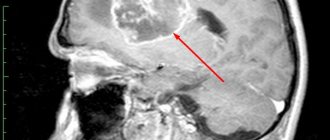
general description
Progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy (Binswanger's disease, subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy) (I67.3) is a chronic progressive disease of the cerebral vessels with damage to the white matter of the hemispheres, developing against the background of hypertension and leading to the development of dementia.
More common in men over 60 years of age.
The etiological factor is arterial hypertension. Hereditary predisposition is noted in 20% of cases. In 50% of patients, periodic transient disturbances occurred in the form of paresis/paralysis or swallowing/speech disturbances, followed by reversal of symptoms.
Leukoencephalopathy of the brain - what is it?
Destructive cell death in the nervous system of the brain, which is provoked by hypoxia from insufficient blood flow to the organ, leads to microangiopathy.
The disease leukoaraiosis, as well as the pathology of lacunar-type infarctions, change the structure of white matter cells. Manifestations of leukoencephalopathy are associated with the severity of the disease, and symptoms depend on the type of pathology. The subcortical type is very often associated with frontal lesions, and is detected in epileptic seizures.
The main causes of brain diffusion:
- Insufficiency of blood flow in the brain (causing ischemia);
- Lack of nutrition for brain cells due to hypoxia;
- Causes that are caused by a number of diseases.
Leukoencephalopathy is a progressive type of encephalopathy, also called Binswanger disease, which affects the white matter of the subcortical tissues of the brain.
Let us say right away that traditional methods of treatment are not appropriate here. Leukoencephalopathy is a disease that cannot be completely cured. If the patient has been diagnosed, the doctor prescribes maintenance treatment with special medications.
Pathology must be treated differently in each case, taking into account the characteristics of the body. Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Drugs that improve cerebral circulation - Actovegin, Vinpocetine, Trental.
- Drugs that stimulate metabolism - Pantocalcin, Cerebrolysin.
- Vitamins – Retinol or Tocopherol.
- Antidepressants – Fluoxetine.
- Zovirax, Viferon, Cyctoferon.
Among other things, encephalopathy can be corrected by: physiotherapy, massage of the collar area, homeopathy, reflexology, and manual therapy.
It is impossible to completely get rid of this disease. Using a number of therapeutic techniques, they only reduce the rate of development of the pathological process. Therapy is selected separately for each patient, using a complex of therapeutic symptomatic and etiotropic techniques.
Reducing the manifestations of the pathological process is achieved by:
- Means for improving blood circulation in the brain in the form of Vinpocetine, Actovegin, Trental.
- Neurometabolic stimulants: Phezam, Pantocalcin, Lucetam, Cerebrolysin.
- Angioprotectors (Stugeron, Curantinl, Zilt).
- Multivitamin complexes containing B vitamins, retinol, tocopherol.
- Adaptogens. In the form of aloe extract, vitreous body.
- Glucocorticosteroids. They help relieve the inflammatory process in the brain. Prednisolone and Dexamethasone have similar properties.
- Antidepressants.
- Anticoagulants to reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Antiviral drugs if the disease is of viral origin.
In addition to drug therapy, it may be recommended to take a course of:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- reflexology;
- acupuncture therapy;
- use of homeopathic and phytotherapeutic remedies;
- manual therapy.
To alleviate the condition, you need to perform breathing exercises and massage the collar area.
Treatment of the disease is quite difficult, since most antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs fail to penetrate the barrier between blood and tissue that protects the central nervous system. Therefore, they do not contribute to the elimination of pathological foci.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy develop over several years. There is often a decrease in patients’ criticism of their condition, so patients’ relatives turn to doctors. The following complaints occur: decreased memory and attention, changes in mood, slowed thinking (70–90%), difficulty speaking (45%). In 50% of cases, slow movements and gait disturbance are observed. Weakness in one half of the body (40%), difficulty swallowing (30%), and urinary incontinence (25%) are observed.
An objective examination of the patient reveals dementia syndrome (intellectual-mnestic decline) (90%), other cognitive dysfunctions (aphasia, apraxia, agnosia) (50%). You can also identify hypo- and bradykinesia, rigidity, dysbasia, and hyposmia. “Senile gait”, ataxia, postural instability with frequent falls are observed in 50% of cases. Hemiparesis, hyperreflexia, pathological signs, pseudobulbar syndrome - in 45%. Pelvic dysfunctions - in 25%.
Features of the pathology
Periventricular leukomalacia in premature infants is a lesion of the white matter localized near the lateral ventricles. It is characterized by necrotic damage to brain tissue due to insufficient oxygen supply and weakened blood flow. PVL occurs mainly in children whose body weight does not exceed 2 kg.
Due to fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen), a cyst gradually develops in the brain, but this process does not occur during intrauterine development. Such formations appear in the first 30 days from birth. Their diameter usually does not exceed 3 mm and the cavities are localized mainly in the parietal and frontal regions.
The focus of leukomalacia can be seen using a neurosonogram. Such an instrumental examination is mandatory for premature babies and is prescribed to all babies from this group.
The following stages are typical for PVL:
- First. In the first 7 days, an increase in echo density in the ventricular region is observed;
- Second. The echo density increases and small cyst-like formations form;
- Third. The echo density remains at a high level and at the same time the number of cystic formations becomes significantly larger;
- Fourth. A high level of echo density spreads to the white matter and cyst-like formations begin to appear in it.
Leukomalacia cerebri can have different symptoms. Damage to brain tissue cannot occur unnoticed. There are such degrees of development of the disease:
- Easy. At the same time, signs of brain damage are noticeable throughout the week.
- Average. Over the course of ten days, the child experiences convulsions, disturbances in autonomic functions, and increased intracranial pressure.
- Heavy. The deep layers of brain tissue are damaged, and children often fall into a coma.
Among the main manifestations of the disease are:
- Suppression or significant increase in neuro-reflex excitability.
- Cramps.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Symptoms of brain stem damage.
- Paralysis.
- Visual impairment, which manifests itself as strabismus.
- Increased activity, impairment of intelligence and psychomotor development.
Neurological symptoms may not appear in the acute period. In most children, after the end of the exacerbation period for 5-9 months, their condition improves. This period is called imaginary well-being. After this, symptoms of nervous tissue atrophy appear.
The location of the nerve pathways around the ventricles leads to impaired motor function. Therefore, if a child has leukomalacia, its first manifestation will be cerebral palsy. Its severity depends on the degree of brain damage.
Due to damage to the brain stem and cranial nerves, strabismus and impaired swallowing and breathing develop. At the age of 6 months, seizures appear.
With severe damage to the parietal and frontal lobes of the brain, cerebral palsy with mental retardation develops. If the pathways are affected, paralysis occurs without a decrease in intelligence and developmental disorders.
Children who suffered oxygen deprivation during perinatal age suffer from attention deficit and hyperactivity. This variant of the course of the disease can be considered favorable, since the child’s condition can be normalized with the help of special medications.
With moderate or severe damage, speech development is inhibited, the baby untimely begins to walk, roll over and perform other actions typical of children of his age.
More attention should be paid to the development of hypertonicity, which causes pain to the child. Because of this, the baby sleeps poorly, often cries and is capricious.
The sucking reflex is impaired, so breastfeeding may remain in question.
The presence of a neurological deficit is most pronounced at one year of age and is expressed by cerebral palsy and delayed psychomotor development.
At the end of the recovery period, children experience:
- slowdown in psychological and speech development;
- mood instability;
- sleep and attention disorders;
- in severe cases, cerebral palsy develops.
In adults, the disease may progress more favorably and does not distinguish them from other people.
Diagnostics
- Computer/magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (extensive bilateral leukoaraiosis, possible lacunae in the subcortical gray matter, hydrocephalus, cerebral atrophy).
- Single photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography (areas of hypoperfusion and decreased metabolism).
- Neuropsychological testing (disorders of the subcortical-frontal type with the early appearance of affective disorders such as depression, emotional lability, apathetic-abulic syndrome).
Differential diagnosis:
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Parkinson's disease.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Radiation encephalopathy.
- Mental illnesses.
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Pathogenesis
As a result of these reasons, necrosis of the white matter of the brain occurs, after which degeneration of astrocytes (stellate
PVL develops in the first hours, but can also occur later – up to 10 days after birth. Leukomalacia can also affect in utero - if the course of pregnancy is pathological (preeclampsia, exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis, hepatitis, fetoplacental insufficiency).
Clinical picture
Already in the maternity hospital, children experience depression of the central nervous system. It is expressed by a decrease:
- muscle tone;
- specific reflexes;
- motor activity;
About a quarter of newborn babies have seizures. Almost half of children suffer from hyperexcitability syndrome. Some infants may experience brainstem symptoms (cardiovascular and respiratory disorders). In some cases, there may be no abnormalities in the neonatal period, and in some cases, PVL is fatal, regardless of treatment.
This pathological process is characterized by the presence of a stage of “imaginary well-being,” which can last 3–9 months, after which signs of cerebral insufficiency develop. This is manifested by impaired consciousness, swallowing reflexes, breathing, and increased blood pressure.
Periventricular leukomalacia becomes the cause of cerebral palsy (CP) in almost 90% of cases, and convergent strabismus in 60% of cases.
The severity of cerebral disorders depends on the number and area of leukomalacial cavities. However, in cases where the lesions are distributed thinly around the ventricles, the prognosis is more favorable.
The percentage of apparently healthy infants with PVL is approximately 4%. The consequences of defeat for them may be insignificant.
Treatment of progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy
- Symptomatic therapy.
- Blood pressure correction, antiplatelet agents, neuroprotectors.
- Bladder catheterization.
- Rehabilitation.
- Social adaptation.
- Secondary prevention.
Treatment is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Lisinopril (cardioprotective, vasodilating, antihypertensive agent). Dosage regimen: orally, regardless of food intake. For arterial hypertension, patients not receiving other antihypertensive drugs are prescribed 5 mg 1 time per day. If there is no effect, the dose is increased every 2-3 days by 5 mg to an average therapeutic dose of 20-40 mg/day. The usual daily maintenance dose is 20 mg. The maximum daily dose is 40 mg. The full effect usually develops within 2–4 weeks. from the start of treatment.
- Clopidogrel (antiplatelet drug). Dosage regimen: orally 75 mg 1 time per day.
- Cerebrolysin (nootropic drug). Dosage regimen: IM (up to 5 ml), IV (up to 10 ml), IV, by slow infusion (from 10 to 50 ml). The recommended optimal course of treatment is daily injections for 10-20 days.
- Piracetam (nootropic drug). Dosage regimen: orally, during meals or on an empty stomach with liquid. At the beginning of treatment, 800 mg is prescribed in 3 doses; as the condition improves, the single dose is gradually reduced to 400 mg. The daily dose is from 30 to 160 mg/kg, the frequency of administration is 2 times/day, if necessary 3-4 times/day. The course of treatment is continued from 2 weeks to 6 months. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated.
- Prozac (antidepressant). Dosage regimen: initial dose orally 20 mg/day. for one appointment.
Drug therapy for leukoencephalopathy
It is impossible to completely recover from this pathology, therefore any therapeutic measures will be aimed at containing the pathological process and normalizing the functions of the subcortical structures of the brain.
Considering that vascular dementia in most cases is the result of viral damage to brain structures, treatment should primarily be aimed at suppressing the viral focus.
The difficulty at this stage may be overcoming the blood-brain barrier, through which the necessary drugs cannot penetrate.
In order for a drug to pass this barrier, it must be lipophilic in structure (fat-soluble).
Today, unfortunately, most antiviral drugs are water-soluble, which creates difficulties in their use.
Over the years, medical professionals have tested various medications with varying degrees of effectiveness.
The list of these medications includes:
- acyclovir;
- peptide-T;
- dexamethasone;
- heparin;
- interferons;
- cidofovir;
- topotecan.
The drug cidofovir, which is administered intravenously, can improve brain activity.
The drug cytarabine has proven itself well. With its help, it is possible to stabilize the patient’s condition and improve his overall well-being.
If the disease occurs against the background of HIV infection, therapy with antiretroviral drugs (ziprasidone, mirtazipime, olanzapime) should be carried out.
Leukoencephalopathy is a pathology that is incurable. The goal of drug treatment is to stop the progression of the disease and extend the patient several years of life.
This pathology must be treated comprehensively with the use of medications, as well as:
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage;
- Manual therapy;
- Treatment with phytomedicines;
- Acupuncture.
Drug therapy is selected according to an individual scheme by the treating doctor:
- Drugs to improve blood flow in the cerebral vessels - the drug Trental, as well as Actovegin;
- Nootropic drugs - Phezam, Cerebrolysin;
- Drugs from the group of angioprotectors - the drug Curantil;
- Multivitamin complexes with B vitamins, as well as tocopherol;
- Drugs from the group of glucocorticosteroids - the drug Prednisolone, or Dexamethasone;
- Antidepressant drugs - Fluoxetine;
- Anticoagulant drugs can protect the brain from arterial thrombosis - the medication Heparin;
- To treat viruses, the medicine Zovirax or Cycloferon is used.
Despite the development of modern medicine, scientists have not been able to find an effective cure for leukoencephalopathy. Any of its forms will gradually progress and it will not be possible to completely stop the disease.
The course of treatment drawn up by a neurologist is aimed at maintaining the patient’s condition. Its goal is to slow down the development of pathology, relieve symptoms and restore the level of mental abilities.
Gradually, some drugs may be completely discontinued or replaced with other drugs with altered dosages.
Recommendations
A consultation with a neurologist and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 4.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 4.2 |
Prognosis and prevention
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure the disease. It is difficult to accurately determine the life expectancy of patients with this diagnosis; according to statistics, in the absence of therapeutic treatment, an adult lives no more than 6 months. Antiviral treatment can prolong life by up to two to three years or more if the brain structure has not been severely affected. Of course, death can occur earlier if this is a baby who has received a terrible illness from birth.
Currently, the pathology is incurable and always ends in death. How long people live with leukoencephalopathy depends on whether antiviral therapy was started on time.
When treatment is not carried out at all, the patient’s life expectancy does not exceed six months from the moment the disorder in the brain structures is detected.
With antiviral therapy, life expectancy increases to 1-1.5 years.
There have been cases of acute pathology that ended in the death of the patient a month after its onset.
The prognosis for leukoencephalopathy is extremely disappointing. In most cases, the patient's life span ranges from 1 month to 2 years. To prevent the development of a pathological process, it is recommended to follow the following rules of prevention:
- Before sexual intercourse, you must ensure that you have a contraceptive;
- You should choose only regular sexual partners, and not change them every month;
- Bad habits, such as smoking cigarettes and using drugs and alcohol, should be abandoned;
- The diet should contain a lot of vegetables and fruits and it is advisable to additionally consume vitamin complexes;
- It is advisable to avoid stressful situations, as well as physical and mental overload.
There is no cure or reliable means of prevention for leukoencephalopathy, but by following certain rules you can reduce the chances of its occurrence to a minimum. If the disease does occur, it is necessary to immediately undergo diagnosis and begin a course of maintenance therapy to prolong life.
Symptoms
| Occurrence (how often a symptom occurs in a given disease) | |
| Memory loss (memory impairment, poor memory, memory impairment, forgetfulness) | 90% |
| Mood swings (mood swings) | 70% |
| Slowness of movement | 60% |
| Gait disturbance, difficult to specify (abasia) | 55% |
| Absent-mindedness | 50% |
| Difficulty speaking (speech disorder, speech disorder, speech problems) | 45% |
| General weakness (fatigue, tiredness, weakness of the body) | 40% |
| Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia, difficulty swallowing, swallowing disorder) | 30% |
| Decreased thinking | 30% |
Symptoms
The symptoms of the pathology are quite diverse; irreversible processes can develop from mild dysfunction to a more serious problem. Focal symptoms manifest themselves in severe speech impairment and even blindness, and some disorders of the motor system progress and often lead to disability.
- headache;
- mental disorder (anxiety);
- general state of weakness;
- nausea;
- unsteady gait;
- spasms;
- involuntary urination;
- dementia;
- blurred vision;
- slow speech.

The severity of the above symptoms depends on the person’s immune system. For example, in patients with poor health, the gray matter is more affected than in people with normal immunity.