What is emotional stress and how does it affect your health?
When you are in a constant state of emotional stress, it can be especially painful and challenging, and can have more severe consequences than other forms of stress. Part of the reason is that normal stress management measures, such as thinking carefully about the reasons that led to an uncontrollable emotional reaction, can only make the situation worse, whereas in a “normal” state of stress this may work perfectly. A professional psychologist is best suited to overcome such a period. But in this article we will also talk about what you can do yourself to deal with the consequences and prevention.
Important! Stress takes a toll on our daily lives and creates strong emotional reactions because our relationships (which can trigger emotional stress) directly affect our lives—for better or for worse. Healthy relationships provide not only joy in good times, but also resources to help in times of need, added stability in times of anxiety, and even longevity and good health in old age.
However, conflictual relationships and “enemies” worsen tension and can even lead to serious physical consequences. However, relationships are not the only stressor. Financial crises, an unpleasant work environment, health conditions or a variety of other stressors can cause such a psychological shock that sometimes we are driven to unhealthy behavior in order to overcome the shock and cope with the consequences, especially when everything seems hopeless. Perhaps one of the most difficult aspects of coping with stress is the feeling of being unable to control what is happening. The feeling of loss of control is one of the most severe and difficult for a person to accept, and in itself is a source of severe stress. But, if we find it difficult or impossible to change/eliminate the cause of stress, we can always work on our attitude and reaction to it, and get help along the way if necessary.
Here are some strategies you can use to help you overcome negative consequences.
Causes of emotional stress
Stress can be caused by both sudden and ongoing negative events in a person’s life. If a tragedy occurs, or, conversely, a person has been a prisoner of a difficult situation for a long time without the opportunity to rest or switch attention from the traumatic situation, a kind of “mental burnout” may occur. At the same time, the source of serious emotional stress can be both real traumatic events and a person’s excessively negative perception of various, for most people, events that are not something serious. In this case, the risk group will be people with an easily excitable psyche, suspicious, rigid, and unable to switch.
Specific causes of emotional stress for most people:
- death or serious illness of a loved one
- disaster
- war
- job loss
- serious illness
- divorce
- change of residence
- loss of source of income
- breaking up with a loved one
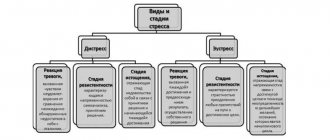
46. Concept of emotional stress
Being simultaneously an independent physiological, mental and social phenomenon, stress at its core is another type of emotional state. This condition is characterized by increased physiological and mental activity. Moreover, one of the main characteristics of stress is its extreme instability. Under favorable conditions, this state can be transformed into an optimal state, and under unfavorable conditions - into a state of neuro-emotional tension, which is characterized by a decrease in the performance and efficiency of functioning of systems and organs, and depletion of energy resources.
Under stress
understand the body’s nonspecific response to external or internal demands placed on it.
The term "non-specific" may be interpreted in this definition to mean unusual or unusual. This concept was proposed by G. Selye
. He was able to establish that to adverse influences of various kinds, for example cold, fatigue, fear, humiliation, pain and much more, the body responds not only with a protective reaction specific to each exposure, but also with a general, complex response of the same type, regardless of what irritant affects the body. At the same time, certain processes unfold in the interval between the impact and the body’s response. These processes were described in the classical studies of G. Selye, proving that the stages of stress are characteristic of any adaptation process.
In the first phase
–
the alarm phase
– the body’s defenses are mobilized, increasing its stability. At the same time, the body functions under great stress. However, at this stage, it still copes with the load with the help of superficial, or functional, mobilization of reserves, without deep structural changes. Physiologically, primary mobilization is manifested, as a rule, in the following: the blood thickens, the content of chlorine ions in it decreases, an increased release of nitrogen, phosphates, potassium occurs, an enlargement of the liver or spleen is noted, etc. In most people, by the end of the first phase there is a slight increase performance.
Second phase
usually called
the phase of resistance
(stabilization), or maximum effective adaptation.
At this stage, there is a balance in the expenditure of the body’s adaptive reserves. All parameters brought out of balance in the first phase are fixed at a new level. This ensures that the body’s response to environmental factors differs little from the norm. However, if stress continues for a long time or the stressors are extremely intense, then the third phase
- the phase of exhaustion. Having exhausted its functional reserves in the first and second phases, the body begins to carry out structural changes, but when these are not enough for normal functioning, further adaptation to the changed environmental conditions and activities is carried out at the expense of the body’s irreplaceable energy resources, which sooner or later ends in exhaustion.
It should be noted that not all exposure causes stress. Weak influences do not lead to stress; it occurs only when the influence of a stressor (an object, phenomenon, or any other environmental factor that is unusual for a person) exceeds the individual’s normal adaptive capabilities. Thus, stress occurs when the body is forced to adapt to new conditions, i.e. stress is inseparable from the adaptation process.
The essence of the stress response lies in the “preparatory” excitation and activation of the body necessary to prepare for physical stress. Consequently, it can be assumed that stress always precedes a significant waste of the body’s energy resources, and then is accompanied by it, which in itself can lead to the depletion of functional reserves. However, stress cannot in any way be considered a negative phenomenon, since it is only thanks to it that adaptation is possible. In addition, moderate stress has a positive effect on both the general condition of the body and the mental characteristics of the individual.
Stress as a holistic phenomenon should be considered as a positive adaptive reaction that causes mobilization of the body. Nevertheless, there are stress reactions that, on the contrary, lead to the demobilization of body systems. This extremely negative manifestation of stress is called distress
. It is distress that carries factors that have a destructive effect on the body. The transformation of stress into distress occurs under excessively intense influence of environmental factors and living conditions, under which the functional reserves of the body are very quickly depleted or the activity of mental regulation mechanisms is disrupted.
The multidimensionality of the phenomenon of stress in humans is so great that it was necessary to develop a whole typology of its manifestations. Currently, it is customary to divide stress into two main types: systemic
(physiological) and
mental
.
Mental stress is conventionally divided into two types: informational
and
emotional
. Information stress occurs in situations of significant information overload, when a person cannot cope with the task of processing incoming information and does not have time to make the right decisions at the required pace, especially with high responsibility for the consequences of decisions made. Most authors associate the occurrence of emotional stress with situations of threat, danger, resentment, etc. From this point of view, it is customary to distinguish three forms of emotional stress: impulsive, inhibitory and generalized. With emotional stress, certain changes in the mental sphere are noted, including changes in the course of mental processes, emotional shifts, transformation of the motivational structure of activity, disorders of motor and speech behavior.
However, it should be emphasized that such a division of mental stress into informational and emotional is very conditional. This classification is based on the main characteristics of factors causing stress. In practice, it is very rarely possible to separate informational and emotional stressors and determine which of the stressors is the leading one. Most often, in a stressful situation, informational and emotional stressors are inseparable, since the formation of feelings is always associated with the processing of information. Very often, as a result of an erroneous assessment of the situation, a person develops a feeling of resentment or anger. In turn, the so-called information stress is always accompanied by high emotional arousal and certain feelings. However, the feelings that arise in this case can also occur in other situations not related to information processing.
Mental stress can be characterized as a state of the body that arises in the process of interaction of an individual with the external environment, accompanied by significant emotional stress in conditions when the normal adaptive reaction is insufficient.
Signs of emotional stress
The concept of emotional stress was first introduced by the physiologist Hans Selye in 1936. By this, he meant a reaction unusual for the body in response to any adverse impact as a way of adapting to changed conditions. Due to the influence of stimuli (stressors), the body's adaptation mechanisms are in tension. The adaptation process itself has three main stages of development - anxiety, resistance and exhaustion.
Signs of emotional stress will appear in different people to varying degrees of severity.
- Increased irritability
- Tearfulness
- Increased heart rate
- Change in breathing rate
- Loss of control over your reactions and behavior
- Anxiety
- Memory and concentration problems
- Sudden jumps in blood pressure
- Feeling of fear, feeling of despair
- Weakness
- Excessive sweating
- Muscle tension (clamps)
- Feeling short of air
- Constantly feeling tired
- Headache and muscle pain
- Increase or, conversely, decrease in body temperature
- Changes in sleep patterns—drowsiness or insomnia
- Changes in appetite
- Depersonalization - the feeling of being outside the body
Relief and prevention of emotional tension and stress
Fortunately, although you can't always influence the stressor, you can reduce the intense tension you feel and the damage that stress causes. Here are some exercises that you can introduce into your daily life to effectively cope with difficult times. This is also a good prevention of possible stressors:
5 Ways to Cope with Emotional Tension and Emotional Stress
- Practice mindfulness
. When we experience emotional stress, it also often feels like physical stress: a heavy feeling in your chest, an unsettled feeling in your stomach, a dull headache, you feel drained, literally empty. While people usually try to distance themselves from these feelings, but this only serves to increase tension, it is actually quite helpful to go deeper into the experience and use mindfulness to help you notice where exactly these emotional reactions are felt physically. But at the same time, it is very important not to get emotionally involved in the experience, to observe yourself as if from the outside, without judgment, otherwise, immersion in the problem will not bring relief, but will aggravate stress. When you learn to be aware and not emotionally experience the situation, you will notice how stress weakens, the causes of stress cease to take over you entirely, become manageable and solvable, and this is also a good prevention for the future.
- Take a break
. This is another way to prevent and relieve severe stress. It is believed, and not unreasonably, that if we do not express all the emotions we experience (or at least the strongest ones), then they manifest themselves in other ways. Yes, it's true: studying and tracking our emotional states is useful in order to learn from what emotions are trying to say, and unhealthy ways of coping with stress, including trying to ignore emotional stress, can lead to other, more serious problems. but in no way to remove it. However, it has also been found that distracting oneself from emotional (and, by the way, physical) pain through emotionally healthy practices - such as watching a good movie, fun activities with friends, or solving an interesting, important mental task - can reduce emotional pain and help relieve stress. factors and a feeling of improvement.
- Book some time to worry
. If you find that mindfulness and trying to distract yourself in healthy ways are not working, and thoughts about a stressful situation are constantly overwhelming you, schedule some time, such as an hour a day, to fully absorb and think about the current emotional situation. This will help in relieving stress. Perhaps when you allow yourself to fully think about your situation, and think about all the possible solutions, come up with hypothetical possibilities and ways out of the current situation, reproduce strong reactions, or otherwise allow yourself to become fully immersed in the problem, you will feel an emotional urge to do something something that will help resolve the situation. This is great self-help. In order not to pricelessly ruminate, simply stressing yourself out, but to actually help, try journaling - it is a great technique to try, especially if you do it as an exploration of the inner emotional world and the potential for resolution. You can spend this hour talking with your loved one about this emotional issue if you wish. And after the planned time has passed, be distracted by something else and stop spinning thoughts in your head. This technique for dealing with emotional stress works well for two reasons:
- If you truly have an obsessional urge, this technique will satisfy that urge in a limited context.
You may feel more relaxed throughout the day because you know there will be time later to focus on your emotional pain point.
. Meditation greatly helps to be aware, to feel the moment “here and now” and, as a result, not to be influenced by stress factors, and any emotional tension that lasts for any long time definitely falls into the category of stressors that meditation helps with. The practice allows you to take a break from thinking by actively redirecting your thoughts, and provides experience in choosing thoughts that can help relieve stress in the long term. Try some meditation techniques today.
. If you find that your stress levels are interfering with your daily activities or threatening your well-being, you may want to see a therapist for help dealing with your emotional problems. It is best to use one of the online services, such as Helppoint, to find a psychologist or psychotherapist. Here you can choose a trusted specialist according to your request and solve your problem with his help, completely immersing yourself in yourself, without the risk of getting stuck in a stressful situation even deeper. Whatever the trigger for extreme stress, you can work to reduce it, manage it, prevent future troubles, and feel better in the process without losing the “important messages” that emotions bring.
The information presented in this material is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional advice from a physician. If you find signs of emotional stress, consult a specialist!
Editorial staff of the Helppoint portal
What is stress and how to get rid of it
Let's look at a very important question for many about what stress is and how to get rid of it. It is quite possible to do this yourself.
Translated from English, the word “stress” means effort, a state of increased tension.
The most famous stress researcher was the Canadian physiologist Hans Selye. Back in 1936, he published his book, where he gave the following definition: “Stress is a nonspecific response of the body to any demands placed on it.”
What this mysterious set of words means is not very clear. Let's try to understand stress in a more understandable language.
Good stress
We can be in a calm, balanced state. And we can be in an excited state.
A state of excitement can be caused by good reasons, then it will be eu-stress from the Greek word for “good”.
For example, a state of intense love is stressful. More precisely, eustress.
Sex with orgasm, naturally, is also an excited state of the body, that is, eustress.
There may also be a state of joyful excitement before receiving a well-deserved reward, for example. You have won a competition or competition, and now you are waiting for the moment of awarding. You are shaking with joyful anticipation. This is also eustress.
There is also a state of excitement when you are captivated by some idea and you are eager to implement it. You are excited, many ideas arise in your head, and you are actively implementing your project.
These are all good conditions, although stressful. And you would hardly want to get rid of them.
Destructive stress
And there is another type of stress - di-stress, from the Greek word for loss. This is also a state of excitement, but it is destructive, or excitement with negative consequences.
By now you should understand that all strong negative emotions are related to distress.
That is, anger, rage, resentment, jealousy and other strong negative emotions are one of the forms of stress, or more precisely, distress.
This is obvious, since emotion is the body's reaction to external or internal changes.
It’s just that the concept of stress is broader than the concept of emotion.
Two types of stress
That is, we can say that the concept of stress includes two types of excitation of our psyche:
Type 1.
Mental arousal caused by a violation of our idealizations, that is, stress in the form of a negative emotion.
View 2.
Mental arousal created by the Reptilian brain to create our compliance with external conditions or internal processes.
These two types of stress are removed in different ways.
Let's look at what you need to do to avoid Type 1 stress.
Removing stress of the first type
The first type of stress is the result of negative emotions, as you should already understand.
If you remember, a negative emotion arises when there is a discrepancy between Reality and our important expectations. Our Reptilian brain generates emotions.
If you don't know about this yet, watch this video
What can we change about these three creators of our stress?
Can we change our Reptilian brain's response to danger?
Theoretically, this could happen when the Reptilian brain itself decides that you live in absolutely safe conditions and has nothing to protect.
This is roughly how residents of wealthy countries in Central and Northern Europe assessed their lives twenty years ago. But today, due to the migration of millions of residents of underdeveloped countries, the growth of terrorism and general tension in Europe and other countries, no one feels completely safe.
The reptilian brain of the vast majority of people feels that the world is unsafe and that the person needs to be helped to survive. Including in our country.
That is, it is not possible to somehow force the Reptilian brain to stop performing its protective functions.
What else is in the top three creators of our stress?
There is also Reality. It is the behavior of other people that we want to change according to our expectations. But people don't want to change just because we don't like something about them. So it’s difficult to do anything with Reality. A simple example: can you force yourself to stop worrying if your weight is higher than the generally accepted norm? Most likely no.
What else remains? There remain very important expectations for us about what and how should happen in us and around us.
For example, the expectation that people should be honest. That no one should limit your independence. That the child should study well. That your loved one should not cheat on you. That the boss must be fair, and so on.
Since childhood, each of us has formed our own picture of the world, our own set of ideas, beliefs, beliefs and everything else.
Those of our ideas or expectations that we attach excessive importance to for a variety of reasons are called idealizations.
They are stored in our Center for Ready Solutions, or in the Subconscious.
Our Reptilian brain is well aware of them, and constantly monitors so that no one violates them.
And as soon as a violation of our extremely important expectations occurs in Reality, the Reptilian brain regards this situation as dangerous. And immediately takes measures to protect our idealizations.
What are these measures? This is what we call negative emotions.
We become agitated and try to defend our idealizations. Or, if the violator of our expectations is stronger than us, then we experience fear and try to hide.
Any violation of your idealization inevitably creates a negative emotion in you, or what is the same thing, distress.
And you may have three, five, or even ten idealizations from different areas of life. And every idealization your Reptilian brain must protect.
Is it possible to do something about your idealizations? Moreover, you yourself hardly understand where they came from in you.
Fortunately, this is possible. It’s not easy, of course, it’s not a pill to swallow. It takes effort. But the result will be more than wonderful.
We remove idealizations - stress goes away
If you remove your idealizations from yourself, then your Reptilian brain has nothing left to protect. He no longer excites you because you have taken away from him what he used to protect by force.
You no longer have negative emotions, that is, no stress. Your body relaxes, your blood pressure returns to normal - if your blood vessels are more or less healthy, of course.
The people around you don't change, and they can still lie, walk around, not complete your tasks, and do many other things that used to infuriate you.
And now you treat this situation calmly and reasonably. Is someone lying to you? You calmly take measures to ensure that these lies do not harm you.
Is your husband trying to cheat on you? Here you also make a very conscious decision. If your husband suits you in many ways, then you can simply not pay attention to his moves to the left.
Or, if he is not so good, you can set a condition for him that if he cheats again, you will get a divorce. And so that he trusts you, you conclude a notarized marriage contract with him, where you indicate what he will lose in case of betrayal. And then let him think for himself what is more valuable to him.
If your subordinates do not perform your tasks the way you want, then you make a very conscious decision about what you will do with them. Perhaps you will make their pay level more dependent on the results of their work. Or is it worthwhile to provide them with additional training. Or simply look for other, more responsible and proactive employees.
That is, your Reptilian brain will no longer be involved in making your decisions. You will make all decisions with the help of your Conscious Decision Making Center, that is, the Mind.
This is all possible, you just need to make these changes according to the correct algorithm, it is shown in the figure below.
According to this algorithm, in the first step you need to identify your idealizations. This is only possible by keeping records in the Self-Observation Diary for two to three months. No other methods will allow you to pull out your idealizations; this has been tested many times.
Then you need to free your body from the emotional blocks that have accumulated in it during your long struggle for your idealizations. We suggest doing this using the Effective Forgiveness technique, if your health allows it.
If it doesn’t allow it, then you can use audio tunes for forgiveness from the psymarket.ru store
You cannot start with forgiveness, because your experiences will disappear and you will not have material to identify your idealizations.
And then in Step 3 you will need to translate your super-important ideas or expectations into ordinary, ordinary ones. Ones that your Reptilian brain will not respond to.
This is easy to do, for example, using the Effective Self-Programming technique. Or using audio settings to remove idealizations, such are available in the psymarket.ru store
As a result, all the stress in the form of negative experiences that bother you so much now will go away.
Attention!
You cannot skip Step 2, because without this it will be very difficult for you to load new behavior programs into yourself.
You also can’t stop working at Step 2 when all your worries disappear. Since you do not remove your extremely important expectations - idealization, then if they are violated, your Reptilian brain will again give out its defensive reactions and create new emotional blocks. Moreover, this will happen faster than before.
Therefore, you need to complete all the steps of the algorithm; they are minimal and mandatory.
The easiest way to complete all these steps is in Section 13. Tools. Let's remove our idealizations
. Everything there is adapted for liberation from idealization.
And then you will need to observe yourself, and as you identify the remnants of idealizations, work them out according to the above algorithm.
That's all. You will no longer need alcohol, excess food or pills to calm you down.
Removing stress of the second type
Let us remind you that the second type of stress is mental arousal created by the Reptilian brain to create your compliance with external conditions or internal processes.
When does this stress occur?
For example, tomorrow you have to defend your dissertation, into which you have invested several years of your life.
Or this is a speech before the Board of Directors of a company, where you defend a project that is very important to you.
Or you have passed the entrance exam and are now waiting for the decision of the examination committee.
And so on.
There seems to be no fear as a reaction to danger. But there is excitement, and it doesn’t let you sleep.
Is it stress? Yes, this is stress, a strong agitation of your psyche.
Who creates this excitement in you? Your Reptilian Brain via the Limbic System, most likely.
Is it distress, that is, fear, for example?
Most likely no.
Of course, there may be some concerns that things will not work out the way you want. That is, Reality will diverge from Expectations that are very important to you.
But most likely, you do not have pure recurring fear. And there is excitement that creates problems with sleep or health for you.
This means that this excitement needs to be removed.
How to do it?
There are also multiple players in this stress.
It is you.
These are very important one-time expectations for you.
This is the Reptilian brain, which knows about expectations that are very important to you.
What can you influence?
What can you do to reduce your arousal level?
Of course, you can influence your body and slow down the processes occurring in it. For example, drink alcohol or a sedative pill. But this is not the best way out; it is practically a chemical struggle with oneself. With unknown consequences.
You will not be able to influence yourself psychologically; your Reptilian brain will not listen to your commands from the Mind. The Reptilian brain is busy with important work, it helps you behave with dignity in difficult conditions, so it will not listen to commands to calm down from the Mind.
Can you influence the level of assessment of the importance of an upcoming event? Probably yes. You can convince yourself that the upcoming result is not too important to you. And then the Reptilian brain will reduce your level of arousal.
This can be done through self-programming, when you plant statements in your Subconscious that you calmly and benevolently accept any outcome of the upcoming event.
It's not easy, but it's possible. You can also use technical means, for example, the encoded audio tune “Live Easy”
, it is available in the store psymarket.ru
That is, with distress of the second type, you need to use slightly different tools to devalue the upcoming result than in cases of violation of your idealizations.
But it is quite possible.
Artificial threat to life
Many people artificially create stress in themselves in order to feel an energy boost. And feel the so-called “taste of life”.
On a mass scale, this is what fans of any sports team do.
Those who like to watch action or horror films. Or dramas and tragedies.
What kind of stress are these people experiencing? If your team wins, then eustress. If you lose, then distress.
But what kind of stress do you get when you quite consciously create a situation that threatens your life, for example, by driving a car too fast? Or when you climb to the top of a mountain, constantly risking your life?
Do you have fear at this moment? Of course have. But you overcome your fear through willpower.
You get pleasure due to the overexcited state of your psyche, which is trying to somehow protect you. Your Reptilian brain really assessed the threat to your life and created a strong protective arousal in you. Most likely the same fear.
But by an effort of will you overcome your fear and continue your action. If everything ends well, then you get pleasure from overcoming your fear. And from the excited state that you just experienced.
The specificity of this stress is that it is not a reaction of the Reptilian brain to events that arise on their own.
This is stress that occurs when you make conscious efforts that threaten your life.
Why do people create such overexcited states for themselves?
One of the possible answers is that when excited, light drugs from the category of amphitamines are synthesized in the human brain. That is, people are capable of producing narcotic substances within themselves with additional stimulation of their psyche. Moreover, it is completely free and non-punitive. This is what they do either in numerous conflicts or by creating a threat to their lives.
So you have a tool to eliminate stress from your life. But whether you use them is up to you.
You can remove all your stress yourself in Section 2.4 Removing Your Stress