Structure
Externally, neurons are very unusual. They have processes, the number of which can vary from one to many. Each section performs its own function. The shape of a neuron resembles a star, which is in constant motion. It is formed:
- soma (body);
- dendrites and axons (processes).
An axon and a dendrite are present in the structure of any neuron in an adult organism. They are the ones who conduct bioelectric signals, without which no processes can occur in the human body.
There are different types of neurons. Their difference lies in the shape, size, and number of dendrites. We will consider in detail the structure and types of neurons, divide them into groups, and compare types. Knowing the types of neurons and their functions, it is easy to understand how the brain and central nervous system work.
The neuron is the final point that sends and receives the bioelectrical signal. These cells provide absolutely all processes in the body and are of paramount importance for the body.
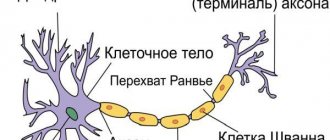
The body of the nerve fibers contains neuroplasm and most often one nucleus. The processes are specialized for certain functions. They are divided into two types - dendrites and axons. The name of dendrites is associated with the shape of the processes. They really look like a tree with many branches. The size of the processes ranges from a couple of micrometers to 1-1.5 m. A cell with an axon without dendrites is found only at the stage of embryonic development.
The task of the processes is to perceive incoming irritations and conduct impulses to the body of the neuron itself. The axon of a neuron carries nerve impulses away from its body. A neuron has only one axon, but it can have branches. In this case, several nerve endings (two or more) appear. There can be many dendrites.
Vesicles that contain enzymes, neurosecretions, and glycoproteins constantly run along the axon. They are directed from the center. The movement speed of some of them is 1-3 mm per day. This current is called slow. If the movement speed is 5-10 mm per hour, such a current is classified as fast.
If the axon branches extend from the neuron body, then the dendrite branches. It has many branches, and the terminal ones are the thinnest. On average there are 5-15 dendrites. They significantly increase the surface of nerve fibers. It is thanks to dendrites that neurons easily contact other nerve cells. Cells with many dendrites are called multipolar. There are most of them in the brain.
But bipolar ones are located in the retina and the apparatus of the inner ear. They have only one axon and dendrite.
Neurons, like many other cells, contain organelles. These are permanent components, without which they cannot exist. Organelles are located deep inside cells, in the cytoplasm.
Neurons have a large round nucleus that contains decondensed chromatin. Each nucleus has 1-2 fairly large nucleoli. In most cases, the nuclei contain a diploid set of chromosomes. The task of the nucleus is to regulate the direct synthesis of proteins. Nerve cells synthesize a lot of RNA and proteins.
Neuroplasm contains a developed structure of internal metabolism. There are many mitochondria, ribosomes, and a Golgi complex. There is also Nissl substance, which synthesizes protein in nerve cells. This substance is found around the nucleus, as well as on the periphery of the body, in the dendrites. Without all these components, it will not be possible to transmit or receive a bioelectric signal.
The cytoplasm of nerve fibers contains elements of the musculoskeletal system. They are located in the body and processes. Neuroplasm constantly renews its protein composition. It moves by two mechanisms - slow and fast.
The constant renewal of proteins in neurons can be considered as a modification of intracellular regeneration. Their population does not change, since they do not divide.
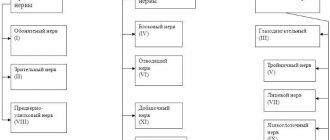
Neurons can have different body shapes: stellate, fusiform, spherical, pear-shaped, pyramidal, etc. They make up different parts of the brain and spinal cord:
- stellate are motor neurons of the spinal cord;
- spherical ones create sensitive cells of the spinal ganglia;
- pyramidal ones make up the cerebral cortex;
- pyriforms create cerebellar tissue;
- fusiform are part of the tissue of the cerebral cortex.
There is another classification. It divides neurons according to the structure of their processes and their number:
- unipolar (only one process);
- bipolar (there are a pair of processes);
- multipolar (many processes).
Unipolar structures do not have dendrites, they are not found in adults, but are observed during embryonic development. Adults have pseudounipolar cells, which have a single axon. It branches into two processes at the point of exit from the cell body.
Bipolar neurons have one dendrite and one axon. They can be found in the retina of the eyes. They transmit impulses from photoreceptors to ganglion cells. It is the ganglion cells that form the optic nerve.
Most of the nervous system is made up of neurons with a multipolar structure. They have many dendrites.
Dimensions
Different types of neurons can differ significantly in size (5-120 microns). Some are very short, and some are simply gigantic. The average size is 10-30 microns. The largest of them are motor neurons (they are found in the spinal cord) and Betz's pyramids (these giants can be found in the cerebral hemispheres). The listed types of neurons are classified as motor or efferent. They are so large because they must receive so many axons from other nerve fibers.
There is also a classification of neurons that takes into account their functions. It contains neurons:
- sensitive;
- insertion;
- motor.
Thanks to the "motor" cells, orders are sent to the muscles and glands. They send impulses from the center to the periphery. But along sensitive cells the signal is sent from the periphery directly to the center.
So, neurons are classified according to:
- form;
- functions;
- number of shoots.
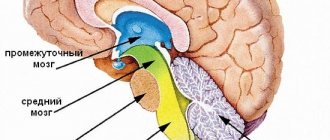
Neurons can be found not only in the brain, but also in the spinal cord. They are also present in the retina of the eyes. These cells perform several functions at once, they provide:
- perception of the external environment;
- irritation of the internal environment.
Neurons are involved in the process of excitation and inhibition of the brain. The received signals are sent to the central nervous system thanks to the work of sensory neurons. Here the impulse is intercepted and transmitted through the fiber to the desired area. It is analyzed by many interneurons in the brain or spinal cord. Further work is performed by the motor neuron.
Brain energy
The brain produces energy equivalent to a 10-watt light bulb.
Cartoons where characters have a light bulb hanging over their heads while they are thinking are not too far from the truth.
Your brain generates as much energy as a small light bulb, even when you sleep.
Meanwhile, the brain is the organ with the highest energy consumption. It takes about 20% of energy from the body,
it accounts for 2% of the total body weight. Much of this energy is spent exchanging information between neurons and between neurons and astrocytes (a type of cell).
Neuroglia
Neurons are not able to divide, which is why the statement appeared that nerve cells do not regenerate. That is why they should be protected with special care. Neuroglia cope with the main function of the “nanny”. It is located between the nerve fibers.
These small cells separate neurons from each other and hold them in place. They have a long list of features. Thanks to neuroglia, a constant system of established connections is maintained, the location, nutrition and restoration of neurons is ensured, individual mediators are released, and genetically foreign substances are phagocytosed.
Thus, neuroglia perform a number of functions:
- supporting;
- delimiting;
- regenerative;
- trophic;
- secretory;
- protective, etc.
In the central nervous system, neurons make up the gray matter, and outside the brain they accumulate in special connections, nodes - ganglia. Dendrites and axons create white matter. At the periphery, it is thanks to these processes that the fibers that make up the nerves are built.
Formation process
The topic of nerve cell regeneration is still controversial among scientists. The majority adheres to the axiom that neurons are acquired by a person only at birth (it is not for nothing that there are several billion of them even then) and die throughout life. Therefore, it is important to take care of your nervous system and not succumb to constant stress. This is what can lead to various disorders of the central nervous system in old age.
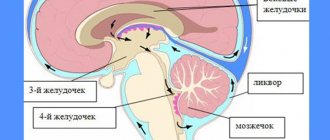
If we consider the ability of the brain to restore and recreate nerve cells as possible, then such a process will be called neurogenesis. Despite the fact that it is generally accepted that the generation of neurons is a one-time step still inside the womb, some scientists are of the well-founded opinion that certain areas of the brain are capable of creating nerve endings in human infancy. But, in addition to this, in the 90s of the last century an experiment was conducted, as a result of which it was found that the hippocampus (the part of the brain responsible for the ability to learn, remember and reproduce emotions) is capable of generating new neurons throughout life. This discovery turned out to be enormously important, because thanks to it, scientists opened the way to studying treatments for degenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusion
Human physiology is striking in its coherence. The brain has become the greatest creation of evolution. If we imagine the body in the form of a coherent system, then neurons are wires through which signals pass from the brain and back. Their number is huge, they create a unique network in our body. Thousands of signals pass through it every second. This is an amazing system that allows not only the body to function, but also contact with the outside world.
Without neurons, the body simply cannot exist, so you should constantly take care of the state of your nervous system. It is important to eat right, avoid overwork, stress, and treat diseases in a timely manner.
general information
In short, it is a component unit of the nervous system.
Just as there are thousands of small parts in a huge mechanism, there is an uncountable (literally, scientists calculate about ten units to the eleventh power) number of neurons in the human nervous system. And each cell is responsible for receiving information, processing it, redirecting it to other “brethren,” and storing it in the body’s memory. About 86 billion of the total are concentrated in the brain. It's quite simple: you flip the switch, in a split second the current runs through the wires to the light bulb, and the light comes on. The reaction of the nerve endings in the body occurred in a similar way: you touched the switch, and in a couple of moments the brain already knows that the switch is slightly rough and at room temperature. That’s the whole “magic” of nerves.
Symptoms of central motor neuron damage
Damage to central motor nerve cells most often occurs during stroke. When ischemia or hemorrhage occurs in the substance of the cerebral hemispheres, a section of tissue dies. Such lesions are almost always unilateral.
As a result, when central motor neurons are damaged, muscle dysfunction on one side is observed. The most noticeable symptom is unilateral paralysis, leading to the inability to actively move the arm and leg.
On the same side, muscle tone in the torso and facial muscles decreases. Damage to the central motor areas is accompanied by a number of changes in reflex activity.
Clinically, this is expressed in the appearance of various pathological reflexes. Their combination, decreased muscle tone and sensory disturbances allow the doctor to make a diagnosis.
Human brain and water
80%
The brain is made of
water.
Your brain is not the solid gray mass you see on TV. It is soft and pink due to the blood pulsing there and the high water content.
So, when you feel thirsty, it is also because the brain
requires water.
Interesting fact!
The average human brain weighs 1.4 kg and is extremely sensitive to water loss. If the brain is dehydrated for a long time, its proper existence will cease.