The drug "Carbamazepine" is widely used in modern narcology. It is well tolerated, has a low incidence of side effects, and has very low hepatotoxic and hypnotic effects.
Alcoholism is an addiction with a complex pathogenesis and a variety of symptoms. A variety of medications and therapies are used to overcome alcohol addiction.
Alcoholism occurs after prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages. As a result of alcohol addiction, a person’s activity of all organs and systems is disrupted. This is reflected in the concept of alcoholic visceropathy and alcoholic illness.
Medicine has proven that alcoholism disrupts all types of neuromediation, such as:
- the metabolism of catecholamines (dopamine and serotonin) changes,
- the functioning of the opioid, GABAergic and enzyme systems changes.
Chronic alcoholism leads to poisoning of the body and entails pathological changes in the activity of calcium, potassium and sodium channels. The result of this is severe disturbances in the functioning of the brain, which are aggravated on days of abstinence from alcohol.
The main symptom of the disease is a pathological craving for alcohol, which occurs due to disruption of the activity of certain structures of the brain stem and limbic system.
A variety of pathologies of the brain and internal organs will necessarily lead to the emergence of pathological cravings for alcohol intoxication, sleep disturbances, affective disorders, the occurrence of seizures and psychotic states.
Call us right now: +7 (812) 454-00-50
or make an appointment online
By clicking on the button, you accept the terms of the company's privacy policy and give permission to process your personal data.
Prices for Ultramed clinic services
What it is?
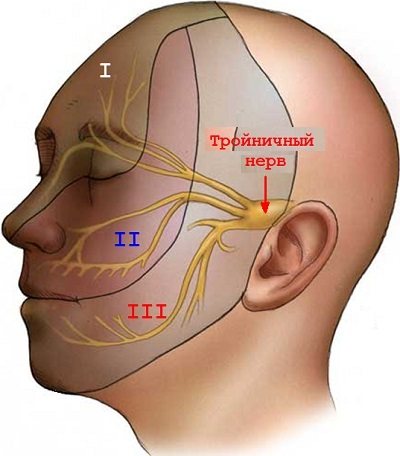
Trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal neuralgia) is a chronic disease manifested by attacks of intense, shooting, burning pain in the areas of innervation of the trigeminal nerve.
Trigeminal neuralgia is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as a syndrome characterized by sudden, short-term, intense, recurring pain in the innervation of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve, usually on one side of the face.
There is a primary (idiopathic) form of trigeminal neuralgia, which occurs in the absence of other diseases or pathological processes due to compression of the trigeminal nerve root, and a secondary (symptomatic) form, caused by a complication of another disease (infection, tumors, multiple sclerosis).
Types of neuralgia
Conventionally, all types of trigeminal neuralgia can be divided into primary (true) and secondary neuralgia.
- Primary (true) neuralgia is considered a separate pathology that occurs as a result of compression of the nerve or impaired blood supply in this area.
- Secondary neuralgia is the result of other pathologies. These include tumor processes and severe infectious diseases.
Neuralgia can affect all nerve branches at once, or manifest itself as inflammation of one or two branches.
Drug analogues
Analogs of "Carbamazepine" are well known. There are several of them produced in Russia and in different forms. Among the most popular we have highlighted the following:
- "Tegretol". The drug has a release form suitable for small children. Tablets can contain up to four hundred milligrams of the active substance, which is quite convenient in the treatment of certain diseases. However, this drug is considered one of the most expensive among others similar to Carbamazepine.
- "Carbalepsin". This drug has a reasonable price.
- "Mazepin." Many patients claim that the medicine has very convenient packaging and a minimum of contraindications.
Analogues of Carbamazepine also include Stazepin.
Causes of neuralgia
According to the mechanism of occurrence of trigeminal neuralgia, this pathology can be primary or true (isolated damage to only the trigeminal nerve) or secondary (manifestation of neuralgia as a symptom of systemic diseases of the nervous system).
The exact cause of the development of trigeminal neuralgia is not clear; as mentioned above, it is an idiopathic disease. But there are factors that most often lead to the development of this disease.
Factors that contribute to the development of trigeminal neuralgia:
1) Compression of the trigeminal nerve in the cranium or its branches after exiting the skull:
- injuries and post-traumatic scars;
- injuries in the area of the maxillotemporal joint;
- congenital anomalies of the development of bone structures of the skull;
- tumor formations of the brain or facial area along the branches of the trigeminal nerve;
- proliferation of connective tissue (adhesions) as a result of an infectious inflammatory process, sclerosis with damage to the myelin sheath of nerve fibers;
- dilatation of cerebral vessels: aneurysms (pathological dilatations of blood vessels), atherosclerosis, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, increased intracranial pressure as a result of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, congenital abnormalities of vascular development, and so on - the most common cause of the development of trigeminal neuralgia.
2) Odontogenic causes (teeth related):
- reaction to anesthesia of dental canals;
- jaw injury with damage to teeth;
- dental flux;
- “unsuccessful” filling or tooth extraction or other surgical interventions in the face and oral cavity.
3) Diseases of the nervous system:
- multiple sclerosis;
- infantile central palsy (CP);
- meningitis, meningoencephalitis (viral, tuberculous);
- epilepsy;
- brain tumors and circulatory disorders in the area of the nuclei and fibers of the trigeminal nerve and so on;
- encephalopathy due to head injuries, infectious processes, hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the brain), lack of nutrients;
4) Viral nerve lesions: herpes infection, polio, neuro-AIDS.
Side effects
Carbamazepine has quite a lot of side effects. They are usually divided into several groups:
- The central nervous system can respond to taking pills with drowsiness, headaches, general weakness of the body, nausea, neuritis, and so on.
- When taking Carbamazepine, heart disease worsens. The patient may develop thrombophlebitis, arrhythmia and angina, and an exacerbation of coronary artery disease is also likely.
- Common side effects are diarrhea, nausea and abdominal pain.
- The endocrine system reacts very sharply to the drug. Many patients notice a sharp increase in weight, swelling and similar phenomena.
- Some patients note the appearance of hallucinations, disorientation in space, loss of appetite and increased aggression.
- Among the side effects, a wide range of allergic reactions was identified.
In some experimental groups, when taking the drug, changes in taste preferences, worsening or decreased hearing, clouding of the lens and activation of psychosis were observed.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
Neuralgia of the facial nerve, according to the nature of the symptoms, is divided into the following groups: reflex and movement disorders, pain syndrome, vegetative-trophic symptoms.
Intense, paroxysmal, burning, sharp, excruciating pain. At the time of an attack, patients sometimes freeze and describe the sensation as a shooting sensation, the passage of an electric current. The duration of the spasm is from 3 seconds to several minutes, in some cases the frequency of repetitions reaches 300 per day. Localization of pain syndrome:
- Mandibular nerve: chin, lower cheek, lower lip, neck, back of the head, teeth and surface of the lower jaw.
- Maxillary: lower eyelid, upper jaw and teeth, upper cheek, nasal mucosa, upper lip, maxillary sinus.
- Ophthalmic nerve: bridge of the nose, forehead, upper eyelid, anterior scalp, inner corner of the eye, ethmoid sinus.
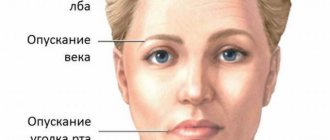
Motor and reflex disorders:
- Muscle spasms of the face (pain tic). During an attack, an involuntary muscle contraction occurs in the circular muscles of the eye, which is called blepharospasm. The symptom affects the masticatory and other facial muscles, often spreading to the entire half of the face.
- Changes occur in the corneal, superciliary, and mandibular reflexes, which is determined during examination by a doctor.
Vegetative-trophic symptoms appear during an attack; in the first stages they are mild, but as the pathology progresses they become more noticeable:
- runny nose, drooling, lacrimation;
- local redness or pallor of the skin color is observed;
- in the later stages, dry/greasy skin, swelling of the face, and loss of eyelashes develop.
If the disease is not treated in time, a point of painful pathological activity is formed in the thalamus. This causes a change in the location and nature of the pain. At this stage, eliminating the disease does not lead to recovery.
This stage is characterized by the following symptoms:
- spreads over the entire half of the face;
- any touch to the face causes pain;
- loud sound, bright light become irritants and a provoking factor of pain;
- in some cases, even the memory of the illness leads to paroxysm;
- pain syndrome develops from paroxysmal to constant (chronic);
- vegetative-trophic disorders intensify.
The disease is more common in middle-aged people. Signs of trigeminal neuralgia are diagnosed at 40-50 years of age. In most cases, the right side of the face is affected (70%). Rarely, trigeminal neuralgia can be bilateral, the disease has a cyclical nature: exacerbation is replaced by remission and deterioration occurs again, exacerbations occur in the autumn-spring period.
brief information
What does Carbamazepine help with? This is the first thing that interests patients to whom it was prescribed. Doctors may recommend taking this drug for many problems. But most often these are convulsions, epileptic seizures, depression, involuntary muscle contractions and other disorders of the nervous system.
The drug is prescribed to people of all ages. For some diseases, the tablets are even indicated for adolescents, but in no case should you take Carbamazepine (this is mentioned several times in the instructions for use) without the recommendation of your attending physician. In the case of this drug, self-medication is strictly contraindicated.
Therefore, be very careful and do not be thoughtless about the health of yourself and your loved ones.
Diagnostics
Drug therapy can eliminate pain, but with neuralgia it is necessary to identify and eliminate the underlying cause of the disease. Otherwise, attacks of pain will become more severe and appear more often.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Dental examination. Neuralgia often occurs against the background of dental diseases and poor-quality dentures.
- Consultation with a neurologist. Based on the results of the initial examination, the doctor determines further types of examination.
- MRI. The study helps to see the structure of nerves, the presence and localization of vascular pathologies, and various types of tumors.
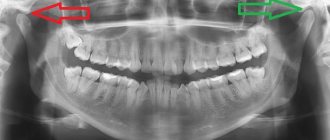
- Panoramic x-ray of the skull and teeth. Helps to see formations that could be pinching a nerve.
- Blood test - allows you to exclude the viral origin of pathological changes in the trigeminal nerve.
- Electromyography is designed to study the characteristics of the passage of impulses along a nerve.
pharmachologic effect
Antiepileptic drug.
Has a psychotropic effect. The severity of the side effect is dose-dependent.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Nervous system: accommodation paresis, headaches, asthenia, ataxia, dizziness, rarely observed abnormal involuntary movements (tics, dystonia, tremor), paresthesia, peripheral neuritis, choreoathetoid disorders, speech disorders, oculomotor disorders, orofacial dyskinesias, nystagmus, symptoms of paresis, myasthenia gravis.
Mental areas: activation of psychosis, disorientation, agitation, aggressive behavior, anxiety, decreased appetite, depression, visual hallucinations, auditory hallucinations. Allergic reactions: skin itching, erythroderma, urticaria, photosensitivity, Lyell's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Hematopoietic organs: aplastic anemia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, reticulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, lymphadenopathy. Digestive tract: pancreatitis, stomatitis, glossitis, epigastric pain, stool disorders, liver failure, jaundice, granulomatous hepatitis, increased liver enzymes.
Cardiovascular system: exacerbation of coronary artery disease, worsening of CHF, atrioventricular block with fainting, bradycardia, instability of blood pressure, impaired intracardiac conduction, arrhythmia, thromboembolic syndrome, thrombophlebitis. Metabolism, endocrine system: hyperprolactinemia, decreased L-thyroxine levels, hyponatremia, weight gain, swelling, fluid retention in the body, hypercholesterolemia, osteomalacia.
Genitourinary system: frequent urination, disturbances in the renal system, interstitial nephritis, decreased potency, hematuria, oliguria, albuminuria. Musculoskeletal system: convulsions, myalgia, arthralgia.
Sense organs: changes in the perception of pitch, hypoacusia, hyperacusia, tinnitus, hearing impairment, conjunctivitis, lens opacification, impaired taste perception. Increased sweating, acne, purpura, alopecia, skin pigmentation disorders, and hirsutism are also possible.
Metabolism of the drug is carried out using cytochrome CYP3A4. When administered simultaneously with inhibitors of this cytochrome, an increase in its concentration is observed, and, accordingly, the severity of side effects increases. Cytochrome inducers accelerate metabolic processes, reduce the level of drug concentration in the blood, reducing the severity of its therapeutic effect.
The concentration of the drug in the blood increases: Nicotinamide, Verapamil, Cimetidine, fluvoxamine, Fluoxetine, Viloxazine, Dextropropoxyphene, Felodipine, Diltiazem, acetazolamide, Desipramine, Danazol, Trefenadine, macrolides (troleandomycin, Clarithromycin, Josamycin, Erythromycin), azoles (Fluconazole, Itraconazole , Ketoconazole ), ritonavir, propoxyphene, isoniazid, Loratadine.
Phenobarbital, Cisplatin, Rifampicin, Theophylline, Primidone, Phenytoin, valproic acid, Valpromide, Doxorubicin, Cisplatin - reduce the concentration of the drug in the blood.
When the drug is combined with maprotiline and tricyclic blood pressure medications, psychosis and confusion may occur.
The active component "Carbamazepine", the instructions for use confirm this, has an antidiuretic, neurotropic, antiepileptic and psychotropic effect. The medication eliminates irritability, aggressiveness, depression, anxiety and the frequency of seizures in patients with epilepsy.
For neuralgia, this drug prevents the occurrence of paroxysmal pain. As for alcohol withdrawal syndrome, the medication for this pathology reduces tremor, increased nervous excitability, and also increases the threshold of convulsive readiness.
As an antipsychotic and mood stabilizer, Carbamazepine tablets, which help with mental problems, are very often used in the treatment of affective disorders. For diabetes insipidus, the medicine significantly reduces diuresis and thirst.
In the pediatric field, to achieve a therapeutic effect, this pharmacological agent is used in very high doses, which cannot be said about adult patients. This is due to physiological features.
The following side effects may occur during treatment:
- worsening or development of congestive heart failure;
- arrhythmias;
- arthralgia;
- taste disturbances;
- skin pigmentation disorders;
- nausea, vomiting;
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- erythema multiforme and nodosum;
- muscle weakness and paresis;
- interstitial nephritis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- depression;
- swelling;
- collapse;
- exacerbation of coronary heart disease (including the appearance or increase in frequency of angina attacks);
- anxiety;
- tics;
- lupus-like syndrome;
- abdominal pain;
- increased prolactin levels (may be accompanied by galactorrhea and gynecomastia);
- hallucinations;
- excitation;
- peripheral neuritis;
- impaired renal function (albuminuria, hematuria, oliguria, increased urea/azotemia);
- disorientation;
- general weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- angioedema;
- ataxia;
- glossitis;
- sweating;
- anaphylactic reaction;
- pulmonary hypersensitivity reactions characterized by fever, shortness of breath, pneumonitis or pneumonia;
- decrease or increase in blood pressure;
- bradycardia;
- cataract;
- headache;
- stomatitis;
- photosensitivity;
- intracardiac conduction disorders;
- drowsiness;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- oculomotor disorders;
- dry mouth;
- erythroderma;
- hives;
- purpura;
- thromboembolic syndrome;
- activation of psychosis;
- atrioventricular block with fainting;
- hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia;
- aseptic meningitis with myoclonus;
- aggressive behavior;
- alopecia;
- acne;
- pancreatitis;
- frequent urination;
- renal failure;
- changes in the perception of pitch;
- sexual dysfunction/impotence;
- nystagmus;
- paresthesia;
- dizziness;
- urinary retention;
- exfoliative dermatitis;
- weight gain;
- conjunctivitis;
- leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, leukocytosis, lymphadenopathy, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia.
How to treat trigeminal neuralgia?
The treatment method is selected depending on the cause that provoked the disease.
Carbamazepine is considered the main drug for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. It develops inhibitory processes in nerve cells that are prone to paroxysmal activity (painful excitation). The dosage of the drug is selected by the doctor, so we will not dwell in detail on the drug regimens used. Let's just say that carbamazepine is taken for a long time, up to 8 weeks.
In addition, the drug is quite toxic. Affects the liver, urinary and bronchial systems. Side effects from taking carbamazepine include various mental disorders, memory impairment, and drowsiness. Carbamazepine is contraindicated in pregnant women. The drug has a teratogenic effect - it has a toxic effect on the embryo. Carbamazepine should also not be taken by persons with glaucoma, heart blocks, or blood diseases.
During treatment with Carbamazepine, grapefruits should not be consumed, since fruit increases the manifestation of adverse reactions of the drug. To enhance the effect, it is recommended to take Carbamazepine together with Pipolfen. The duration of treatment rarely exceeds 30 days.
Other types of drugs:
- anticonvulsants – Phenibut, Baclofen;
- tranquilizers – Dizepam;
- neuroleptics – Pimozide;
- Vasotonics are prescribed for damage to cerebral vessels - Trental, Nicotinic acid.
In addition to tablets, vitamin injections of ascorbic acid and B vitamins are used in therapy. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of injections or tablets are used as painkillers - Neurodiclovit, Milgama, Diclofenac. Antidepressants for neuralgia - Amitriptyline, help eliminate nervous tension and stress in the patient. To improve metabolic processes and prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques, Atoris is prescribed.
Physiotherapy is no less useful. It can enhance the effect of any drug, as well as its effectiveness. Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is carried out using the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Electrophoresis
- Phonophoresis
- Ultrasound.
- Acupuncture.
- Laser therapy. It relieves pain because it slows down the passage of nerve impulses through the fibers.
- Exposure to electromagnetic field.
- Irradiation with ultraviolet or infrared rays. Makes it possible to eliminate pain.
Drug therapy is selected for each patient individually, depending on the severity of the pathology, as well as the characteristics of his body. [adsen]
Use of the drug "Carbamazepine" in Russia and abroad
In foreign countries, Carbamazepine has been used to relieve alcohol withdrawal syndrome since the mid-1980s.
The fact is that when relieving withdrawal symptoms, which are characterized by a decrease in the threshold of convulsive readiness, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of convulsive paroxysms.
In Russia, the drug was first used in 1973 to relieve alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The drug effectively relieves psychotic states, alcoholic hallucinosis and full-blown white fever states. In these cases, the daily dose of the drug should be no more than 1.2 g, 0.4 g 3 times a day. In psychotic conditions, the dose of the drug is increased to 1.8 - 3.4 g. In addition to the pronounced sedative effect, Carbamazepine has an antipsychotic effect. After psychosis, the drug promotes long-term sleep. According to some scientists, it is important that treatment with Carbamazepine be carried out in combination with detoxification therapy. The drug can be combined with antipsychotics, tranquilizers, antidepressants and nootropics. Combination with various psychotropic drugs expands the range of use of the drug.
Carbamazepine was also used to relieve cravings for alcohol intoxication. Clinical studies have made it possible to consider pathological cravings for alcohol as an expression of latent epileptiform activity. This was clearly manifested during the paroxysmal onset of craving for alcohol, which is often observed in female alcoholics. Carbamazepine is effective in suppressing pathological cravings for alcohol and preventing relapse of the disease.
Surgery
In the absence of effect from conservative treatment at home, as well as in cases where trigeminal neuralgia is caused by compression of the root by an anatomical formation, surgical methods are used:
- if the cause of compression is a pathologically altered vessel, then microvascular decompression is performed. The essence of the operation is to separate the vessel and the nerve using microsurgical techniques. This operation is highly effective, but very traumatic;
- percutaneous balloon compression: stopping pain impulses along a nerve by compressing its fibers using a balloon brought to the nerve using a catheter;
- percutaneous stereotactic rhizotomy: the nerve root is destroyed using an electric current supplied to the nerve using a needle in the form of an electrode;
- nerve destruction using ionizing radiation: non-invasive technique using radiation;
- glycerin injections: destruction of the nerve using glycerin injections into the nerve branch sites;
- if the cause is a tumor process, then, of course, removal of the tumor comes to the fore;
- radiofrequency ablation: destruction of nerve fibers using high temperature.
A characteristic feature of all surgical methods is a more pronounced effect when performed early. Those. The earlier this or that operation is performed, the higher the likelihood of cure. It should also be borne in mind that the disappearance of pain attacks does not occur immediately after surgical treatment, but somewhat remotely (the timing depends on the duration of the disease, the extent of the process and the type of surgical intervention). Therefore, all patients with trigeminal neuralgia need timely consultation with a doctor.
List of contraindications
“Carbamazepine” (we will give analogues and the price of the drug in the following sections of the article) has a rather modest list of contraindications for use. They can be placed in several points of a small list:
- the drug cannot be used in case of hypersensitivity to one or more components included in its composition;
- These tablets are also contraindicated for heart block, and for any type of blockade;
- the doctor will not prescribe Carbamazepine to a patient with bone marrow hematopoiesis disorders;
- It is impossible to take tablets simultaneously with certain medications (for example, you cannot combine Carbamazepine with monoamine oxidase inhibitors).
In addition to obvious contraindications, there is a certain group of people who should be very careful about taking the medicine we describe. These patients include people with kidney and liver failure, patients with diagnosed heart failure, and the elderly. Also, high intraocular pressure may be an obstacle to the prescription of Carbamazepine.
Gymnastics
Movements and contractions of the facial muscles not only cause relief during the next attack of the disease, but also help reduce compression of the nerve branches in the future. Additional positive effects of gymnastics:
- improved blood circulation;
- optimization of lymph outflow;
- restoration of the conductivity of nerve impulses (if it is disrupted);
- preventing the development of muscle congestion.
To perform the exercises, it is recommended to stand in front of a mirror to exercise better control over the process. One gymnastics session includes the following activities:
- Tilts and circular rotations of the head (2 minutes).
- Stretching the neck and head as far as possible towards each shoulder (4 times).
- Stretching the lips in a smile, bringing them into a “tube” (6 times).
- Drawing air into the cheeks, exhaling it through a narrow gap in the lips (4 times).
- Cheek retraction (6 times).
- Closing and opening the eyes with strong squeezing of the eyelids (6 times).
- Raising the eyebrows up while simultaneously fixing the forehead with the hand (6 times).
special instructions
Monotherapy for patients with epilepsy begins with small dosages with a gradual increase in the amount of the drug to achieve the desired effect. In combination therapy, it is advisable to determine the plasma concentration of carbamazepine to select the optimal dosage. When the drug is abruptly discontinued, epileptic seizures . If it is necessary to discontinue carbamazepine, they try to transfer the patient to another antiepileptic drug. During therapy, monitoring of the performance of the liver system and blood condition is required. Carbamazepine has a weak anticholinergic effect , which requires constant monitoring of intraocular pressure. The drug can reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, which requires the use of additional methods to protect against pregnancy.
MNN: Carbamazepine.
New developments
The most modern and effective methods of treating trigeminal neuralgia can be called radiosurgery using Cyber Knife. This device uses a photon beam for treatment, which penetrates precisely into the area of inflammation and eliminates it. Treatment with Cyber Knife provides high precision radiation doses, comfortable and fast healing. In addition, the procedure is absolutely safe for the patient.
Modern treatment using Cyber Knife can be considered the most effective. This technique is used not only abroad, but also in the vast expanses of the former USSR: in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus. For your information, treatment in Moscow will cost 180,000 rubles.
Features of taking the drug
During treatment, you should stop drinking alcohol and not drive a car, since Carbamizepine affects concentration.
In case of pathology of the cardiovascular system and hematological abnormalities, the medicine is taken with increased caution. The same applies to patients with impaired liver and kidney function, as well as those suffering from increased intraocular pressure. In rare cases, the drug is prescribed to elderly people and those suffering from latent psychoses.
Women planning a pregnancy need to take extra folic acid. At the beginning of treatment, it is worth monitoring the patient’s condition using an ECG. If the duration of the complex is 100 ms, then therapy is carried out with parallel administration of sodium bicarbonate.

Preventive measures
Prevention of the disease is:
- Try to eat a balanced diet and take multivitamins.
- If infectious diseases occur and are detected, especially of the oral cavity and nasopharynx, try to cure them promptly and completely.
- Avoiding hypothermia of both the face and the entire body as a whole. Dressing for the weather is much smarter than treating (sometimes unsuccessfully) severe pain.
- Systematic visits to the dentist to identify an infection that can subsequently cause illness.
- Atherosclerosis (the appearance of plaques in the blood vessels of the body, the brain is no exception), to which people of the older age group are more susceptible, is one of the causes of trigeminal neuralgia.
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat, so emphasis should be placed on preventing trigeminal neuralgia in order to avoid its consequences. If it happens that the disease has taken over, do not self-medicate, do not prescribe painkillers that relieve pain for a couple of hours, but contact an experienced specialist for a rational and complete course of treatment.
Compatibility of tablets and alcohol
Carbamazepine and alcohol are incompatible. The instructions indicate that the drug has proven to be very effective in the treatment of alcohol dependence as part of complex therapy. Based on this, many patients are confident that they can freely drink alcoholic beverages during treatment.
However, it is not. Alcohol and carbamazepine should not be taken at the same time. This rule should be followed during the entire course of treatment, since if it is violated, the patient faces serious complications.
Forecast
Neuralgia does not pose a direct threat to life. Trigeminal neuralgia is no exception. However, the human psyche can be greatly affected by this disease. Frequent and very intense pain syndromes quickly drive the patient into a state of depression. He begins to avoid communication and begins to lead an antisocial lifestyle. The development of a wide variety of mental pathologies may begin.
Timely treatment will minimize damage to a person’s mental health. Even in the most difficult situations, you should not endure pain. It is better to decide on surgery, since the disease can be effectively treated even in the most difficult situations.