Craniotomy
Its implementation is due to a large focus of the formed hematoma, which puts significant pressure on other parts of the brain, causing unbearable pain in the patient, increased pressure, and pre-fainting conditions.
With this intervention, the skull is opened and the accumulated blood is removed using special equipment. The removed part of the skull can be replaced with a plate.
The size of the bone removed may be small, medium or large. It is used in cases that clearly threaten the life of the victim.
For large lesions (extensive stroke), decompression trepanation is used. As a result, part of the skull is removed to relieve pressure on healthy areas of the brain.
Postoperative period
Therapy during the recovery period is to prevent the progression of cerebral edema and prevent recurrent hemorrhage. In addition, possible serious complications may include:
- paralysis;
- changes in speech and motor activity;
- loss of vision;
- disorders of the central and autonomic nervous system (memory impairment, slurred speech, etc.).
A significant factor is the timing of the operation - the patient’s condition in the postoperative period remains unstable for a long time if the surgical intervention was performed late. There may be a temporary or permanent decrease in the patient's intellectual abilities, speech impairment and clouding of consciousness.
The main complication after stroke surgery is swelling of the brain tissue, which can last up to two weeks. This condition is life-threatening; to eliminate it, the patient is administered osmotic and diuretics (for example, Mannitol, Lasix), barbiturates (Sodium Thiopental), and hyperventilation is performed in sessions of short duration.
In addition, it is necessary to constantly monitor the patient’s blood pressure, since hypertension can provoke new or worsen old bleeding. The level of systolic pressure should not exceed 130 mmHg, otherwise drugs with a short duration of action are prescribed for better correction of hemodynamics.
After the operation, the patient may complain of general malaise, gastrointestinal upset, and nausea. Temporary clouding of mind and dizziness are possible. The postoperative period is characterized by a general loss of strength and sudden weight loss. In addition, patients who have suffered a stroke often suffer from stress and nervous exhaustion, so during this period they especially urgently need care and attention from loved ones.
In addition, it is necessary to constantly monitor the patient’s blood pressure, since hypertension can provoke new or worsen old bleeding. The level of systolic pressure should not exceed 130 mmHg, otherwise drugs with a short duration of action are prescribed for better correction of hemodynamics.
Indications for surgery
- Hemorrhage (a common consequence of hemorrhagic stroke). The cause is a ruptured aneurysm. Blood spreads through the brain tissue, penetrates the ventricular system, where it stagnates. Consequences - formation of hematomas, dropsy.
- Severe, persistent headache. This is a sign of increased intracranial pressure. Pressure increases due to stagnation and poor circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The cause may be a dead piece of brain tissue that needs to be removed immediately.
- For ischemic stroke, surgery is performed in the presence of blood clots and severe narrowing of the carotid arteries.
Trephination involves creating holes in the skull in order to gain access to the brain and further work with it. The procedure is performed both planned and as an emergency when the pressure on the brain is dangerously high or other methods are ineffective.
What surgery is done for a cerebral stroke?
Stroke surgery is becoming the main method of helping patients suffering from circulatory disorders in the brain. With an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, the patient’s brain suffers from a lack of oxygen, nutrients, and compression of the soft tissues by the resulting hematoma. In this case, it is necessary to resolve the situation as soon as possible and restore normal blood circulation. Every minute more and more nerve cells die, and it will be more difficult to restore brain function. And this is provided that the patient can be saved from death.
As a rule, few people plan such surgical interventions. After all, even if the patient knows about circulatory defects in the brain, the risk of a stroke is high, and hemorrhage can happen at any time. The most favorable time for surgical intervention is the first three hours after an attack. As a last resort, you can postpone surgery until six hours after getting a stroke, otherwise doctors do not give forecasts for survival and return to your previous life.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
The manifestations of this type of pathology are diverse - they depend on the location of the lesion and the extent of ischemia. In the vast majority of cases, the carotid artery and the areas fed by it are affected.
Table. Manifestations of stroke in different parts of the brain
| Damaged artery | Symptoms |
| Middle cerebral | Impaired speech and motor functions. Decreased vision, paralysis of the upper or lower extremities. Loss of sensation in the upper or lower half of the body. |
| Forebrain | Paralysis of the arms and legs on the right or left, paresis of the facial muscles. |
| Posterior brain | Loss of visual fields, visual hallucinations. |
| Vertebro-basilar | Signs of damage to the cranial nerves, paralysis of an arm or leg. |
The diagnosis is confirmed after a computed tomography scan.
Mostly used for ischemic stroke. Aimed at correcting blood pressure, dissolving blood clots, and eliminating vascular spasm. Infusion therapy with sodium chloride solution or colloidal solutions is used. Against this background, osmotic diuretics are administered. These measures are aimed at preventing cerebral edema.
Types of operations
In a hemorrhagic stroke, in which blood flows from a vessel through its rupture, stroke hematomas are formed, compressing nearby tissues and vessels. As a result of this, a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition occurs, in which more or less pronounced stroke symptoms are observed. During the operation, blood clots are removed as much as possible. Doctors make every effort to avoid damaging the brain structures and tissues located near the blood clot.
Surgery for stroke is prescribed depending on the degree of damage that occurs. In some cases, to restore normal cerebral circulation, it is enough to simply ensure the correct position of the aneurysm.
- Aneurysm clipping. With this intervention, the integrity of the cranium is not compromised. In order for the special coil that will fix the aneurysm to reach the brain, a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery. The recovery period after this intervention is minimal, as is the risk of complications.
- Open surgery. Craniotomy is performed in less than a quarter of patients diagnosed with hemorrhagic stroke. Such an intervention is considered difficult and risky, which is why possible consequences are assessed in advance. Such treatment is carried out exclusively in cases where the patient cannot be helped in any other way.
- Stending (bypass) of blood vessels. This operation is performed to restore their lumen. A special stand is injected into vessels that are at risk for stroke and can provoke a recurrence of the disease.
- Selective trobolysis. The operation allows you to dissolve the blood clot that led to the blockage of the vessel and restore normal cerebral circulation. In this situation, a catheter is inserted through a puncture in the femoral artery. When it is in the area of the blocked vessel, a composition will be supplied there that will dissolve the blood clot.
- Carotid endarterectomy. This operation is performed on the most severely ill patients, in whom, due to the presence of large plaques in the carotid artery, the risk that a hemorrhagic stroke will recur is very high. In this case, a section of the artery is removed. The intervention is successful in the vast majority of cases. It is carried out in almost all neurosurgical departments.
"Course in Clinical Pharmacology"
Contraindications
Surgeries after a stroke are recommended taking into account contraindications. If the patient's age is more than 50 years, then surgical intervention is strictly prohibited. During the course of oncological diseases in the human body, manipulation is not carried out. The doctor does not advise using the surgical method for purulent pathological processes in the meninges.

If a person is in a coma, he is prohibited from undergoing surgery. It is not performed for diabetes mellitus. A contraindication to the use of this treatment method is neurological deficit.
If a patient was diagnosed with a stroke or heart attack less than six months ago, he is prohibited from undergoing surgery. It should be discontinued if blood pressure rises. For cardiac, renal or liver failure, the therapeutic technique is not used.
After surgery, a person may lose weight. A common consequence of manipulation is memory impairment. Surgical treatment of the pathological process leads to the development of epilepsy. After a stroke, a person's speech is impaired. He not only speaks slurred, but also cannot understand the speech of others. The operation leads to partial or complete paralysis.
Contraindications to surgery
Surgery is not indicated for patients over 75 years of age, as it is accompanied by deterioration of the condition and progression of neurological disorders, and stroke recurrences occur quite often. This contraindication is considered relative, however, most neurosurgeons consider such operations futile.
Surgical treatment is not recommended if:
- severe forms of cardiac, pulmonary or renal failure;
- liver damage;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- a pronounced decrease in blood coagulation activity;
- acute purulent processes;
- oncological diseases.
Stereotactic technique of surgery
- severe forms of cardiac, pulmonary or renal failure;
- liver damage;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- a pronounced decrease in blood coagulation activity;
- acute purulent processes;
- oncological diseases.
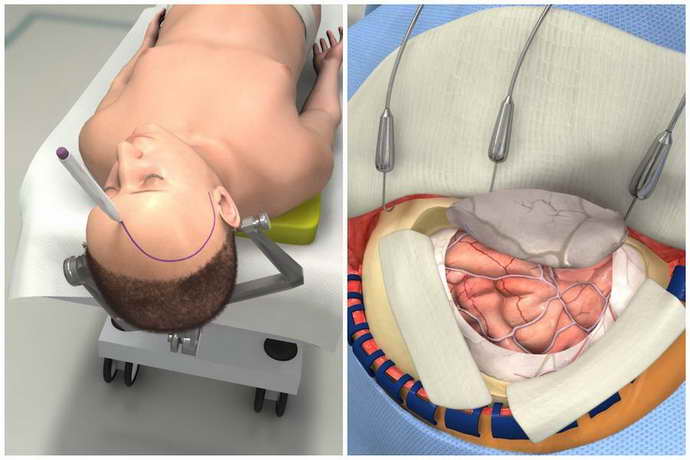
Features of craniotomy
Craniotomy is a long and complex procedure. A neurosurgeon spends 5 to 15 hours at a time at the operating table. Restoring cerebral circulation requires the care, precision and experience of a doctor. Open surgery is rarely prescribed, as there is a high risk of life-threatening complications. However, in some cases, craniotomy is the only way to help a sick person.
Open surgery for stroke consists of the following steps:
- Preparing the patient for trepanation. An anesthesiologist puts a sick person under anesthesia. Medicines are delivered through a vein or endotracheally. When the patient falls asleep, his head is fixed in a special device to ensure complete immobility. To reduce the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, a lumbar drain is placed in the lower part of the spine.
- Opening the skull. First, the neurosurgeon makes an incision with a scalpel along the hairline. The bones and skull are separated from the skin. A hole is made with a drill. Using a medical saw, a skull flap is removed from the area of future surgical intervention, which is put back in place after the operation is completed.
- Opening of the meninges. The neurosurgeon puts on special glasses with a microscope. This allows you to record the slightest changes in brain tissue. To avoid damaging healthy areas, the doctor operates with a very thin instrument. The dura mater is opened, the effects of hemorrhage are removed.
- Closure of the cranial cavity. When the main problem is solved, the neurosurgeon replaces the sawed flap of the skull and secures it with special metal staples. Cosmetic stitches are applied to the surface of the skin. The scar on the head is not visible in the future, since the operated area is overgrown with hair.
For ischemic stroke accompanied by extensive edema, decompressive craniotomy may be required. In order to reduce compression of the brain tissue, a specific section of the skull bones is removed. Decompression surgery is rarely performed because it has unintended consequences. Removal of a cranial flap is prescribed when other treatment methods are impossible or for certain reasons ineffective.
- epilepsy;
- intracranial bleeding;
- extensive swelling;
- violation of the integrity of tissues and blood vessels;
- infection;
- partial or complete paralysis;
- problems with memory and speech;
- weight loss;
- prostration;
- improper digestion;
- temporary clouding of reason;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and migraines;
- difficulties with the perception of surrounding reality.
Surgical intervention

Sometimes surgery becomes the only correct solution to save a person from inevitable consequences.
Such a proposal may come from a neurosurgeon if the diagnosis clearly determined the development of pathological processes when scanning the internal cavity of the brain. When there is no other option, such as cutting out the hematoma or clipping the formed aneurysm in the carotid arteries.
This takes no more than 10–15 minutes. In some cases, the patient may have reasonable ailments when stroke surgery is contraindicated, for example, if there is existing instability of blood pressure. In this case, surgery is used only after the main indicators of the condition have stabilized.
Surgery for cerebral stroke - consequences
ACVA, regardless of its type, is a therapeutic pathology that has an organic substrate. In more accessible language, stroke is a disease in which pathogenetic mechanisms form a focus of necrosis in the cerebral cortex (hereinafter referred to as BM) or in subcortical structures. Accordingly, it will be an organic lesion, and the entire existing clinic is determined by its size and location.
As you know, neurocells (neurons) are restored very slowly, and the body will never have enough of its own strength to restore a dead focus - even if it takes up very little space.
The brain is the most complex structure of the human body, so even a slight damage to it will lead to catastrophic consequences.
Taking into account all of the above, it becomes clear that it will not be possible to restore dead cells. That is why all approaches to the treatment and rehabilitation of patients who have suffered stroke are aimed exclusively at helping to improve the functioning of the surviving neurocells. Today, this is the only approach that allows one to achieve relatively good results with timely, qualified medical care.
However, there is one important point - all these algorithms work only if the spread of the pathological focus of necrosis has stopped. Otherwise, when nearby cells continue to die, therapeutic methods turn out to be completely meaningless, and surgical intervention becomes the only possible way out of the situation. And even then, it is not a fact that neurosurgeons will undertake such a complex procedure; here the decision is made in seconds, and only the ratio of possible benefits and risks is taken into account.
As you know, neurocells (neurons) are restored very slowly, and the body will never have enough of its own strength to restore a dead focus - even if it takes up very little space.
Is it possible to do anesthesia
Patients after a stroke may require surgery for other diseases. Therefore, a logical question arises: is it possible to do general anesthesia after a stroke, and how can it affect the blood vessels of the brain? It must be said that any anesthesia is a risk for a person who has a history of stroke.
But sometimes it is impossible to do without surgery and anesthesia. In this case, you must inform your doctor about the illness you have suffered, and also consult a neurologist.
Important! Much depends on how long ago the stroke was suffered, the age of the patient, the severity and type of stroke, and so on, so the issue of the safety of anesthesia is decided on an individual basis.
Any operation is accompanied by the use of anesthesia, this can be spinal, epidural or general anesthesia. After a stroke, the danger is that interference with the blood flow can provoke repeated cerebral ischemia, and causes a second stroke.
However, with a competent approach from the anesthesiologist, the prognosis can be favorable. It is optimal to use epidural anesthesia with morphine and Naropin, the main thing is that the anesthesiologist is fluent in this technique.
We invite you to watch a useful video on the topic:
Any operation is accompanied by the use of anesthesia, this can be spinal, epidural or general anesthesia. After a stroke, the danger is that interference with the blood flow can provoke repeated cerebral ischemia, and causes a second stroke.
Indications for surgery
Every year the number of options for non-invasive effects on the brain is growing. And yet there are a number of conditions in which opening the skull cannot be avoided. Before prescribing a planned procedure, the patient is required to undergo a CT or MRI of the head, angiography or duplex ultrasound of the vessels. This allows you to determine the location of the organ lesion with maximum accuracy and determine the working area.

Craniotomy is prescribed for:
- Hemorrhagic stroke - surgery after a stroke allows you to stop bleeding in a short time and prevent the formation of a hematoma;
- tumors, hematomas, abscesses in the brain;
- injuries to the skull, in which bone fragments begin to put pressure on the brain matter;
- abnormalities of the skull;
- cerebral aneurysm.
There are several options for craniotomy. The optimal one is selected depending on the specifics of the situation, the severity of the patient’s condition, and the availability of the necessary tools.
- Hemorrhagic stroke - surgery after a stroke allows you to stop bleeding in a short time and prevent the formation of a hematoma;
- tumors, hematomas, abscesses in the brain;
- injuries to the skull, in which bone fragments begin to put pressure on the brain matter;
- abnormalities of the skull;
- cerebral aneurysm.
Postoperative period

In the post-stroke period, older people who are unaware that alcohol and smoking lead to the formation of atherosclerotic growths in the vessels of the brain are in greater need of the help of surgeons.
In some cases, even after surgery, the likelihood of further complications increases under the following circumstances:
- The patient has diabetes mellitus.
- Incorrect functioning in the organs of the cardiovascular system is observed.
- Regular irregularities in the sequence of heart contractions.
- Numerous atherosclerotic formations.
- Excessive accumulation of fat deposits.
Treatment and recovery after ischemic cerebral stroke: effective approaches and methods
Just a few decades ago, a stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident) almost always ended in the death of the patient. Death due to impact was common. His victims were Bach, Catherine II, Stendhal, Roosevelt, Stalin, Margaret Thatcher... The development of pharmaceuticals and neurosurgery increased the chance of salvation. Doctors have learned to save patients with blockages or even ruptures of blood vessels in the brain.
But interrupting the process of nerve cell death is half the battle. It is equally important to cope with the consequences of those violations that occur in the first minutes of an attack, even before the ambulance arrives. According to statistics, about 70% of people who survive a stroke become disabled: they lose vision, hearing, speech, and the ability to control their arms and legs. It is no secret that some of them, in a fit of despair, tend to regret being alive, feel like a burden to their relatives and see no hope in the future.
Taking into account the fact that the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in developed countries continues to grow, such a medical area as post-stroke rehabilitation is becoming increasingly in demand. In this article we will cover:
- what role do rehabilitation courses play in the prognosis of recovery of patients who have suffered a stroke;
- How does rehabilitation in specialized medical centers differ from rehabilitation at home?
But interrupting the process of nerve cell death is half the battle. It is equally important to cope with the consequences of those violations that occur in the first minutes of an attack, even before the ambulance arrives. According to statistics, about 70% of people who survive a stroke become disabled: they lose vision, hearing, speech, and the ability to control their arms and legs. It is no secret that some of them, in a fit of despair, tend to regret being alive, feel like a burden to their relatives and see no hope in the future.
Forecast
With ischemic damage, the prognosis depends on a number of factors, primarily on the volume of the pathological focus. Mortality reaches 20%. Surviving patients experience neurological impairment of varying severity.
With hemorrhagic lesions, the prognosis is more unfavorable. The number of deaths reaches 70%. Two thirds of patients remain deeply disabled.
To avoid the development of a stroke, the following preventive measures should be followed:
- avoid physical inactivity;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid physical and emotional fatigue;
- promptly treat hypertension and atherosclerosis;
- undergo a medical examination annually.

Cerebrovascular accident is one of the most serious diseases, accompanied by a high risk of death. People who have had a stroke remain disabled to varying degrees of severity.
Some interesting facts about stroke and surgical treatment can be learned from the video:
What surgery is done for a cerebral stroke?
Stroke surgery is becoming the main method of helping patients suffering from circulatory disorders in the brain. With an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, the patient’s brain suffers from a lack of oxygen, nutrients, and compression of the soft tissues by the resulting hematoma. In this case, it is necessary to resolve the situation as soon as possible and restore normal blood circulation. Every minute more and more nerve cells die, and it will be more difficult to restore brain function. And this is provided that the patient can be saved from death.
As a rule, few people plan such surgical interventions. After all, even if the patient knows about circulatory defects in the brain, the risk of a stroke is high, and hemorrhage can happen at any time. The most favorable time for surgical intervention is the first three hours after an attack. As a last resort, you can postpone surgery until six hours after getting a stroke, otherwise doctors do not give forecasts for survival and return to your previous life.
Clinical manifestations of HI
Shortly before the attack, pre-stroke clinical symptoms may precede the attack (not always), by which one can suspect impending danger:
- tingling, numbness of one facial half;
- numbness in fingers or toes;
- sudden weakness, dizziness, noise in the head;
- severe pain in the eyes, spots, double vision, vision in red;
- sudden staggering when walking;
- causeless tachycardia;
- attacks of hyperhidrosis;
- increased blood pressure;
- unreasonable occurrence of nausea;
- inhibition in communication and perception of other people's speech;
- flushing of the face, hyperthermia.
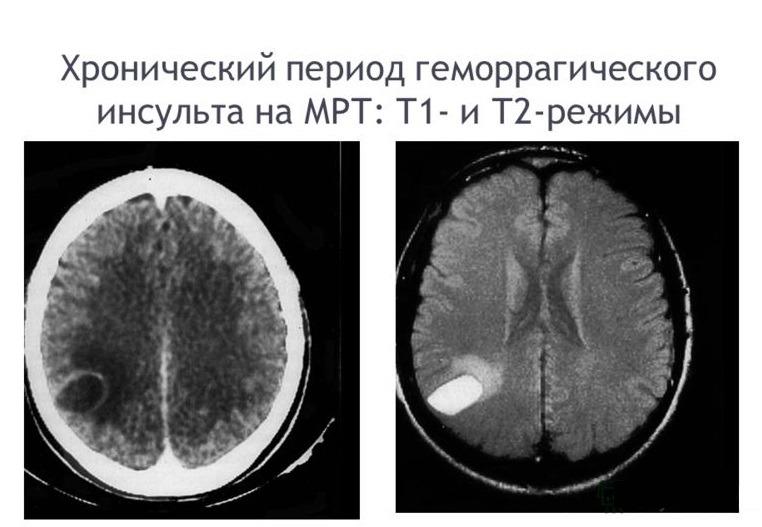
A cerebral stroke with hemorrhage is still characterized by an immediate acute onset without warning signs, which occurs during or almost immediately after vigorous activity, a stressful situation, or excitement. A hemorrhagic stroke is indicated by classic symptoms that develop suddenly, are pronounced and rapidly progress:
- sharp and severe headache;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- prolonged depression of consciousness, coma;
- blood pressure above 220 mmHg.
Common signs of shock are also noisy breathing, epileptic seizures, lack of pupillary response to light, and spastic miosis. Depending on the location of the lesion, there may be a rotation of the head and rotation of the eyeballs in the direction of the affected hemisphere or contralaterally. Having discovered signs of GI in a victim, a person nearby must immediately call an ambulance!

Acutely developed hemorrhage leads to the fact that blood flows freely into certain structures of the brain, saturating them and forming a cavity with a hematoma. The bleeding continues for several minutes or hours until a blood clot forms. Over a short period of time, the hematoma quickly increases, exerting a mechanical effect on the affected areas. It stretches, presses and displaces the nervous tissue, causing its swelling and death, which leads to an intensive increase in neurological deficit (respiratory depression, loss of sensitivity of one half of the body, speech disorders, loss of vision, paresis of the swallowing muscles, etc.).
The size of the blood accumulation can be small (up to 30 ml), medium (from 30 to 60 ml) and large (more than 60 ml). The volumes of spilled liquid can reach critical levels, up to 100 ml. Clinical observations show that with intracranial hemorrhages exceeding 60 ml, the pathology ends in death in 85% of patients within 30 days.
- sharp and severe headache;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- prolonged depression of consciousness, coma;
- blood pressure above 220 mmHg.
Useful video
Watch the video about a new method of treating stroke:
Unfortunately, coma after a stroke is not uncommon. Doctors give a cautious prognosis, since it differs in the elderly and young, after hemorrhagic and ischemic. Recovery from a deep coma can occur in a few years, or in a couple of hours. How do you get out of a deep coma? How long can the maximum number of people stay in it without consequences?
A rather dangerous hemorrhagic stroke can develop even from heat stroke. The reasons for the extensive left hemisphere lie in stable arterial hypertension. Coma can happen instantly, with increasing symptoms. Treatment may not be effective.
If there was an ischemic stroke of the brain, the consequences remain quite severe. They differ depending on the affected area - left and right side, brain stem. Symptoms of the consequences are pronounced, treatment takes more than a year.
A real threat to life is a brainstem stroke. It can be hemorrhagic or ischemic. The symptoms resemble a heart attack and are also similar to other diseases. Treatment for a long-term, complete recovery after a brain stem stroke is almost impossible.
When an ischemic stroke occurs, recovery takes a fairly long period. Is full recovery possible? Yes, if you complete a full course of rehabilitation, incl. to restore speech. What are the deadlines? What is needed after a major stroke of the cerebellum on the left side?
Features of care

Every patient needs careful care for any type of surgery in the head area. Patients need restorative procedures to return movements and abilities to basic self-care.
Relatives need to help the patient not only with eating, but also with hygienic cleanliness. This includes oral care, skin care, preventing bedsores, and performing a variety of rehabilitation exercises at home.

Close people can invite a nurse to their home for a while so that she can care for the patient, change the bed, change diapers if necessary.
Postoperative care for stroke victims includes treatment with drugs: antipsychotics, sedatives, antidepressants, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents that eliminate the spread of ailments that have arisen.
How to restore memory
To help a person remember any events in his life, relatives will need to hold special events
First of all, it is surrounding the patient with love and attention. Do not stop treatment at the first improvements
Only full-fledged therapy will help restore a person’s memory.
Finger games will be effective. For example, bending fingers, clenching fists, clapping hands is carried out in parallel with reciting simple children's poems. At the same time, you can stroke the patient’s palms and rub them
This will help focus a person's attention on gestures, as well as stimulate speech and memory
Over time, you can begin to try to learn simple rhymes with the patient, which is good for memory training. This must be done gradually: today learn one line, and tomorrow – the second, etc. Poems are taught in a playful and friendly environment.
If the person performing the manipulation is nervous and irritated, this also negatively affects the patient himself: he may withdraw into himself, which will affect the final result of the recovery period.
Together you can remember any pleasant events and incidents that happened before your illness. You can restore memory by playing a simple game - cities: the conductor names the city, and the patient independently tries to remember what pleasant event once happened there.
You should not direct the victim to thoughts related to the disease, its cause, or to remember the professional activity in which he was previously engaged, because, probably, he will no longer be able to return to it.
It is recommended to pronounce and read simple texts together. Children's quatrains, poems, and simple stories are perfect. You can use the alphabet. Over time, you need to ask the patient simple questions, for example, what city does he live in, what is the weather outside, what color is his clothes, etc.
Every day the exercises need to be complicated by adding additional elements. You can use a relative as an example, create a visual image: try together to remember the smell of his perfume, his clothes.
Rehabilitation after trepanation
Surgery, and even more so trepanation, is a risky and aggressive intervention in the functioning of the body.
The rehabilitation period takes a long time and can last a lifetime. The duration of recovery depends on the causes and treatment, the age of the patient, the general condition of the body, and patient care. Rehabilitation goals:
- counteracting disorders in brain activity;
- relapse prevention;
- smoothing or elimination of postoperative complications;
- control over the patient’s condition and prevention of possible negative changes.
A set of rehabilitation measures includes professional help, drug therapy, diet, exercise therapy, and psychological support.
Features of care
The patient spends the first 10 days in a hospital under medical supervision. This is the most dangerous period. During the day after the operation, the patient is under observation, because he is just recovering from anesthesia and the basic functions of the body are supported artificially, through equipment.
Then he is allowed to get up and eat on his own. Observation continues, and if negative consequences are detected, the length of stay in the hospital increases. Depending on the patient’s condition, medications are selected, diet, physiotherapy, and a set of exercises are prescribed. If necessary, a psychotherapist works with him.
After discharge, it is important to follow all doctor's instructions. Relatives or social workers care for the patient
A person who has suffered a stroke becomes vulnerable and is often depressed after the incident. He may have problems with memory, speech, hearing and vision, and his behavior may change. You can't get irritated or show indifference. Relatives need to support the person in everything, monitor medications and nutrition.
The patient may be bedridden - temporarily or for the rest of his life. It is necessary to provide him with clean linen and clothes, carry out hygiene measures every day, frequently ventilate the room, wipe bedsores, and communicate with the stroke victim.
Restoration of blood circulation
Restoring blood circulation is the primary goal of treatment. The functions of dead cells cannot be restored
It is important to prevent the progression of the pathological process and preserve neurons in the areas closest to the lesion
During the acute period, treatment is carried out in the hospital. Subsequently, the patient is prescribed medications that improve blood supply to the brain, prevent blood clots, as well as nootropics and psychostimulants.
Anticonvulsants, antiemetics, and antipyretic drugs are used as auxiliary agents as needed.
Blood pressure and water-electrolyte balance are constantly monitored.
Risk factors
In the medical environment, there are a number of factors prohibiting operations in the brain area. The most undesirable age after a stroke is the period from 70 years. In such situations, doctors look for and choose the most gentle folk remedies or medications for older people.
In some situations, surgery in the head area is still prescribed.
The risk of complications during or after stroke surgery occurs:
- In people with diabetes mellitus who have irreversible reactions in the internal environment of the body.
- For diseases of the kidneys, cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Due to purulent foci of damage to internal organs.
- For cancerous formations.
- Due to the lack of conscious brain activity. Basic life support functions work only through the connection of artificial equipment.
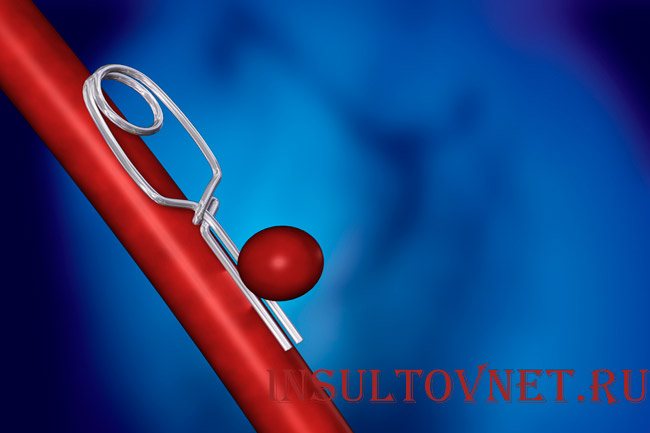
Hemorrhage occurs due to the dissection of large arteries of the brain, as well as due to the formation of atherosclerotic layers. This process ends with a sudden filling of the aneurysm with blood, followed by damage. A clot of dried hematoma forms, which is removed during surgery to prevent pressure on adjacent areas.
At this moment, to save the life of the patient, it is important to perform brain surgery as soon as possible. Late treatment for an aneurysm increases the risk of recurrent stroke.
The doctor of the neurosurgical department chooses which of the following types of surgical techniques will be used for a particular patient:
- Aneurysm clipping. Access to the site of the pathological process is carried out through a small incision of 2 mm in the area of the femoral artery. Using a thin catheter, an angiographer can reach almost any disturbance in blood flow in the brain. The treatment allows you to avoid additional interventions on the part of the upper layer of the head, as with craniotomy.
During stroke surgery, the aneurysm is gradually compressed using special means resembling clips, releasing the blood sac.
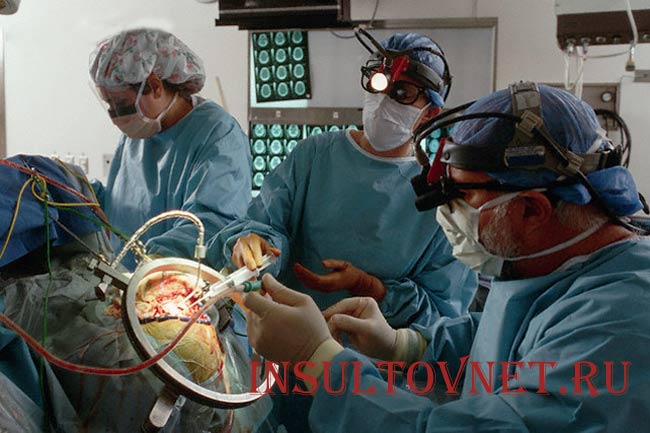
- Means of craniotomy. Surgery takes a long time, as does the road to recovery. For stroke it is prescribed extremely rarely, only in 24% of cases.
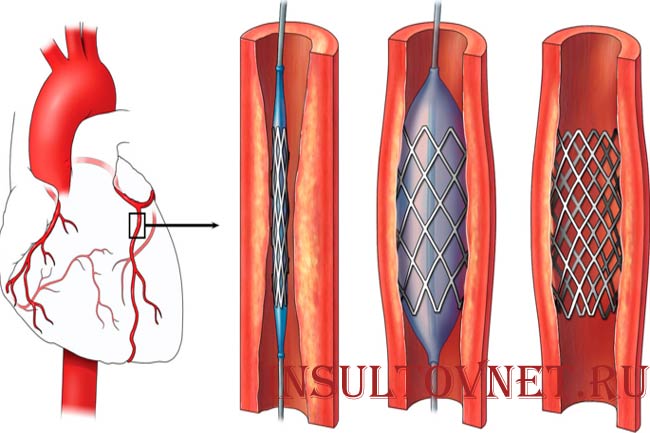
- Vascular stenting. Treatment is used for preventive purposes. During such an intervention, a thin tube (catheter) with a special expanding balloon is inserted into the passage of the artery with an atherosclerotic growth. Due to the resulting lumen, a stand in the form of a mesh is inserted into the vessel, which plays the role of an expander to enhance blood flow.
- Carotid endarterectomy. Prescribed for severe stroke. The process involves completely removing the cholesterol plaque to restore nutrition to the brain tissue.
- Selective thrombolysis. Treatment is carried out by using a drug that reduces the volume of growth in the arteries, helping to thin the blood and preventing further blockage of the lumen.
The doctor decides for himself how to treat a victim after a stroke; it depends on the age category of the patients, and on the results of the final scan of the condition of the blood vessels.
Types of interventions
If a large artery dissects, it leads to hemorrhage. In pathology, the aneurysm suddenly fills with blood, after which its complete damage is observed. Next, the formation of a dry hematoma clot is observed, which is recommended to be removed surgically in order to prevent pressure on adjacent areas.
Read also: Bulbar stroke
The operation is performed using several methods, which are selected by neurosurgeons in accordance with the indications. To treat the pathological process, it is recommended to:
- Cupping of an aneurysm . Surgery for stroke is performed through a small incision of up to 2 millimeters. It is done in the area of the femoral artery. An angiograph uses a thin catheter to penetrate the area of circulatory problems in the brain. for surgical intervention there is no need for access through the upper layer of the head.
- Vascular stenting . Therapy of the pathological process with this method is carried out to prevent complications. The operation involves inserting a thin tube into the area of the femoral blood vessel. The tube has a special expanding cartridge. A lumen is formed in the vessel, which allows a mesh-shaped stent to be inserted into it. This ensures improved blood flow.
- Trepanation of the skull . Surgical intervention involves opening the skull and going through a long rehabilitation period. Craniotomy is performed in extremely rare cases.
- Selective thrombolysis . During therapy, a special agent is used to reduce the growth in the arteries. Against this background, the blood thins, which leads to the elimination of further blockage of the lumen.
- Carotid endarterectomy . Surgery is recommended if the disease is severe. During the operation, the cholesterol plaque is completely removed, which restores tissue nutrition in the brain.
There are several types of operations after a stroke, which provides the opportunity to select the most appropriate option for the patient. The choice of surgical intervention is made by the doctor depending on the age of the patient and the severity of the disease.
Restoration of blood circulation

It is impossible to completely return a person to life after a stroke using one method of treatment. Various methods are used to prevent the consequences and development of further complications due to low oxygen supply to the brain.
It is possible to treat patients with pathologies if, together with a complex of physiotherapeutic, medicinal and surgical procedures, they also take folk remedies.
- You can prepare a medicine from the same ratio of lemons and oranges. First pass through a blender, mix the resulting mixture with 30 ml of bee honey. Infuse for 24 hours, then it is advisable to store the citrus mass in a cool place. Treatment is carried out daily three times a day, as an addition to tea, 15 grams of the finished drug. Improves blood pressure, removes toxins, frees blood vessels from cholesterol build-ups.
Read also: Medicine stroke

- Infusions from a collection of medicinal plants: valerian root, hawthorn berries, dry motherwort and evasive peony.
Each herb is infused in 100 ml of ethyl alcohol and mixed with 3 tablespoons of eucalyptus tincture, Corvalol medicine and mint tincture in the same ratio. The finished potion is poured into a dark glass container, into which a few cloves are added. Leave for two weeks in a dark place, stirring periodically. Treatment is carried out 30 minutes before meals, 1 tsp per half glass of liquid.

- Folk remedies can be prepared from 10 mulberry petals, infused in two glasses of boiling water and kept on the stove for 180 seconds. It is recommended to prepare the medicine in enamel containers. Bring to an acceptable temperature and take for at least 90–120 days. Helps treat weakened blood vessels, normalizes blood pressure.
Doctors do not recommend abusing the use of folk remedies without prior consultation.