Causes
Children often fall and may suffer head injuries.
The frequency of TBI and the reasons for their occurrence are specific to each child’s age. Thus, newborns account for 2% of all cases of childhood TBI, infants – 25%, toddlers – 8%, preschool children – 20%, schoolchildren – 45%.
It is clear that infants and infants receive TBI due to the oversight or carelessness of their parents, falling from the changing table, from the stroller, and even from the hands of their parents. After a year of starting to walk, a baby may be injured when falling from his own height, and a little later when falling from a slide, ladder, swing, from a window, from a tree, etc.
Moreover, the fact of injury is not always known to parents if the child remained under the supervision of relatives, nannies, older children, or employees of preschool institutions. Older children themselves may, for whatever reason, hide the fact of a fall.
It should also be remembered that brain injury can occur without a direct blow to the head. We are talking about the so-called “shaken baby” syndrome.
SHM can occur during sudden braking or acceleration of the body when running, when jumping from a height and landing on the feet, and even during intense rocking of the baby.
Consequences of a head injury
Often, if a concussion occurs, a person regains consciousness quickly. It is important to give him a comfortable position. He should lie horizontally, his head slightly raised. If the person continues to be unconscious, there is no need to identify anything. It should be given a “rescue position” so that no additional problems can appear. This requires:
- put it on your right side;
- throw back your head, turn your face slightly towards the ground;
- bend your left arm and leg at a right angle at the elbow and knee. It is important to determine what fractures are present on the body in places whose position will have to be changed and whether there are any fractures at all. If present, the described areas should not be touched.
This position ensures the normal passage of air into the lungs and, if there are liquids in the mouth, their unhindered flow. Even with an abnormal position of the tongue, respiratory function is not impaired. For bleeding wounds, it is important to bandage the head. It is important to know what to do if you have a concussion so that you can provide the person with the necessary help if they need it.
In case of a concussion, it is necessary to visit a doctor and carry out certain procedures. It is necessary to determine the presence of hemorrhages in the brain and changes resulting from the blow. If you have a concussion, you should know what to do and what to do. Even a person’s life may depend on it.
People around a person with an injury need to know how to identify a concussion in order to take timely measures to provide help. The victim requires bed rest for 1-3 days. Then, if the disease has subsided, the condition has returned to normal, discharge from the hospital and outpatient treatment are possible. Its duration is about 14 days.
After hitting your head, especially if you hit it hard, certain complications and consequences may arise. Some of them appear immediately, others gradually, maybe even after several months or years. The main consequences if a bruise to the back of the head occurs and no treatment is given:
- Deterioration in performance due to traumatic asthenia;
- problems with concentration;
- Depressive states;
- Deterioration in memorizing information;
- The occurrence of irritability and insomnia;
- Constant headaches, migraines;
- Reaction to weather changes.
To prevent a head blow from becoming a cause of suffering, at the first sign of it you need to be examined and treated.
Every person who has ever hit their head needs to know what to do if they hit their head. So, if you hit your head on something, you should proceed with the following actions:
- Apply a pressure bandage to the head. With its help you can prevent the occurrence of hematoma.
- Make a cold compress by applying ice wrapped in a cloth or any product from the freezer to the bruise. Such compresses should be left on the damaged area for twenty minutes and repeated throughout the day. This action will narrow the blood vessels, relieve pain and prevent the hematoma from spreading.
- If there is damage to the skin, for example, an abrasion or a small cut, then you need to carry out antiseptic treatment with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine. Covering the wound with brilliant green or iodine is not necessary. If the cut is large, it is necessary to contact a surgeon for suturing.
- Starting from the second day, you can resort to warming up the injured area using warm compresses, lotions, and a heating pad. This helps the swelling to resolve faster. It is unacceptable to heat the bruise on the first day, as this can intensify the inflammatory process.
- To make the bruise go away faster, you can use special ointments, creams or gels for bruises, but it is better to discuss their use with your doctor.
- If a crust forms at the site of skin damage, it is important not to rip it off, otherwise a scar may remain. It is better to use softening creams, then a crust will not form.
- If you have a severe headache, you can take a painkiller. But if there is subcutaneous hemorrhage, then you should not use aspirin, as it interferes with blood clotting and can cause the hematoma to become even larger.
Timely first aid for a head injury will help reduce the risk of negative consequences.
Signs of a concussion
The symptoms of FMS in children differ from those in adults (loss of consciousness, nausea, dizziness, headache, vomiting, memory loss, etc.). The children's brain has distinctive features. For this reason, children rarely present with the classic signs of FMS seen in adults.
The younger the child, the fewer obvious symptoms of a concussion. In children, loss of consciousness occurs only in rare cases.
Characteristics of SGM for young children will be:
- anxiety;
- causeless crying;
- regurgitation (or repeated vomiting);
- loss of appetite;
- pale skin;
- bulging fontanel in infants;
- sleep disturbance (drowsiness or poor sleep).
For school-age children, the clinical symptoms of SHM are as follows:
- loss of consciousness is more common;
- in some cases, amnesia (loss of memory for the circumstances of the injury) is possible;
- nausea;
- vomiting (may be repeated);
- headache (to varying degrees);
- slow or rapid heart rate;
- instability of blood pressure;
- pronounced pallor;
- sweating;
- disturbed sleep (insomnia or drowsiness);
- irritability or apathy;
- tearfulness and whims.
Sometimes after an injury or a little later, children experience post-traumatic blindness, lasting from several minutes to several hours, which then disappears on its own. More often, this symptom appears after a blow to the occipital region of the head, where the visual center is located.
One of the features of the symptoms of BMS in a child is that they may not occur immediately, but after some time (from several hours to several days). In this case, symptoms can increase very quickly.
When a child is injured, it is difficult to determine whether there has been brain damage. Even imaginary well-being for a long time does not exclude the presence of an internal hematoma, manifested by a progressive deterioration of the condition in the future.
Considering these features of the clinical manifestations of TBI in children, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion of injury, even with mild symptoms, without complicating the situation.
The danger with SHM is not the pain from bruising the soft tissues of the head, but the possible deep-seated damage to the nervous system. An internal hematoma (bleeding) that occurs in the brain tissue poses a greater danger than in an adult.
In such cases, children are examined by a pediatric traumatologist (or neurosurgeon) and a pediatric neurologist.
If necessary, doctors prescribe additional examination methods:
- neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) – for young children (up to 2 years);
- echoencephalography (after 2 years);
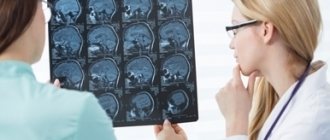
- CT scan of the brain;
- MRI;
- lumbar puncture;
- electroencephalography.
To identify occult skull fractures, a skull x-ray is prescribed.
Here's what experts say about concussions in children and first aid for injuries:
Head injury in a child: what to do? Advice for parents - Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Symptoms
Treatment after a head impact always depends on the symptoms, while the symptoms themselves and their severity depend on the severity of the injury and its location. The following signs may indicate that the soft tissues of the head have been damaged:
- pain arising from vasospasm;
- the formation of a bruise that forms a lump;
- the presence of a small bruise or extensive hematoma;
- nosebleeds;
- short-term increase in body temperature;
- weakness in the arms;
- confusion or complete loss of consciousness;
- the occurrence of nausea and vomiting.
A bruise to the back of the head may be accompanied by a disturbance in visual function, because the endings of the nerves that are responsible for vision are located in the back of the head. If the frontal part is bruised, bruises may form under the eyes. If the temporal lobe is injured, it can lead to tinnitus. In fact, this is not the entire clinical picture, but if these signs occur, treatment should be immediate.
After receiving a blow to the head, certain symptoms can be observed, from which it is possible to understand that it is a concussion and not another problem.
Symptoms of a concussion:
- Stupor. It is expressed in the appearance of confusion in a person, a state similar to stunning occurs. The muscles on the face tense, the face ceases to express emotions, as the muscles freeze. This reaction occurs due to inhibition of movements in the body. Nerve signals begin to be transmitted incorrectly in the brain, which is why the condition arises.
- Loss of consciousness, concussion. The patient stops reacting to external irritating factors and stops feeling anything. The duration of this state ranges from a couple of seconds to 5-6 hours. It all depends on the damage caused and the force of the impact. The condition occurs due to changes in the transmission of signals along the nerves. The body feels an acute lack of oxygen due to changes in blood circulation.
- Vomit. Occurs once. Breathing becomes frequent, salivation and severe tearing begin. There are several vomiting attacks. The condition occurs due to changes in the vomiting center.
- Nausea. The occurrence of unpleasant sensations, severe heaviness in the abdomen. Disturbances in the vomiting center, located in one of the parts of the medulla oblongata, affect it. The part is irritated, causing a corresponding reaction to appear.
- Dizziness. May intensify with changes in body position. The functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted.
- Change in heart rate. The determining factor for the appearance is the occurrence of oxygen starvation due to increased pressure in the cranium. Pressure may occur on some centers, causing a corresponding reaction.
- Pallor. It may be replaced by the appearance of redness or various other shades, of which there can be any number of them and they manifest themselves differently in different people due to the malfunction of the vegetative organs. The arterial network on the face begins to narrow or expand, causing the skin color to change.
- Headache. Pulsations in the back of the head or at the site of impact. A bursting pain begins due to increased pressure in the head, irritation of the receptor network on the head.
- Noise. May appear as hissing or loud ringing. Due to the blow, the large ear nerve can be compressed, which causes a disruption in the functioning of the auditory organs. Therefore, it seems to a person that there is noise somewhere outside.
- An additional symptom is pain when moving the eyes. The pressure in the skull increases, so discomfort may occur when a person turns his eyes. Treatment of a concussion with such a symptom becomes more complicated, because important organs or systems may be affected.
- Loss of coordination. There is a feeling that the body stops listening. Motor functions are performed as if with a slowdown. Due to a slowdown in the passage of signals from the brain to the muscles.
- Signs of a concussion include increased sweating. The internal organs control the sympathetic system, which controls sweat secretions. She gets very excited, tension arises there. Therefore, a person produces a large amount of sweat in comparison with the usual regime.
Immediately after the injury, the first symptoms of a concussion may appear:
- The pupils narrow or dilate. A diagnostic point that is important to immediately recognize: the reaction to light should be normal, no unusual sensations should be observed. But if it is noticed that the pupils are of different sizes, we are talking about serious violations, greater than a simple injury. A similar reaction appears due to the action that can be exerted on the central parts of the autonomic system. They control the movements of the muscles that work to reduce or enlarge the pupils. Treatment of a concussion becomes more difficult with this symptom.
- Trembling of the eyeballs when the eyes move to the sides. The symptom also manifests itself in the following: it becomes difficult to see objects that are on the side without turning the head. A similar phenomenon occurs as a result of damage to the inner ear and cerebellum. Such systems control the rate of muscle contraction. Diagnosis of a concussion is simple. But if the described symptoms occur, it is important to contact a medical facility as soon as possible.
It turns out that a person cannot fix his gaze on a certain object on the side of him. It is important to treat a concussion with such symptoms immediately so that the condition does not worsen.
Effect of skull fractures on the spine
A skull fracture can cause damage to the spine. This is due to the fact that the brain is connected to the spinal cord. Also, the cervical spine is attached to the cranium. A traumatic brain injury that leads to disruption of the functionality of the spine is called combined.
Injury to the spine leads to partial or complete paralysis of the human body. In most cases, such consequences are observed if the injury affects the cervical spine or affects the spinal cord. Spinal repair can occur, but only in rare cases.
Spinal trauma after a skull fracture in children is more treatable than in adults. But it may take many years to fully restore the functionality of the spine, depending on how strong the child’s body is.
Hit to the temple - now my head hurts when I hit my temple
There are a number of situations in which a person may experience head injuries. It is worth considering them in more detail:
- Hitting your head after a fall.
- A hard object or stone was thrown at a person's head.
- A blow to the temple with a bat or brass knuckles, which causes a severe headache.
- Injury as a result of a traffic accident.
- Hit to the head during a street fight.
- Throwing a punch during sports training.
- Intentionally beating a person.
After injury, a large hematoma may appear on the head. In more complicated situations - extensive bleeding. Bleeding is especially common when the frontal part is affected.
https://www..com/watch?v=A5rnIK3I4gA
Many falls result in a concussion, which can cause a person to lose consciousness and develop memory problems.
In addition, it is after a blow to the head that people may develop mental illnesses.
When immediate medical attention is required
Man is designed in such a way that the most vulnerable part of his head is the temporal region.
If a person hits himself or is hit in the temple, there is a risk of a concussion and loss of consciousness. But if it was hit by a professional, it would be completely fatal.
There is a list of main pathologies that can develop after a bruise in the temporal region. They are:
- Paralysis of the limbs.
- Epileptic seizures.
- The appearance of an aneurysm.
- Development of acute cerebral hemorrhage.
A slight blow to the temple is manifested by mild pain, which can be relieved independently, with the help of medications and temporary rest.
If the head, or rather the temple, hurts more and more after the blow, then you need to immediately call an ambulance.
After a head injury, a person should carefully study the nature of the pain. You need to go to the hospital when the following symptoms are observed:
- Prolonged headaches that do not disappear for several days.
- The pain is not relieved by taking strong painkillers.
- There is pulsation in the temple area or noise in the ears.
- You feel stiffness in your neck or pain when you turn your head to the sides.
Signs of a concussion include the following symptoms: severe dizziness, fainting, darkness in the eyes, problems with vision and speech, increased weakness, bruises under the eyes and nausea accompanied by vomiting.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must carefully examine the patient, examine his face and oral cavity, and palpate the tissues and skull.
If there is a suspicion of a bone fracture, the specialist will prescribe an x-ray.
In the event that a person has received a strong blow to the temple and then has a headache, he should immediately call an ambulance.
While the doctors are traveling, you need to try to help the victim yourself:
- Turn the person onto their side, slightly lifting their head and shoulders. Such actions will help prevent the victim from choking on his own vomit.
- The most important thing is to ensure that the person does not move, because the head must remain in its original position.
- After a blow to the temple, ice should be applied to the bruised area so as not to put pressure on the area of the hematoma. The same should be done with any bumps that appear.
In the case when a woman hits her head and develops a bleeding wound, you need to use hydrogen peroxide and treat the site of the impact.
How to cope with pain on your own
If a person has injured his head, he may experience pain for some time. Some people find tea with mint and honey and proper rest helpful.
In addition, it would be a good idea to take a warm bath with some relaxing essential oil added.
If it is not possible to take a bath, then you can pour water into a container, drop a little oil into it and place the bowl next to your head.
When the blow hits your temple, you should apply cold to it. For example, an ice cube or a piece of meat from the freezer, wrapped in a soft cloth.
In addition, cabbage leaves taken in the refrigerator will cope well with the problem.
Among medications, healing ointments are allowed. For example, Diclofenac or Fastum Gel.
Traditional medicine
A compress made from potatoes, mashed to a pasty state, has a very good effect on the nervous system.
To do this, grate the potatoes, wrap them in gauze and place them on your temple. After this, it is recommended to lie down and rest a little.
You can use potato decoction, tomato and beet juice, a cocktail of parsley, sorrel and broccoli.
When an injury causes a drop in blood pressure, doctors recommend drinking motherwort or a decoction of St. John's wort.
It is worth considering that a person who has suffered a head injury may suffer from sudden changes in weather conditions and changes in atmospheric pressure.
Therefore, it is better to consult a doctor and follow all his recommendations.
Source: https://optika-stil.ru/budet-esli-udarit-visok/
Traumatic brain injury in a child
Fractures of the temporal and parietal zone are often diagnosed in children. The causes of such an injury can be different: from birth trauma to being hit by a heavy object. As a result of damage to the parietal region, the child's bone is pressed inward. Since newborn babies lack bone in the parietal area, such an injury can occur very easily. The consequences for the child are very serious.
As a result of trauma in the parietal area in children, hematoma, swelling and abrasions form. Tissue rupture and heavy blood loss may also occur. With more serious traumatic brain injuries, children may experience bleeding from the ears, throat, and nose. Even if a child hits his head slightly on something, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
Treatment
If you receive an injury such as a skull fracture in the temple or other area, you must provide first aid to the victim and call an ambulance. After the patient is taken to a medical facility, treatment will begin.
First of all, a person with a skull fracture is examined and all necessary actions are taken to restore his condition. After the victim’s condition has stabilized, he is sent for diagnostics. In emergency cases, diagnosis is carried out while the patient is being prepared for surgery.
Diagnostics includes a number of laboratory and hardware tests:
- general tests;
- X-ray;
To establish a complete clinical picture, consultation with several doctors of different specialties may be required. Only after the general picture of the pathology has been established is the method of eliminating it determined.
Treatment methods
Depending on the area of injury, as well as the complexity of the fracture, treatment can be carried out using different methods. Head trauma is a serious pathology, therefore, in most cases, surgical intervention is performed for fractures. This type of operation is dangerous for children and adults. An elderly person with a traumatic brain injury does not undergo surgery due to the high risk.
In some cases, conservative treatment is allowed. It is mainly used if subluxation of the temporomandibular joint is diagnosed.
Treatment of a temporal lobe fracture
One of the important actions for a fracture of the temporal bone is first aid. All that needs to be done in such a situation is to apply a bandage to the ear and urgently hospitalize the patient. If the injury occurs in a child, then he must be taken to the hospital, even if there are no external signs of injury. You should not do any unnecessary actions to independently diagnose the condition of children.
In case of a closed temporal lobe fracture and no brain damage, treatment is carried out conservatively. Therapeutic treatment includes taking antibacterial drugs to eliminate the risk of infectious complications. Prophylaxis against cerebral edema can also be carried out. The operation should be done only if a vascular rupture or purulent otitis media is diagnosed.
With an open fracture of the temporal bone, the likelihood of death is high. Conservative treatment in such a situation is unacceptable. Therefore, only surgery is performed to restore all tissues, followed by therapy. After treatment is completed, long-term rehabilitation will be required.
Treatment of dislocation and subluxation
Damage to the temple, resulting in subluxation of the mandibular joint, is eliminated with the help of reduction. All actions are performed by a traumatologist. You cannot reduce a dislocation or subluxation yourself. Treatment should only be carried out in a medical facility.
Treatment is not carried out through surgery. Using hand movements, the traumatologist realigns the jaw, after which he applies a special bandage - a retainer. This bandage is removed after a week.
Before the jaw is realigned, the patient must be examined to rule out the possibility of a fracture. If there is a fracture of the jaw bone, then the actions of the traumatologist may result in the victim receiving a more serious injury, which will already be corrected surgically.
Consequences
A skull injury cannot go unnoticed for a person. Even after a few years, complications may appear. As a result of serious fractures, there are always negative consequences.
- Chronic headaches and vestibular disorders.
- Hearing loss.
- Complete or partial paralysis of the face or limbs.
- Infectious (purulent) meningitis.
- Brain atrophy.
The worst result of head injury is death. Any, even the most minor injury to the skull can lead to the death of the victim. In the absence of treatment or incorrect actions of a specialist, a person who has suffered a traumatic brain injury may remain disabled.
Dangers of pillow fights
A blow from a pillow, unlike blows from other objects, usually does not cause harm to the body, since pillows are soft. However, some strikes are quite dangerous. For example, a pillow can knock a child off his feet, especially if he is standing on a soft and unstable surface, such as the edge of a bed. If the blow is very strong and is applied from above to the head by a fairly heavy pillow or is “pinched” between the pillow and the wall, this can lead to a concussion and spinal injury.
Also, in the turmoil of a fight, a person can accidentally get hit by an elbow, head, etc., get tripped up and fall.
First aid for head injuries
First aid for a blow to the back of the head is necessary for the victim immediately after the incident, without waiting for the ambulance to arrive. Of course, an ambulance also needs to be called, since in the future the wounded person will need professional treatment from doctors. What to do in this situation:
- Place the injured person on the floor or sofa (depending on location) so that he remains at rest.
- Apply a compress to the bruised area. This could be a frozen product from the freezer or a piece of ice wrapped in a towel; also use a bottle with cool liquid. The compress should be applied for no more than 15 minutes, then removed for half an hour and applied again.
- If the victim experiences a feeling of nausea, he must be turned on his side.
Note! You only need to do what will alleviate the condition of the wounded person, but you should not give painkillers immediately after a bruise until an ambulance arrives. This may interfere with the examination and diagnosis of the injury.