A chronic, inflammatory, gradually progressive disease, which is characterized by damage to the joints of the spinal column, iliosacral joints, their ligaments and cartilage, is called ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis). It develops due to excessive growth of bone tissue. As a result, the elements of the spine lose their flexibility, ossify, turning into a monolithic, inactive axis.
The pathological process may involve joints of other locations (knees, hips, etc.) and completely other organs and tissues (heart, gastrointestinal tract, eyes, skin, kidneys).
Reference : this disease was first described independently by V. Bekhterev, P. Marie, A. Strumpel at the end of the 19th century, therefore another name for ankylosing spondylitis is Bekhterev-Strumpel-Marie disease.
The incidence mainly affects young men (under 30 years of age) with a thin build. In them, ankylosing spondylitis occurs 5-10 times more often than in females, and is characterized by a more severe course.
The causes of ankylosing spondylitis remain unclear. An autoimmune mechanism for the development of the disease is assumed, i.e. activation of the body's immune system cells against its own tissues. Hereditary predisposition plays a significant role.
Interesting to know : Famous historical figures suffered from ankylosing spondylitis: chess player Vladimir Kramnik, writer Karel Capek, Aristotle Onassis.
About reflexes
Newborn children up to a certain age react to various stimuli completely differently than adults. And what is the norm for them is later regarded as a pathology and requires close attention. Including from them, you can understand how correctly the baby’s nervous system is developing, and whether there are any peculiarities or problems.
For infants, a certain set of reflexes is necessary for survival. The search reflex, when in response to a touch on the cheek the child turns his head towards the stimulus, is needed to establish nutrition. Children grab their fingers if you touch the center of their palms. They hold on so tightly that they do not let go of the support, even if they are lifted in this way. This and much more increases the chances of survival and helps the baby develop and grow.
But, of course, it happens that a person produces “extra” reactions that he cannot control. As a rule, this indicates serious problems that can be diagnosed and treated by a neurologist.
Rossolimo G.I.
There is a pathological flexion reflex, named after the Russian scientist, which is one of the main signs of late spastic paralysis. It's worth learning a little about this researcher.
Grigory Ivanovich Rossolimo was born in 1860 in Odessa into a family of Greek origin. In 1884, he graduated from the medical faculty of Moscow University, where he met and became friends with A.P. Chekhov. Rossolimo's interests included mainly neuropathology, psychology and defectology.
In 1890, he became the head of the clinic for nervous diseases, while simultaneously conducting scientific activities and teaching at the university, which he left in 1911. Research by G.I. Rossolimo made an invaluable contribution to the diagnosis of brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, and polio.
He also dealt with the issues of raising children with mental development problems, developed a method for assessing intellectual abilities, and invented medical devices such as a dynamometer, clonograph, and brain topograph. However, he is best known for clarifying the course of conductors in the nervous system and describing the pathological flexion reflex that currently bears his name. It is widely used in diagnostics today, although Grigory Ivanovich’s work on this issue was published in 1902 - more than 100 years ago.

If you touch a hot object, your hand will reflexively withdraw. This is a simple self-preservation mechanism that is almost impossible to control. The set of reflexes is huge, and is especially clearly seen in the example of very young children, which is convenient when diagnosing diseases, because a child cannot say that, for example, it hurts, and the body’s reaction speaks for itself.
About reflexes
Newborn children up to a certain age react to various stimuli completely differently than adults. And what is the norm for them is later regarded as a pathology and requires close attention. They can also be used to understand how correctly the baby’s nervous system is developing, and whether there are any peculiarities or problems. For infants, a certain set of reflexes is necessary for survival. The search reflex, when in response to a touch on the cheek the baby turns its head towards the stimulus, is needed to establish nutrition. Children grab their fingers if you touch the center of their palms. They hold on so tightly that they do not let go of the support, even if they are lifted in this way. This and much more increases the chances of survival and helps the baby develop and grow. But, of course, it happens that a person produces “extra” reactions that he cannot control. As a rule, this indicates serious problems that can be diagnosed and treated by a neurologist.
Rossolimo G.V.
There is a pathological flexion reflex, named after the Russian scientist, which is one of the main signs of late spastic paralysis. It's worth learning a little about this from researchers. Grigory Ivanovich Rossolimo was born in 1860 in Odessa into a family of Greek origin. In 1884, he graduated from the medical faculty of Moscow University, where he met and became friends with A.P. Chekhov. Rossolimo's interests included mainly neuropathology, psychology and defectology. In 1890, he became the head of the clinic for nervous diseases, while simultaneously conducting scientific activities and teaching at the university, which he left in 1911. The research of G.V. Rossolimo became an invaluable contribution to the diagnosis of brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, and poliomyelitis. He also dealt with the issues of raising children with mental disabilities, developed a method for assessing intellectual abilities, and invented medical devices such as a dynamometer, clonograph, and brain topograph. However, he is best known for clarifying the course of conductors in the nervous system and describing the pathological flexion reflex that currently bears his name. It is widely used in diagnostics today, although Grigory Ivanovich’s work on this issue was published in 1902 - more than 100 years ago.
Rossolimo reflex
Usually, when this term is used, we are talking about the feet, but in fact it can also be recorded with irritation of the fingers, although the latter is sometimes called by the name of the researcher Tremner. The Rossolimo reflex is recorded in almost all cases in children up to 6 months of age, after which - in 30% of cases. As a rule, after 2 years it becomes negative, and after 3, a positive review can indicate serious problems of the nervous system.
Upper
Usually, when they talk about the Rossolimo reflex, they mean a reaction that can occur with a certain impact on the toes. But there is also its analogue in the upper extremities, called the carpal. In order to check the reaction, the neurologist applies a short, abrupt blow-touch to the fingers of the subject (except the thumb), while the hand is in a palm-down position. In the case of pathology, rhythmic flexion movements will be observed that the patient is unable to control.
Lower
The situation is similar with the feet. The subject is positioned horizontally in a relaxed position. The doctor applies short blows to the pads from the plantar side. In case of a positive reaction, flexion movements are observed. In this case, the thumb, on the contrary, moves back. From the observer's perspective, it will look as if the subject is trying to grab the stimulus with his foot.
Conditioning
The reaction to the stimulus manifests itself in connection with the passage of impulses along a certain path, which depends on the specific reflex being tested. Reflex arcs are the same “paths” that make up a complex that includes a receptor, afferent (neuron process), central, efferent link and, finally, an effector (executive organ). This term was introduced in 1850 and is now considered incorrect in some cases, since it does not fully reflect the reaction mechanism and the presence of feedback. Instead, he was proposed the concept of a reflex ring, which, however, is not always used. If we talk about the lower pathological flexion reflex, the reflex arcs will be as follows: plantar receptors - tibial nerve - sciatic - spinal cord neurons. Here, two types of cells participate in the formation of the reaction: sensory and motor. Next, through the sciatic and tibial nerves, the impulse returns to its original area, to the muscles, which causes flexion of the fingers.
Causes
The Rossolimo reflex belongs to the pyramidal signs. That is, a positive reaction after a certain age indicates serious neurological problems. A certain group of pathological reflexes is so named because they help diagnose damage to the central neuron of the cerebral cortex, or the corticospinal cord (pyramidal tract. The damage can be of a different nature, but, as a rule, they talk about organic. If we talk about children, then up to a certain age the pathological reflex is not such for them due to the insufficient development of the pyramidal tract immediately after birth. After some time, the reaction fades away, after all the necessary connections are established. Do not think that a child who shows a positive reflex is immature. Up to 6 -12 months is the norm.
The Rossolimo flexion reflex is a manifestation of a central motor neuron lesion. In this case, the flow of inhibitory impulses into the spinal cord stops, and therefore it becomes possible to register a positive reaction to stimulation. Moreover, unlike some other pathological reflexes, this does not indicate an acute lesion (except for injury with spinal shock), but is a late manifestation of a disease such as central (spastic) paralysis. The cause of this disease lies in damage to the motor neuron. Since the fibers and cells in it are located very closely, manifestations often spread to entire parts or even halves of the body. With this disorder, loss of motor functions, muscle hypertonicity, hyperreflexia, clonus (contraction in response to stretching), etc. are observed.
Treatment
Spastic paralysis itself, and after it pathological reflexes and synkinesis (friendly movements) is only a manifestation of the underlying disease. But the defeats they signal can be as follows:
- injuries;
- oncological diseases;
- metabolic disorder;
- infections;
- intoxication;
- congenital disorders.
In 60% of cases, spastic paralysis is a consequence of a stroke, and the causes listed above account for the rest. In each specific case, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition, identifies the causes of the problems and prescribes appropriate treatment. These could be drugs that improve blood circulation or help restore brain cells. Also, of course, attention is paid to the underlying disease that caused the damage, if possible. If it is an infection, then appropriate antibiotics are prescribed. If we are talking about poisoning, then it is necessary to take appropriate actions to cleanse the body tissues - dialysis, forced diuresis, etc. In addition, physiotherapy and reflexology, special baths, massage are often prescribed. It is usually not possible to restore the affected structures if a positive Rossolimo reflex is recorded, but symptomatic treatment can significantly improve the patient’s condition and improve his quality of life. It is likely that with the development of medical technology, complete recovery will become possible, but for now this is only a goal.
Upper
Usually, when they talk about the Rossolimo reflex, they mean a reaction that can occur with a certain impact on the toes. But there is also its analogue in the upper extremities, called the carpal.
In order to check the reaction, the neurologist applies a short, abrupt blow-touch to the fingers of the subject (except the thumb), while the hand is in a palm-down position. In the case of pathology, rhythmic flexion movements will be observed that the patient is unable to control.
How to determine ankylosing spondylitis? What are the diagnostic criteria?
Not every back pain is a symptom of ankylosing spondylitis, but there are a number of its specific features:
- young age (up to 30-40 years);
- highest intensity at rest;
- reduction of pain when moving;
- pain at night;
- gradual progression.
Based on the clinical picture and x-ray signs, the New York criteria for the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis have been developed.
Clinical:
- Constant back pain at rest lasting more than three months, which decreases with movement;
- Limitation of mobility of the lumbar spine;
- Reduced volume of respiratory movements of the chest cavity.
X-ray:
- 2-sided sacroiliitis stages 2-4;
- 1-sided sacroiliitis stage 3-4.
The diagnosis is made if at least 1 sign from both groups is present.
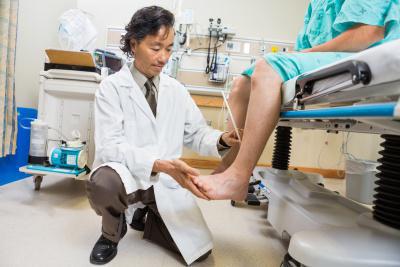
Lower
The situation is similar with the feet. The subject is positioned horizontally in a relaxed position. The doctor applies short blows to the pads from the plantar side. In case of a positive reaction, flexion movements are observed. In this case, the thumb, on the contrary, will move back. From the observer's perspective, it will look as if the subject is trying to grab the stimulus with his foot.

Conditioning
The reaction to the stimulus manifests itself in connection with the passage of impulses along a certain path, which depends on the specific reflex being tested. Reflex arcs are the same “paths” that make up a complex that includes a receptor, an afferent (neuron process), a central, efferent link and, finally, an effector (executive organ).
This term was introduced in 1850 and is now considered incorrect in some cases, since it does not fully reflect the reaction mechanism and the presence of feedback. Instead, he is offered the concept of a reflex ring, which, however, is not always used.
If we talk about the lower pathological flexion reflex, the reflex arcs will be as follows: plantar receptors - tibial nerve - sciatic - spinal cord neurons. Here, two types of cells participate in the formation of the reaction: sensory and motor. Next, through the sciatic and tibial nerves, the impulse returns to its original area, to the muscles that cause flexion of the fingers.
Causes
The Rossolimo reflex belongs to the pyramidal signs. That is, a positive reaction after a certain age indicates serious neurological problems. A certain group of pathological reflexes is so named because they help diagnose damage to the central neuron of the cerebral cortex or the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract. The damage can be of a different nature, but, as a rule, it is said to be organic.
If we talk about children, then until a certain age a pathological reflex is not such for them due to the insufficient development of the pyramidal tract immediately after birth. After some time, the reaction fades out, after all the necessary connections are established. Do not think that a child showing a positive reflex is immature. Up to 6-12 months this is the norm.
Features of further diagnostics
Identifying the causes of such pathological reflexes as Gordon's symptom seems to be a difficult task. By the way, the name itself here suggests that this is not a separate disease, but just its manifestation, not a cause, but a consequence. And even damage to the pyramidal tracts is also only a symptom.
Neurologists certainly need to find out the reason that underlies these symptoms. That is, identifying the reflex should be considered only the first stage in making a diagnosis.
Further diagnosis will be based on detailed medical history. Typically, tools such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are used to make a correct diagnosis.
If medical institutions do not have equipment for these studies, then the patient may be prescribed echoencephaloscopy (this will allow, for example, to identify the fact of displacement of brain structures) or craniography (it can be used to detect intracranial hypertension).
And when the exact cause of the symptom is established and the diagnosis is determined, the patient will be prescribed a timely and competent course of treatment. The methods used today to combat neurological diseases are very effective and varied.
Meaning
The Rossolimo flexion reflex is a manifestation of a central motor neuron lesion. In this case, the flow of inhibitory impulses into the spinal cord stops, and therefore it becomes possible to register a positive reaction to stimulation.

Moreover, unlike some other pathological reflexes, this one does not indicate an acute lesion (except for injury with spinal shock), but is a late manifestation of a disease such as central (spastic) paralysis.
The cause of this disease lies in damage to the motor neuron. Since the fibers and cells in it are located very closely, manifestations often spread to entire parts or even half of the body. With this disorder, loss of motor functions, muscle hypertonicity, hyperreflexia, clonus (contraction in response to stretching), etc. are observed.
Treatment
Spastic paralysis itself, and after it pathological reflexes and synkinesis (friendly movements) are just a manifestation of the underlying disease. But the defeats they signal can be as follows:
- injuries;
- oncological diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- infections;
- intoxication;
- congenital disorders.
In 60% of cases, spastic paralysis is a consequence of a stroke, and the causes listed above account for the rest. In each specific case, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition, identifies the causes of the problems and prescribes appropriate treatment. These could be drugs that improve blood circulation or help restore brain cells.
Also, of course, attention is paid to the underlying disease that caused the damage, if possible. If it is an infection, then appropriate antibiotics are prescribed. If we are talking about poisoning, then it is necessary to take appropriate actions to cleanse the body tissues - dialysis, forced diuresis, etc. In addition, physiotherapy and reflexology, special baths, and massage are often prescribed.
It is usually not possible to restore the affected structures if a positive Rossolimo reflex is recorded, but symptomatic treatment can significantly improve the patient’s condition and improve his quality of life. It is likely that with the development of medical technology, complete recovery will become possible, but for now this is only a goal.
general description
Rossolimo-Melkersson syndrome (G51.2) is a pathological condition characterized by the following symptoms: recurrent paralysis/neuritis of the facial nerve, angioedema of half the face, usually the lips, cheilitis and folded tongue.
Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome is polyetiological. Infectious allergies, hereditary predisposition to vasomotor disorders, pathology of the lymphatic system in the head and neck area, the presence of chronic foci of odontogenic infection, and sinusitis are of great importance. A neurodystrophic genesis of the disease is possible. There is a seasonal nature of relapses of the disease. The average age of patients is 25–35 years. Provoking factors: hypothermia, taking medications (antibiotics, sulfonamides, etc.), alcohol abuse. There are bilateral (up to 75%) and in rare cases unilateral lesions.