Semax - nasal drops with nootropic, antihypoxic, cerebroprotective and antioxidant effects. This allows them to be used for a wide range of disorders of the nervous system.
Semax nasal drops are available with a prescription. The drug should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, with strict adherence to the recommended dosage.
What are nootropics
Nootropics are drugs or psychometabolic stimulants designed to activate the integrative functions of the brain
That is, in essence, they are called upon
improve memory, restore mental activity, encourage learning, increase the organ’s resistance to external influences, etc.
At the same time, nootropics do not calm a person and do not activate the bioelectrical activity of the brain. Do not confuse them with psychostimulants. Nootropics only stimulate the transmission of excitation in its central neurons. They also make the process of transmitting information between the hemispheres easier
Moreover, these substances, when taken regularly, normalize the blood supply to the brain and can improve a number of energy processes. They prevent hypoxia, that is, they increase antihypoxic activity
Nootropics are valued by representatives of official medicine for their ability to activate human abilities
mnestic - i.e. working with memory, with the ability to store information for a long time and repeatedly enter it into the sphere of consciousness and behavior and intellectual
At the same time, human physical activity only in combination with the psychostimulant drugs mentioned above, as well as with actoprotectors - specific stimulants of physical activity
In some cases, they can help in this matter for people with an asthenic physique or a weakened body
The word “nootropics” itself comes from a combination of the Greek words thinking and striving.
This term has a number of synonymous words and expressions
Nootropics Neurometabolic stimulants Nootropics Neuroregulators Neurodynamic stimulants Metabolite cerebroprotectors Eutotrophic stimulants
The first officially recognized nootropic was Piracetam. It appeared in the early 60s of the last century. Belgian pharmacologists noted that those who take this drug have better memory and ease of learning. They also noticed that this drug does not cause the side effects that usually entail psychostimulants
The term “nootropics” that exists today originated in 1972. It was proposed by one of these researchers to refer to a class of drugs that are designed to stimulate higher brain functions
Side effects
When conducting studies to study the effect of the active substance of the drug on the human body, practically no negative reactions were identified.
In rare cases, sleep disturbances and excessive excitability may occur.

Immediately after administering the solution, irritation of the nasal mucosa is sometimes felt, especially if long-term treatment is prescribed.
The most dangerous side effects are:
- hives;
- rhinitis;
- facial skin hyperemia;
- Quincke's edema.
They appear due to individual intolerance to the drug. If alarming symptoms are detected, you should immediately seek medical help from specialists.
What are nootropics?
Currently, there are more than a dozen pyrrolidine nootropics (racetams) , which are in the trial phase, but are already officially recognized in some countries
Oxiracetam

Aniracetam Etiracetam Pramiracetam Dupracetam Rolziracetam Cebracetam Nefiracetam Izacetam Detiracetam
In addition to these drugs, other types of nootropics
Cholinergic GABAergic Glutamatergic Peptidergic
Nootropic properties have also
glutamic acid memantine and levocarnitine
Moreover, signs of nootropic activity have been experimentally established in some neuropeptides , as well as in their synthesized analogues
oxytocin

somatostatin vasopressin thyroliberin melanostatin cholecystokinin neuropeptide Y substance P angiotensin II cholecystokinin-8 peptide analogs of piracetam, etc.
The nineties of the last century became a time of active research into existing nootropic drugs and the creation of new drugs with similar effects. And to this day, the search for new generation drugs that can not only activate higher functions of the brain, but also cause a minimum of side effects, has not stopped. Today we can say with confidence that modern nootropics to one degree or another meet the specified parameters
Analogs
If necessary, the doctor selects a substitute for Semax, which has identical pharmacological properties.
Among the popular analogues:
- Aminalon (tablets, 50 pcs.) – 143 rubles;

- Vinpocetine (tablets, 30 pcs.) – 87 rubles;
- Gamalate B6 (tablets, 20 pcs.) – 350 rubles;
- Calcium hopantenate (tablets, 50 pcs.) – 228 rubles;
- Picamilon (tablets, 30 pcs.) – 83 rub.
It is strictly prohibited to independently change the drug recommended by the doctor or make adjustments to the treatment regimen.
An incorrectly selected remedy will, at a minimum, not give the expected therapeutic effect, and, at a maximum, will provoke serious complications.
Nootropics in sports medicine
In medicine, it is believed that it is advisable for professional athletes to take nootropic drugs during important training and even competitions. This is due to the ability of these drugs to correct the functional resources of the body . Typically, these are the following drugs
Piracetam

Etiracetam Aminalon Sodium hydroxybutyrate Phenibut
Phenotropil (carphedon) belongs to class S6 of the list of prohibited substances and methods (2008), and therefore it is prohibited to take it during sporting events
They are used
In case of brain injuries In case of dizziness In the presence of cerebrovascular disorders in the body In case of motion sickness In order to enhance concentration of attention And also during the period of recovery of the athletes’ body after serious competitions and difficult training
Indications and contraindications
Indications for use depend on the dosage of the active component. Semax 0.1% is prescribed to achieve the following results:
- increasing the body's adaptability in the event of extreme conditions;
- treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy;
- elimination of neurotic disorders of various types that arise for the first time;
- restoration of brain function after a stroke;
- minimizing the consequences of anesthesia;
- treatment of toxic-allergic and inflammatory neuritis;
- elimination of ischemic attack;
- neutralization of the consequences of traumatic brain injuries and neurosurgical intervention;
- treatment of optic nerve atrophy;
- reduction of fatigue during monotonous work.
Semax 1% is indicated for ischemic stroke of varying severity as part of complex therapy.
There is a list of contraindications to the use of drops:
- presence of serious mental disorders;
- anxiety syndrome;
- history of seizures;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- intolerance to components;
- drops 0.1% – for children under 7 years of age;
- with diseases in the field of ophthalmology and neurosurgery - up to 18 years of age;
- drops 1% - up to 18 years.
See also:
Instructions for use of the Nootropic drug, indications, contraindications and reviews
Action of nootropics
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies drugs as nootropics that can
directly influence learning processes improve mental activity and memory increase the brain’s resistance to various types of external influences, in particular aggressive ones
The results of taking nootropic drugs can be
Improvement of cognition processes, as well as cognitive functions of the brain Increased speed of memorization, reproduction and use of information entering the brain As a result, a general increase in intellectual activity Weakening of memories of pain and stress Normalization of disrupted metabolic processes in the nervous system Improvement of higher nervous activity General improvement of mental state
Moreover, these drugs do not in any way affect the functioning of the brain and nervous system of mentally healthy people
Price
Nasal drops that have a nootropic effect can be purchased at a pharmacy or through an online store.

One of the main conditions for the sale of the drug is the presence of a prescription , which is written out in Latin.
The cost of a 0.1% solution (3 ml bottle) is determined by the range of 360-380 rubles .
Semax 1% in a bottle of the same volume will cost more - 1700-1790 rubles .

To select the appropriate concentration of the drug and treatment regimen, you must consult your doctor.
Classification of nootropics
In modern pharmacology, there are several classifications of nootropic drugs. We invite you to familiarize yourself with one of the most popular, according to which these drugs are divided into groups according to their chemical structure
Racetams - pyrrolidone derivatives
piracetam etiracetam aniracetam oxiracetam pramiracetam dupracetam rolisiracetam, etc.
Dimethylaminoethanol derivatives (precursors of acetylcholine)
deanol aceglumate meclofenoxate
Pyridoxine derivatives
pyritinol biotredin
GABA derivatives and analogues
γ-aminobutyric acid (aminalone) nicotinoyl-GABA (picamilon) γ-amino-P-phenylbutyric acid hydrochloride (phenibut) hopantenic acid calcium pantogam γ-hydroxybutyrate (neurobutal)
Cerebrovascular agents - ginkgo biloba
Neuropeptides and their analogues - Semax
Amino acids and substances affecting the excitatory amino acid system
glycine biotredin
Derivatives of 2-mercantobenzimidazole - ethylthiobenzimidazole hydrobromide (bemityl)
Vitamin-like products - idebenone
Polypeptides and organic composites
cortexin cerebrolysin cerebramin
Description of the dosage form
The nootropic drug is released in the form of nasal drops.
The therapeutic effect is achieved thanks to the active component - the synthetic polypeptide Semax.
The compound, called methionyl-glutamyl-histidyl-phenylalanyl-prolyl-glycyl-proline, lacks hormonal activity.
For better absorption of the polypeptide by tissues and cells of the body, the following is also used in the preparation of the drug:
- parahydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester;
- distilled water.
The solution is produced in different concentrations of the active substance: 1% and 0.1%.
The medicine is packaged in 3 ml bottles. The container is equipped with a pipette stopper or a dropper stopper.
The drops appear transparent, colorless, and have no specific odor.
Nasal drops 0.1% 1 l
Semax (in terms of 100% substance) 1 g
parahydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester (Nipagin) 1 g
purified water up to 1 l
in bottles with a pipette stopper dosing 3 ml; 1 bottle in a cardboard pack.
Nasal drops 1% 1 l
Semax (in terms of 100% substance) 10 g
parahydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester (Nipagin) 1 g
purified water up to 1 l
in 3 ml bottles with a dropper stopper, 1 bottle in a cardboard pack.
Colorless transparent liquid.
Substances of other pharmacological groups with a nootropic component
correctors of cerebrovascular disorders
nicergoline vinpocetine xanthinol nicotinate vincamine naftidrofuryl cinnarizine
general tonics and adaptogens
succinic acid ginseng extract melatonin lecithin
psychostimulant drugs - salbutiamine
antihypoxants and antioxidants - oxymethylethylpyridine succinate (Mexidol)
acephen and its derivatives
Even more often, experts use the classification of nootropics
by the nature of their origin
by mechanism of influence
on the brain and the body as a whole
on effectiveness
as well as the breadth of application
Drug groups
Based on these parameters, existing drugs can be divided into two groups, each of which has a number of subgroups
The first group is drugs with dominant or predominant mnestic effects (cognitive enhancers), the main effect is the effect on memory (mnestic)
Pyrrolidone derivatives , namely cyclic GABA (racetams)
piracetam (nootropil) pramiracetam (pramistar) etiracetam nefiracetam aniracetam phenotropil, etc.
Cholinergics
cholinesterase inhibitors
galantamine hydrobromide (Nivalin) rivastigmine (Exelon) donepezil ipidacrine (Neuromidine) aminostigmine
enhancing mediator synthesis
choline chloride choline alfoscerate (gliatilin) lecithin, etc.
M-, N-cholinomimetics - bethanechol
substances with a mixed type of action - deanol aceglutamate
Neuropeptides and their analogues - Semax, Cerebrolysin, Cerebrocurin, Actovegin, solcoseryl, thyroliberin.
Drugs affecting the excitatory amino acid system
glutamic acid nooglutyl
Preparations of glycine and its derivatives
glycine noopept
The second group is mixed drugs with a wide spectrum of action (neuroprotectors)
Brain Metabolism Activators
pentoxifylline acetyl-L-carnitine
Cerebral vasodilators
vinpocetine (Cavinton) oxybral (Vicamine) nicergoline (Sermion), etc.
Calcium antagonists
nimodipine cinnarizine flunarizine, etc.
Substances affecting the GAM K system
aminalon membraton pantogam picamilon sodium hydroxybutyrate phenibut (Noofen), etc.
Antioxidants
mexidol pyritinol a-tocopherol, etc.
Drugs from different groups
naftidrofuryl etimizol ginkgo biloba extract (tanakan, memoplant) melatonin huato boluses, etc.
Properties of nootropics
In this section we will look at
how the drug is absorbed and excreted, how it is metabolized, whether it accumulates in the body
The pharmacokinetic properties of these drugs largely depend on the method of their administration to the body.
Piracetam (2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide) is well absorbed when taken orally. It takes half an hour to reach the maximum concentration in the blood, and after some time (about an hour to four hours) piracetam accumulates in the brain. This drug is able to overcome the placental and hematoencephalic barriers It is almost not metabolized Part of the drug is excreted from the body 4-5 hours after administration, while 90% of it is excreted in its original form through the kidneys
Phenotropil (M-carbamoyl-methyl-4-phenyl-2-pyrrolidone) is easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract Easily overcomes the blood-brain barrier Maximum concentration in the blood occurs an hour after administration Oral administration of the drug ensures its complete bioavailability It is eliminated from the body within three days after intake, with 40% exiting through the kidneys, and the remaining 60% through bile
Aminalon (γ-aminobutyric acid) is also characterized by rapid absorption Maximum concentration in the blood - after an hour Difficult to overcome the blood-brain barrier After a day, this drug is no longer detectable in the plasma, however, it tends to accumulate in the brain if it is pathologically damaged It is broken down by the liver to succinic acid It, in turn, enters the Krebs cycle. A small proportion of the drug undergoes a transamination process, which produces γ-guanine butyric acid, and after some time it is converted by the kidneys and liver into gamma-aminobutyric acid and urea
Nicergoline (1,6-dimethyl-8p-(5-bromo-nicotinoyl-hydroxymethyl)-10a-methoxyergoline) has 80% absorption Maximum one and a half hours after administration it is extremely concentrated in the blood Most of the drug is metabolized by the body, and then broken down and exposed During the glucuronidation process, 80% of nicergoline is excreted through the kidneys, the rest through feces. This happens 2.5 hours after administration. Metabolites of the drug are released within 17 hours
Oxibral is absorbed quickly and is half-excreted from the body within an hour to an hour and a half after taking it. At the same time, only 6% of the drug is excreted in the urine in its original form. It is metabolized in the liver.
Vinpocetine (ethyl ester of apovincamic acid) is also well absorbed and quickly passes through the blood-brain barrier. Maximum concentration in the blood an hour after administration. This drug is 91% bioavailable. Excreted from the body after about 5 hours, mainly in urine in its original form. At the same time, vinpocetine is broken down in the liver to apovincamic acid, which has some pharmacological activity. Drug metabolites are excreted in the same way
Pentoxifylline (3,7-dimethyl-1 -(5-oxohexyl)-xanthine or 1 -(5-oxohexyl)-theobromine) is absorbed completely and quickly Concentrated in the blood an hour after oral administration Forms two metabolites in the body, which are excreted by kidneys The half-life of the drug varies from half an hour to an hour. Up to 4% of the drug is excreted in the feces, some of it can be excreted through breast milk.
Picamilon (N-nicotinoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid sodium salt) is completely absorbed Easily bypasses the blood-brain barrier Comes out in its original form
Nooglutil also has a good degree of absorption Maximum concentration in the blood 2-3 hours after administration More than 90% bioavailable Half-life from the body is just over 3 hours
Cinnarizine (trans-1-cinnamyl-4-diphenyl-methylpiperazine or N-benzhydryl-N-trans-cinnamylpiperazine) is quickly and well absorbed, and then after some time (from 1 to 3 hours) it is maximally concentrated in the blood. It forms metabolites in the body, 30% of which comes out in urine, and 60% in feces
Nimodipine (2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinecarboxylic acid methoxyethyl isopropyl diester) is well absorbed. If the drug is administered intravenously, its maximum concentration in the blood occurs after 3 minutes after injection, when taken orally - after an hour Bioavailability - 13% Half-life - from 8 to 9 hours Metabolites are excreted from the body in feces
Pyriditol (bis-(2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-oxymethylpyridyl-5-methyl)-disulfide dihydrochloride) is quickly and well absorbed, quickly overcomes the blood-brain barrier and is maximally concentrated in the blood half an hour to an hour after administration. The drug is bioavailable in on average by 76-93% In the liver, the drug is broken down into metabolites, and also accumulates in the gray matter. It passes into breast milk. It is excreted in the urine. Half-life is 2.5 hours.
Glycine is also rapidly absorbed and excreted from the body through the kidneys.
Melatonin is well absorbed, easily overcoming the body's barriers. Maximum concentration in the blood half an hour after ingestion. Almost 100% bioavailable. Almost not metabolized. It leaves the body quickly.
Noopept (ethyl ester of N-phenylacetyl-L-propylglycine) is absorbed well, passing the blood-brain barrier. The maximum concentration occurs 15 minutes after oral administration. At the same time, noopept is concentrated in the brain more than in the blood. In the body it forms metabolites, including phenylacetic acid, as well as phenylacetylproline and cyclopropylglycine Almost 100% bioavailable Excreted quickly
Ginkgo biloba extract is rapidly absorbed. The maximum concentration of the drug in the blood occurs an hour and a half after oral administration. Half-life is approximately 4.5 hours.
The pharmacodynamic properties of these nootropic drugs are realized through
metabolic mechanism And also through the neurotransmitter, which affects the mediator systems
GAM K choline-, glutamate- and glycinergic
These drugs also affect the following receptors that are involved in mnestic processes
adrenocholine-serotonin opiate dopamine adenosine benzodiazepine
More and more evidence supports the involvement in the mechanism of action
glutamate NMDA receptors, which are involved in the transport of cations across the cell membrane and ACPD receptors, which regulate enzyme systems and are involved in the implementation of mnestic action
Effects on glycine receptors are also associated
with the permeability of chloride channels and with the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and acetylcholine
Modern nootropic drugs
increase the speed and level of active energy supply - stimulate the synthesis and utilization of ATP and phosphatidylcholine
accelerate the turnover of information macromolecules, as well as protein and RNA synthesis
activate adenylate cyclase, synaptosomal phospholipase A, utilize glucose in brain tissue, reduce the activity of Na"-K+-ATPase, as well as the cortical release of L-proline, which inhibits memory processes
increase membrane fluidity, inhibition of lipid peroxidation processes (for piracetam and similar drugs)
increase cerebral circulation
Cerebrovasoactive drugs can dilate blood vessels
Nimodipine, cinnarizine - block L-type calcium channels mainly in the smooth muscle of cerebral vessels
Pentoxifylline is able to block phosphodiesterase and adenosine receptors, accumulate cAMP, and reduce the amount of calcium inside cells
Vinpocetine and oxybral block sodium channels, phosphodiesterase, and reduce the degradation of GAM K
Nicergoline has an α-adrenergic blocking effect on cerebral vessels
Nootropics or nootropics also have the following effects
psychostimulating antiasthenic calming tranquilizing antidepressant invigorating increase clarity of consciousness antiepileptic nootropic mnemotropic vasovegetative adaptogenic antiparkinsonian antidyskinetic
However, there are drugs with an inhibitory effect
phenibut sodium hydroxybutyrate
And some nootropics can have a stimulating effect . This
piracetam phenotropil aminalon pyriditol and others.
Indications for the use of nootropic drugs, when they are recommended for use
psychoorganic syndromes of vascular, traumatic, infectious, intoxication, somatic origin acute vascular pathology chronic alcoholism epilepsy chronic depressive states neurotic reactive somatogenic states schizophrenia correction of learning disabilities in children and adults
Pay attention to possible side effects from taking these medications.

Hyperexcitability State of weakness and drowsiness Dizziness Tremor State of restlessness Problems sleeping Nausea up to vomiting Digestive disorders Skin rashes Increased pain with headaches and others
Also, modern pharmacology has complex medicines. They can have an effective effect on the body if both components are taken in small concentrations according to the principle of synergy
Binotropil (aminalon + melatonin) Diapiram (piracetam + diazepam); melatonin-apik (melatonin + pyridoxine) Thiocetam (piracetam + thiotriazoline) Ozatropil (piracetam + aminalon) Orocetam (piracetam + orotic acid) Phezam (piracetam + cinnarizine). Yucalip (melatonin + valerian extract)
See also:
Treatment of autism in children. Autism. Recovery method
Find out more about free recovery programs for autism, cerebral palsy and epilepsy based on biohoney principles with natural products Tentorium
Seminar schedule HERETentorium beekeeping products restore every cell of the body naturally according to the principles of naturopathy or biomedical correction of the body. They saturate the body with necessary enzymes, vitamins and microelements
Disclaimer The information provided in this article is for the reader's information only. It is not intended to be a substitute for advice from a medical professional
Instructions for use
Nootropic nasal drops are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
The specialist takes as a basis the treatment regimen proposed in the annotation, or develops an individual regimen for taking Semax.
The drug must be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor in order to eliminate side effects and complications of concomitant pathology.

Self-medication is prohibited, even in the absence of contraindications.
The method of administration of the pharmacological agent is intranasal.
For convenient administration of drops, a bottle pipette is used.
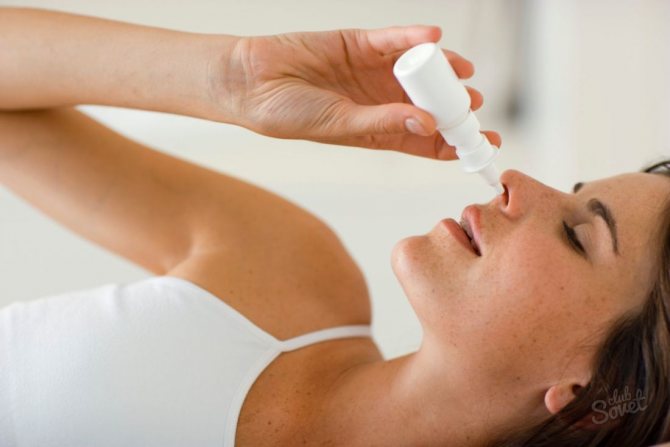

- Before using the drug for the first time, you need to cut off the tip of the pipette so that the cap closes tightly.
- After preparing the hole, the bottle is turned upside down so that the liquid fills the cavity of the pipette (if the solution does not penetrate well into the hole, you need to lightly tap the bottom with your finger).
- The medicine enters the nasal opening after pressing the wide part of the dropper with your fingertips. There is no need to insert the pipette deeply into the nasal passage; it is enough to touch the mucous membrane with the head slightly raised.
Recommended doses (for drops of concentration 0.1%)
A single dosage of the medicine is 50 mcg of active substance, which corresponds to 2-3 drops.

In some cases, it increases to 300 mcg (about 6 drops). This dose should be divided into 2-3 injections with an interval of 10-15 minutes.
The amount of medication is calculated taking into account the patient’s body weight:
- single dose - 3 to 30 mcg are prescribed per 1 kg, which corresponds to 200-2000 mcg of the active substance;
- daily norm - per 1 kg is prescribed from 7 to 70 mcg, which corresponds to 500-5000 mcg.
The course duration recommended by the manufacturer is 3-5 days. But the attending physician may recommend longer treatment (up to 14 days).
Common treatment regimen for an adult patient:
- a single dose of solution is 2-3 drops;
- number of repetitions per day – 2-3 times (corresponds to 600-900 mcg/day);
- Course duration – 10 days.
For children, the following scheme is recommended:
- single dose – 1-2 drops;
- number of repetitions per day – 2 times (corresponds to 200-400 mcg/day);
- Course duration – 1 month.
Recommended doses (for 1% concentration drops)

For a patient diagnosed with the acute phase of a stroke, the following treatment regimen is recommended:
- inject the solution into each nasal passage, 2-3 drops (approximately 2000-3000 mcg);
- the interval between procedures is 3-4 hours (in total no more than 4 times per day);
- daily norm – 6000-12000 mcg;
- Course duration – no more than 10 days.
For seriously ill patients, doses can be increased to a single administration of 3-4 drops, repeated up to 5 times a day.