Neurogenic bladder is a fairly common pathology in children over 2 years of age. The disease is characterized by disturbances in the functions of filling and emptying the bladder and is associated mainly with problems of the central nervous system. According to statistics, the disease is registered in 10 out of 100 babies and necessarily requires a competent approach to treatment. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, the pathology will lead to serious diseases of the genitourinary organs and will also negatively affect the mental development of the child.
Mechanisms of pathology
The neurogenic bladder in a child consists of neurological disorders of varying intensity.
They cause insufficient coordination of the activity of the external sphincter. The disease can develop with the following pathologies:
- diseases of the central nervous system of an organic nature;
- birth defects and injuries;
- degenerative processes in the spine, brain and spinal cord;
- trauma during childbirth;
- spina bifida;
- agenesis and dysgenesis of the coccyx region;
- functional weakness of the micturition reflex;
- disruption of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, as a result of which neurohumoral regulation is inhibited;
- delayed maturation of voiding centers;
- changes in the sensitivity and extensibility of the bladder muscles.
Which doctor should I contact?
If your child urinates more frequently, you should contact your pediatrician. After examination and initial diagnosis, the doctor will be able to make or suggest a diagnosis.
In some cases, it is necessary to consult a urologist (for bladder damage), a nephrologist (for kidney disease), an endocrinologist (for diabetes), a neurologist (for pathology of the spinal cord or brain), and a psychiatrist (for neurotic disorders).
If a girl is pregnant, she is observed by an obstetrician-gynecologist; in case of tumor processes in the pelvis, the child is treated by an oncologist.
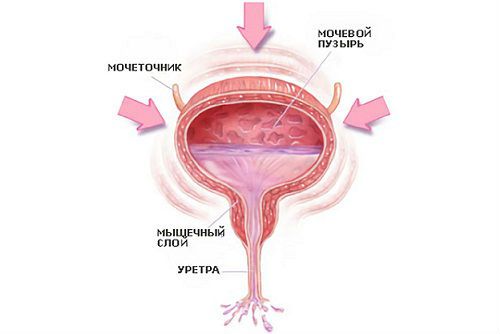
How does the bladder work?
The bladder is an important organ in the system for removing waste fluid from the body. The main burden in the formation of urine is taken by the kidneys: they cleanse the blood of waste products that accumulate in the pelvis and then enter the bladder through the ureter.
The accumulation phase begins. The walls of the organ gradually smooth out and tighten, and the pressure inside increases. Nerve nodes located in the bladder itself or neighboring tissues send a signal about this to the brain, from where a “response” quickly comes, and the person experiences the urge to urinate (elimination phase).
They can be contained for some time, but the amount of waste fluid will increase and cause even more discomfort. 700 ml is the maximum permissible volume of urine; once it is reached, there is a high probability of involuntary urination.
Classification of violations
Depending on the level of the nervous system at which the failure occurred, differences in the functioning of various muscles of the bladder can cause 2 types of pathology of the organ:
- Hyperreflex bladder is a pathology characterized by a sudden urge to urinate. A person feels the need to immediately empty the bladder of fluid long before its optimal amount has accumulated. The disorder is accompanied by urinary incontinence, as well as frequent urges during the day and night. The main cause of a hyper-reflex bladder is the spastic state of its muscles, which the patient is not able to control - the person sometimes does not have time to run to the toilet.
- A hyporeflex bladder is the opposite situation, in which the detrusor does not work even if the volume of accumulated fluid significantly exceeds.
An overactive bladder does not fill completely
Bladder dysfunction in children can have a mild form (enuresis, incontinence due to stress, frequent urination during the day), moderate (“lazy” or unstable bladder) and severe, areflex, in which the walls of the organ do not contract on their own, and are also observed involuntary urination.
Neurogenic bladder occurs in every tenth child aged 3 to 5 years. The overwhelming majority of young patients are girls, since due to the higher level of estrogen in the body, the sensitivity of the detrusor receptors increases. Most often, the pathology manifests itself as urinary incontinence. As they grow older, this problem disappears in many children, and by adolescence it remains in only a small percentage.
Numerous studies have revealed the role of hereditary factors in the causes of the development of bladder pathologies: if one of the parents had problems with the regulation of urination, then the probability of problems occurring in the child is about 35%, if both - 70%.
Diagnostics
As soon as parents notice a violation of the urinary process in their child, they should immediately contact an experienced specialist. The attending physician begins the examination of the baby by collecting an anamnesis: possible injuries to the head, back or pelvic area, complaints of the little patient, features and disorders of bladder emptying.
For a clearer picture of the pathology, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods will be required:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood biochemistry (to determine the amount of metabolic products);
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko (gives information on the content of red blood cells, leukocytes and protein);
- bacteriological culture of urine (allows us to identify pathogenic microflora in urine);
- urine analysis according to Zimnitsky (can show the degree of urine concentration in the bladder);
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys (allows you to determine the degree of organ damage, the residual amount of urine in the bladder after emptying);
- fluoroscopy using a contrast agent;
- excretory urography.
In the absence of an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional examinations aimed at carefully studying the functioning of the urinary canals: uroflowmetry, electromyography, cystometry. If the problem of a neurogenic bladder does not lie in the organs of the urinary system, a more thorough examination of the child’s central nervous system will be required. For this purpose, methods such as encephalography of the brain, CT, MRI, and X-ray of the spine are prescribed.
Symptoms
- uncontrolled urination in children over 5 years of age;
- frequent urges (more than 10 times a day and 3 per night) in small portions;
- urination in several stages;
- inability to delay gratification of urges;
- urinary incontinence;
- in neurogenic cases - deterioration of the condition in situations where the child is nervous (at school, before an exam, in an unfamiliar environment, after a quarrel, etc.).
It is important to remember that all of these symptoms should only cause alarm if they are observed in children 4-5 years of age and older. Until this age, the child learns to control his urination.
Overactive bladder syndrome also occurs in adults and is associated primarily with infections and loss of pelvic muscle tone.
Bladder dysfunction is expressed by disorders of the act of urination. The clinical picture depends on the type of organ pathology.
In the case of a hyperreflex bladder, the following symptoms are observed:
- imperative (urgent) urges, sometimes so strong that the patient can restrain them for only a second;
- daytime pollakuria - frequent urination with a normal total volume of urine;
- urinary incontinence;
- enuresis.

Hypotension of the bladder has the opposite signs:
- weakening or absence of the urge to urinate;
- rare urination when the organ is full or even full;
- feeling of incomplete emptying;
- large volume of residual urine;
- overstrain of the abdominal wall with sluggish urination;
- spontaneous release of urine (the pressure of a full bladder leads to a gaping of the external sphincter);
- constipation;
- urinary tract infections;
- innervation of the bladder (absence of urge with normal functioning of the muscles of the organ).
Lifestyle
To prevent relapses, patients need to switch to a balanced diet. Certain foods irritate the walls of the bladder, causing frequent urges to empty the organ.
The list of prohibited substances includes the following products: spicy, sour, canned vegetables, chocolate and its derivatives, citrus fruits, coffee, fermented milk products, smoked, spicy, salty.
Experts recommend stopping the use of alcohol, low-alcohol, and tobacco products. Healthy ingredients of the daily diet include cereals, watermelon, green tea, plum juice, and seafood. Patients should not forget that the body requires drinking at least two liters of clean drinking water per day.
Doing sports, daily walking, and maintaining a balanced psychological background will help you get rid of the pathology. Patients should learn to distance themselves from the negative influence of external factors and perceive conflicts less. For people with increased excitability, it is recommended to visit a psychologist.
Drug therapy for hypotonic process
In the presence of a hyperactive process, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Frequent urination (up to 8 times a day), during which urine comes out in small portions.
- Imperative urges, which are characterized by suddenness. The child has to urgently run to the toilet.
- A sufficient volume of urine does not accumulate in the bladder, since it comes out at short intervals.
- There is urinary incontinence day and night.
Stress urinary incontinence is common among girls during adolescence. With this pathology, urine is released in small portions during physical activity.
During the postural process, involuntary urination occurs in the daytime after the body moves to a standing position after lying down. Urination at night is not impaired.
With reduced tone, therapy is much more difficult. It is necessary to control the excretion of urine. Forced emptying is also provoked.
Modern treatment of neurogenic bladder in children with a hypotonic course of the disease involves the use of “Aceclidine”, “Distigmine”, infusion of Eleutherococcus or Schisandra.
For the purpose of prevention, uroseptics are prescribed in small doses. The use of Furazidine, Nitroxoline, and Levamisole is also justified. The use of intradetrusor and intraurethral injections of botulinum toxin is indicated.
In case of bladder hypotension, forced urination is carried out every 2-3 hours, periodic use of a catheter. Since this pathology is characterized by stagnation of urine, the child is prescribed medications that help relieve the inflammatory process. Antimicrobial therapy is an extremely important part of treatment, as it helps to minimize all possible complications.
Drugs that enhance bladder activity are prescribed only to those children who have hypotension of the bladder walls.
Any therapy is accompanied by the use of vitamin complexes that support the immune system at an optimal level. Antioxidants are also used.
What do pediatricians say about such a disease as neurogenic bladder? Komarovsky (a pediatrician whose name is widely known) often mentions a non-drug method of treatment that involves urination training. This therapy does not have any side effects, does not limit other methods of therapy, and can also be combined with medications.
It is very important to provide the child with the necessary conditions for proper rest. The daily routine should be normalized, which should include a two-hour nap during the day. Before going to bed at night, the child should be calm.
Walking in the fresh air has great benefits. They help calm the nervous system.
Psychotherapy has a positive effect, which can normalize the mental state of a small patient, increase adaptive strength and self-esteem.
A number of non-drug methods should include:
- Establishing a urinary routine. Emptying the bladder occurs at a certain time. After some time, changes are made to this regime, consisting in increasing the time interval between urinations.
- In order to strengthen the pelvic muscles and optimize the functionality of the sphincter, the child is recommended to perform a set of Kegel gymnastic exercises. They are based on the principle of feedback at the biological level. As a rule, this method is used for adult children.
In the treatment of pathologies such as neurogenic bladder dysfunction, physiotherapeutic procedures are highly effective.
Doctors usually use:
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- electrophoresis;
- electrical stimulation of the bladder;
- hyperboric oxygenation;
- thermal procedures;
- diadynamic therapy;
- amplipulse;
- baths with sea salt.
Treatment
Therapy for bladder pathology should only be comprehensive and include monitoring the baby’s lifestyle and nutrition, drug treatment, therapeutic exercises, and physiotherapy. If there is no positive result of this therapy, the doctor decides to perform a surgical operation.
Traditional
Includes a whole range of activities:
- Normalization of the daily routine . Increase the time of night and day rest (up to 1-2 hours), improve the child’s diet. They add daily walks in the fresh air and eliminate negative factors that contribute to traumatizing the baby’s psyche. Evening activities (games, watching TV) are completely eliminated.
- Carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures : electrophoresis with the use of drugs, electrical stimulation of the urinary organ, diadynamic therapy, laser therapy, heat treatment, ultrasound.
- Psychotherapy sessions . Sand therapy and relaxation methods are used.
- Physiotherapy . It is recommended to perform Kegel exercises, which help strengthen the muscular wall of the pelvis. To do this, you need to strain your pelvic muscles and hold them in tension for several seconds. The exercise is performed 10-15 repetitions 3-4 times a day.
- Drug treatment . Includes the use of various drugs, for example, for hyperreflex bladder, anticholinergic blockers (Oxybutynin, Melipramin), vitamin-mineral complexes, calcium antagonists, nootropic drugs, amino acid (Glycine) are indicated. For hyporeflex organs, anticholinesterase drugs (Ubretide), tincture of Eleutherococcus, and cholinomimetic drugs (Galantamine) are prescribed. In addition, catheterization of the bladder and maintenance of the urination regime are necessary (the child needs to visit the toilet every 3 hours, and over time the interval is gradually increased). To exclude an infectious process, small doses of antimicrobial drugs (nitrofurans) are prescribed.
- Surgical intervention . Transurethral resection of the bladder neck, injection of collagen into the ureters, and correction of the nerves responsible for the urinary process are performed. To increase the volume of the bladder, cystoplasty surgery is prescribed.
Folk remedies
Therapy for neurogenic bladder disorder is treated not only using traditional methods; folk recipes also provide good results. Medicinal herbs used to treat the disease can reduce infectious processes that arise due to urine accumulated in the organ and have a calming effect.
For hypotension, it is recommended to take a decoction of lingonberry leaves, which has an antiseptic and diuretic effect. Sage, rose hips, and carrot juice help combat the problem.
Possible complications
Neurogenic bladder in a child, reviews of which indicate that the disease has an extremely negative impact on the organ, causing significant disturbances in its nutrition. Frequent interstitial cystitis is noted.
The result of the pathological process is tissue sclerosis and organ shrinkage.
It is also possible to develop:
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- nephrosclerosis;
- chronic kidney disease.
If left untreated, problems with urination can lead to various complications and the development of concomitant diseases.
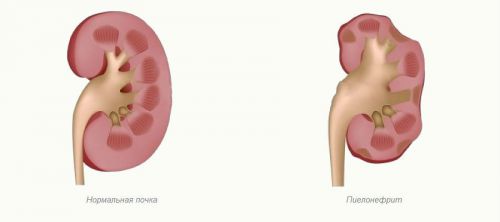
Pyelonephritis often complicates the course of bladder dysfunction
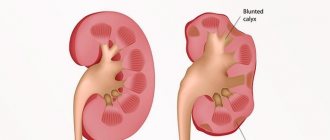
Very often, cystitis and pyelonephritis or vesicoureteral reflux become accompaniments of neurogenic disorders in the bladder. The latter can lead to complications such as arterial hypertension, renal failure, reflux nephropathy, ureterohydronephrosis.
A hyporeflex bladder in a child can cause inflammation of the urinary tract, impaired blood flow in the kidneys, wrinkling of the kidney or scarring of its parenchyma, nephrosclerosis.
Therapeutic methods
It is very important to undergo laboratory and instrumental tests when identifying signs of urinary neurosis. The laboratory method involves passing the necessary tests.
Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys, cystoscopy, and urodynamic studies are considered excellent methods of instrumental examination.
Bladder neurosis is characterized by the presence of inflammatory processes, in particular cystitis.
Since each urinary organ is healthy when neurosis manifests itself, the only difference is functional deviations in the functioning of this system, which can cause significant problems for the patient due to its symptoms.
What types of bladder neurosis are there?
Several types of neuroses can be distinguished, in particular paruresis and neurogenic diuretic bladder syndromes. Each of which has its own characteristics and nuances, which is worth talking about later in this article. For example, paruresis is a classic type of the disease itself, when the patient is unable to empty himself using the bladder.
As a rule, such a problem makes itself felt only in the presence of strangers. Turning to the statistics, you can see that a huge number of citizens suffer from a similar syndrome, the causes of which can be hidden even during school, growing up and developing a personality.
Often, with prolonged manifestation of the disorder, the patient cannot go to the toilet even in an empty stall, which already indicates the neglect of this situation. Sometimes such manifestations can be found at home, which can also be explained by psychogenic personality disorders.
The appearance of urinary retention in children can be associated with the development and progression of various pathological conditions or diseases, as well as short-term functional failures or even physiological causes.
Therefore, when this unpleasant phenomenon appears in a child at any age, it is necessary to timely determine the cause of this symptom.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor carefully diagnoses the patient, paying attention to previous surgeries, medications, sex life, and reproductive function. Gives recommendations and writes out referrals for laboratory tests.
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction in children
Signs of a neurogenic bladder in children with reduced organ function include:
- Rare (1-3 times a day) urination.
- Large volume (up to 1.5 l) of urine excreted.
- Sluggish urination.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The examination shows that approximately 400 ml of urine remains in it.
A “lazy” bladder is characterized by a combination of rare urination with incontinence, the presence of infections in the urinary tract, and constipation.
For an overactive bladder, drug therapy is prescribed to help weaken muscle tone.
For hypertension, the following are prescribed:
- m-anticholinergics;
- tricyclic antidepressants (“Imimpramine”, etc.);
- Ca antagonists (“Terodiline”, “Nifedipine”, etc.);
- herbal preparations (infusion of valerian and motherwort);
- nootropic drugs (“Picamilon”, “Hopantenic acid”, etc.).
Neurogenic bladder in a child over 5 years of age can be treated with Desmopressin. This drug is an analogue of the pituitary antidiuretic hormone. Also in this age category, the use of Oxybutynin is indicated.
Pathological changes may begin to develop in the bladder, which, as a rule, are based on insufficient coordination of the muscular lining of the organ, its neck or external sphincter. As a rule, the cause of such changes is a dysfunction of the nervous system.
Children most often suffer from disorders of the urinary system, but adults, especially older people, are also susceptible to neurogenic urinary dysfunction.
Preventive measures are extremely necessary to prevent the occurrence of problems in the urinary system and prevent further progression of the existing disease.
A regular full examination of children in a clinic is necessary for timely diagnosis of the disease, the child’s adherence to a sleep schedule, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Adults should closely monitor how the child adapts to the team in kindergarten and school, since it is often socialization problems that become the impetus for the development of bladder dysfunction.
It is important for people at risk to be constantly monitored by a doctor and periodically study urodynamics. For the purpose of prevention, the doctor may prescribe herbal medicine, physiotherapy, or taking small doses of medications appropriate to the type of pathology.
Diseases of the urinary system can seriously affect a person's quality of life. Considering that children are more susceptible to bladder dysfunction, parents need to monitor the child’s psychological and physical condition, as well as the frequency of trips to the toilet, from an early age. At the first symptoms of the disease, you must consult a doctor and strictly follow the prescribed course of therapy.
Failure of urination function is a fairly common disease. Neurogenic bladder in children occurs in 10% of young patients and manifests itself in infancy. The disease is congenital or acquired, depending on the causes of the nervous disorder. However, boys are less likely to experience the disease than girls.
General information
Neurogenic bladder is a term that implies a failure of its reservoir, valve or evacuation function. The human bladder accumulates, holds and removes urine from the body. This process is closely related to the activity of the kidneys, ureters and central nervous system. The slightest disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system negatively affect urination.
Children suffering from this disease have problems with uncontrolled urine production. This creates many physiological and psychological problems. The child cannot cope with the problem and is often ridiculed by his peers. As a result, a number of diseases develop - cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, depression.
The controlled urination reflex is conditional in nature and depends on the child’s brain activity and the functioning of his central nervous system. Any neurological disorders contribute to disruption of the detusor or external sphincter. The causes of the disease are divided into congenital and acquired. Failures occur due to the following problems:
- birth injuries;
- pathologies of the activity of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland;
- cerebral palsy;
- congenital anomalies;
- HIV;
- diabetes mellitus;
- strokes;
- spinal hernia.
The following can lead to disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system:
- injuries;
- bladder muscle strain;
- inflammation of the ureters;
- malignant or benign tumors of the spinal cord or brain.
Neurogenic bladder in a child manifests itself depending on the causes of its occurrence, stage and type. Signs of illness not only signal illness, but also make it possible to diagnose a specific type of disease. With bladder hypertension in a child, the following can be observed:
- imperative urge to urinate;
- a small amount of urine excreted;
- pain during urination;
- frequent (up to 10 times a day) urination.
A hypoactive neurogenic bladder is characterized by:
- rare urination (1-3 times a day);
- constant feeling of fullness of the bladder;
- feeling that urination is incomplete;
- a large amount of urine;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
If a child is affected by Hinman syndrome, he suffers from chronic constipation, kidney and genitourinary tract infections. At the same time, the child wants to go to the toilet only when he moves from a horizontal position to a vertical one. Ochoa syndrome, having all of the above symptoms, is hereditary and is accompanied by arterial hypertension.
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction results in loss of urinary control.
The first signs appear at the age of one and a half to 4 years, since the reflex of control over the body’s needs for emptying should already be formed by this time.
It should be noted that in teenage girls, uncontrolled urination more often occurs during physical activity and even laughter. This is due to the fact that estrogen levels increase significantly in women (especially during puberty).
How to cure
Therapy includes several independent directions, depending on the source of the syndrome. Treatment includes medication, physiotherapy, folk remedies and changes in the patient’s usual lifestyle.
Drug therapy
The urgent nature of the disease requires the use of medications. The first stage includes the prescription of antidepressants and sedative medications to stabilize the patient’s mental background, deviations in which provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
The pathological process is stopped with the help of M-anticholinergic blockers, which reduce the activity of the bladder detrusor, botulinum toxin - the drug is introduced into the wall of the organ, causing muscle relaxation. Therapy is carried out for several months, after a year all procedures are repeated. Treatment allows you to stabilize the process of bladder release, suppressing the main symptomatic manifestations.
Surgery is performed in rare cases. Manipulation involves excision of the muscle tissue of an organ, which allows increasing the volume of the organ, replacing it with a piece of the large or small intestine. Operations can provoke various complications, so they are rarely performed.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies is represented by a variety of infusions and decoctions:
- St. John's wort and bearberry are taken in equal parts - 3 tablespoons each, the mixture is poured with a liter of fresh boiling water, infused for several hours, consumed a quarter of a glass, three times a day;
- Take two spoons of elecampane per spoon of thyme, brew with a liter of boiling water, the mixture is kept for 3 hours, filtered and consumed throughout the day.
Complex procedures
Physiotherapeutic manipulations are prescribed by the attending physician depending on the general condition of the body, indications, and contraindications. Treatment is carried out with electrophoresis, paraffin applications, galvanization, directed ultraviolet light, electrosleep, galvanic collar.
In addition to professional procedures, the patient is recommended to train using the Kegel technique - to train the muscle tissue of the pelvis. Regular exercise allows you to strengthen both the muscular and reproductive systems.
Signs of Ochoa syndrome
The following symptoms are typical for this pathology:
- urinary incontinence;
- relapses of infectious processes in the urinary tract;
- constipation that becomes chronic;
- spontaneous acts of defecation;
- the absence of any pathologies in the nervous system, as well as anomalies of the urinary tract of any degree;
- weak expression of psychological status.
In the development of this syndrome, the genetic basis plays a fundamental role. The pathology usually develops in boys between the ages of 3 months and 16 years.
The main symptoms include:
- involuntary urination;
- chronic constipation;
- infectious processes in the urinary tract.
The child complains that his bladder hurts. There is a high probability of developing arterial hypertension and chronic nephritis.
Use of the drug “Picamilon”
“Picamilon” for neurogenic bladder in children is prescribed for urination disorders that are organic in nature. The drug is used to optimize the functionality of the bladder.
The drug has the highest degree of effectiveness in relieving neurogenic urinary dysfunction, as well as changes in the dynamics of urine excretion.
The product is approved for use from 3 years of age. Many parents are interested in how justified the use of this drug in infants is. “Picamilon” is often prescribed to children under 1 year of age for general development and maintenance of muscle tone. This issue can only be clarified with your doctor. He will prescribe the required dosage.
On average, the duration of treatment is 1 month. The drug is easily digestible and quickly dissolves in the stomach.
The drug is contraindicated for children with a high threshold for an allergic reaction. It is also prohibited for use in the presence of acute kidney pathologies.
Treatment and its types

Treatment for neurogenic bladder depends on the symptoms and type of disease. It is important to carry out complex therapy in the fight against the disease in young patients. It includes monitoring the child’s nutrition and lifestyle, drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises, psychotherapy and, if the disease does not respond to conservative methods, surgical intervention is indicated.
Lifestyle and nutrition
Children suffering from urinary disorders need care and constant monitoring from their parents. They must monitor compliance with the daily routine and diet prescribed by doctors. First of all, adults should ensure healthy daytime sleep for their child. The baby should not be exposed to stress; physical activity is contraindicated for him. The body needs fresh air, so the patient's room should be ventilated. Nutrition should be balanced. Sour, salty or spicy foods should be avoided. Drinking regime and urination time should be monitored by parents and a doctor.
Physiotherapy
Although physical activity is contraindicated for pathologies of bladder function, physical therapy is one of the methods of complex therapy. A set of Kegel exercises is considered effective. It is aimed at improving the functioning of the pelvic muscles and, in particular, the bladder. As a result of this course, the muscles stretch and become toned. This makes it possible to retain urine in the bladder and improve the act of urination.
Physiotherapy
Correctly selected physical procedures have a beneficial effect on the restoration of bladder function. However, children should undergo them exclusively under the supervision of a doctor, in order to avoid negative reactions of the body. With neurogenic pathology of urination, a child may undergo:
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- electrosleep;
- hyperbaric oxygen therapy;
- electrical stimulation of the bladder;
- magnetic wave therapy;
- ultrasound procedures;
- heat therapy.
Drug treatment

Prescription of drugs for neurogenic bladder in children depends on the type of disease. In this case, the doctor chooses the means that have the least number of side effects on the young body. In the treatment of any type of bladder dysfunction, vitamin preparations are necessarily used, namely vitamins B1, B6, B2, PP, A and E. In case of hypertonicity of the bladder muscles, the disease is combated by:
- anticholinergics - “Atropine”, “Oxybutynin”, “Bellataminal”, “Melipramin” (for children over 5 years old);
- calcium antagonists - Nifedipine, Teradidlin;
- tinctures of motherwort or valerian;
- "Desmopressin" - if there is a frequent urge to urinate at night.
To combat a hypotonic bladder, the ureters need to be catheterized periodically. The child should urinate every 2-3 hours, gradually increasing the intervals. Additionally used:
- "Ubretid";
- "Aceclidine";
- "Glycine";
- tincture of Eleutherococcus.
Not only the genitourinary system needs complex therapy. Do not forget that the smooth functioning of the child’s central nervous system largely influences the elimination of the causes of the disease. For this, young patients can understand “Glutamic acid”, “Piracetam”, “Picamigon” or “Pantogam”. The choice of drug and dosage prescription always remains with the attending physician.
Surgical intervention
Conservative methods of therapy make it possible to overcome the disease. If this does not happen, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. Depending on the clinical picture of the disease, it is possible to:
- ganglion surgery;
- implantation of callogen under the entrance gate of the ureters;
- transuretal excision of the bladder neck;
- increase in bladder volume.
Surgical methods of treatment
How else can neurogenic bladder be eliminated in children? Treatment involves the use of surgical methods. Surgeries on the neurogenic bladder are performed using endoscopic methods.
Pediatric urology uses the following surgical interventions in practice:
- Transurethral resection of the bladder neck.
- Implantation of collagen at the mouth of the ureter.
- Surgery on the nerve ganglia that control urination.
- Intestinal cystoplasty. Doctors perform plastic surgery on the muscle layer of the organ and correct the nerve fibers. Surgeons use intestinal tissue to expand the bladder. However, such surgery often causes serious complications due to incompatibility of intestinal and bladder tissues. Therefore, such an operation is resorted to in extremely rare cases.
- If the disease is complicated by oncology, they resort to removing the bladder.
Many types of treatment are accompanied by forced elimination of urine. For this purpose, a catheter is installed in the child. This procedure is particularly effective in the presence of pathology such as vesicoureteral reflux.
How to distinguish bladder neurosis from other diseases, its symptoms and treatment
This problem has another name - urinary cystalgia. But there are no general reasons linking it with cystitis. The only signs that are similar are those that indicate the emergence of a problem and signal that a course of treatment should be started urgently.
Frequent desires to urinate or false sensations are the most likely symptoms confirming the development of bladder neurosis. The patient begins to understand that he cannot control the output of urine himself. For this reason, symptoms appear, characterized by the sensation of urine not being released in full.
Patients may complain that they no longer feel their own bladder. This is aggravated by the forced measure of going to the toilet on a schedule, without waiting for the urge to do so.
In the article, we will analyze what bladder neurosis is, how to distinguish it from other common diseases, based on symptoms similar to neurosis. How does this type of neurosis manifest in children and adolescents? And most importantly - what to do in this situation, which doctor to go to and how to treat?
Concept of neurogenic bladder
Prognosis and prevention
Timely initiation of therapy, which takes into account the individual characteristics of the little patient’s body, allows one to avoid undesirable consequences.
Children who have been diagnosed with neurogenic bladder dysfunction are required to be registered at the dispensary. Doctors constantly conduct studies of the dynamics of urination in order to be able to record any functional changes, and, if necessary, make timely adjustments to therapy.
The prognosis is more favorable with detrusor overactivity. The presence of urine residue provokes impaired renal function, up to and including renal failure.
The prognosis for the young patient is generally favorable. However, the prospects depend on the timeliness and correctness of the prescribed treatment. Most preschool children who have problems with urination get rid of them safely.

Some types of neurogenic urinary dysfunction are most often cured without complications. First of all, this concerns detrusor hyperactivity.
With a hypotonic inactive bladder, the risk of complications is greater. This is explained by the factor of residual urine present in the clinical picture in this form of the disease. Residual urine accumulates and thereby allows bacteria to spread, which can cause the development of kidney and urinary tract diseases. With urinary incontinence, there is also a risk of progression of the pathology into serious diseases: cystitis, pyelonephritis, renal failure.
The list of preventive measures is not very long. First of all, you need to regularly visit your doctor, carefully monitor your child, and talk to the doctor about any problems you notice. If bladder problems are your case, then it is important to get a diagnosis and begin treatment as early as possible.
You need to try to create a friendly atmosphere of love, support and warmth around your baby. After all, we are considering cases where urination disorders in a child are associated with disorders of the nervous system. From the point of view of disease prevention, it is also important to monitor brain function and regularly undergo preventive medical examinations with doctors.
Support your child, do not scold him over trifles. He will definitely learn to go to the potty and use the “adult” toilet, he just has some minor health problems that you will soon successfully resolve.
Types of pathology
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction in children is caused by the ability of the muscles to contract during the accumulation of urine or emptying. It is customary to classify a neurogenic disease taking into account the type of disorder. Additional indicators may be the form of the disease or the amount of urine in the body before bowel movement occurs. There are neurogenic urea types:
- Hyporeflex (hypotension of the bladder). At the stage of urine excretion, the bladder muscles contract weakly. This leads to excessive filling. The result is incontinence.
- Hyper-reflexive bladder. During the urine accumulation phase, muscles contract more often than normal. As a result, urine is not retained in the bladder and is released through the ureters often and in small quantities.
- Areflexonic - a bladder whose muscles do not respond to the volume of urine contained in it and do not contract. Thus, the function of urination is uncontrolled by the central nervous system.
Due to the ability of the bladder muscles to stretch and adapt to the volume of urine, the organ can be adapted or non-adapted. In this case, it manifests itself in mild forms (enuresis, stress incontinence, incontinence due to physical overexertion). It may be of moderate severity (reflex excretion of urine) or be in a severe advanced phase (Ochoa syndrome, Hinman syndrome).