Symptoms
Dislocation syndromes are classified in different ways. There are nine names found in the specialized literature, but the most common are the first four from the list below.
The unconscious state lasts at least 60 minutes and can last for several days. Loss of consciousness is caused primarily by decreased blood flow to the brain. The patient suffers from memory lapses, which, as in the case of concussion, are not limited to the phase immediately after the injury, but also extend to the time before the accident.
If DP worsens and ICP increases, the patient may fall into a prolonged coma. In the worst case, the patient may die. There is also a risk of permanent brain damage. With DS, the patient also suffers from other injuries. These are skull fractures or subdural hematoma (bruises below the meninges).
Regardless of the etiology of the pathological process that provoked the dislocation of brain fragments, an increase in intracranial pressure values more often occurs, which is accompanied by the appearance of the Cushing reflex. The pathological reflex combines the following symptoms: an increase in arterial (systolic, top number) and pulse (the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure) pressure, respiratory dysfunction, bradycardia (disturbance of the sinus rhythm of the heart).
Brain dislocation syndrome manifests itself depending on the type of displaced structures and direction. If the medulla moves under the falx process, the following symptoms are observed:
- Hemiparesis (paresis in one half of the body).
- Hemihypesthesia (loss of sensation in one half of the body).
- Pathological reflexes (grasping, oral automatism).
- Hemiataxia (impaired motor coordination in one half of the body).
- Mental disorders characteristic of damage to the frontal lobe (blurred consciousness, memory impairment, disorientation).
- Hyperkinesis (pathological involuntary movements).
In the axial form, signs appear at an early stage: hyperthermia (overheating of the body), tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), flickering consciousness (alternating periods of conscious and unconscious states), hypercatabolism (increased catabolism involving tissue proteins), apnea (short-term cessation of breathing), narrowing pupils. There is also an increase in muscle tone.
The late stage is manifested by loss of consciousness, coma, immobility, lack of response to painful stimuli, and hormetonic type convulsions (cyclical, rhythmic spasms). Progression of the pathological process can lead to the development of coma and terminal condition, death. Clinic of dislocation syndrome with temporal lobe shift:
- Pupil dilation (unilateral).
- Weakening of the pupil's reaction to a light stimulus.
- Gaze paresis.
- Hemiparesis (paresis in one half of the body).
- Hemiplegia (loss of the ability to make voluntary movements).
- Hyperthermia (body overheating, excessive heat accumulation).
- Bradycardia (disturbance of sinus rhythm of the heart).
The progression of the pathological process is accompanied by the development of stupor, coma, and severe oculomotor disorders. If left untreated, a terminal condition develops. When there is a herniation into the foramen magnum, symptoms (rigidity and pain in the occipital muscles, cerebellar disorders, bradycardia, bulbar disorders) usually increase rapidly.
Relatively uncommon, but the pathology process can result in a coma. When swelling of the brain is infected with an infectious virus of the nervous system, the patient does not fall into a coma.
To stabilize the patient’s condition, it is worth starting to identify and eliminate the causes of the disorders. For this purpose, comprehensive diagnostics are carried out.
The examination includes:
- Echoencephalography. It allows you to assess the degree of displacement. The results will show whether there is a lateral form of development of the disease. It involves moving structures under the falx process.
- Antiography. Allows you to find out what form the blood vessels are in.
- Computed tomography to assess the functioning of the internal structure of the organ that is being examined.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to obtain the most detailed information, thanks to which it is used to diagnose most diseases.
If you suspect the presence of a pathology, you should not subject the patient to a lumbar puncture or puncture. This can lead to a decrease in the pressure of the fluid constantly circulating in the ventricles of the brain.
If its increase was previously observed, a process of displacement of brain tissue relative to solid formations may occur. This causes problems that can lead to death.
This pathology is usually accompanied by a coma in the patient. However, loss of consciousness is not always observed.
For example, if the disorder was caused by a sudden process, swelling of the brain or an infectious lesion of the nervous system, the person may remain conscious.
Other factors can also lead to the development of brain dislocation, under the influence of which the abnormal process proceeds more slowly.
Typically it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- convulsions;
- temporary or permanent loss of vision;
- severe headaches;
- frequent vomiting and nausea.
Symptoms
Brain dislocation is a very serious condition that deserves intensive treatment, sometimes with the use of surgery. When the brain is dislocated, most often the person is in an unconscious state, that is, in a coma. Read about what it is here.
There are other causes of dislocation, in which the displacement of brain structures does not occur so quickly and suddenly. The shift occurs gradually and consciousness is preserved. One of these reasons may be a neoplasm - a cyst or tumor that grows gradually. Despite its gradual growth, this neoplasm can also cause brain dislocation . Symptoms:
- severe headaches
- nausea and repeated vomiting
- decreased vision - persistent or transient
- convulsions
- depression or complete loss of consciousness
Similar symptoms will accompany cerebral edema, which can cause dislocation and dislocation syndrome , among other things; read more about cerebral edema here. Dislocation syndrome is all the symptoms a person has and the changes that occur in his body during brain dislocation (described above). When examined by a neurologist, meningeal (meningeal) symptoms are revealed, as well as pathological reflexes, for example Babinski's symptom.
The essence of the disease
Brain dislocation is a displacement of some organ structures in relation to others. The fact is that the brain does not occupy the entire volume of the skull. Between this organ and the arachnoid membrane is the subarachnoid space.
In some places, its expansion is observed, which forms subarachnoid cisterns.
When pressure increases in a certain area of the brain and skull, displacement processes occur. This means that for various pathologies, the same structures take part in the development of dislocation syndromes. We can say that the clinical picture of brain dislocation is not related to the etiology of this process.
In this case, the disease can be accompanied by various symptoms - it all depends on the speed of development of the disease, its location and severity.
What is brain dislocation?
Dislocation of the brain is a displacement of its anatomical structures in the cranial cavity, as a result of any mechanical pressure on this structure or as a result of pronounced swelling of areas of the brain, which is able to displace and compress some part of it. The brain is the control center of our body due to the presence of nerve centers in it - clusters of neurons (nerve cells) that perform a specialized function.
For example: speech center, respiratory center, vascular center, etc. So, when the anatomical parts of the brain are displaced (dislocations), these same nerve centers can be compressed, as well as the nerve pathways along which nerve impulses pass from parts of the body to the brain and back. Simply put, the functions for which nerve centers and nerve pathways are responsible are lost.
I think there is no need to explain what happens, say, when the breathing center is compressed...? - That's right, his stop. The same fate can befall any nerve center that is under pressure. A similar situation occurs, for example, when the brain stem is dislocated into the foramen magnum and is compressed, and this happens with a large stroke, for example a hemispheric one.
Forms and types of syndrome
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish several types of dislocation syndromes, the following are distinguished:
- displacement of the cerebral hemispheres under the falciform process;
- temporotentorial displacement;
- displacement of the cerebellar tonsils in the area of the occipital bone;
- displacement of the medullary pons, which passes through the foramen of the tentorium;
- displacement of the gyri of the frontal zone in the direction of the chiasm cistern;
- filling the middle and side tanks of the bridge;
- cerebellar-tentorial displacement;
- displacement of the posterior region of the corpus callosum in the dorsal direction into the cistern of the same name;
- external dislocation.
Doctors distinguish several stages in the development of dislocation syndrome. These include the following:
- protrusion;
- wedging;
- infringement.
When a certain area of brain tissue protrudes into a large hole, which is located in the back of the head or in a fissure, venous congestion appears on it. The consequence of this process may be local swelling and minor hemorrhages.
Herniation does not stop the progression of symptoms of local edema. As a result of this process, the size of the pathological focus increases. Moreover, it takes on a hernial shape.
What is cerebral edema
The essence of the accepted definition of this condition is a nonspecific reaction of the whole organism in response to the influence of severe damaging factors. The latter are the reason:
- disorders of blood microcirculation in brain tissue;
- lack of oxygen transport to the brain, especially in combination with excessive accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood;
- disturbances of water-electrolyte, protein and energy metabolism with accumulation of lactic acid in nerve cells;
- violations of the acid-base state of the blood;
- changes in osmotic (electrolyte) and oncotic (protein) pressure of plasma.
Prognosis and prevention
To make a correct diagnosis, the results of the Echo EG and the patient’s complaints are compared. The decoding is carried out either by a neurologist or a laboratory specialist. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. When interpreting data, the doctor’s experience and precise adjustment of the equipment are important.
To decipher Echo EG data, the doctor looks at three indicators of the echo signal:
- Initial complex. The signal is reflected from the bone, soft tissue, meninges and lateral ventricle on the side where the scanning occurs.
- Ultimate complex. This is the reflection of an ultrasonic wave from the bones of the skull and soft tissues of the head of the opposite hemisphere.
- Between them, a stable M-echo signal is recorded, which is reflected from the middle parts of the brain: epiphysis, pineal gland, septum pellucidum, and others. M-echo is essential for diagnosis.
Features of the examination
Echo EG is a diagnostic method, the essence of which is the action of ultrasound. With its help, doctors monitor the state of brain structures.
The study makes it possible to study the displacement of the median structures and recognize the severity of the disorders. This helps the doctor prescribe appropriate therapy.
Diagnostics is non-invasive, with its help the accuracy of disease detection increases by 40-50%.
They use diagnostics as an independent study or in conjunction with other types in order to recognize the true state of the brain.
Synonyms for echoencephalography in medicine are the following terms:
- electroencephaloscopy;
- echoencephaloscopy (Echo ES);
- echoencephalogram. This concept, in fact, is not a synonym, but is a graphical representation of ultrasound signals.
A method similar to Echo EG, but examining the heart, is echocardiography or, for short, echogram.
Echo EG is a safe method, short-term and completely painless. Its essence lies in the fact that special equipment supplies ultra-frequency electric waves, which set in motion plates applied to a person’s head.
Ultrasound travels through the tissues of the brain and skull, and in those areas where disturbances are observed, the signals are echolocated. All waves are recorded by equipment.
What does the monitor show? A graphic picture on the basis of which experts make a conclusion.
The value of the method lies in the fact that doctors can use it to examine individual brain structures, determine median pulsations when measuring ICP, and study the state of the pericerebral space.
The procedure is carried out in two modes:
- Transmission. 2 sensors are placed on opposite sides of the head so that they converge in the same axis. One sensor sends a signal, the other receives it.
- Emission. Only 1 sensor is used, which is installed in a place that facilitates better results.
Preparation
No preparation is required for echoencephalography of the brain in children. This study is performed at any time of the day. There are no restrictions on diet or daily routine. If the baby is afraid of doctors and various medical procedures, then parents should reassure him and explain that doing an ultrasound does not hurt. Especially if it is a small child under 6 years old.
Then he will be more calm during the examination, which will make his work easier for the doctor. Ultrasound can be performed on the same day as other diagnostic procedures or therapeutic manipulations. In this case, it is better to start with echoencephalography. Because after unpleasant procedures, an ultrasound scan will be perceived negatively by the child. This will affect his behavior.
Treatment
Treatment is often carried out in intensive care units, neurosurgery or neuroreanimation, where they try by all means to relieve compression of brain structures and reduce its dislocation. Of course, one of the main directions is to reduce cerebral edema, which is why diuretics (diuretics) are often used. In addition to drugs in this group, they also use substances that support vital functions, which can also suffer during edema.
Often, one of the main and effective methods of treatment is surgery, or more precisely, neurosurgical operation, in which neurosurgeons seek to remove the source of the dislocation (intracerebral hematoma, tumor, edema, cyst, etc.). Although this method is the main one in treatment, it is not always applicable. Often, a neurosurgical operation is not allowed to be performed due to contraindications, which may carry greater risks than the benefits of the operation.
You can thank me for the article by subscribing to the channel about neurology and neurorehabilitation. Thank you!
Brain dislocation is a very serious condition that deserves intensive treatment, sometimes with the use of surgery. When the brain is dislocated, most often the person is in an unconscious state, that is, in a coma. Read about what it is here.
Causes of pathology
Decoding Echo ES is the competence of a neurologist, diagnostician or neurophysiologist. Normally, it is believed that the signal from the first sensor should be identical to the signal from the second. A signal that deviates by 1-2 mm from the original value can be called pathological (an error of up to 3 mm in children is acceptable).
If the initial signal changes, it means that within the cranium there is a dislocation of structures due to a volumetric process, which can be:
- tumor;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- cyst;
- purulent abscess;
- tuberculoma;
- accumulation of parasites.
- volumetric inflammation.
However, different diseases have specific signs on the monitor:
- Tumors and cysts. They greatly displace brain structures compared to other brain diseases, and therefore increase the difference between the original and received signal.
- Trauma to the skull and brain. They show a difference of within 3mm due to the formation of edema. Later, injuries can provoke the development of cysts, which increases the difference between signals from 3mm.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident. Intracerebral hemorrhage makes a big difference. The value of the lateral echo signal increases due to the presence of a focus of hemorrhage in the tissue. Ischemic stroke, cerebral infarction and softening of brain tissue produce subtle signal differences.
- Hydrocephalus. This pathology produces a signal difference of more than 7 mm.
Before you begin deciphering the results of echoencephalography, you should familiarize yourself with some theoretical issues. The fact is that echoencephalography includes three main signals called complexes. We are talking about:
- the initial signal complex, located closest to the sensor, generated by ultrasound as a result of reflection from the skin, muscles, skull bones and surface structures of the brain;
- the median complex (M-echo) signal, which occurs when ultrasound comes into contact with those brain structures that are located in the middle, in other words, between the hemispheres;
- the final signal complex, which is formed when ultrasound comes into contact with the hard membrane of the brain, bones of the skull, and soft tissues of the head.
The results of deciphering echoencephalography are:
- M-echo occupies a middle position between the two complexes. The distance to the M-signal on both the right and left is MD=MS.
- Expansion or splitting of the M-signal from the third ventricle is not allowed; otherwise, it is possible to speak of increased intracranial pressure.
- The M-echo pulsation limit (P) should reach 10-30%. An excess of up to 50-70% indicates the development of skin-hydrocephalic syndrome in the patient.
- Between the initial complex and the final M-echo sign there should be a uniform number of smaller signals, symmetrical in amplitude.
- The average sellar index should be 3.9-4.1 or more. If its value is reduced, there is a suspicion of increased intracranial pressure.
- the index of the third ventricle should be 22-24;
- medial wall index 4-5;
- an upward displacement of the M-echo by 5 mm or more indicates a hemorrhagic nature of the stroke, a downward displacement or not exceeding 2.5 mm indicates an ischemic stroke.
How does this happen
The GM does not occupy the entire volume of the skull. Between it and the bone walls there is a space in which there are three meninges that provide physical protection and nutrition. When a factor appears that increases pressure inside the skull, the sections shift to free places where the subarachnoid space is located.
As a result of dislocation, hernias are formed - areas in the head that protrude into the cracks and openings of the skull. The presence of a cerebral hernia in itself does not lead to serious disorders. The danger lies in a complication - pinched cerebral protrusion - a condition in which the displaced area of the brain stops receiving blood and dies.
There are two types of offsets:
- Lateral dislocation of the brain
- Axial dislocation (axial displacement).
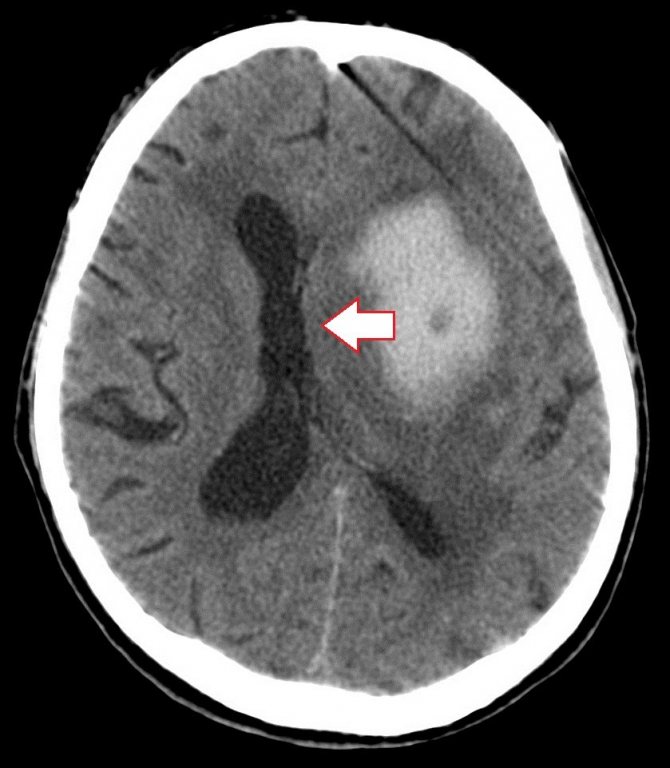
Brain dislocation is a displacement of brain structures in relation to each other. The main reason is an increase in pressure inside the skull, which is caused by:
- tumors;
- purulent abscesses;
- edematous phenomena;
- massive hemorrhages.
The tumor and other space-occupying formations mechanically push aside and change the localization of structures relative to the walls of the cranium.
Tumors of the posterior cranial fossa. Clinic. Diagnostics.
Types of intravascular embolization of AVM 1. Embolization in the flow (uncontrolled). 2. Stationary balloon occlusion of the feeding arteries of the spinal column. 3. A combination of temporary or permanent balloon occlusion with flow embolization. 4. Superselective embolization or thrombosis of AVM. (N-butylcyanoacrylate (Hystoacryl) fat-soluble contrast agent).
- OPEN TBI - there are injuries to soft tissues (skin, periosteum) or a fracture of the bones of the base of the skull, accompanied by leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose or ear. There is a high risk of infection.
- Penetrating – damage to the dura mater, therefore, communication of the subarachnoid space with the external environment.
- Non-penetrating.
- CLOSED TBI - these changes are absent or there are minor superficial injuries. Basic forms:
- shake;
- injury;
- compression of the brain;
- diffuse axonal damage - caused by rotation of the head with sharp acceleration and deceleration.
Based on severity, TBI is classified into mild, moderate and severe.
You'll like this:
The brain has different acoustic impedance and reflects to varying degrees, which is used for diagnostic purposes (see Ultrasound diagnostics).
E. makes it possible to detect volumetric lesions of the brain (hematomas, abscesses, etc.), hydrocephalus, intracerebral hypertension, and cerebral edema. The method has no contraindications and can be used in all cases where it is possible to ensure a tight fit of the ultrasonic sensor (probe) to the scalp.
Echoencephalography is carried out using ultrasound encephalographs. There are one-dimensional and two-dimensional (ultrasound) E. Special preparation of the patient is not required. E. is usually performed with the patient lying down, but it can also be performed with the patient sitting. Ultrasonic, the working surface of which is lubricated (to ensure acoustic contact) with petroleum jelly, is sequentially applied to different areas of the head, also pre-treated with petroleum jelly. Ultrasound signals converted into electrical impulses appear on the device screen in the form of a curve - an ultrasound encephalogram (echoencephalogram), which is photographed and analyzed. Optimal conditions for receiving an echo signal are created by installing the sensor on the side surface of the head at 4-5 cm
above the external auditory canal along the binauricular line passing through the parietal region.
On the echoencephalogram ( Fig.
) distinguish between the initial complex (IC), the final complex (CC), (M) and impulses of various non-median brain structures (ES). The initial complex is a section of the echoencephalogram, consisting of a generator impulse and echo signals from the soft tissues of the head, skull bones and superficial structures of the brain. The final complex is formed from echo signals from the inner surface of the skull bones, soft tissues of the head, interface boundaries -; the most constant echo is from the inner surface of the skull bones. The remaining elements of the CC appear only when ultrasound completely passes through the bones of the skull.
Between the two main complexes of the echoencephalogram, a large number of impulses appear, caused by the reflection of ultrasound from various structures of the brain. Some impulses are unstable, others are relatively stable, and some impulses appear only in the presence of a pathological process in the brain. The most constant echo signal is from the midline structures of the brain (third ventricle, septum pellucidum, etc.).
1. Small medical encyclopedia.
— M.: Medical encyclopedia. 1991-96 2. First aid. - M.: Great Russian Encyclopedia. 1994 3. Encyclopedic Dictionary of Medical Terms. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. — 1982-1984 Synonyms
:
See what “Echoencephalography” is in other dictionaries:
- Echoencephalography ... Spelling dictionary-reference book
Method of ultrasound diagnosis of brain diseases ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
Echoencephalography of the brain (ultrasound of the brain, echoencephaloscopy) is a method for studying brain structures based on the properties of an ultrasound wave. It is used in children and adults in emergency cases - to identify life-threatening brain pathologies: tumors, hemorrhages, injuries, abscesses
.
An analogue of EchoEG in infants who still have an open large fontanel is neurosonography.
Only in this case does it allow visualization of all brain structures, in contrast to echoencephalography: an EG echo only indirectly, using a specific graph, indicates that there is a pathological formation in the cranial cavity.
When should you do an encephalogram?
An ultrasound signal is obtained by deforming a special plate located in the probe, which is used to conduct the study. This plate is capable of not only sending a signal, but also simultaneously receiving it in reflected form.
Different tissues have different densities for the ultrasonic wave. The skin and subcutaneous tissue will have one reflected signal, a liquid formation (hematoma, cyst) will have another, normal brain tissue will have a third. This is how the image is formed on the device monitor.
Echoencephalography of the brain can be carried out both in one-dimensional mode (a synonym for this study is the M-method) and in two-dimensional mode (ultrasound scanning).
Using the first technique, a graph is obtained in which there are several peaks reflecting the internal structures of the cranial cavity; With a two-dimensional ultrasound of the brain, a flat image is displayed on the monitor.
For what diseases is echoencephalography performed?
- tumor in the cranial cavity
- brain abscess
- intracerebral and intracranial hemorrhage
- brain gumma
- brain tuberculomas
- edema-swelling of the brain substance
- ischemic stroke
- assessment of the degree of hydrocephalus
- inflammatory diseases of the brain
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of cranial cavity pathologies.
Two-dimensional echoencephalography is important for additional diagnosis of the following pathologies and symptoms
- concussion
- headache
- dizziness
- brain contusion
- symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
- encephalopathy
- signs of a pituitary tumor
- Parkinson's disease
- impaired blood supply due to damage to the vertebral artery
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Echoencephalography in children is performed in such cases
- for head injuries
- for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- assessment of the effectiveness of treatment of neurological diseases (ventricular plexus cysts, hydrocephalus, ventriculomegaly), when a minimum of symptoms remain, NSG cannot be performed due to the closure of the fontanelles, and MRI is inappropriate
- for sleep disturbances
- muscle hypertonicity
- delayed physical development
- assessment of the degree of hydrocephalus
- if there is enuresis, encopresis, tics, stuttering, or other neurotic reactions.
How to prepare for echoencephalography (echoencephaloscopy)
Echoencephalography of the brain in children and adults is a type of study that does not require any preparation.
There is no need to follow a diet, fast for any period of time, or specifically drink liquid.
Echoencephalography (EchoEG) can be done at any age, as well as during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Only if there are open wounds on the head in those areas where you need to apply a sensor, it is better to conduct another type of study of the brain matter - computed tomography or MRI.
If encephalography of the brain is performed on a small child, parents will need help to hold the baby’s head in one position for some time.
Although the method is completely painless, the researcher needs to change the scanning plane several times, and for this the head should not be in motion. Sedation or anesthesia is not required for echoEG.
How the research is carried out
Echoencephaloscopy of the brain is usually performed in a supine position, but can also be performed while sitting.
This research method is often used as an emergency diagnosis, because the devices are small in size and easy to carry. One-dimensional echoencephaloscopy can be performed in a specialist’s office, in an ambulance, at home, and on the street, if the device is equipped with a battery.