A method for determining the mass of individual heart parts by Muller-Ilyin.
Described in 1883 by W. Müller. Based on a study of 775 hearts of adults (16-90 years old), Muller determined the average figures for the net weight of the muscle mass of the heart and its ventricles, freed from subepicardial tissue, vessels and valves, as well as the ventricular index (the ratio of the net weight of the muscle mass of the right ventricle to the weight of the muscle left ventricular mass) and the percentage of muscle mass of each ventricle. They were given the distribution of these indicators by gender and age. The average figures for the net weight of the heart, its parts and the weight ratios obtained by W. Berblinger (1947), G. I. Ilyin (1956), G. S. Kryuchkova and Kh. M. Odina (1967) differ little from Muller’s data ); they used this method to determine the average normal values and the degree of hypertrophy of the ventricles of the heart. The method of separate weighing of the heart, along with some others, was recommended by the WHO Commission of Experts (1961).
Features, functions and norm
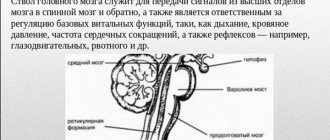
All ventricles are united into a common system, but the third has some peculiarities. If deviations in its performance are detected, it is necessary to immediately consult a specialist, because the consequences can be extremely unfavorable.
So, its acceptable size should be no more than 5 mm in infants, and 6 mm in adults. However, only it contains vegetative centers that ensure the process of inhibition of the autonomic nervous system, which is associated with visual function and is the central custodian of cerebrospinal fluid.
Its pathologies have serious consequences depending on the ventricles of a different type. It plays a significant role in the functioning of the central nervous system, the performance of which depends on their functionality. Any violations can cause poor health, which often leads to disability.
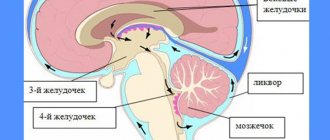
The third ventricle externally resembles a kind of ring, which is located between two tubercles, and the inner surface contains a gray substance with subcortical centers. Below it is in contact with the 4th ventricle.
In addition, certain functions are distinguished:
- CNS protection;
- cerebrospinal fluid production;
- normalization of the microclimate of the organs of the central nervous system;
- metabolism, preventing unnecessary substances from entering the brain;
- circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Proper performance of the liquor system is a continuous and refined process. However, failure or any disturbance in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid is possible, which will affect the well-being of children or adults. Despite this, the norm is determined, which is different for each age:
- For infants, acceptable values are 3 – 5 mm.
- For children under 3 months, the value should not exceed 5 mm.
- For a child under 6 years of age – 6 mm.
- For an adult – no more than 6 mm.
Method of separate weighing of the heart
The heart is freed from adipose tissue (which makes up 5-50% of the total weight of the heart) and divided into four parts: both atria with their septum are separated along the atrioventricular groove, then the walls of the ventricles are separated from their septum. Thus, we get both atria with their septum, the left ventricle, the right ventricle and the interventricular septum. After this, the mass of each part of the heart is determined. Considering that the interventricular septum contains the muscles of both the right and left ventricles, it is evenly divided between the ventricles, having previously determined the mass of the entire septum. The mass of the entire septum (g) should then be divided by the mass of both ventricles (g) to determine how much of the septal mass accounts for 1 g of the total muscle mass of both ventricles. The resulting quotient is multiplied by the number of grams of each ventricle. The results are the mass of the septum of each ventricle, which is added to the mass of the corresponding ventricle. Thus, the result is atrial mass, left ventricular mass, and right ventricular mass.
Using separate weighing of the heart parts, the following indicators are determined:
- 1) net weight of the left ventricle,
- 2) net weight of the right ventricle,
- 3) ventricular index,
- 4) cardiac index,
- 5) “percentage” of the left ventricle,
- 6) “percentage” of the right ventricle.
The total mass of the atria and ventricles is called net heart mass (NHM)
.
Ventricular index
Ventricular index
determined by the ratio of the total mass of the right ventricle to the mass of the left ventricle. In cases where cardiac hypertrophy is not observed, the mass of the right ventricle is 70 g, the left - 150 g, and the ventricular index is 0.46.
The normal ventricular index is between 0.4 and 0.6. If the ventricular index is more than 0.6, there is a shift characterizing right ventricular hypertrophy, less than 0.4 - left ventricular hypertrophy.
Cardiac index
Cardiac index
, or the ratio of the net mass of the heart to the body mass, is expressed as the quotient of the net mass of the heart divided by the body mass.
The normal cardiac index ranges from 0.004 to 0.006.
Percentage of heart ventricles
Left Ventricular (LV) Percentage
calculated by the formula: % = (LV mass × 100) / NMR
Right Ventricle Percentage
: : % = (weight of pancreas×100) / BMS
The left ventricle percentage is 59 and the right ventricle percentage is 26.
Possible pathologies and diagnosis in children
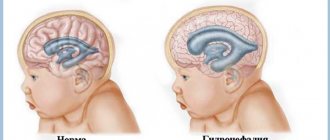
Often, problems with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid are observed in children - infants and children under 12 months of age. The main pathology is intracranial hypertension, and in a more acute form - hydrocephalus.
During pregnancy, the parent is required to undergo an ultrasound examination of the fetus to detect the presence of congenital diseases of the nervous system in the early stages. If the examination reveals an enlargement of the 3rd ventricle, then it is worth taking additional diagnostic measures and carefully monitoring the development of the situation.
If the cavity continues to expand, then upon birth the child will need shunt surgery to normalize the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. In addition, all newborns at the age of 2 months are sent for examination by a neurologist, who determines changes and the possibility of complications. Such children require specialized examination - neurosonography.
If the ventricle is slightly dilated, observations from a pediatrician are sufficient. If serious complaints arise, then you should seek advice from a neurosurgeon or neurologist. There are certain symptoms that indicate the presence of violations:
- the child sucks poorly at the breast;
- a small hole in the skull is tense and protrudes above its surface;
- the saphenous veins on the head are dilated;
- Graefe's symptom;
- a sharp and loud cry;
- vomit;
- the sutures on the skull are coming apart;
- the head increases in size.
If such symptoms are present, specialists prescribe a different treatment: vascular medications, massage and physiotherapy are prescribed, but surgical intervention is possible. After therapeutic methods, children restore their health, and at the same time their nervous system, in a short period of time.
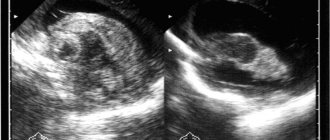
MRI with asymmetry of the lateral ventricles
The ventricles of the brain are designed to regulate the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the brain. Tanks have a certain space that can increase in size.
The largest are the lateral ventricles. Through the interventricular foramina the cavities are connected to the third ventricle. Anatomical connections ensure the flow of cerebrospinal fluid when intracerebral pressure changes.
The fourth ventricle is located between the medulla oblongata and the cerebellum. This anatomical formation has a diamond shape.
In a healthy person, a constant relationship between the described structures is ensured. Blockage of one of the ventricles leads to an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid with a subsequent increase in pressure. MRI detects ventricular asymmetry early, before clinical symptoms occur. Without signs, it is difficult to determine indications for referral to magnetic resonance therapy.
MRI asymmetry of the lateral ventricles
Causes of enlargement of the cerebral ventricles
Throughout life, there is a gradual increase in the spaces containing cerebrospinal fluid. Some pathological conditions lead to compression of the ventricular structures:
- Hydrocephalus - accumulation of fluid inside the brain with the development of dropsy;
- Birth injury;
- Long-term inflammation of the meninges with the formation of adhesions;
- Hemorrhagic hemorrhages;
- Strokes, hemorrhages.
There is a fundamental difference between the concepts of asymmetry and ventricular dilatation. The second nosology is an independent disease. It is formed under the influence of intrauterine infections and acquired pathology.
Asymmetry is caused by additional cerebral formations (tumors, limited accumulation of blood). Immediately after birth, the condition is detected by ultrasound through open fontanelles.
After healing of the cranial sutures, soft tissue components are shown by MRI.
The clinical picture of the asymmetrical arrangement of cerebral structures depends on the location and degree of compression. Small imbalances in the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid are compensated by the reverse absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
The cause of dilation may be overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid. In most cases, the etiological factor of the nosology is a violation of oxygen supply (hypoxia). The condition provokes increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid in order to improve the supply of nutrients and vitamins to the brain formations.
Pathogenesis of ventricular asymmetry
Main morphological options:
- Atrophic;
- Hypertensive.
The latter option is characterized by an increase in intracranial pressure. The condition causes compression of the ventricles. Formed in people with hypertension, secondary essential hypertension.
Atrophic forms are provoked by hydrocephalus, hemorrhages, and infections. Nosology in children causes a large number of cerebral palsy.
Symptoms of dilatation of the lateral ventricles
In an adult, clinical symptoms are rarely observed. Symptoms of dilatation in children:
- Dizziness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Apathy;
- Feeling of constant anxiety;
- Impaired walking coordination.
The clinical picture is nonspecific, so manifestations vary from person to person. In more rare cases, pathology of sensitivity, muscle paresis, cognitive disorders, and problems with head tilt occur.
Manifestations in newborns
The clinical picture in newborns is determined by the severity of the pathology. Immediately after birth, a number of external signs are noted:
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Tendency to throw the head back;
- Low muscle tone;
- Tremor;
- Paralysis;
- Nervous excitability;
- Decreased peripheral sensitivity;
- Constant crying;
- Refusal to eat.
Identification of any symptom requires an ultrasound scan of the brain. Ultrasound rays penetrate well through unclosed fontanelles.
Hydrocephalus in a baby is determined by the appearance of the skull. The increase in head size is caused by excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor causes dilatation (expansion) of the ventricles (lateral, third, fourth).
Inflammatory processes in the cerebral parenchyma provoke bacterial and viral infections that newborns contract in utero (syphilis, chlamydia, mycoplasma, cytomegalovirus, herpes).
What is the MRI normal for the lateral ventricles in an adult?
The dimensions depend on the cause of the pathology. An asymmetrical arrangement of cerebral structures is observed in neoplasms, intracranial hypertension, and hydrocephalus. Some differences in the measured values depend on the type of examination - native or contrast magnetic resonance imaging.
Tomographic indicators of the cerebral ventricles
MRI of the head shows the lateral ventricles as anechoic zones (density below surrounding structures). Three-dimensional modeling allows us to distinguish the anatomical structures of the lesion:
- Triangle (atrium);
- Body;
- inferior temporal horn;
- Occipital (back) part;
- Frontal (front) zone
The size of the ventricular spaces increases with age. In the gestational period, the value is several tenths of a millimeter. In a mature child, the ventricular spaces are slit-like. MRI determines the width of the space in the area of the foramen of Monroe, where the norm is 2 mm.
The expansion in adults begins posteriorly, so any examination requires clear visualization of the occipital structures.
Pathological dilatation is diagnosed when the diameter of the anterior horns, determined on coronal sections, increases over five millimeters.
Magnetic resonance scanning can accurately determine when the lateral ventricles are dilated and when disposition occurs.
Consequences of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles and hemispheres
A mild degree of pathology in children leads to minor clinical symptoms. The child develops slowly, but the condition gradually passes. The lag behind peers is observed during the first year of life.
High intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus are dangerous conditions. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and hemorrhages cause damage to the cerebral parenchyma and provoke cerebral palsy.
The expansion of the ventricular spaces provides changes in brain properties. The nosology causes nervous disorders and a drop in intracranial pressure. Disruption of liquorodynamics is first observed at the level of the brain, then from the spinal cord.
Symptoms of intracranial hypertension syndrome
- Rapid decrease in vision;
- Severe headaches;
- Deterioration of health in the evening;
- Nausea;
- Frequent vomiting (regurgitation in small children).
- Congestive changes in the fundus.
Severe forms of nosology lead to death. Dangerous consequences can be prevented if the disease is detected early in its development.
Source: https://mrt-kt-golovnogo-mozga.ru/article/mrt-assimetriya-zheludochkov
Colloid cyst
It is one of the most common pathologies that are present in people under 40 years of age. A colloid cyst is characterized by the appearance of a benign tumor located in the cavity of the ventricle. In this case, rapid growth and metastases are not observed.
Often it does not pose a serious danger to human health. Complications arise when the cyst increases in size, which impairs the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, the patient experiences neurological symptoms caused by hypertension inside the skull. This is characterized by:
- Headache.
- Vomit.
- Vision problems.
- Cramps.
Diagnostics and the choice of optimal treatment depend on the neurosurgeon and neurologist. It is possible to find out what size the tumor is by examination; if it is large, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. The main examination technique is neurosonography - ultrasound examination. This method is applicable to newborns because they have a small hole in the skull. Thus, thanks to a special sensor, the doctor receives information about the state of the brain organs exactly down to location and size. When the 3rd ventricle is enlarged, more accurate tests and diagnostic methods are needed - tomography. In the postoperative period, the outflow normalizes, and the symptoms no longer bother you.
The third ventricle of the brain is a significant element of the cerebrospinal fluid system, the pathologies of which can result from many complications. Attention to your own health and timely examination in medical centers will help prevent the development of the disease and cure the patient.
Computed tomography anatomy of the brain, page 3
| Gray matter density | HU | 30-35 |
| White matter density | HU | 25-29 |
| Density of periventricular zones | HU | 5-8 |
| Width of front horns | mm | 2-5 |
| Lateral sulcus width | mm | 3-5 |
| Width of the third ventricle | mm | 2,5-4,5 |
| Width of the IV ventricle | mm | 12-14 |
| III ventricle index | abs. | 0,3-0,4 |
| IV ventricle index | abs. | 11-13 |
| BJ body index | abs. | 18-22 |
| BZ anterior horn index | abs. | 24-26 |
It is generally accepted that the normal volume of all sulci in young people is approximately equal to the volume of the ventricles; with atrophy, the volume of the ventricular system can significantly lag behind the volume of the grooves on the surface of the brain.
To assess the liquor-conducting system, the linear dimensions and index of the bodies of the lateral ventricles of the brain, and the linear dimensions of the subarachnoid spaces of the cerebral hemispheres are used.
The ability to detect various diseases and brain injuries using CT is associated either with a disruption of normal anatomical relationships in the cranial cavity, or with various attenuation of X-ray radiation by normal and pathologically altered tissues.
Thus, normally the ratio of densities of all structural elements of brain tissue is stable. During pathological processes it changes. For example, an increase in water content in the intra- and extracellular space leads to a decrease in tissue density, which is observed with cerebral edema. That's why low-density
the contents of most cystic formations appear. The reason for the decrease in density during demyelinating processes is the structural degradation of lipids.
If the tumor tissue is rich in blood vessels or the degree of differentiation of its cells is low, then such a pathological process looks denser than the surrounding brain matter and its density increases significantly after intravenous administration of a radiocontrast substance due to increased microcirculation and disruption of the blood-brain barrier (high-density structure).
The density of some pathological structures may change over time. Thus, when a blood clot is formed, its image density initially increases to 60-90 HU, due to an increase in the concentration of the protein fraction of hemoglobin and the removal of plasma from the clot. Therefore, all traumatic or spontaneous hematomas in the acute period look like high-density
outbreaks;
As the hematoma ages, by day 14-20 it becomes iso-dense,
and then
low-density.
If the cellular elements of the tumor are at a high stage of differentiation or the tissue is poor in blood vessels, then it will look on computer tomograms as a low-density pathological formation, or will have a density equal to the surrounding tissues, that is, it will be isodense.
Along with densitometric indicators, an important criterion for evaluating a CT image is the detection of violations of spatial anatomical and topographic relationships in the studied area of the head. The presence of any additional pathological focus leads to the development of secondary changes in the form of compression of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces, displacement of the midline structures of the brain: the transparent septum, the third ventricle and the pineal gland (“mass effect”) - signs of lateral dislocation.
Their movement in the vertical direction with the development of signs of transtentorial herniation of the brain stem are signs of axial dislocation.
Computed tomography
must be carried out by
an R -laborator
from the beginning to the end of the study.
The question of contrast enhancement is decided by the doctor.
Contrast Enhancement:
if it is necessary to increase the contrast of the image of brain structures, 40 ml of a 60-76% solution of a triiodinated water-soluble radiopaque substance, or non-ionic drugs (omnipaque, ultravist, vizipak), are injected intravenously, after which a CT scan is performed.
With the introduction of a radiocontrast substance, the X-ray density of the brain substance normally increases slightly - by 2-4 HU, which is associated with the presence of the blood-brain barrier, and therefore the parenchymal phase of enhancement is practically absent.
CT angiography –
is one of the variants of image enhancement technique
,
the purpose of which is to visualize blood vessels.
This study involves rapid intravenous bolus administration of a water-soluble radiopaque non-ionic drug of various concentrations (Omnipaque-240, 300, 350; Visipaque, or Ultravist-300-370 mg/ml), using an automatic syringe, in an amount of 50-100 ml at a speed of 2. 5-3.5 ml/sec. In this case, it is optimal to perform SCT, the beginning of which is determined by the scanning delay time.
Scanning of the anatomical region of interest is performed during the period of greatest contrast enhancement of the lumen of the vessels, usually during the first passage of a bolus of contrast agent. The data obtained from CT angiography includes not only images of blood vessels, but also other anatomical structures, as with conventional CT. Arterial and venous structures are displayed simultaneously.
The advantages of the method are the speed of the study and good correspondence of the data obtained to the results of intraarterial angiography. Disadvantages of the method include the use of a contrast agent and the lack of information about flow characteristics. The technique has virtually no specific artifacts.
With a native CT examination, only the external contours of the vessel are clearly visible. Improvements in CT installations of the third and fourth generations have led to a reduction in the time of one scanning cycle to 2-3 seconds, which has made it possible to increase the number of tomograms obtained during a bolus injection of a contrast agent to 4-5 per minute. The introduction of spiral CT technology into clinical practice has significantly changed the methodology for studying cerebral vessels. The total head scan with spiral CT is only 20-30 seconds.
The use of CT angiography in neuro-oncology makes it possible to assess changes in vascular topography, identify stenosis of great vessels due to the impact of a tumor, and visualize the structural features of the tumor’s own vascular network (including intratumoral shunts). Perfusion computed tomography of the brain:
A method that allows one to evaluate the temporal and volumetric indicators of perfusion of brain matter by assessing the dynamics of its passage through the vessels of the brain.