Types of Leadership
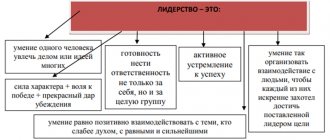
When we pronounce the word “leader,” we imagine a confident, decisive person with unquestionable authority. In general, the portrait is quite standard, but why don’t leaders act the same? It's all about the different types of leadership they use. There are several classifications of forms of manifestation of leadership qualities; we will consider the two most common.
Democratic and authoritarian type of leadership
Quite often they use division in the relationship between a manager and his subordinates. On this basis, types of leadership are divided into two large groups:
- Authoritarian style
. All power is concentrated in the hands of the leader; he single-handedly chooses goals and chooses ways to achieve them. Communication between group members is minimal, and they are also controlled by the leader. The main weapons are the threat of punishment, demandingness and a sense of fear. This style saves time, but suppresses the initiative of employees, who turn into passive performers. - Democratic type of leadership
. Most researchers recognize it as the best. Since the behavior of such leaders is usually respectful towards group members. Subordinates have the opportunity to take initiative, but their responsibility also increases. Information is available to the team.
Weber's typology
The classification proposed by M. Weber is generally accepted today. He considered leadership to be the ability to give orders and command obedience. To achieve this, leaders use various resources, depending on the types of which, they distinguish charismatic, traditional and rational-legal types of leadership.
- Traditional type
. Relies on rituals, traditions and force of habit. The transfer of power is inherited, the leader becomes such by birthright. - Rational-legal type
. Here power is based on a set of legal norms recognized by others. The leader is elected in accordance with these norms, which also regulate the actions available to him. - Charismatic type of leadership
. It is based on the belief in the exclusivity of man or his chosenness by God. Charisma becomes a combination of the actual qualities of a person and those that his followers endow the leader with. Quite often, the personality of the leader plays a secondary role in this process.
Simply put, the types of leadership listed are based on habit, reason, or emotion. Weber believed that the main engine of development is the charismatic management style, since only it is not associated with the past and can offer something new. But in calm periods, rational-legal leadership will be optimal.
Leader and leadership - concept, classification
Leadership is the process of social organization and management of communication and activities of group members, carried out by a subject (leader) endowed with a certain power [5].
24 pages, 11558 words
Leadership theories. The role of the leader in managing an organization
...possible and appropriate, leadership. Destructive leaders, for example, leaders of groups of opponents of innovations, drinking buddies... decisions, can cause great damage to personnel management and the activities of the organization as a whole. 3. Management of leadership in an organization The primary importance of leadership for the effectiveness of management, its positive and negative impact on personnel management is given ...
The word leader comes from the English lead (to lead).
This means that a leader is one who leads the way.
A leader is a member of an organization who has a high personal status, has a strong influence on the opinions and behavior of the people around him, members of any association or organization, and performs a set of functions [5].
Practice shows that no single factor provides greater benefits and benefits for an organization than effective leadership. Leaders are needed to determine goals and objectives, to organize, coordinate, ensure interpersonal contacts with subordinates and select optimal, effective ways to solve certain problems. Obviously, organizations with leaders can achieve all this much faster than organizations without leaders.
Leadership can be defined as a type of management interaction based on the most effective combination of various sources of power for a given situation and aimed at encouraging people to achieve common goals. From this definition it follows that leadership is a function of the leader, followers and situational variables.
Leadership is based on the specific needs of complex systems. These include, first of all, the need for self-organization, streamlining the behavior of individual elements of the system in order to ensure its vital and functional ability.
This ordering is achieved thanks to the vertical (management - subordination) and horizontal (correlative one-level connections, for example, division of labor and cooperation) distribution of functions and roles, and, above all, the allocation of the management function and the structures that carry it out, which for their effectiveness usually require a hierarchical, pyramidal organization [3]. The top of such a management pyramid is the leader.
In small groups based on direct contacts of their members, the institutionalization of leadership positions may not occur. Here, the individual qualities of a person, his ability to unite a group and lead it, come to the fore. In large associations, the effectiveness of collective actions of which requires clear functional-role differentiation and specialization, as well as efficiency of management and rigidity of subordination, institutionalization and formalization (official consolidation) of leading positions, vesting them with relatively large powers of authority are mandatory.
7 pages, 3139 words
Features of a leader in modern organizations. Analysis of the role of a leader in an organization (using the example of the organization “NefteKhimRemontStroy”)
... the basics of the role of a leader in a modern organization 6 1.1. The concept and nature of leadership 6 1.2. The importance of a leader in managing an organization. The leader... builds more on facts and within established goals. A leader inspires people and instills enthusiasm in employees by conveying to them... builds more on facts and within established goals. A leader inspires people, instills enthusiasm in employees, conveying to them his...
Modern production belongs to this type of association. It pursues certain, fairly stable goals, the implementation of which requires the coherence of the actions of many people, their coordination and regulation based on the division of labor. Because of this, in labor organizations it is mandatory to institutionalize leadership, its constitution into leadership, which, based on positions of power, comes to the forefront of management.
According to the mechanism of his nomination, a leader can be formal or informal. In the first case, he is appointed from above or nominated and elected, and he thus acquires the official status of a leader.
An informal leader can emerge and gain recognition in a team or organization due to his pronounced individual, social, political, psychological and other qualities.
In modern conditions, effective leadership is not an iron or firm hand, but a high sensitivity to the needs of followers, which is manifested in the development of employees, in including them in group work, in helping them achieve personal goals.
The richness of the sides and aspects of leadership determines the diversity of its typology. The simplest and most widespread classification of leadership in an organization is the identification of three types (sometimes called leader roles) [2]:
1. Business leadership. It is typical for groups that arise on the basis of production goals. It is based on such qualities as high competence, the ability to solve organizational problems better than others, business authority, experience, etc. Business leadership has the greatest influence on management effectiveness.
2. Emotional leadership. It arises in socio-psychological groups on the basis of human sympathies and the attractiveness of interpersonal communication. An emotional leader inspires trust in people, radiates warmth, inspires confidence, relieves psychological tension, and creates an atmosphere of psychological comfort.
21 pages, 10162 words
Guidelines for organizing the activities of psychological, medical and pedagogical commissions (PMPK)
The documents proposed in the Guide were prepared on the basis of a detailed analysis of actually used and currently used documents in all regions of the Russian Federation. The guidance can form the basis for improving the activities of the PMPC and developing a standard regulation on the PMPC. Section I general provisions Introduction 1. This Guide presents...
3. Situational leadership. Strictly speaking, by its nature it can be both business and emotional. However, its distinctive feature is instability, time limitation, connection only with a certain situation. A situational leader can lead a group only in a certain situation.
There are other classifications of leadership depending on the types of leaders. Is not it. Umansky identifies six types (roles) of a leader [4]:
- leader-organizer (performs the function of group integration);
- leader-initiator (dominates when solving new problems, puts forward ideas);
- leader-generator of emotional mood (dominates in shaping the mood of the group);
- leader-erudite (distinguished by the breadth of knowledge);
- leader-standard (is the center of emotional attraction, corresponds to the role of a “star”, serves as a model, ideal);
- leader-master, craftsman (specialist in some type of activity).
According to the nature of the activity, they are distinguished:
- universal type, i.e. constantly demonstrating the qualities of a leader;
- situational, showing leadership qualities only in a certain situation.
Leadership varies in the power of influence on members of the group (organization).
People obey one leader unquestioningly, while they follow the advice or instructions of another only as long as they do not conflict with their own interests and attitudes.
Depending on the direction of influence on the implementation of the organization’s goals, leadership is divided into:
- constructive (functional), i.e. contributing to the achievement of the organization's goals;
- destructive (dysfunctional), i.e. formed on the basis of aspirations that are detrimental to the organization (for example, leadership in a group of thieves or bribe-takers formed at the enterprise);
- neutral, i.e. not directly affecting the efficiency of production activities (for example, leadership in a group of amateur gardeners working in the same organization).
Of course, in real life the lines between these types of leadership are fluid, especially between constructive and neutral leadership.
10 pages, 4802 words
Analysis of the leadership style and leadership characteristics of the head of the organization
... management of the organization 6 1.2 Leadership style: concept, essence and factors influencing style 13 1.3 Classification of leadership styles (Theories of development of leadership styles) 18 2. Analysis of leadership styles in ... .) activity. Unlike the leader, the manager has formally regulated rights and responsibilities, and also represents the group in other organizations /17, p.62/. Supervisor …
Constructive leadership, as already noted, is one of the most important components of effective leadership. The optimal thing for a leader is to combine the qualities of a formal and informal leader. However, combining these social roles in one person, especially the role of a manager and an emotional leader, is difficult to achieve. For management to be effective, it is usually sufficient for the manager to also be a business leader. Of course, the level of position occupied by the leader in the system of emotional relations also affects the effectiveness of leadership. It should not be excessively low, turning into antipathy. In the latter case, emotional hostility can significantly undermine the business and official authority of the manager and reduce the effectiveness of his activities.