Stroke is a serious pathology accompanied by a sudden acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. Doctors know several types of this disease. The most common of them is hemorrhagic stroke. It is most often encountered by older people as a result of cerebral hemorrhage. An important question arises: how often to give IVs after a stroke.
Types and treatment of stroke
All apoplexy strokes are divided into two types:
- Hemorrhagic stroke. Formed due to a hemorrhage in the brain. The causes are traumatic brain injury, hypertensive crisis, aortic aneurysm. In any of the cases, the vessel ruptures and further blood volume enters either the brain tissue or the subarachnoid space between the two membranes - the arachnoid and the medulla.
- Ischemic stroke. Occurs due to blockage of a vessel by a blood clot or its sudden spasm.
Important:
Regardless of the type of stroke, the patient's blood supply to the brain tissue is seriously affected. As a result, within 15–20 minutes the death of brain cells—neurons—begins.
To stabilize the condition of a patient admitted to the hospital, depending on the severity of the manifestations of neurological disorders, a man or woman is treated in the following ways:
- drug therapy;
- surgical intervention;
- rehabilitation measures.
All drugs for drug therapy are selected individually after a thorough diagnosis of the patient’s condition. Dosages are also prescribed by the doctor strictly individually with mandatory subsequent monitoring of hemodynamics.
How to quickly identify symptoms of ischemic stroke in women and men?
In English-speaking countries, doctors came up with a convenient and simple abbreviation FAST. If you read it together, you get a word that is translated into Russian as “quickly.” Each letter represents a specific symptom:
- Face drooping - lowering the face. Ask the person to smile. The corner of the mouth on the affected side will remain drooping.
- Arm weakness – weakness in the hand. Ask them to raise both hands. They will rise to noticeably different heights, or one will remain lowered.
- Speech difficulty - difficulty speaking. Say a phrase and ask the person to repeat it. He will have difficulties and his speech will be slurred.
- Time to call 911 – time to call an ambulance. Have you noticed any of these signs of ischemic stroke in a woman or man? Don't waste time! Even if you are not completely sure, it is better to be safe!
Drug resuscitation therapy
In intensive care conditions, the patient is prescribed the following drugs to restore basic vital functions:
- Reduction and prevention of cerebral edema, which forms due to malnutrition and when its tissues are compressed by a hematoma (during a hemorrhagic attack). As a rule, the patient is administered intravenously Dexamethasone, Reogluman or Mannitol. The last two are diuretics. Dexamethasone can be used only for ischemic stroke and if the patient has no history of diabetes mellitus or hypertension.
- Normalization of pressure. It is carried out with the aim of increasing systolic pressure by about 10, and bringing diastolic pressure to 120 mmHg. Art. Urapidil and Enalapril, Esmolol or Captopril work effectively here.
- Normalization of heart rate. Here the fight is against bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, which are the consequences of a stroke. The doctor may prescribe drugs such as Atropine, Verapamil, Cordarone or Propranolol. The latter drug is used less frequently because it can block normal brain function.
- Preventing blood clots in ischemic stroke. Anticoagulant and thrombolytic drugs are used. These drugs are designed to thin the blood. The simplest of these drugs are Aspirin tablets. If the patient is unconscious or swallowing is impaired, Heparin is administered intravenously. Dicumarin or Warfarin are also used. During the acute period, Contrical or Gordox can be prescribed.
- Vasodilation to improve blood flow in ischemic stroke. Vasodilator medications include Parvenin or Isoxsuprin. However, the prescription of such drugs is not always justified, since in some cases they worsen hemodynamics in the area of the blocked cerebral vessel.
- Normalization of brain function against the background of oxygen starvation. Nootropics and neuroprotectors are prescribed. Such drugs for cerebral stroke significantly improve cerebral circulation and prevent the death of neurons. Mainly used for neuroprotection are Glycine (tablets), Cerebrolysin, Magnesium or Cavinton. At the same time, “Glycine” additionally has a calming effect on the patient’s body.
- Neutralization of seizures with anticonvulsants. To relieve convulsions and prevent epileptic seizures, Diazepam is often used.

In addition, in case of vomiting, the patient is given antiemetic drugs (Metoclopramide). When the temperature rises, antipyretics are used. They are often administered by intramuscular injection.
Important:
To prevent the patient from developing a stress ulcer, he is prescribed Omeprazole.
Prices for treatment of ischemic cerebral stroke
One of the main directions in the treatment of the consequences of stroke is drug therapy. It includes 3 main vectors:
- preventive methods of treating stroke, the main function of which is to prevent another stroke, activation of vascular defects in the brain
- pathogenetic methods for treating the consequences of stroke, the main function of which is to reduce the pathogenic processes occurring in the brain after a stroke and with vascular defects of the brain leading to stroke
- syndromological treatment methods, the main function of which is restoration of speech, emotional state, muscle tone, pain relief
It must be remembered that any medicine that the patient takes should only be prescribed by a doctor. And it doesn’t matter that your friend was helped by this or that medicine, because what is suitable and helps one person may be categorically contraindicated for another.
Medicines used after a stroke are prescribed depending on the stage of the disease.
- At the very first stage of the development of the disease, when the first signs of a developing stroke appear, medications are prescribed depending on exactly what signs are observed. For example, for hypertension, medications that lower blood pressure are prescribed. In order to keep blood circulation in the brain within normal limits, doctors often prescribe nootropic drugs. The period of their administration depends on the severity of the patient’s condition. If the first signs of a stroke appear in a person as a result of stress or overwork, then sedatives are indicated.
- During the critical period of disease development (the first 2-3 hours), it is necessary to prescribe anti-stroke medications that will help stabilize normal blood circulation in the brain. Drugs to reduce blood clotting are very effective, as they significantly help to avoid paralysis, if, of course, they are used on time. Drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain will help prevent the recurrence of this disease. Analgesics should be used to reduce pain.
- If the patient’s condition has already stabilized, treatment of the patient continues at home. In most cases, medications used after a stroke are prescribed by a doctor for life. If a stroke victim still has a fear of another attack, the doctor prescribes sedatives, sleep aids, and sometimes mild antidepressants. For quite a long time, taking medications that thin the blood is indicated, since the likelihood of blood clots is quite high. If the patient continues to have seizures, medications are prescribed to prevent them. If necessary, the patient takes analgesics if the pain is quite severe.
Muscle relaxants
Muscle relaxants are intended to make motor rehabilitation more successful. Typically, increased muscle tone in a patient does not appear immediately, but increases by the third month from the moment of the stroke. Muscle hypertonicity is one of the most serious consequences of impaired cerebral circulation.
Unfortunately, having achieved a positive effect in reducing muscle hypertonicity, the patient, having stopped taking drugs from the group of muscle relaxants, may feel it again. This should not frighten the patient and his relatives, since taking these drugs helps prepare for rehabilitation measures to restore motor activity of the limbs. Over time, muscle tone decreases, and the need to take muscle relaxants is eliminated.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are necessary for those people who are depressed in the post-stroke period. As statistics show, this number is more than 80%. And it is quite natural that a person who is unable to move independently or do basic things falls into depression. Drugs in this group should be taken by patients strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Not all stroke survivors need antidepressants. Some patients maintain a stable emotional state, are quite cheerful and filled with enthusiasm.
Anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants are a group of drugs designed to reduce the severity of seizure symptoms. When taking anticonvulsants, you need to be very careful, as they cause increased drowsiness, impair memory, cause weakness in the body, and frequent dizziness. Most often, doctors prescribe carbamazepine, a little less often - phenytoin.
Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are drugs that prevent blood clots. Medicines from the group of antiagents are prescribed to patients whose blood has changed its consistency, namely, its viscosity has increased. With increased blood viscosity, there is a high probability of blood clots, which is why the blood needs to be thinned. Often doctors prescribe Aspirin, Thrombo ACC, Ticlopidine.
Anticoagulant drugs should be taken by patients who have a predisposition to excessive blood clotting. This is dangerous because blood circulation in the vessels is disrupted, and this can lead to the formation of blood clots.
It is very important to know and remember that when taking drugs from the group of anticonvulsants and antiplatelet agents, it is necessary to regularly do a biochemical blood test, since taking them is fraught with bleeding. Symptoms of complications of taking these drugs are dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and the causeless occurrence of hematomas in different places. If such symptoms appear, you must urgently call an ambulance.
Neurometabolic cerebroprotectors are aimed at activating metabolic processes in the tissues of the nervous system. Their action helps eliminate such body disorders as ischemia, anoxia, and intoxication. Drugs in this group stimulate the utilization of glucose and activate the metabolic processes of nucleic acids. The usual name is nootropics and neuroprotectors.
There are a huge number of medications prescribed to patients to treat the consequences of a stroke.
Which drugs are suitable for a particular person should only be determined by a doctor.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate if you value your life and health. Let's look at the most effective medications after a stroke.
- Actovegin is prescribed to the patient to improve cellular metabolism. The drug stimulates intracellular glucose utilization and ATP metabolism. The energy properties of cells increase. Actovegin activates blood supply.
- Cerebrolysin is a drug that activates neurotrophic stimulation of nerve cells of the central and peripheral nervous system. Cerebrolysin helps activate protein synthesis in cells. Protects neurons from damage due to insufficient oxygen saturation. Improves memory.
- Piracetam well accelerates metabolism in the cerebral cortex and well increases brain interactive activity, improves memory.
- Pantogam helps control the amount of oxygen that reaches the brain. This drug protects the brain from intoxication, has a mild sedative effect, and also has a moderate stimulating effect. Prevents seizures, reduces motor activity. Stimulates performance. Has an analgesic effect.
- Vinpocentine is a drug that activates blood circulation in the brain. It promotes vasodilation, oxygen saturation of tissues, thins the blood, and has neuroprotective properties.
A number of studies show that vitamins are very effective in restoring brain function after a stroke. But in no case should you overdo it with the dosage.
The most effective vitamins after a stroke:
- Vitamin A normalizes the active growth of cells and tissues
- vitamin B and B1 stabilizes blood pressure, normalizes neuron function and improves cerebral circulation
- Vitamin C promotes the regeneration of blood vessels, which improves blood circulation
- Vitamin D is necessary to maintain a safe blood consistency. This vitamin has a positive effect on the nervous system and blood circulation.
- Vitamin E prevents the formation of free radicals. The doctor must draw up a regimen for taking vitamins with clearly established proportions. Prescribing vitamins on your own is dangerous.
The main advantage of dietary supplements is that they are a natural product. At different stages of therapy, doctors recommend taking different types of dietary supplements. For example, in the first 1-2 months after an illness, one type is prescribed, and during the entire subsequent year, completely different ones are prescribed. In the first few months of the post-hospital period, the main task for the patient is to restore the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and immune system. Dietary supplements do an excellent job of this.
Both medications and vitamins and dietary supplements must be taken under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
The effectiveness of rehabilitation measures after a stroke is higher, the sooner they begin. Rehabilitation is necessary for people who have suffered a stroke in order to prevent recurrence of the disease, stabilize the patient’s psychological state, and restore speech, vision, and motor function.
Rehabilitation is carried out using the following methods: therapy with medications, physical therapy, psychotherapeutic measures, therapeutic massage, following a special diet, the use of herbal infusions and essential oils, classes with a speech therapist.
To prevent or treat ischemic stroke, standard medications are prescribed, but they must be taken only with a doctor’s prescription, since each of the components is aimed at a specific area of the brain and affects certain parts of the body. There are a large number of such tablets and injections, but the latest drugs are constantly being released that have the maximum therapeutic effect without harm to the body, since they are based on natural ingredients, herbs and oils. List of drugs that are distinguished by their reliability and quality:
- Cerebrolysin and glycine
- ancrod-preparations based on snake venom
- encephabol
- actovegin
- oxygen cocktails
First emergency treatment for an unknown diagnosis
Emergency care when a patient is admitted to hospital is very important. Even if the type of apoplexy has not yet been identified. In any case, to prevent serious complications, the patient is prescribed the following primary treatment:
- Magnesia droppers. The drug has a mild sedative effect. In addition, it normalizes blood pressure and relieves seizures. Often, for high blood pressure, magnesia is mixed with Diazepam and also administered drop by drop. In addition to magnesium, at low blood pressure, intravenous administration of Dibazol, Clonidine or simply saline is used.
- For focal symptoms, the patient is administered Nootropil (aka Piracetam).
Drug therapy depending on the type of stroke
In case of a hemorrhagic stroke, the doctor prescribes medications that constrict the blood vessels and stop the bleeding. Here, in the first stages, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- Aminocaproic acid.
- Vitamin K
- Calcium chloride.
All of them intensively inhibit the bleeding process.
Important:
When a large hematoma forms, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention.
In the treatment of ischemic apoplexy, a number of drugs are prescribed:
- Dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow. "Curantil" or "Aspirin", which reduce vascular resistance and thin the blood.
- Improving blood flow and preventing the formation of blood clots. Trental is more often used here.
- Ensuring normal heart function against the background of oxygen starvation. This is Nitroglycerin.
Decreased blood clotting
Most often, a stroke occurs due to increased blood clotting. It also impairs brain function. In this case, the concentration of the liquid medium is less than platelets. Doctors must bring the platelet count back to normal within the first two hours after the patient is admitted to the hospital. For this, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Antiplatelet agents, for example, Tiklid. This drug improves blood flow and eliminates stagnation. But it also improves blood circulation in the brain.
- Warfarin is prescribed as an anticoagulant. It prevents platelets from sticking together. This medicine is prescribed during the period of intensive treatment of a stroke victim. People use this medication not as a permanent medication for therapy, but as an emergency aid in the form of injections.
- The patient is prescribed Streptodecas. This drug is used only after surgery to prevent blood clots and restore blood flow.
- In case of high blood pressure, the patient is prescribed Clonidil.
- If the patient is hospitalized with low blood pressure, he is prescribed Gutron. Prednisol is used as an analogue of this drug.
Treatment of the patient after discharge home
Home treatment during the patient’s rehabilitation period also involves taking medications prescribed by the attending physician. Here, not only symptomatic therapy is carried out to restore lost functions, but also preventive therapy. That is, it is important to prevent a recurrence of the blow. So, depending on the type of complications, the following medications are prescribed:
- Muscle spasm in paralyzed limbs. To remove it and restore the movement of paralyzed limbs in the future, it is recommended to use medications that relax muscles after a stroke according to a doctor’s prescription. The most effective are Sirdalud, Mydocalm or Baclofen. The use of muscle relaxants shows positive dynamics in young and elderly patients, subject to systematic massage and gymnastics. Because to restore and improve blood flow in paralyzed limbs, you need to relax their muscles and tissues.
- Depression and apathy. Here the patient is prescribed antidepressants as prescribed by a psychotherapist. Modern drugs such as Cipramil, Fluoxetine, Melipramin, etc. are often prescribed, which do not cause adverse reactions.
- Speech disorders and other cognitive disorders. Here, during the recovery period after hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, Ceraxon, Gliatilin, Cerebrolysin, etc. can be prescribed.
- Increased blood pressure. In this case, diuretics are more often prescribed, which will reduce blood pressure by removing fluid from the body. But it is worth noting that the medications are quite potent and put a strain not only on the heart, but also provoke an exacerbation of gout, so they cannot be prescribed for kidney pathologies.
- Pain. If the patient often has a headache, then neurological pain can be relieved with the help of Amitriptyline.
- Improving metabolic processes. To speed up metabolism in brain tissue, Actovegin in ampoules or mildronate tablets (Mildronat) are prescribed. According to the instructions, the medicine is used in the form of injections or intravenous injections through a dropper. The drug can also be injected intra-arterially.
- Decreased memory and impaired brain function. Taking Nimotop in capsules or intravenously is indicated. This neurorehabilitation helps improve the functioning of brain neurons by improving microcirculation in its tissues. A drug similar in action is Mexidol.
- Meldonium is also used as part of complex therapy. Can be used in the form of capsules, syrup or injection. However, it is worth remembering that the drug is contraindicated in case of increased intracranial pressure and under the age of 18 years.
It is important to understand that using drug therapy alone will not work a miracle. During the recovery period after apoplexy, it is very important to work comprehensively, including systematic massages and gymnastics, physiotherapeutic procedures and memory/speech training sessions in the treatment. In addition, the determination of the patient himself also plays an important role.
Important:
All information in the material is for informational purposes only and cannot be a guide to action. For all prescriptions, you must contact a specialist who monitors the patient’s condition.

Stroke refers to severe pathologies in which a sudden acute disturbance of cerebral circulation occurs.
In clinical practice, there are several types of stroke, among which intracerebral or hemorrhagic is considered the most common, as it is diagnosed in 70% of all patients.
Stroke most often occurs in mature and elderly people. According to statistics, cerebral hemorrhage occurs mainly in people aged 40 to 60 years.
After stopping the attack, patients experience multiple disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system: complete or partial paralysis, speech and vision impairment.
Essential vitamins
For a speedy recovery, the patient needs vitamins. Most often, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- The drug Cerebrolysin can be taken without fear for the patient’s condition. This drug allows you to restore blood circulation to the brain and reduce the likelihood of relapse. People with chronic hypertension are advised to keep this medication with them.
- Mannitol is a strong diuretic that reduces swelling of the affected areas.
- Patients who have suffered a cerebrovascular accident know the drug Glycine very well. It improves memory and brain function. Thanks to him, rehabilitation is accelerated.
At the first stage of the disease, vitamin therapy is supplemented with homeopathy, which gives a positive result and does not affect other remedies.
The patient is also prescribed antihypertensive medications containing vitamins. Thanks to them, not only blood pressure is normalized, but also the number of relapses is reduced. Such drugs must be used for a long time. This is the best stroke prevention.
In addition to medications, the patient is recommended to take vitamins in their natural form. Foods containing vitamin A include kidneys and grapes. It is recommended to include foods with a high concentration of vitamin B in the diet, for example, fish, walnuts, carrots.
How effective is drug therapy against stroke?
After a stroke, the patient’s condition leaves much to be desired, since with any type of hemorrhage he experiences an extensive complex of pathological changes:
- loss of muscle tone in the limbs or complete paralysis;
- impaired sensitivity of certain parts of the body;
- changes in sensitivity to cold, heat and other irritants;
- lack of coordination in space;
- memory impairment;
- impaired fine motor skills of the hands or its complete absence;
- speech apparatus disorder.
All of these disorders arise as a result of a critical lack of oxygen and nutrients in certain areas of the cerebral cortex. Cerebral circulation can only be restored by taking special medications. Medicines will also help to eliminate symptoms and associated disorders: headaches, dizziness, memory loss, muscle pain, etc.
The depressive state into which more than 90% of all patients fall is also of no small importance. Due to the inability to control their body, physical helplessness, and the inability to express themselves, they begin to experience shame, anger, and sometimes become aggressive or withdrawn. This situation can also be corrected only with the help of medications.
A stroke can occur at the most unexpected moment and the reaction of others determines whether a person will survive or not. What to do in case of a stroke - first aid to a patient during an attack.
We will tell you about the consequences after a stroke on the right side of the brain here.
In a hemorrhagic stroke, an artery in the brain ruptures. Follow the link https://neuro-logia.ru/zabolevaniya/insult/gemorragicheskij/lechenie.html for information on how conservative therapy is carried out, as well as surgical intervention for this pathology.
Inhibitors and diuretics
After a mini-stroke, the patient is prescribed inhibitors. These medications help reduce the activity of angiotensin-converting enzymes. As a result, pressure decreases. The most common drugs in this group are listed below:
- Enalapril and its analogue Enap.
- Quinapril, also known as Accupro.
- Ramipril, otherwise called Tritace.
- Moexipril.
Captopril is also prescribed as an inhibitor. Among its disadvantages, it is worth highlighting the ability to provoke a dry cough and a low level of activity. In addition, it must be used frequently, since it has a short period of action.
After a stroke, the functioning of the joints and knees deteriorates. In this case, the patient is prescribed a diuretic, for example, Arifon or Indapamide.
These drugs can reduce swelling of the vascular walls and reduce blood pressure. In addition, they have a vasodilating effect.
These medications worsen gout, so they are not recommended for use in patients with kidney failure.
Men who use these good drugs may experience impotence, which goes away after stopping the drugs.
What medications are prescribed for stroke?
Elimination of pathological changes requires taking at least 3 types of medications belonging to different groups.
The following groups of drugs are most in demand in rehabilitation therapy after a stroke:
- muscle relaxants - to reduce reactive tension in the muscles of the arms and legs;
- antidepressants - to overcome the post-hospital crisis;
- anticonvulsants - to eliminate seizures, if any;
- anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents - to prevent re-formation of blood clots;
- antihypertensive drugs - to lower blood pressure if the cause of the stroke was hypertension;
- neurometabolic cerebroprotectors - to restore brain activity, processes and its higher functions.
Prescription of medications depending on the clinical picture
The list of medications prescribed to restore body functions in patients depends on the existing clinical picture. Thus, with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, patients experience hemiplegia and/or hemiparesis, that is, complete or partial loss of motor ability and sensitivity of certain areas of the body, as well as difficulties with remembering information and speech.
Since the nature of such pathologies is a violation of cerebral circulation, experts prescribe cerebroprotectors and nootropic drugs.
If paralysis is accompanied by painful tension in the muscles of the limbs, patients are advised to take muscle relaxants.
And if the condition is accompanied by the appearance of convulsive muscle contractions, the doctor may decide to use anticonvulsants.
In case of psychological instability, expressed in mood swings, emotional lability, depression, playfulness and reluctance to make contact, antidepressants, sedatives or, on the contrary, stimulants are prescribed simultaneously with nootropic drugs and cerebroprotectors.
If there are underlying and/or concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, arterial hypertension, attention must be paid to preventing their exacerbations. This will help avoid new difficulties on the road to recovery.
Regardless of the clinical picture and type of stroke, patients are advised to administer anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs. Their use is especially important at the initial stage of recovery, that is, already on the first day after an attack. This will avoid the formation of large blood clots and will help restore cerebral circulation.
What medications are effective for stroke?
What medications should I take after a stroke? The list of drugs that are indicated after a stroke is quite extensive. It includes the following medicines:
- Actovegin is a drug for intravenous administration that significantly improves blood circulation in the brain and helps restore its functions.
- Cerebrolysin is a drug with properties similar to the previous drug for intravenous administration.
- Piracetam is an old cerebroprotective agent that activates memory and the transmission of nerve impulses, promotes the restoration of brain cells.
- Pantogam is a nootropic drug in tablet form that activates metabolic processes in the brain.
- Vinpocetine is a tablet with a protective and restorative effect that helps restore metabolic processes in brain cells and improve impulse transmission.
Also during the recovery period, drugs with lecithin and succinic acid are used. They also improve cerebral blood flow and help stabilize the patient's condition.
Doctors' recommendations
According to European recommendations, when prescribing medications, doctors must take into account the characteristics of the patient’s body. This is necessary for the treatment to be effective. The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- Ceraxon, which contains Citicoline. The principle of action of this medicine is to improve metabolic processes in cells. Thanks to the drug, cerebral edema is relieved, and the intensity of cognitive abnormalities and brain dysfunction is reduced. This medicine can be taken both during an exacerbation and during the recovery stage.
- For ischemia of the brainstem, the patient is prescribed a Gliatilin tablet. Drug therapy with this drug is recommended for patients in a coma. The principle of action of this remedy is to increase blood flow. The duration of treatment is three months. If necessary, you can repeat the course.
- If the patient has diabetes, he is prescribed Actogevin. This remedy is used for prevention and recovery. This drug can be combined with any medications. It stimulates brain function. Actogevin is the optimal measure for patients with any form of pathology.
- Mexidol is an injection drug. Its important advantage is increasing the resistance of tissues to hypoxia. This drug is combined with Mexidol, which creates conditions for rapid rehabilitation of the patient. The medicine can be combined with Cortexin, aimed at reducing the effects of ischemia.
Today there are injections for stroke that completely eliminate the consequences of impaired blood circulation in the brain. It must be administered within two hours after an exacerbation. Due to enzymes, the likelihood of complications is reduced. Injections in the abdomen should only be given by medical professionals.
What kind of IVs are used for a stroke?
Droppers can also be used to restore brain functions according to individual indications. Along with the previously mentioned Cerebrolysin and Actovegin, Pentoxifylline, a solution of Piracetam and Vinpocetine are used for this purpose.
In addition, in recent years, pharmacological companies have been actively developing new organic products containing amino acids, which are intended for emergency resolution of blood clots and restoration of blood circulation.
They should be used directly during an attack - within several hours after the onset of the attack.
Thanks to it, fluid is redistributed in the body and cerebral edema is eliminated. Also, saline solution allows you to increase the degree of absorption of medications.
What dietary supplements can you take after a stroke?
The use of dietary supplements after a stroke is possible only after the end of intensive drug therapy. Such products include plants that have noorthopic properties and promote enhanced restoration of blood circulation in the brain.
Unfortunately, all the remedies mentioned above cannot guarantee complete recovery after a stroke.
To increase the chance of a favorable prognosis, it is recommended to follow all the instructions of your doctor.
In old age, the risk of stroke increases, so you need to know how to prevent a cerebral stroke and what prevention consists of.
The degrees of cerebral ischemia and the main methods of treatment are described in this article.
What is the prognosis for stroke in old age?

Experts warn that stroke is especially dangerous in old age, since in adulthood it is almost impossible to prevent cell damage and the occurrence of brain dysfunction. According to statistics, thousands of citizens die from this disease every year, and those who manage to survive most often become disabled. That is why every person should understand why a stroke occurs, how it manifests itself, and what measures need to be taken to avoid trouble. Acute cerebrovascular accident is a dangerous pathology that leads to the most tragic consequences. Experts warn that stroke is especially dangerous in old age, since in adulthood it is almost impossible to prevent cell damage and the occurrence of brain dysfunction. According to statistics, thousands of citizens die from this disease every year, and those who manage to survive most often become disabled. That is why every person should understand why a stroke occurs, how it manifests itself, and what measures need to be taken to avoid trouble.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
The attack occurs more often at rest or during sleep. Ischemic stroke is characterized by a gradual development, but despite this, periods of rapid increase in unpleasant symptoms can be observed.
At the onset of an attack, the following symptoms occur:
- Paralysis or paresis of limbs on only one side of the body.
- Partial loss of performance of facial muscles. Obvious symptoms of a brain stroke are drooping of one corner of the mouth, eyelids, and muscle distortion. The nasolabial fold is also smoothed. When trying to smile, one part of the mouth remains at rest. In some cases, eyebrows are raised.
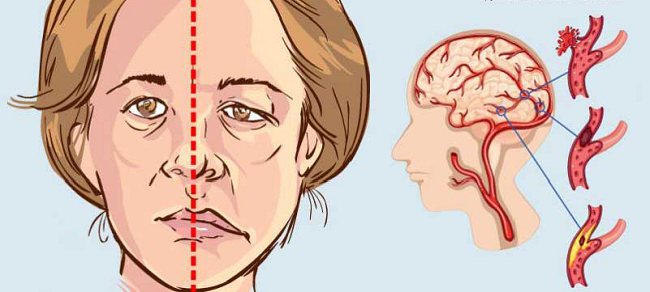
- Decreased sensitivity of the limbs on the affected side.
- The appearance of light flashes before the eyes, hallucinations, loss of visual fields.
- Lack of intelligible speech.
- Apraxia. Characterized by the inability of a person to perform purposeful actions.
With ischemic cerebral stroke in elderly people, psychoemotional disorders and difficulty in determining the relative position of objects and the distance between them are also observed.
The clinical picture largely depends on which part of the brain is affected. When a cholesterol plaque blocks the lumen of an artery in the spinal column, blood circulation in the stem part of the organ is disrupted. As a result, the following symptoms arise:
- Unsteady gait, unsteadiness.
- Diplopia, characterized by double vision.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of coordination.
- Loss of visual fields.
- Strabismus.
- Difficulty swallowing and chewing food.
- Decreased hearing quality.
There is also weakness in the limbs on one side of the body. General cerebral symptoms in this case are secondary. They occur as a result of swelling of the brain, which is accompanied by severe headaches, nausea, vomiting and a feeling of daze. This condition leads to cerebral coma.
With ischemic cerebral stroke in elderly people, psychoemotional disorders and difficulty in determining the relative position of objects and the distance between them are also observed.
Possible complications
It is impossible to predict exactly what the impact of a stroke will be on the human body. Most often, after a cerebral hemorrhage, patients encounter the following abnormalities:
- complications of the musculoskeletal system, the victim loses the ability to walk;
- local or complete paralysis;
- anemia of the limbs;
- lack of vision and development of strabismus;
- speech dysfunction;
- violation of the swallowing reflex;
- severe hearing impairment up to the appearance of deafness;
- malfunction of the intestines and genitourinary system.

It is impossible to say exactly how the body will behave after a cerebral hemorrhage, since much depends not only on the treatment method, but also on the age of the patient, and on the individual characteristics of the body. Experts warn that an unfavorable prognosis can be assumed based on the following signs:
Causes of stroke
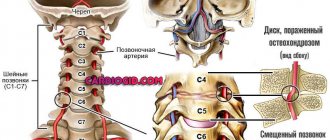
The most common cause of stroke is thrombosis (blockage with a blood clot) of atherosclerotic changes in the cerebral, carotid or vertebral arteries. Cerebral vascular thrombosis is the cause of stroke in 75% of cases.
In 20% of cases, cerebral hemorrhages occur. They are caused by a rupture of one of the arteries of the brain or an aneurysm of the arteries of the circle of Willis. An aneurysm can be congenital, or may be associated with a weakening of the vascular wall, with a rupture of an atherosclerotic artery without aneurysmal changes, or occurs with brain angiomas or other intracranial tumors.
About 5% of strokes were caused by emboli (broken pieces of blood clots) clogging the blood vessels of the brain. Such blood clots formed in the left side of the heart. Usually, cardiac arrhythmia was observed. The described phenomena occurred after heart surgery, with rheumatic or other lesions of the heart valves.
Another cause of stroke is considered to be “spasm” of the arteries of the brain, but it is impossible to register these changes. Spasm of the arteries can hypothetically explain rapidly passing disturbances of cerebral circulation.
After taking 3-4 drugs in a row (with a short break), take a break for 1-2 months. In the future, it is possible to repeat Venomax, Midivirin, Neurostim.
Features of treatment in the elderly group
Treatment of stroke in old age is very different from the tactics that are offered to people under 60-65 years of age. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the body, its susceptibility to side effects - coma occurs more often, and consequences arise after taking potent medications.

To increase the chances of a favorable outcome, it is necessary to treat stroke in older people in a hospital. If the patient undergoes a full course of treatment and subsequent rehabilitation, his life will be much easier. Even after a coma or in a state of unconscious sleep, a person will receive the necessary help , and subsequently will be able to recover faster from the blow suffered.
The main goal of therapy is to restore blood circulation, the functioning of the cardiovascular system, as well as protect brain cells from total destruction.
The prescription of drugs and methods of physiotherapy occurs after the patient has been removed from a serious condition.
If signs of a stroke occur in an elderly person, ammonia should not be used to recover from fainting . Doctors also prohibit holding limbs if convulsions occur. No drugs that can get stuck when swallowed should be given to the patient.