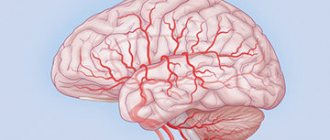
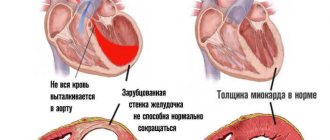
Oxygen starvation can occur both with insufficient oxygen content in the surrounding atmosphere and with certain pathological conditions. Brain hypoxia is observed in: cerebrovascular accidents, shock conditions, acute cardiovascular failure, complete transverse heart block, carbon monoxide poisoning, asphyxia of various origins, operations on the heart and great vessels, as well as in the early postoperative period, etc. This develops a variety of neurological syndromes and mental changes, with general cerebral symptoms and diffuse dysfunction of the central nervous system predominating. Pathomorphology Microscopically, cerebral edema may be observed. An early sign of hypoxia is a violation of the microvasculature, which is determined by: stasis, plasma impregnation of the vascular walls, necrobiotic changes in the vascular walls, impaired permeability of the vascular walls, release of plasma into the pericapillary space. In severe forms of acute hypoxia, varying degrees of damage to neurocytes, including irreversible ones, are detected early. In brain cells the following is found: vacuolization, chromatolysis, hyperchromatosis, crystalline inclusions, pyknosis, acute swelling, ischemic and homogenizing state of neurons, shadow cells, gross disturbances of the ultrastructure of the nucleus, its membranes, destruction of mitochondria, osmiophilia of some nerve cells are noted. The severity of cell changes depends on the severity of hypoxia. In cases of severe hypoxia, cell pathology may deepen after the cause that caused the hypoxia is eliminated; in cells that do not show signs of serious damage for several hours, after 1 - 3 days and later, structural changes of varying severity can be detected. Subsequently, such cells undergo decay and phagocytosis, which leads to the formation of foci of softening; however, gradual restoration of normal cell structure is also possible. In chronic hypoxia, morphological changes in nerve cells are usually less pronounced; During chronic hypoxia, glial cells of the central nervous system are activated and intensively proliferate. Clinical manifestations. When acute oxygen deficiency occurs, excitation of the nervous system often develops, followed by inhibition and increasing depression of its functions. Excitement is accompanied by motor restlessness, euphoria, increased heart rate and breathing, pallor of the skin, and the appearance of cold sweat on the face and limbs. Following a more or less long period of excitement (and often without it), phenomena of depression develop with the appearance of darkening in the eyes (after the previous “flickering” before the eyes), dizziness, drowsiness, general lethargy, stupor, with a gradual depression of consciousness. Disinhibition and inductive enhancement of the activity of subcortical formations are accompanied by erratic motor activity, convulsive muscle contractions, general tonic and clonic convulsions. This period is usually short-lived. Further spread of inhibition is accompanied by a change in unconditioned reflexes: first, cutaneous reflexes—abdominal, plantar, cremasteric—lose; then periosteal - carpal-radial, superciliary; subsequently - tendon, which at first sharply intensifies and then fades away, usually first on the upper and then on the lower extremities; then the pupillary and corneal reflexes disappear. However, the sequence of disappearance of reflexes is not always the same; There are cases of long-term preservation of individual reflexes in the absence of others. Movement disorders are characterized by the development of spastic paralysis with increased muscle tone, reflexes, the appearance of pathological and protective reflexes, and then muscle tone decreases, reflexes fade. With the rapid development of deep oxygen starvation, loss of consciousness occurs within a few tens of seconds, and after 1 - 2 minutes coma develops. As a result of brain hypoxia, the following neurological syndromes can develop: (1) comatose states (depending on the prevalence of depression of brain functions and the level of regulation of the remaining functions): decortication state (subcortical coma), anterior brainstem (diencephalic-mesencephalic or “hyperactive”) coma, posterior trunk (“flaccid”) coma, terminal (transcendental) coma; (2) states of partial impairment of consciousness: stupor, stupor, somnolence; (3) syndromes of diffuse organic damage: severe posthypoxic encephalopathy (with mnestic, visual, cerebellar, striatal disorders), moderate posthypoxic encephalopathy; (4) asthenic conditions: posthypoxic asthenia with symptoms of hyposthenia, posthypoxic asthenia with symptoms of hypersthenia. The listed syndromes may be phases of manifestation of the consequences of brain hypoxia. The most severe degree of comatose state (exorbitant coma) is based on depression of the functions of the central nervous system, clinically manifested by: areflexia, muscle hypotonia, lack of electrical activity of the brain (“silence”), and breathing disorders. The activity of the heart and the automatic activity of other organs are preserved due to peripheral autonomic regulation. When the functions of the caudal sections of the trunk are restored, spontaneous breathing is resumed (sometimes disturbances in its rhythm are noted), corneal reflexes are evoked - this is a “flaccid” or post-trunk coma; further restoration of the functions of the anterior parts of the trunk can manifest itself as mesencephalic and diencephalic symptoms in the form of tonic convulsions, shudders, pronounced vegetative symptoms - hyperthermia, migrating hyperemia, hyperhidrosis, sharp fluctuations in blood pressure - this is “hyperactive”, or anterior trunk. Partial restoration of the functions of the subcortical nodes is associated with the features of subcortical coma, or the state of decortication. Its clinical picture is characterized by: pronounced symptoms of oral automatism (sometimes sucking and chewing movements); increased activity of subcortical reflex levels (stem, spinal, peripheral, autonomic); tendon reflexes are increased, skin reflexes are depressed, foot and hand pathological reflexes are caused; phenomena of irritation are manifested by choreiform and athetoid hyperkinesis, myoclonic twitching in individual muscle groups; EEG reveals diffuse slow waves. As consciousness is restored, patients develop a state of stupor. A deeper stupor is defined as stupor; mild degrees of stupor are gradually replaced by somnolence, which corresponds to the restoration of the functions of the cerebral cortex. In this case, signs of recovery are combined with symptoms of loss and irritation. The clinical features are largely determined by the state of the limbic-reticular complex. In soporotic states there are only the most elementary reactions to external stimuli. The EEG is usually dominated by slow waves. Stunning is accompanied by difficulty for the patient to understand complex phrases, limited ability of voluntary movements, and difficulty memorizing. Patients usually lie motionless. Against the background of stunning, dream-like (oneiric) states sometimes occur. In doubtful states, patients can be easily brought out of a drowsy state; they answer questions adequately, but get tired extremely quickly. Against the background of a state of stunning, mnestic, gnostic, praxic disorders, symptoms of damage to the cerebellum and extrapyramidal system, as well as other organic symptoms are revealed. Such disorders are defined as posthypoxic encephalopathy, which is characterized mainly by severe disorders of consciousness, memory, agnosia, apraxia, speech disorders (in the form of aphasia, dysarthria or mutism), cerebellar symptoms, striatal hyperkinesis, diffuse focal organic symptoms. Subsequently, with the restoration of functions (sometimes far from complete), neurasthenia-like symptoms characteristic of posthypoxic asthenia persist for a long time. These conditions are based on: a weakening of the inhibitory process with the development of irritable weakness, increased excitability, insomnia, decreased attention and memory - the hypersthenic form, or a weakening of both inhibitory and excitatory processes, accompanied by lethargy, drowsiness, and general retardation - the hyposthenic form. Treatment and prevention. Of particular importance is maintaining the activity of the cardiovascular system, respiration, water-salt balance and acid-base state. In the treatment of the consequences of circulatory hypoxia, narcotic drugs, neuroleptics, general and cerebral hypothermia, extracorporeal circulation, and hyperbaric oxygenation are of particular importance. To prevent microcirculation disorders, it is advisable to use anticoagulants, rheopolyglucin. For cerebral edema, often a consequence of hypoxia, decongestants are used. However, it should be taken into account that cerebral edema sometimes occurs many hours after the development of circulatory disorders and therefore may coincide in time with the phenomenon of “recoil” (an increase in osmotic pressure due to previously used dehydrating agents). Antihypoxic drugs are very promising, but so far they are used mainly in experiments. Attempts to create new quinones (based on orthobenzoquinone) deserve great attention. Drugs such as gutimin, sodium hydroxybutyrate, as well as drugs from the group of nootropics have protective properties.
Description of the disease
PE is a pathology that is not inflammatory or infectious in nature, but entails a degenerative disorder of brain tissue. Such lesions are caused by a lack of oxygen and are diffuse in nature. Due to hypoxia, neurons (nerve cells) undergo hypoxic shock and eventually die.
This disease carries with it a variety of disorders of the central nervous system, since it all depends on which area of the brain is affected. These include:
- Motor dysfunction
- Disorder of the functions of internal organs
- Sensation and perception disorder
- Functional disorders of higher nervous activity
It is important to know: oxygen starvation can be a consequence of a number of reasons: stroke, suffocation, etc.
We will find out exactly how PE is subdivided below in the article.
Rare variants of posthypoxic encephalopathy
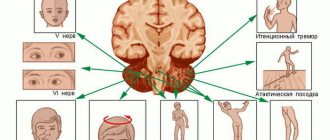
Posthypoxic kinetic myoclonus (Lance-Adams syndrome) - manifests itself immediately after restoration of consciousness. Any voluntary movement is accompanied by myoclonus. In addition to provocation by action, they can be provoked by noise, light, etc., while intellectual functions are not affected. A person cannot stand on his own with intact muscle strength, since muscle tone is lost during verticalization.
Delayed posthypoxic encephalopathy – suddenly interrupts the period of improvement. The patient's condition, after suffering clinical death or mechanical asphyxia, initially seems stable. But after a certain period of time, general cerebral symptoms appear in the form of confusion, apathy or psychomotor agitation. In focal symptoms, symptoms of damage to the subcortical nuclei most often prevail, which is manifested by parkinsonism syndrome (rigidity of muscle tone, gait in small steps, bent posture, etc.). Symptoms progress steadily over 1-2 weeks and ultimately lead to death.
Stages and types
The initial stage of this disease is mostly asymptomatic and very difficult to detect. The general development of pathology is typical for both children and adults:
- Compensatory stage
- Decompensation
- Terminal stage
Unfortunately, the disease is often diagnosed only at stages 2-3.
It is important to know that the last stage is the most dangerous and can lead to death.
In addition, the disease has several types, depending on the cause and signs of pathology:
- Primary diffuse. Develop due to problems with the functioning of the heart or lungs
- PE due to excess weight or pathologically narrowed blood vessels
- PE due to a person being in a coma
- Secondary toxic. Occurs due to toxins entering the blood
- Secondary circulatory. This type is associated with a decrease in the volume of circulating blood, which was, for example, caused by blood loss
- Local ischemic. Formed during hypoxia of a certain area of the brain
It is important to know: hypoxia may well cause increased ICP or cerebral edema.
Causes
Why does the disease occur?
There are a lot of reasons for the appearance of pathology. For example, PE can develop as a complication during childbirth: with untimely passage of the placenta or with strong entanglement of the baby’s umbilical cord around the neck.
If during labor the expectant mother suffered oxygen starvation as a result of cardiac arrest, then if the child is not removed in a timely manner, the fetus may also suffer.
In addition, the development of this disease can be facilitated by intense blood loss, as a result of which a state of shock is observed and the third stage of the pathology occurs. First, there is a decrease in oxygen supply due to this phenomenon or vascular spasm, and then depression of the respiratory center, which, in turn, is considered an extremely dangerous condition. This is why people who have suffered severe injuries are given oxygen therapy as first aid.
It is important to know that the appearance of the last stage can be caused not only by severe blood loss, but also by other diseases and more terrible injuries.
In addition, the cause of PE may also be a hereditary predisposition. If you have relatives in your family with such a pathology, then you need to closely monitor your health and undergo the necessary diagnostics in case of the slightest disorder.
The disease can be detected only when three forms develop: acute, subacute or chronic. Let's look at each of them in more detail below:
- The fulminant form of the pathology may well cause the death of the patient, and within a fairly short period of time - up to two minutes. At the same time, the rapidity of oxygen starvation over such a minimum period does not allow identifying clinical signs of the disease
- In the acute form of the pathology, there is a failure of absolutely all body systems, but the parts of the central nervous system are the first to be affected, then the respiratory and cardiovascular ones, a drop in blood pressure occurs, the heart rate slowly decreases, and breathing weakens. If hypoxia is not eliminated at this stage, then the state of the body described above becomes aggravated and turns into a coma.
- Subacute, chronic form. They are expressed by hypoxic syndrome. The main symptoms of this condition: convulsions, lethargy, drowsiness, headache, dizziness. Since the brain is most susceptible to a lack of oxygen, this results in rapid foci of necrosis, hemorrhage and other types of cell death. At an early stage of the development of hypoxia, euphoria, excessive excitability and increased motor activity occur.
In the future, this leads to depression of the higher part of the central nervous system, namely the cerebral cortex, and the following symptoms arise:
- Excessive daytime or nighttime sleepiness
- Decrease in activity
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Tinnitus
- Dizziness
- Lethargy
- Impaired consciousness
- Convulsions
- Uncontrollable bowel movements
- Uncontrolled bladder emptying
- Disorder of movement coordination and balance
In this case, convulsions appear in stages. They begin with the facial muscles, then move to the limbs and abdomen. This phenomenon can be triggered by a number of external factors, for example, light, loud sound or fear.
Causes
Posthypoxic encephalopathy is a fairly common disease. The reasons for its appearance depend on exactly when the pathology appeared. If the problem is diagnosed in a newborn, then the following provoking factors can be identified.
The lack of oxygen could occur due to heart failure in the mother, or due to diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. When taking nicotine, alcoholic beverages or drugs during pregnancy, various abnormalities in the fetus can be observed, including encephalopathy. The cause of the pathology is also the incompatibility of the Rh factor of the embryo and mother. Lack of oxygen is often observed during multiple pregnancies.
The disease is often diagnosed in children who were born later than expected or were born premature . The disease can appear directly during childbirth. It occurs due to significant blood loss, compression of the neck by the umbilical cord, incorrect position of the baby, or due to stimulation of the birth process.
If encephalopathy was acquired in the first week of life, then the cause may be a heart defect or respiratory pathology. If we talk about adults, then the disease appears due to poor blood supply to the brain, suffocation, serious head injury and heart attack. There may be a hereditary factor, therefore, if your relatives have been diagnosed with encephalopathy, then you should be more attentive to your health and, if symptoms appear, be checked by a doctor.
PE in babies
Often, signs of such a pathology appear immediately after experiencing hypoxic shock.

There is also congenital PE, which is associated with poor blood supply to the brain in the womb, during labor or after it. The main reasons that can cause this disease are neuroinfections (diseases affecting the nervous system that could be caused by infectious agents), hypoxia, trauma during childbirth, and fetal intoxication. The most common cause of this pathology is cesarean section.
Many experts claim that this disease is the main cause of neurological pathologies in children, but not many agree with this.
In some cases, this pathology resolves without serious complications, but often it carries serious consequences, namely hydrocephalus and cerebral palsy. The disease provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, which subsequently leads to epilepsy and brain dysfunction.
Often, the severity of the baby’s damage is assessed using the Apgar score and the presence of the baby’s original feces in the amniotic fluid.
Perinatal PE can often be detected from the first day of a baby’s life, primarily by disturbances in motor activity. There are three degrees of severity of the pathology. Below we will describe each of them in more detail with symptoms.
Mild degree of PE:
- Increased muscle tone
- Drowsiness
- Anxiety
- Weak sucking reflex
- Irritability
As a rule, after a few days, such signs return to normal.
Severe degree of pathology:
- The baby is in a state of lethargy, i.e. he is too lethargic, muscle tone is significantly reduced
- Severely reduced sucking and grasping reflex
- The baby may experience respiratory arrest
- Seizures occur
Atrophic changes in newborns
Atrophy affects not only elderly patients, but also newborn children. The reasons for such changes are considered to be:
• Malformation of the central nervous system at birth; • Development of hydrocephalus of the brain; • Ischemic-hypoxic changes in the brain;
The cause of all the described cases may be different, depending on many factors. For example, the effect of radiation while the fetus is in the womb, the harmful effects of medications, drugs, alcohol and tobacco products, infectious lesions, injuries during labor.
It is good that the baby’s brain during childbirth is quite plastic and, with any impact, quickly recovers and continues to perform its functions without any disturbances. The only condition is to carry out timely diagnostic measures and prescribe adequate treatment after identifying the primary disease. Otherwise, post-hypoxic changes in the brain in newborns can lead to undesirable and serious consequences - the development of DCI, oligophrenia and other diseases.
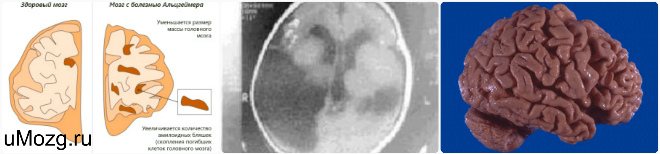
Diagnostics
Information plays a huge role, i.e. the fact of hypoxia and its duration. When undergoing electroencephalography, various disorders can be detected depending on the severity of the pathology: deviation from the alpha rhythm to symptoms of epileptic activity.
According to the results of spiral computed tomography, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain and diffuse atrophic changes can be observed. When undergoing magnetic resonance imaging, a focus of ischemia can be detected in the white or gray matter.
Treatment of the disease
After the diagnosis is made, they proceed directly to its treatment. Both drug and non-drug treatment are used. Severe disease is treated in hospital. Therapy for such a pathology takes a long time; in this situation, complex treatment and great patience are necessary.
Treatment for this pathology in children depends on age. Typically, several courses are required each year.
Drug treatment includes the use of the following drugs:
- Antihypoxants
- When epileptic seizures occur, anticonvulsant medications are used
- Diuretics
- Medicines are used to improve metabolism in brain tissue and their blood supply
- Vitamin complexes
Therapy in adults is similar to that described above. In addition, patients need to give up bad habits and eat right. In addition, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations.
Non-drug methods include massage, physiotherapy, various exercises, herbal and aromatherapy.
Often, the prognosis with a competent approach is rather favorable, especially for childhood PE. With each passing year of the baby, the signs of pathology will gradually disappear. Ultimately, the disease completely recedes, and the child continues to live a full life. This is especially true if the pathology was identified at an early stage of development, but this does not always happen. In some situations, the consequences of pathology remain for life.
In adults, the following consequences of the disease may be observed:
- Depression
- Dizziness
- Fast fatiguability
- Sleep disorder
- Memory disorder
- Decreased mental performance
- Speech impairment, etc.
In addition, this disease in children can lead to serious complications:
- Epileptic seizures
- cerebral palsy
- Hydrocephalus of the brain
- Mental retardation
But such consequences arise only if therapy was not carried out at all or PE was detected untimely.
It should also be noted that medicine does not stand still; many scientists are interested in this disease and, most likely, new methods of treating PE will be presented in the near future.
PE is a serious disease, but with the right and timely approach, the prognosis is very favorable. It is necessary to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, take rest breaks and avoid stressful situations. If you notice symptoms of the disease, consult a specialist; this is the only way you can avoid serious consequences.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
What is posthypoxic encephalopathy
When a patient is left without oxygen for a long time, he develops a pathological condition such as posthypoxic encephalopathy. As a result, brain cells suffer from a lack of blood supply and begin to gradually deteriorate. The disease progresses slowly and causes many serious neurological problems.
In medicine, this diagnosis can be seen as the abbreviation PE. The pathology is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture, which includes a lot of mental and nervous system disorders.
All these symptoms develop due to a long-term lack of oxygen access to the brain matter. This condition is typical for stroke, terminal stage and other life-threatening problems.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist !
- Health to you and your loved ones!
Very often, posthypoxic encephalopathy is diagnosed in newborns. This develops as a result of damage to the blood vessels of the brain during delivery or cesarean section.
A post-hypoxic state means that the brain has been without access to oxygen and other nutrients that are transported to it along with the blood for some time. Against this background, the so-called hypoxic shock develops, which causes the destruction of parts of the brain matter.
Perinatal posthypoxic encephalopathy is often diagnosed in newborns. Its consequences can lead to serious disorders that will remain for the rest of your life.
Therapeutic measures are selected depending on the symptoms.
These same manifestations determine the type of pathological condition:
- Primary diffuse. It develops against the background of a malfunction of vital organs (heart, lungs), as a result of which the concentration of oxygen in the blood is significantly reduced. This type also occurs in infants.
- PE due to pathologically narrowed blood vessels and obesity.
- Posthypoxic encephalopathy, which developed as a result of the patient being in a coma.
- Secondary toxic. Occurs when toxic substances enter the bloodstream.
- Secondary circulatory. It is diagnosed when there is a significant decrease in the volume of circulating blood in the body. The cause may be massive bleeding, vasospasm in newborns, or hypotension. Treatment consists of eliminating the root cause.
- Local ischemic. Occurs when a certain area of the brain is deprived of oxygen.
Treatment of posthypoxic encephalopathy
All treatment methods for posthypoxic encephalopathy are aimed at correcting the following conditions:
- Combating insufficient blood circulation: restoring circulating blood volume, treating hypotension, eliminating pinched blood vessels in infants.
- Control and treatment of neurological disorders.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the functioning of areas of the brain in which functions have been restored with the help of treatment.
- Treatment of symptoms that have developed against the background of cerebral hypoxia, in particular, disruption of the heart and other vital organs.
- Normalization of blood chemical parameters.
To bring blood counts back to normal, antihypoxants are prescribed.
These include:
- Neotone;
- Mexico;
- Actovegin;
- combination drug Cytoflavin.
The patient also takes nootropic drugs to stimulate metabolism and antioxidants.
In addition to medications, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures, and they can be carried out in a state of complete health, since they strengthen the vascular walls. You need to eat more foods rich in vitamin E, C, and fiber.
Grapes, nuts, kiwi, and red berries have these properties. It is not recommended to drink drinks containing alcohol.
Try to get more rest, take frequent walks in the fresh air, and avoid nervous tension. Such measures significantly improve the condition of nerve cells, which is very important for recovery. Moderate physical activity also has a positive effect on health.
Don't forget that encephalopathy can occur due to a genetic predisposition. In such cases, you need to closely monitor your health and undergo examinations at the slightest disturbance.
What is residual encephalopathy in children - read here.
A description of encephalopathy of complex origin can be found at the link.
Principles of therapy
When hypoxic encephalopathy is detected, comprehensive measures are prescribed in order to achieve the best result. Medicines and non-drug treatments are used.
If the patient has a pathology of at least moderate severity, he will have to stay in the hospital. The therapy will be quite long, so you will have to be patient.
Neuralgic disorders are carefully monitored to eliminate negative consequences. It is necessary to solve problems caused by abnormalities in the blood supply. We are talking about ischemia, vascular compression, hypertension. It is important to take care of the treatment of disorders of the cardiovascular system. If necessary, the chemical component of the blood is corrected.
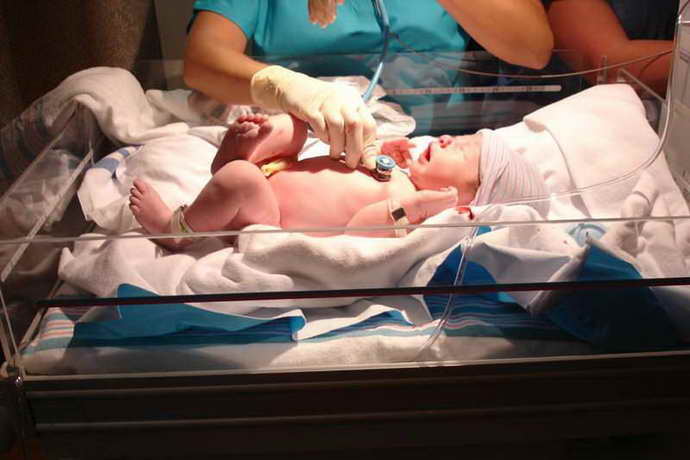
Doctors prescribe antihypoxants such as Mexicor, Neoton and Actovegin. It is recommended to use nootropics, metabolic stimulants and antioxidants. In addition to medications, foods that contain fiber, vitamin E and C are added to the diet . Grapes, kiwi, nuts and red berries are suitable. These products can only be used by adults and children for whom they are already approved by age.
Patients are advised to rest more and spend time outdoors. Overexertion during illness is not permissible, because it can only aggravate the situation. With your doctor's permission, you can perform moderate physical activity, which will increase blood flow and increase the amount of oxygen delivered to the brain.
The patient’s condition must be monitored by a doctor, because it is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. If necessary, treatment methods will have to be reconsidered.
Causes of pathology
Posthypoxic encephalopathy is not a rare disease. Hypoxia suffered by the fetus causes oxygen starvation of the brain, resulting in the death of a certain number of neurons. During pregnancy, hypoxia can be caused by the following factors:
- heart failure in women;
- diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2 in the mother;
- toxic effects of alcohol, nicotine, narcotic substances;
- incompatibility of the Rh factor of mother and fetus;
- multiple pregnancy.

Hypoxia is often suffered by children born postterm. Another factor that provokes oxygen starvation of the fetus is the threat of failure or premature birth.
The disease can develop directly during childbirth for the following reasons:
- severe blood loss;
- malposition;
- entanglement;
- stimulation of labor;
- premature puncture of the bladder.
Thus, the reasons for the development of pathology in children can be due to both intrauterine development and complicated childbirth or birth trauma.
In neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), the first diagnosis is asphyxia, a condition of suffocation in which the baby is unable to take its first breath.
Symptoms
Symptoms of HIE in a newborn are detected using Apgar testing. Often traces of meconium (first feces) are found in the amniotic fluid. A moderate degree of hypoxia may manifest itself slightly in a newborn. Later, changes, including neurological deficits, are detected during an examination by a neurologist or a routine ultrasound examination.
In some cases, the baby immediately requires intensive care. Commonly observed clinical syndromes are:
- Oppression. Lethargy, apathy, physical inactivity, muscle hypotonia, weakened reflexes.
- Comatose. Congenital reflexes do not arise to pain, light and other stimuli, atony (lack of muscle tone), lack of motor activity.
- Convulsive. Convulsions of tonic-clonic or tonic type.
Signs of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborns are identified during instrumental diagnostics and visual examination. The course of the disease varies among patients. Usually the pathology is accompanied by revitalized reflexes and increased nervous excitability (spontaneous motor activity, revived knee reflexes, tremors of the limbs). In parallel, signs of cerebral hypertension are revealed:
- Swelling, bulging of the fontanel.
- Throwing the head back.
- Unreasonable, frequent crying.
- Decreased appetite, refusal to eat.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Increase in skull diameter.
- Horizontal nystagmus.
- Convergent strabismus (the visual axis is deviated towards the nose) type.
- Muscular dystonia (pathological muscle contraction accompanied by involuntary movements).
Developmental features and symptoms
The brain is the most important part of the human central nervous system. Oxygen starvation leads to a lack of oxygen in the brain tissue, as a result of which normal blood flow is disrupted and metabolic processes slow down. Lack of nutrition leads to the death of neurons in some parts of the brain, which is fraught with the development of a number of neurological disorders.
Poor circulation in the brain tissue of a newborn entails a rapid increase in edema. Tissue swelling provokes an increase in pressure, which results in the death of neurons.

An experienced doctor will recognize the symptoms of hypoxic encephalopathy in the first minutes after the baby is born. The following symptoms indicate a dysfunction of the nervous system:
- weak or delayed first cry of the newborn;
- decreased reflexes;
- moodiness, constant crying;
- bluish skin tone.
Diagnosis of hypoxic encephalopathy is usually carried out in the first hours after birth.
Forms of pathology
Depending on the degree of damage to the nervous system, there are three degrees of severity of the disease in infants:
- light;
- average;
- severe encephalopathy.
The mild form of the disease is characterized by sleep disturbances, problems falling asleep and waking up, mild restlessness and twitching of the chin. The child has increased reflex activity. The baby is restless, often screams for no reason and sleeps poorly. This form is characterized by an unreasonable increase in motor activity, with a simultaneous decrease in swallowing and sucking reflexes. The disease is successfully treated in the first few weeks after birth and does not leave any negative consequences in the future.
With moderate hypoxic encephalopathy, the following symptoms are observed:
- weakness of natural congenital reflexes;
- neurological disorders of a local nature;
- weakening of body muscles;
- restlessness, frequent screaming for no reason.

Neurological disorders with moderate severity of the disease are characterized by strabismus, ptosis, and weakening of the eyelid.
A severe form of hypoxic encephalopathy in infants is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent convulsive conditions of a paroxysmal nature;
- complete absence of reflexes characteristic of newborns;
- critically low blood pressure;
- weak pulse;
- complete lack of muscle tone.
A severe form of pathology may be accompanied by disruption of various internal organs.
Symptoms
The signs of encephalopathy depend largely on what stage the disease is at, as well as what causes it. You should know the common symptoms in order to suspect brain pathology in time.
With mild severity of the disease, the following signs are noted:
- Slightly increased muscle tone.
- There is a weak sucking reflex in newborns.
- There is increased irritability or tearfulness.
- The child sleeps more than expected and looks lethargic.
As a rule, these symptoms should disappear in the child during the first week. In this case, parents should not worry, but in any case they should consult a doctor.

Symptoms of moderate illness:
- Cramps.
- Lack of sucking and grasping reflex.
- Severe lethargy of the baby.
- Stopping breathing, which goes away in a short time.
- Muscle hypotension.
It is quite difficult to make an accurate prognosis for moderate encephalopathy. Negative signs may disappear completely in the first two weeks of life. They can also worsen, with increased symptoms observed even after a period of remission. Treatment must take place exclusively in a hospital setting if parents want to achieve a positive effect.

In severe pathology, the following manifestations are observed:
- The child does not respond to external stimuli.
- The baby is in a coma or in a stupor.
- Breathing often stops, which is why it is necessary to connect a special device to the baby to maintain respiratory function.
- There is no reaction to light, while the pupils are constantly dilated.
- There may be cerebral edema, which increases blood pressure and swells the fontanel.
- Arrhythmia is observed.
In severe cases of hypoxic encephalopathy, the newborn may experience disruptions in the functioning of various organs. Treatment is carried out exclusively under medical supervision. If the parents do not go to the hospital, then there is a high probability of death.
In adults, there may be pain in the head, impaired consciousness, uncontrolled bowel movements, decreased activity, and constant drowsiness. Loss of coordination, seizures, and persistent nausea may also occur. Ischemic encephalopathy and other types of pathology should not occur without medical supervision.
Only a doctor can clearly say how dangerous the patient’s condition is in a particular case . If you cannot do without treatment, then the doctor will definitely prescribe it.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment is prescribed depending on the degree of pathology. The cause of mild encephalopathy is a violation of cerebral circulation, so all symptoms disappear safely when blood circulation is normalized. The cause of moderate disease is tissue swelling and a subsequent increase in intracranial pressure.
Treatment of moderate and severe disease is based on the following medications:
- anticonvulsants;
- medications to stimulate the cardiovascular system;
- decongestants.
Drug treatment includes a large list of drugs and is selected individually for each case of the disease in newborns.
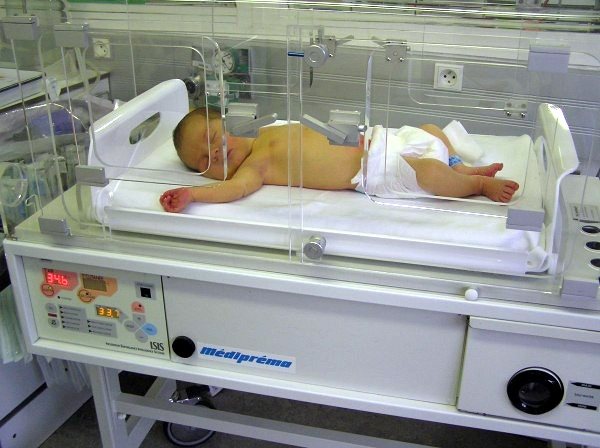
Immediately after birth, the baby is placed in an incubator. For babies with this pathology, tight swaddling, loud sounds and bright light are contraindicated. The baby must be kept at a temperature not lower than 25 0 C. In most cases, a system for ventilation is installed for newborns.
The child is kept in the hospital for a long time. The baby's health requires careful monitoring during at least the first two weeks of life. In the future, the decision to extend hospital treatment is made by the doctor, depending on the severity of the patient’s brain damage.
The purpose of inpatient treatment is:
- saturation of tissues with oxygen;
- normalization of respiratory function;
- relieving swelling of brain tissue;
- normalization of intracranial pressure.
Subsequently, after the acute symptoms have been relieved, the child is prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic procedures to normalize all metabolic processes of the brain.
After discharge from the hospital, treatment continues at home with mandatory examination by a doctor every three to four days. Since seizures often develop with encephalopathy, taking anticonvulsants can last up to six months, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Home treatment largely depends on how the baby develops. If there are no developmental delays, and convulsive seizures do not recur, a regular examination by a neurologist is enough for the child, without additional treatment at home.
With extensive damage to the central nervous system, treatment continues for a long time and is adjusted depending on the patient’s condition.
Possible consequences and prognosis
The prognosis is most favorable for mild disease. In this case, therapy includes saturating the blood with oxygen and stimulating normal cerebral circulation. As a rule, anxiety symptoms disappear successfully in the first weeks of a baby’s life. No negative consequences or neurological disorders are observed.
In all other cases, there is a risk of developing the following consequences:
- child development disorder;
- brain dysfunction;
- disruption of the functioning of some internal organs;
- local neurological disorders;
- hydrocephalus;
- autonomic dysfunction;
- epilepsy.
Impaired brain function may subsequently manifest itself as an inability to concentrate for long periods of time and weakened memory. There is a high probability that such a child will study poorly due to restlessness.
Developmental disorders may manifest as speech therapy impairments and growth retardation. In this case, the baby is indicated for treatment in special medical institutions.
Disruption of the functioning of certain internal organs requires careful monitoring of symptoms and timely treatment in case of exacerbations. You can get rid of this problem only if you pay attention to the alarming symptoms in a timely manner.
Hydrocephalus due to encephalopathy requires timely treatment, including surgery. This disease can also cause a number of neurological disorders.
With severe encephalopathy, the risk of further development of epilepsy is high. This is due to disruption of the functioning of certain areas of the brain and the death of neurons, as a result of which patients experience an increase in the excitability of certain areas of the brain and, as a result, convulsive seizures. However, timely treatment of acquired epilepsy often allows one to successfully get rid of convulsive seizures.
Prognosis and prevention
Due to the serious consequences for the health of the child, the prevention of hypoxic-ischemic processes during intrauterine development and the prevention of asphyxia during childbirth is of great importance. The prognosis for hypoxic conditions depends on the severity of damage to brain structures and the severity of neurological disorders.
The diagnosis of HIE in infancy correlates with pathologies such as brain dysfunction, cerebral palsy, and epilepsy. In adults, posthypoxic encephalopathy causes the development of neurological deficits, deterioration of cognitive abilities, and dementia.
PLEASE, ! 124
How to avoid getting sick

Women with chronic diseases such as epilepsy or diabetes should undergo comprehensive testing before conceiving a child. Having achieved compensation for their own illness before conception, every woman has a high chance of bearing and giving birth to an absolutely healthy baby. Since the cause of pathology in infants is hypoxia in the prenatal period, the duty of every woman is to give up bad habits while bearing a child.
A thorough examination and pregnancy management by a qualified doctor will help you avoid complications during childbirth.