones.
Carrying out diagnostics
The question of how CT scans are done worries many. First, the patient lies on the tomography table with his back and is moved into the apparatus tunnel. The specialist is in the next room and observes the process. Communication between him and the patient is carried out through a microphone built into the device. When the device operates, a ring equipped with scanning sensors will rotate.
If you are not confident in your ability to remain still, you should secure your head with straps.
The result of the examination is a set of images that are sent to the specialist’s computer monitor.
If a contrast agent is injected, a feeling of warmth throughout the body and a metallic taste in the mouth may occur; in other cases, the person does not feel anything, except for the noise from the operation of the device.
The entire procedure lasts from 30 minutes to an hour, with preparatory activities taking up most of the time.
Sometimes specialists prescribe computed tomography for children. At the same time, it is carried out in the same way as for adults, but only under anesthesia so that the baby does not move.
Immediately after diagnosis, a person can return to everyday activities without any restrictions.
Consequences of MRI of the head and brain
Everyone who has to undergo this rather serious examination wonders whether there will be negative consequences from the operation of the tomograph. The answer to this question can be answered with confidence: no. All devices approved for research have passed appropriate tests and proven their safety.
Of course, one should take into account the individual characteristics of each person’s body and its reactions to seemingly the most common procedures. In some cases, nausea, vomiting, headache, and weakness may be felt. A headache may be felt after a contrast test. Other negative consequences are possible, but they are observed no more often than one case per thousand studies.
It is worth saying that sometimes patients complain of feeling unwell due to being in a confined space with constant exposure to loud sound. This has nothing to do with the operation of the diagnostic apparatus and goes away within a day, when the negative experience from visiting the MRI begins to be forgotten.
When a contrast agent is administered, the patient may experience unpleasant changes that are not considered an allergic reaction. They do not become a reason to interrupt or cancel the procedure. These are side effects of administering the drug intravenously. These include:
- nagging pain along the vein into which contrast is injected. Pain sensations may radiate (give) to the armpit;
- coldness or warmth in the vein;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- headache or dizziness;
- blood pressure drop within 20 mm Hg from normal for the patient.
Such sensations do not require drug intervention and disappear after the examination is stopped. But it is necessary to warn the doctor, since they can become harbingers of more serious changes and such a patient will need additional monitoring.
Contrast enhancement
A contrast agent means a drug based on iodine compounds. It is used when computed tomography of the vessels of the brain, medulla, and spine is necessary.
This component helps to clearly see, for example, the border of the tumor and its location.
When performing a CT scan with contrast to diagnose vascular abnormalities, the structure of the blood vessels appears more clearly, since X-rays pass through the contrast agent less well.
When a component is introduced, the following undesirable reactions sometimes occur:
- metallic taste;
- warmth in some areas of the body;
- mild attacks of nausea;
- headache;
- itching and rash;
- breathing problems, including cough.
If the last two symptoms appear, it is necessary to provide the patient with qualified medical care.
MRI of the brain with contrast for children
Conducting a contrast MRI of the head in childhood is subject to the same indications, prohibitions and nuances as in the case of adult patients. The complexity of the situation lies in the fact that even with the usual diagnostic option, it is difficult for a child to lie still for 30-40 minutes. If at the same time it also goes through an injection or installation of a system, the likelihood of its increased activity is very high. Manipulation is carried out only if there are direct indications and there are no other options for diagnosing the baby. Often, to carry this out, the child is put under general anesthesia or light sedatives are used.
Complications after the procedure
There is no need to fear any health problems after the examination. There are usually no complications after tomography, with the exception of allergic reactions during contrast diagnostics. However, these difficulties can be avoided if clinic staff carefully study the medical history and characteristics of a particular patient.
Evaluation of results
Processing does not take much time - on average up to 30 minutes.
Therefore, CT scan of the brain is often used when there is practically no time. The images can be shown to the patient or transferred to the doctor. If the examination reveals a serious threat to health, the information is immediately communicated to the patient. As a rule, it is recommended to consult with highly specialized specialists, depending on the disease.
As a result, you will have a photo of a CT scan of the brain (black and white images), as well as the findings of a radiologist. These images clearly show the skull bones, major vessels and brain. If the diagnosis does not reveal any pathology, then the photo will not contain foreign objects or darkening. Otherwise, non-standard vessel dimensions, ruptures in bone structures, fluid accumulations and swelling will be an alarming sign.
CTG is recognized by experts as one of the most effective and fastest diagnostic methods.
Alternative Methods
Standard radiography is used when no complex pathology is observed. The method allows you to detect foreign objects in the tissues of the head and determine areas of inflammation in the sinuses. However, it does not detect areas of hemorrhage. As a rule, this examination is used in addition to other methods.
If it is necessary to examine a child under one year of age, then neurosonography is used. The method is based on ultrasonic waves penetrating through the fontanel on the baby's head. The method is not suitable for adults due to the fact that ultrasound does not pass through the bones of the skull.
For pathologies of the jaw or teeth, radiovisiography is often used. As a result of diagnostics, you can obtain comprehensive data on dental health. Abnormalities in brain function are not monitored during this procedure.
The functional state of the brain can be determined using electroencephalography. As a result, a study of the activity of the cerebral cortex will be conducted.
Magnetic resonance imaging provides an image of certain tissues of the head and also helps determine their condition.
The method is similar to CT and is used when it is not available. The technique is based on the magnetic properties of tissues and the resonance effect. MRI also has an impressive list of contraindications, so consultation with a specialist before use is required.
Thus, most other methods are narrowly focused and do not provide a complete picture of the state of the brain. CT allows for a comprehensive diagnosis and provides only accurate data. The method works especially well when detecting cavities and fluid accumulations.