Causes of pathology
Neuralgia – pain in the scapula area radiating to the shoulder or lower back – occurs due to the following diseases:
- disorders of the spinal cord or peripheral nerves;
- protrusion of the wall of the intervertebral disc (protrusion) and pinching of the nerve root, which extends into the scapula;
- intervertebral hernia;
- inflammatory process in the muscles of the neck, thoracic or spinal region;
- pathology occurring in the respiratory tract, kidneys, liver, pancreas, gall bladder, stomach, duodenum, heart;
- herpes zoster;
- the formation of a benign or malignant tumor in the spine.
The cause of the symptom in the suprascapular or subscapular region is injury to the spine or thoracic region. Psychosomatics also influences the development of pain.
Scapular neuralgia on the left or right is a symptom of hypothermia, excessive physical activity, or vice versa - a sedentary lifestyle.
Types of pain between the shoulder blades
The nature of the pain can say a lot about the reasons for its occurrence. The pain between the shoulder blades is most often aching, pulling. Therefore, they rarely force people to immediately seek medical help, which leads to the progression of existing diseases. They recur regularly and can persist for quite a long time, which indicates a chronic course of the pathology.
Acute pain in the upper back occurs quite rarely. They appear suddenly, quickly intensify and then gradually disappear. They are the ones who most often bring patients to the doctor. Although chronic mild pain is an equally compelling reason to consult a specialist.
Often the appearance and intensification of pain is facilitated by:
- physical exercise;
- prolonged maintenance of a static position, including prolonged sitting or standing;
- sleeping in an awkward position.
Pain between the shoulder blades can also be burning, which requires making an appointment with a doctor as quickly as possible, and in some situations, receiving emergency medical care.
Initially, pain between the shoulder blades can eventually begin to radiate to the neck, arms and shoulders. This is often accompanied by a feeling of numbness, goosebumps or other sensory disturbances, as well as limited mobility of the arms and body or disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, i.e. the development of radicular syndrome.
It is a consequence of compression of the spinal roots by intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies, their processes or other anatomical structures. In this case, the localization of discomfort directly depends on the level at which spinal motion segment the compressed spinal root is located. If the nerves localized at the level of the first thoracic vertebra are pinched, sensory disturbances will be observed on the inner surface of the forearm, shoulder, and also in the armpit. And with compression of the nerves located at the level of the last, 11-12th vertebra of the thoracic spine, the development of pelvic organ dysfunction is possible, which may be accompanied by disturbance or loss of control over urination and defecation.
Clinical picture
To determine the source of neuralgia under the right or left shoulder blade, an important diagnostic step is to study the nature and frequency of unpleasant sensations. Interscapular neuralgia occurs with sudden lumbago, radiating to nearby areas: limbs, lower back, neck, armpits. The discomfort increases when inhaling and when turning the body.
The clinical picture differs depending on the primary process:
- The functioning of the liver, kidneys, and gall bladder is impaired. Spasms and inflammatory processes are accompanied by acute, cutting symptoms. If the gallbladder ducts are blocked, pain may occur in the intercostal space on the right, the scapular region, or the right half of the neck.
- Coronary heart disease develops, the condition of the spinal column, spinal cord, and digestive system organs is impaired. In such cases, the syndrome occurs paroxysmally only on the left or only on the right side. The pain radiates to the shoulder blade and lower back, accompanied by numbness and tingling. In gastrointestinal pathologies, the intensity of the symptom may depend on food and be seasonal when chronic inflammation is present.
- There is a history of trauma. A characteristic symptom is an increase in the intensity of the attack when moving the body. Edema, swelling appears in the area of injury, and possible damage to the integrity of the skin.
- The cause of pain in the shoulder blade is a psychological factor. The discomfort is acute or dull in nature, spreading to the lower back, limbs, and cervical region. The pain is supplemented by apathy or irritability, increased sweating, and anxiety.
- Herpes zoster develops. Painful symptoms appear around the circumference, covering the shoulder blades and thoracic region (ribs). The intensity of discomfort increases at night.
- The muscles are inflamed. Myositis is accompanied by pain in the scapular region, radiating to the anterior thoracic area, arm, neck, and lower back. Inhalation discomfort increases.
The cause of pain in the scapula area can be determined based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis.
Symptoms. Features of postherpetic neuralgia
The disease is difficult to diagnose and requires careful examination. Signs of neuralgia can be deceptive and often cause the problem to be misidentified. Symptoms may correspond to many inflammatory processes, cardiac pathologies or gastrointestinal diseases.
Characteristic signs of intercostal neuralgia:
- Acute pain in the chest, side, shoulder blade, along the ribs. The feeling of discomfort is so strong, especially at the initial stage of development of the pathology, that it is sometimes mistaken for a symptom of a heart attack.
- Increased pain when moving - lifting limbs and turning the body.
- Shortness of breath and confused, shallow breathing due to increased pain with deep inspiration.
- A sharp increase in pain with a sharp shaking of the body - sneezing, coughing, laughing.
- The peculiarity of the pain is its lightning speed, shooting - the patient stops moving and freezes.
How to distinguish intercostal neuralgia from other diseases? Differentiation of symptoms:
- Extreme calm of the patient. A person tries to find a comfortable body position and does not show concern - this behavior is characteristic of a heart attack.
- Neuralgia may be accompanied by cyanosis of the fingers, nose, lips, ears, hypotension, pale skin and cold, sticky sweat.
- Thoracic radiculitis is characterized by a lack of desire to bend in half, as patients with pancreatitis do.
If you suspect a cardiac nature of the pain, you must immediately give the patient validol or nitroglycerin and call an ambulance.
If the disease occurs against the background of active activity of the herpes simplex virus in the body, then both the symptoms and therapy will be different.
A noticeable sign is that a characteristic blistering rash appears along the intercostal nerves on the surface of the skin. Over time, the formations burst and dry out to crusts, this is accompanied by itching, redness, and swelling in the area of the rash.
The neurotropic herpes virus remains in the human body and cannot be completely cured. Acute manifestations occur against the background of hypothermia, loss of strength, fatigue and decreased immunity. At the first symptoms of virus activation, you must immediately take an acyclovir-based drug and apply the product in the form of a cream or ointment to the skin. Taking the drug is necessary as early as possible, every hour is important, because delay will lead to the fact that the moment will be missed and the patient will suffer from unpleasant and painful symptoms for a long time.
ul
Identifying the cause
First of all, the doctor palpates the diseased area, identifying areas with increased pain and the presence of unnatural neoplasms. Anamnesis is examined: injuries preceding the symptom, concomitant diseases, possible provoking factors.
To confirm the diagnosis and identify the cause of pain, instrumental and laboratory tests are performed:
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography. MRI can detect tumor-like neoplasms and signs of destruction of the nerve sheath. Based on the CT results, areas with the passage of nerves are examined. Before examination, you need to remove all metal products to avoid distortion of the picture on the monitor.
- Electrocardiography. The diagnostic measure allows you to study the electrical activity of the heart. Prescribed if there is suspicion of intercostal neuralgia resembling angina pectoris.
- X-ray examination. The method is used to examine the organs of the respiratory system, scapula for tumor-like and other etiologies of neoplasms, complications after injury.
- Lab tests. Based on the diagnostic results, it is possible to identify signs of an inflammatory process occurring in the body: an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an increase in the volume of leukocytes, red blood cells, etc.
If necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed: oncologist, infectious disease specialist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
Diagnostics
Many people do not know which doctor treats this disease.
To make a diagnosis, you need to consult a neurologist. With intercostal neuralgia, diagnosis does not cause difficulties; symptoms and treatment largely depend on the concomitant disease. The attending physician will perform palpation, during which the patient will feel increased pain in the area of the affected nerve. It is very important to undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude pathologies of the heart and internal organs. The neurologist may refer you to another specialist to rule out pathologies of the heart (for neuralgia on the left), kidneys (for lesions in the lower part of the ribs), and also for an MRI of the spine.
An ECG of the heart, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and kidneys, as well as an X-ray or magnetic resonance examination of the thoracic region are required.
Since pain between the shoulder blades can indicate the course of a variety of diseases and pathologies, subsequent examination is carried out only on the basis of the diagnosis. If you suspect the presence of cardiovascular diseases, you need to do an ultrasound examination of the heart and an electrocardiogram.
To exclude diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of these organs. If musculoskeletal disorders occur, an x-ray and, if necessary, a tomography should be performed. All these examination methods must be performed first in order to exclude the occurrence of more serious problems and disorders in the body.
To determine what exactly could have pinched the nerve endings and for what reasons this happened, you need to perform a CT or MRI. This will allow you to assess the condition of the spine and identify damage or curvature of the intervertebral discs. Electromyography helps determine the presence of damage to the nerve endings responsible for the motor activity of certain muscle groups.
A nerve conduction study is also carried out, which can reveal damaged nerves. It is advisable to perform a manual examination and blood test.
How to treat neuralgia
The main condition for successful treatment is its initiation at stage 1 of the disease.
Medications are prescribed individually, based on the source of nerve damage: anti-inflammatory, chondroprotectors, antitumor, etc. Painful symptoms can be treated with painkillers in the form of ointments, gels, and tablets. Medicines containing diclofenac and ketoprofen quickly relieve pain.
To reduce muscle tone, it is recommended to take muscle relaxants. To strengthen the body's protective function and speed up recovery, vitamin complexes with calcium and B vitamins are prescribed.
During the rehabilitation period after undergoing the main treatment, measures are prescribed to restore the functioning of the nerves:
- sessions of physiotherapeutic procedures (laser exposure, etc.);
- kinesitherapy;
- massage;
- therapeutic exercises.
At home, you can reduce the intensity of pain using folk remedies. This is a first aid measure that acts symptomatically and does not eliminate the cause of neuralgia.
Compositions are prepared from natural ingredients: burdock leaves, black radish, flax seeds, herbs, bee or snake venom, essential oils. They are used for oral administration or rubbing on the affected area.
At home
Treatment at home is possible only if there is a slight manifestation of the disease and it is impossible for some reason to see a doctor.
- During the acute stage of the disease, it is strongly recommended to maintain bed rest for several days. The mattress should be quite rigid; it is better to place some hard surface under it during this period.
- Dry warm compresses can be used to relieve pain.
- It is important to exclude or limit physical activity during the acute period.

It is permissible to take medications at home by agreement with your doctor. Self-administration is not recommended, since the presence of other diseases that give similar symptoms, such as angina, must first be excluded.
Important! Once the acute stage has passed, going to the doctor should not be postponed.
Drug treatment
When treating intercostal neuralgia on the right, a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is first prescribed to relieve pain. It is possible to use painkillers to alleviate the patient's condition.
Ointments and creams are used as a local anesthetic:
- anti-inflammatory and analgesic ointments based on diclofenac;
- anesthetic ointments and gels with the active substance – ketaprofen.

Ointments based on bee and snake venom are used, which not only relieve pain, but also accelerate the elimination of substances that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process and increase blood flow. Turpentine ointment, camphor, and menthol have a local irritant effect that reduces pain, which can either be added to ready-made preparations or purchased creams that contain these substances.
- To reduce muscle spasm, muscle relaxants are taken, which reduces pain and increases mobility.
- For a general strengthening effect, a course of B vitamins and calcium is additionally prescribed.
- As part of a general set of measures, and in case of excessively acute pain, a novocaine blockade can be administered to alleviate the condition.
Preventive measures
In order not to waste time and money on treating neuralgia, it is recommended to take care of prevention in advance:
- exclude local and general hypothermia;
- do not abuse increased physical activity;
- promptly treat postural disorders;
- do not lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- maintain proper nutrition.
If your job requires you to be in a sitting position for a long time, you need to periodically do a warm-up in the form of light exercises: body turns, bending, rotational movements, etc. Pool exercises and horseback riding are useful, which helps strengthen the joint-muscular system and spine.
If pain in the shoulder blade occurs not for the first time, does not go away for a long time, and other symptoms appear (difficulty breathing, making body movements, etc.), you need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment for the symptoms of neuralgia under the shoulder blade on the left and right. Self-therapy rarely leads to recovery and more often, on the contrary, causes additional health problems.
Possible complications, prognosis and prevention

Self-medication or ignoring the first symptoms can lead to complications:
- neuralgia of the brachial nerve takes on a chronic form and becomes fixed;
- the disease degenerates into plexitis (the nerve fibers of the brachial plexus are damaged);
- risk of developing Horner's syndrome (affects the eyeball);
- significant damage to the nerve plexuses leads to loss of sensitivity and decreased mobility;
- in critical cases, paralysis of the arm and complete muscle atrophy are possible.
It is known that preventing a disease is easier than completely eradicating it.
Prevention:
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- exclude situations of injury (ice, moderate sports activities);
- timely treatment of viral infections;
- balanced diet (vitamins, meat, dairy products);
- Hardening, sports and a healthy lifestyle strengthen the immune system and resist any viruses and infections.
In conclusion, brachial neuralgia should be treated immediately . Only in this case is a complete recovery guaranteed without complications or relapses.
All types of pain in the shoulder blades and their treatment
- 3 minutes to read

Pain under the shoulder blades can be a consequence of cardiac, neurological, gastrointestinal diseases, including pathologies of the lungs, bronchi, spine, intervertebral hernia or others. Manifestations may be felt differently, depending on their severity and location.
Content
Treatment with folk remedies
Non-drug remedies can help relieve the condition and reduce pain.
Flax seeds
Steamed flax seeds can be used as a source of dry heat. To do this, they are brewed in boiling water, taken out, dried with a towel and then poured into a cotton bag and applied to the sore spot.
Sage baths
It is also useful to take warm baths with sage and sea salt before bed to relax and reduce muscle spasms. The sage must first be filled with warm water and allowed to brew. Take sage - 4-5 tbsp. l. per glass of water. The infusion is poured into the bathtub, a couple of tablespoons of sea salt are added. Take a bath for no more than 15 minutes.
An infusion of rue herb helps with pain. To prepare it, 2 tbsp. l. the herbs are poured with 1 glass of alcohol, closed tightly with a lid, put in a dark place and infused for a week.
- Steamed and ground aspen buds are used as an ointment, which are mixed with petroleum jelly at a ratio of 1:4.
- Additionally, for a warming effect, you can wear woolen clothes in the form of a vest and make bandages around the sore spot.
Compress
Use a mixture of spices as a warming compress: red chili pepper – 1 tsp, ground ginger – 2 tsp, turmeric – 1 tsp. Add a little water or vegetable oil to the resulting mixture. Apply the mixture to a clean cloth and apply to the sore area and wrap with a clean bandage. The bandage is worn until it begins to burn.
To use as a warm dry compress, you can use boiled eggs; they can be applied both in felt form and in the shell, after wrapping them in a clean rag and holding them until they cool down.
Good afternoon. What kind of tincture exactly?
Hello! Take a Nise tablet and rub it with menovazine and diclofec. Pepper patch.
Hello, this is inflammation. We need to treat.
Discussion:
Hello! Today I had pain under my right shoulder blade and in the thoracic region it seemed that everything was stiff and it was difficult to take a breath. I think this is intercostal neuralgia. What can be done to make it easier?
Take Nemesil or inject Movalis.
It’s possible, but it’s better to consult a neurologist.
There was an acute pain in the right hypochondrium at the back, I took a painkiller, the acute pain went away but the dull pain remained, the doctors prescribed a bunch of painkillers: injections and pills, all very strong, the urine test was good, what else could hurt, I didn’t prescribe an ultrasound, swallow chemistry in such quantities and I don’t want to inject, is there another treatment?
Anna, good afternoon.
If the doctor prescribed a medicine, then you need to take it. Without an examination, you cannot be told what can be done. Just take the medicine according to the instructions!
Good afternoon. After my first child, my back started to hurt. She gave birth to a second one. Heavy. 14 kg per year. 4 days ago the liver area started to hurt. I was scared because My heart is so sick that it can give away. We went for an abdominal and heart ultrasound. It's stable there. But it hurts, they told me to see a neurologist. But now I can’t get there.
You have a dystrophic disorder of the spine; during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, you experienced stress on your back and could not withstand it. I strongly recommend getting an x-ray. Pentalgin will help reduce pain. Do massages and physical therapy - it will be useful for you.
Good afternoon ! Such a problem, the back muscles in the upper part of the spine began to ache on both sides along the spine, when I tilted my head down there was a very strong pain, there was no physical activity, I can’t even associate it with anything! The next day there was a very strong pain in the front right when pressing on the ribs, I couldn’t move, there was a sharp pain!
Anton, hello. Intercostal neuralgia is not necessarily a consequence of excessive physical activity. It may appear against the background of developing osteochondrosis, after suffering stress, hypothermia or infection. First you need to exclude heart pathologies, then do an MRI of the cervical and thoracic spine.
Neuralgia is a complication of some other disease, so the disease requires an integrated approach to treatment. First of all, in case of inflammation of the intercostal nerves, symptomatic therapy is prescribed, aimed at stopping the attack and improving the patient’s mobility.
The following is used as therapy:
- medicinal methods;
- local treatment;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- folk remedies.
Treatment for intercostal neuralgia is selected by a doctor. If you want to supplement therapy with traditional methods, you should consult a specialist. With neuralgia, the consequences are usually favorable if you start treating the attack in a timely manner.
Traditional methods of getting rid of neuralgia are aimed at restoring normal blood microcirculation in the intercostal space, which helps relieve pain, inflammation and muscle spasms. Traditional medicine alone is powerless against the disease, so these methods should be used as a complement to, and not a replacement for, drug treatment.
- Grate one radish and horseradish. Squeeze the resulting mass thoroughly and rub the slightly warmed juice onto the affected area.
- Soak a gauze compress in pepper tincture and apply to the sore spot for 15 minutes.
- Add two drops of peppermint essential extract to regular vegetable oil and rub into the affected area.
- To relieve spasms, warm baths with the addition of coarse sea salt and a decoction of chamomile and sage are recommended. You should take this bath for 20 minutes daily.
Before using folk remedies, it is recommended to consult a doctor about the effectiveness of such treatment.
In the absence of complications, conservative methods successfully cope with pinched nerve endings, and painful manifestations completely go away, after which you can begin therapy with traditional methods. For this, tools such as:
- treatment with ointments;
- taking a bath;
- use of infusions.
To treat pinched nerve endings, ointments prepared from natural ingredients are widely used. To prepare the ointment, you need to grind the bay leaf and juniper needles until smooth. Add a little melted butter to the mixture. The resulting product is applied to the damaged area. The ointment helps relieve pain and helps relax muscles.
Special medicinal infusions are also widely used for therapy. Such products are used for internal and external use. Wormwood infusion is used as a pain reliever. To do this, you need to infuse wormwood inflorescences and rub them into the damaged area. For internal use, yarrow herb is suitable, which needs to be brewed and taken 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.
Symptoms on the left side
Pain under the shoulder blades occurs for various reasons; based on their symptoms, the disease that is the cause of the discomfort can be diagnosed.
Acute
Occurs as a result of physical strain, including sudden lifting of a heavy load. It may periodically weaken, but even with a slight sudden movement it can resume. These are signs of herniated discs, angina pectoris or perforation of an ulcer.
Aching or pulling
They occur as a result of diseases such as pyelonephritis, osteochondrosis, tuberculosis, gastritis or inflammatory processes.
Dumb
Occurs at the bottom of the scapula with a return to the cervical region. If it periodically disappears and reappears, this is a sign of cervical osteochondrosis. The pathology may be accompanied by dizziness and numbness of the limbs.
It especially makes itself felt when you stay in the same uncomfortable position for a long time. Diseases that caused it: pleurisy, inflammatory processes of various types, pyelonephritis, tuberculosis, scoliosis.
Burning
These are manifestations that indicate serious diseases: spinal disc deformation, heart attack, angina. At the same time, the skin becomes pale.
Pressing
A feeling of squeezing occurs with vegetative-vascular dystonia or a pre-infarction state. Similar dysfunctions appear in ischemic heart disease and hypertensive crisis.
Stabbing
Indicates the development of pneumonia, intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis.
Constant
Accompanied by exposure to physical overload, tuberculosis, osteochondrosis, and the presence of tumors. Discomfort in the area of the left shoulder blade disappears, and with loads it increases, accompanied by a burning sensation.
Sharp
This discomfort is caused by intercostal neuralgia. It is most noticeable when inhaling.
Pulsating
They occur as a result of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and stomach ulcers.
Pulling
Occurs in cervical osteochondrosis. They can occur with incorrect movements and uncomfortable postures.
Frequent
Occurs with lung diseases accompanied by coughing or sneezing.
Causes of pain under the left shoulder blade
What does it mean? There are a sufficient number of causes of pain under the left shoulder blade in adults; they can be associated both with problems with the shoulder blade itself and with diseases of the internal organs. Let's look at the most likely causes of this condition below.
Certain diseases of the musculoskeletal system may be accompanied by pain in the area of the left shoulder blade. Most often it manifests itself like this:
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic or cervical spine.
- Intercostal neuralgia.
- Traumatic injury to the scapula (compression injury to the suprascapular nerve).
- Rib fracture.
- Sprengel's disease (scapula alata) - pterygoid scapula.
- Myofascial syndrome.
Cardiac diseases. It cannot be said that the pain is only in the area of the left shoulder blade. The pain then moves to the left arm, then goes to the collarbone area, then falls to the lower abdomen. Depending on the disease, patients experience a feeling of lack of air, a feeling of cardiac arrest or a constriction of the throat. At this time, the chest seems to them to be compressed or overcome by a feeling of heat. These are the following diseases:
- IHD – coronary heart disease.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Pericarditis.
- Angina pectoris (unstable, stable).
- Mitral valve prolapse.
- Less commonly, aortic aneurysm.
Constant pain under the left shoulder blade may indicate diseases of the bronchopulmonary system. In this case, pain sensations are always directed towards the affected lung, they are of medium intensity and aching in nature, and are localized under the left shoulder blade to one painful point. It could be:
- Left-sided pneumonia.
- Pleurisy (dry, left-sided).
- Tracheobronchitis with autonomic dysfunction.
- Acute bronchitis.
- Left lung abscess.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Peptic ulcer (Ulcus gastrica) is a peptic ulcer of the stomach.
- Ulcus duodeni – duodenal ulcer.
- Esophageal spasm.
- GERD – gasesophageal reflux disease.
- Rarely - exacerbation of pancreatitis.
Typical causes of pain under the left shoulder blade are ranked as follows by prevalence:
- Cervical osteochondrosis, which most often manifests itself as unilateral pain at the bottom of the os occipitale - the occipital bone. The pain is aching in nature, intensifies with active movements of the head and constantly radiates under the shoulder blade, into the arm.
- Another disease, a typical symptom of which is pain under the left shoulder blade, is intercostal neuralgia. It is a common consequence of osteochondrosis and is manifested by lumbago and intense pain of a girdle nature, radiating to the right or left, including under the shoulder blade.
- Peptic ulcer (peptic ulcer). The symptom is most often caused by seasonality, depends on the nutritional factor and is characterized by paroxysmal, radiating pain.
Based on this brief anatomical review, all causes of pain under the left shoulder blade can be divided into two large groups:
- Pain associated with pathology of internal organs (cardiovascular pathology, respiratory diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and spleen).
- Pain associated with pathology of the musculoskeletal system and muscle pain, including neurogenic pain.
To find out why there is pain under the left shoulder blade, you should undergo a comprehensive examination, which, based on specific complaints and examination data, will be prescribed by your attending physician. After all, pain in different diseases will vary in nature, intensity and provoking factors.
Symptoms on the right
Pain in the area of the right shoulder blade is divided into several types.
Giving
Indicates cholelithiasis. It appears periodically, is acute in nature, accompanied by high body temperature, nausea, vomiting and fever. The skin has a yellow tint.
Aching
This sign confirms the presence of chronic diseases occurring in the digestive organs.
Dumb
Accompanied by pathologies of the liver or kidneys.
Strong
This sign indicates the presence of many diseases, for example, cholecystitis, renal colic, pancreatitis, pleural perforation, displacement of vertebral discs.
Sharp
It is provoked by pathologies of hepatic colic and diaphragm. In liver diseases it is accompanied by vomiting.
Acute
It intensifies when inhaling air or bending the body, and is a consequence of pathologies of the liver or gall bladder. The causes of discomfort are stress, sleep dysfunction, irritability, and increased sweating.
Pulling
They are a consequence of osteochondrosis of the neck, and less often, it is a sign of the development of tumors of the right organs: kidney, lung or pancreas.
Burning
This sensation is the cause of pinched nerve endings. Sometimes this occurs with the development of angina or the initial stage of pneumonia.
Constant
This is a sign of bile duct pathology, characterized by a yellowish tint to the skin.
Stabbing
It happens with osteochondrosis. It appears unexpectedly and disappears quickly. The reasons may be physical overload or an uncomfortable posture when doing work.
Pressing
It is provoked by diseases of the diaphragm. This pain intensifies when you inhale and is accompanied by low blood pressure and pale skin.
Pulsating
Confirms the presence of chronic pathologies that make themselves felt in this way.
Sudden
Accompanied by hepatic colic or spontaneous pneumothorax syndrome.
Based on the above symptoms, you can determine what examinations to send the patient to clarify the diagnosis and what assistance to provide to relieve pain.
Drug treatment
When treating pinched nerve endings in the area of the shoulder blades, various groups of medications are used, in particular:
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- ointments;
- injections.
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs help eliminate pain and reduce inflammation. For therapy, drugs such as Diclofenac, Movalis, Ketonal, Ibuprofen are used.
Also, in case of pinched and inflamed nerve endings, pain-relieving ointments and gels are used, which must be prescribed by a doctor, as they can provoke allergies. To eliminate painful manifestations, ointments such as Finalgon, Betalgon, Viprosal, Carmolis are used.
Diagnosis of diseases
Depending on the manifestation of symptoms, the neurologist prescribes consultations with other specialists, for example, a surgeon, oncologist, dermatovenerologist, rheumatologist, traumatologist and cardiologist. To clarify the diagnosis, the following examinations are prescribed:
- ultrasonic;
- X-ray;
- tomographic;
- electrocardiograms;
- laboratory tests of the composition of blood, urine, feces;
- biopsy and others.
Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed: inpatient or outpatient - this conclusion is made by the doctor.
Treatment of the disease
A full course of treatment can be prescribed by a doctor after examining and examining the patient. Self-treatment, including taking medications, in this case may not only be useless, but also cause harm to health if another disease is hidden under the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia.
Examinations may include:
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- magnetic resonance imaging or MRI;
- radiography;
- computed tomography or CT scan;
- additional studies - electrospondylography, myelography, contrast discography.
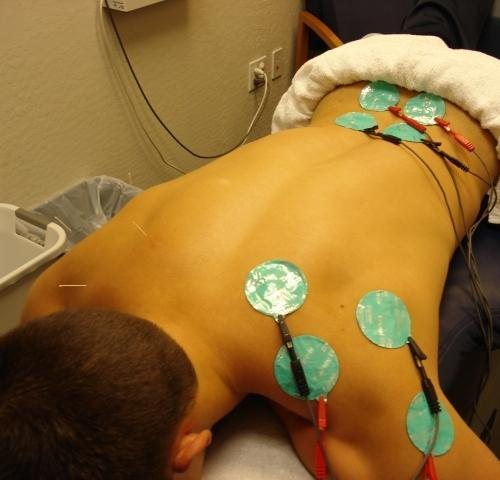
Treatment includes complex measures depending on the causes and source of intercostal neuralgia. Primary measures are aimed at relieving acute pain syndrome with medications.
Next, a course of rehabilitation measures is carried out to restore health, as well as aimed at eliminating the consequences of intercostal neuralgia:
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- kinesitherapy;
- laser therapy;
- massotherapy.
First of all, the main task is to relieve acute pain syndrome, which is extremely inconvenient, causes physical distress and can even lead to immobility of the patient due to acute attacks when trying to move.
Treatment methods
Effective treatment is to eliminate the causes of the disease at the initial stage of their development. Initially, treatment is aimed at eliminating pain, and then at tissue regeneration in the damaged area. As a rule, modern medicine uses reflex methods for neurological causes of pain:
- acupuncture;
- vacuum therapy;
- pharmacopuncture (or injections of drugs at certain points);
- treatment with laser beams;
- magnetotherapy;
- other methods.
If necessary, painkillers, anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant drugs and B vitamins are prescribed.
If repeated intercostal neuralgia occurs, treatment is prescribed aimed at eliminating the patient’s poor health. Among other things, physical therapy is prescribed.
Treatment of any disease should be aimed at eliminating its causes, and only a specialist can correctly prescribe it, according to the results of the research. The causes of pain in the area of the right or left shoulder blades are various pathologies, and for proper treatment it is important to properly identify the disease.
Treatment of pain between the shoulder blades
In the vast majority of cases, conservative therapy is initially prescribed. It is especially effective when intervening during the pathological process in the early stages and allows you to completely eliminate the changes that have arisen. Only if severe complications develop, the patient is immediately referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon, since in case of sequestered intervertebral hernia, severe curvature of the spine or advanced spondylosis, the patient’s condition can only be improved through surgery. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible if pain occurs between the shoulder blades.
Conservative therapy is always comprehensive and involves taking measures to improve the patient’s well-being, as well as eliminating the cause of discomfort. Its main components are:
- drug therapy;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- Exercise therapy.

To increase the effectiveness of treatment, neurologists recommend that patients reconsider their habits and lifestyle, in particular:
- normalize weight (but strict diets and excessive physical activity are unacceptable; a transition to a balanced diet and moderate physical activity is recommended);
- refuse to lift and carry heavy objects, grueling workouts in the gym;
- workers in “sedentary” professions should increase their level of physical activity, do a warm-up every hour, and walk more;
- buy an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- introduce into your daily diet foods rich in vitamins and minerals (fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, etc.).
Regular swimming has a very positive effect on the condition of the spine and the body as a whole. Usually visiting the pool 2-3 times a week is enough.
Drug therapy
The main goals of drug therapy are to eliminate pain between the shoulder blades, inflammation and activate the body's recovery processes. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, widely used both to relieve various types of inflammatory processes and to eliminate pain;
- corticosteroids are drugs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and are prescribed to patients with severe inflammatory processes that cannot be eliminated with NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants - medications that help eliminate muscle spasms caused by pain of vertebrogenic origin;
- chondroprotectors – drugs used in the initial stages of degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs and helping to restore their elasticity and strength;
- B vitamins are agents used to improve nerve conduction and improve the functioning of internal organs.
If the patient has detected pathologies of the heart, gastrointestinal tract and others, additional treatment is prescribed, which involves the use of antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, antihypertensives or other drugs.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy can be called the basis of the treatment of spinal diseases. It should not be confused with therapeutic massage. If the latter only allows you to improve the condition of soft tissues and activate blood circulation, then manual therapy involves the direct impact of a specialist’s hands on the spine.
Thanks to the use of certain techniques of manipulation, mobilization, post-isometric relaxation, osteopathy and especially the Gritsenko technique, it is possible not only to restore the correct position of the vertebrae and the straightness of the spinal column, but also to increase the distance between them to the optimal value. Due to this, the pressure on the intervertebral discs sharply decreases, which creates optimal conditions for their regeneration. Also, a chiropractor can eliminate the pressure of various anatomical structures on the spinal roots, due to which the radicular syndrome is overcome, i.e. pain in the hands, sensory disturbances, a feeling of numbness go away, and the functioning of the pelvic organs also normalizes.
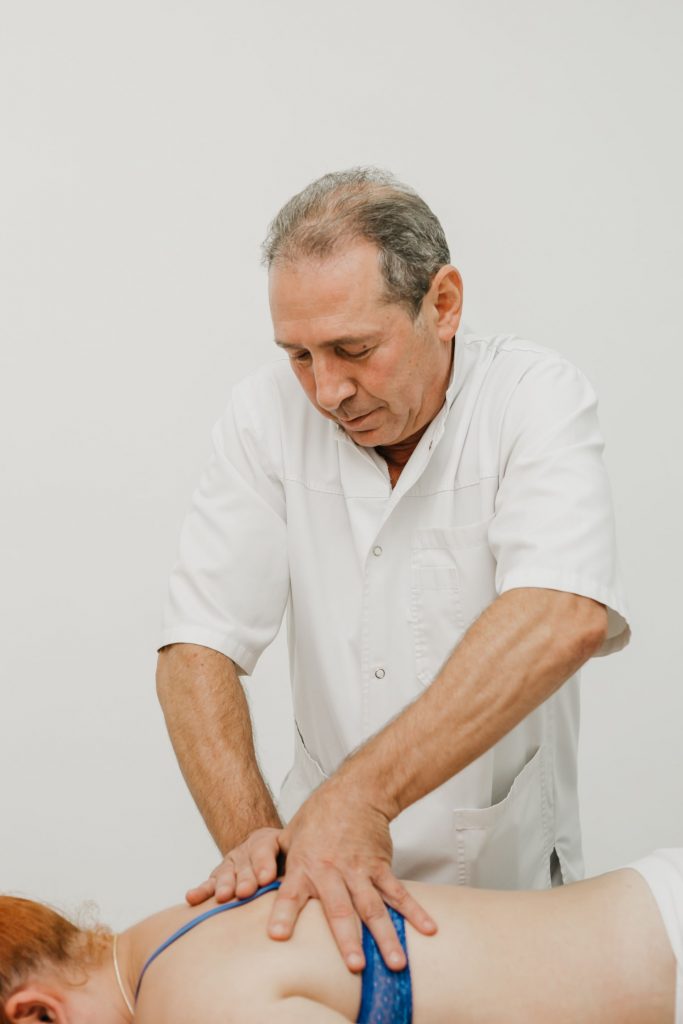

In addition, manual therapy allows you to eliminate functional blocks and muscle spasms, which has a beneficial effect on a person’s mobility and well-being. Since normalization of muscle tone reduces pain between the shoulder blades, improves tissue trophism and transmission of nerve impulses. The manual effect itself, as well as with therapeutic massage, has a beneficial effect on the quality of blood circulation. Thanks to this, all tissues receive the maximum of the substances they need, subject to the correct diet and taking medications prescribed by a doctor, which contributes to their speedy recovery.
An additional “bonus” of manual therapy carried out according to the Gritsenko method is strengthening the immune system and enhancing the body’s adaptive abilities. Patients may notice the first improvements in well-being after the first session. But to obtain the maximum possible, and most importantly, lasting result, you need to undergo a full course of treatment, the duration of which is selected individually.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the acute period of the disease. With their help, you can potentiate the effect of other therapeutic measures, as well as achieve analgesic, anti-inflammatory, reparative, antispasmodic effects, as well as improve microcirculation in tissues.
Often, for spinal pathologies, courses are indicated:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF, etc.
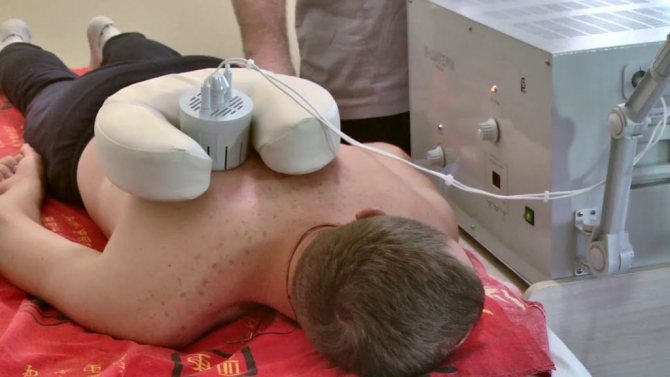
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy is an essential component of the treatment of almost any disease. It involves daily performance of an individually developed set of exercises that will help normalize muscle tone, activate blood circulation and increase the flexibility of the spine.
It is important not to use the complexes presented on the Internet, but to contact a specialist who will individually develop a training program for a specific patient. In this case, it will take into account not only the peculiarities of the condition of the spine, but also the age of the patient, any concomitant diseases he has, as well as the level of physical fitness, which will allow achieving the maximum effect from the exercises and eliminating the possibility of harm to the person.
The first classes are recommended to be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. This is necessary so that the patient can fully master the technique of performing each exercise and perform it correctly in the future at home. During exercise, it is important to avoid any sudden movements and overexertion, and if pain occurs, you should immediately contact your doctor.

Thus, pain between the shoulder blades may indicate the development of serious diseases. Therefore, when it appears, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist, otherwise the disease can lead to complications of various types, including disability. If you start treatment right away, you can almost always quickly achieve complete recovery of the body and eliminate the pain syndrome, along with the causes that cause it.
Why does the pathological condition occur?
Thoracalgia is not an independent disease and occurs as a result of the development of diseases of internal organs or other disorders. The cause of intercostal neuralgia may be severe osteochondrosis, in which case the nerve roots of the thoracic region are compressed due to the impact of the hernia on the spine.
Tumors of the spinal column can similarly affect the nerve fibers of the sternum. The following pathologies can cause intercostal neuralgia:
- hormonal disorders, diabetes or menopause;
- multiple sclerosis and polyradiculoneuritis;
- aortic aneurysm;
- stomach or duodenal ulcers;
- herp infection that occurs after herpes zoster;
- allergic reactions;
- pleural inflammatory processes and various deformities of the thoracic region.
Food, drug or alcohol poisoning often leads to chest pain. This occurs due to the effect of toxins on the nervous system and the body as a whole. Thoracic radiculitis may occur due to other factors, which include:
- hypothermia;
- stressful situations and constant worries;
- exposure to infection;
- lack of B vitamins;
- underwear that is too tight;
- physical stress.
How does the pathology manifest itself?
The chest consists of 12 pairs of ribs, between which are nerve roots. When one or more of them decompresses, pain occurs. Intercostal neuralgia on the left is determined by the unilateral manifestation of pain. In such cases, pain radiates towards the heart and hypochondrium. They can spread under the shoulder blade, with patients experiencing:
- increased pain during chest movements (during inhalation and exhalation, when sneezing or physical activity);
- discomfort in the spine area;
- spread of pain beyond the affected area;
- the appearance or exacerbation of pain in an uncomfortable position.
In this case, the arthralgia itself can be aching, dull or burning. The person freezes in one position. He rarely inhales or exhales to avoid an attack of pain. The following symptoms of the disease appear:
- Spasmodic muscle contraction.
- Redness or excessive paleness of the skin in the area of nerve damage.
- Innervation in the area of localization of the compression process.
There are certain areas where pain occurs upon palpation:
- an area on the back to the left of the spine, with which a certain intercostal space is connected;
- part of the direct lesion;
- on the left side of the chest.
A separate group includes characteristic signs of intercostal neuralgia in women (dizziness and fainting). This is due to difficulty breathing and lack of oxygen. In men, the pain is localized on the lower ribs on the left side.
Treatment and symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left under the scapula in women and men
Acute and sharp pain in the chest can signal the presence of a serious illness. You need to be wary if there is a bright pain in the area of the ribs on the left.
Sometimes some patients perceive this pathology with the localization of burning pain as a disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Paradox! After all, everything is much more complicated.
The cause of such severe pain may be a disease called intercostal neuralgia.
What is left-sided intercostal neuralgia?
Intercostal neuralgia is a pathological disease that is characterized by pinching of nerve endings in the intercostal area. The area of localization of the painful focus in this case falls on the intercostal region on the left. In this case, the pain can be both acute and aching in nature.
Symptoms of the disease
Intercostal neuralgia in adults manifests itself:
- Piercing pain, which is more noticeable when inhaling, sneezing, coughing.
- Acute pain during physical activity.
- The pain can be localized at the back and front of the chest.
- There may be discomfort in the spinal column.
Note! With intercostal neuralgia, the patient most often freezes in one position when feeling pain. The patient is afraid to make any movement in order to avoid a new, even more intense attack of pain.
Symptoms in pregnant women
The birth of a long-awaited baby is the most pleasant and bright event in a woman’s life. But it is precisely at this time that the woman’s body is subject to serious stress.
Pregnant women most often experience intercostal neuralgia with the following symptoms:
- Severe pain of varying strength, from mild to the most intense, radiating to the area of the shoulder blades and lower back.
- A common cause of neuralgia in women in an interesting situation is herpes zoster. A characteristic symptom is rashes, acne on the skin.
Here you can read more about the cause of back pain in the shoulder blade area and its treatment.
Symptoms in children
Although intercostal neuralgia is an “adult” disease, some children are at risk of getting it.
With neuralgia, you can note the following symptoms in your baby:
- Crying, insomnia.
- Complaint of severe pain in the chest area.
- Increased sweating.
- Stuttering.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia on the left
If you suspect that you have neuralgia, then this is a good reason to seek help from a qualified doctor . The consultation should include an external examination, an assessment of sensitivity, and a determination of the location of the pain syndrome.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- X-ray. Thanks to it, you can find out the structure of the bone, as well as identify changes that are traumatic in nature;
- Myelography. This is a rare diagnostic method, the essence of which is the introduction of a special substance into the spinal region;
- Computed tomography. Thanks to it, you can get more complete, reliable information, although its price will surprise many with its high cost;
- Contrasting discography. During it, a contrast agent is introduced into the intervertebral disc;
- MRI. This is the highest quality and highly informative way to learn about the condition of the bone and soft tissues. But you cannot resort to MRI if there are metal formations in the body. Answer to the question: what is the difference between CT and MRI, which is better? – read here.
Differences from other diseases
It is worth noting that patients are often mistaken , confusing the symptoms of neuralgia with the symptoms of another disease. To find out the truth and find out exactly what problem led to the attack, it is recommended to understand the manifestations of illnesses with similar symptoms.
- Cardiovascular problems. Painful sensations in the heart can also occur with neuralgia. But some patients mistakenly believe it is a heart attack. So, how to distinguish heart diseases from intercostal neuralgia? If you have suffered from disturbances in the functioning of the heart, the pain will be constant. The pain is relieved by taking medications, for example, nitroglycerin.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia may be similar to gastritis. In this case, patients report pain varying in severity. The pain syndrome becomes more pronounced during hunger and after eating. In addition to pain, symptoms such as digestive disorders, vomiting, and nausea can be noted. The condition improves significantly when taking enveloping medications.
- Pneumonia or pleurisy. Pleurisy is a disease characterized by pain in the chest area, which intensifies when sneezing or coughing. Pleurisy can easily be confused with intercostal neuralgia.
- Shingles. This is a kind of infectious disease, a kind of neuralgia. It is important to note that, unlike intercostal neuralgia, this disease is characterized by the formation of rashes in the area of the affected nerve.
Treatment of left intercostal neuralgia at home
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia is aimed at eliminating the pain syndrome and the pathology that caused its development. In this case, strict bed rest is indicated; the bed should be hard.
Treatment of left intercostal neuralgia with tablets
Treatment with tablets is most effective in eliminating pain. With the right treatment regimen, you can achieve a speedy recovery in just a few days.
For this purpose it is recommended to use:
- "Analgina."
- "Paracetomol."
- "Sedalgina".
- "Spazgana".
Treat such drugs with caution , do not abuse them or get carried away with them, because the body can get used to the drugs.
In some cases, the following medications are prescribed in tablet form:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Indomethacin".
B vitamins will be very useful.
Treatment of left intercostal neuralgia with ointments
Ointments and gels most often predominate in the home care of sick people . Treatment with ointments is not only very effective, but also somewhat pleasant. In addition, they have a pronounced warming effect and reduce pain. In addition, you will enjoy the massage as your muscles will warm up and relax.
Currently, ointments based on the venom of bees and snakes are relevant:
- "Virapin";
- "Viprosal";
- "Vipratox."
It is better, of course, for a doctor to prescribe a list of ointments, because it must be selected individually for each patient.
Ointments that contain active ingredients have gained good reputation: diclofenac, ibuprofen, indomethacin, etc.
Most often, patients resort to using:
- "Ketorola";
- "Diclorana";
- "Voltaren-gel";
- "Sintradona."
Treatment of left intercostal neuralgia with injections
If the above methods do not bring the desired result, you can turn your attention to injections. But it is worth warning about the possible side effects that hormonal drugs can cause to the patient’s health. Therefore, injections are given in unavoidable cases.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the left using traditional methods
From time immemorial, it was traditional medicine that made an invaluable contribution to the victory over various ailments. Effective recipes based on medicinal herbs and plants help overcome intercostal neuralgia. Use the valuable products that Mother Nature gave us.
Experienced healers advise using medicines and decoctions that contain geranium, birch, laurel, aspen, willow , etc.
Prevention of left intercostal neuralgia
Preventive measures involve self-monitoring of health status. The most important thing is to monitor your posture and perform a set of exercises designed to strengthen your muscle corset.
To preserve youth and beauty, and also to avoid the appearance of intercostal neuralgia:
- Do gymnastics regularly.
- Ensure healthy sleep, don’t worry about every little thing.
- Say no to smoking and alcohol.
- Eat right.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
To clarify the nature of the pain syndrome, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the heart and internal organs. If necessary, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are performed, which are among the most effective diagnostic methods. You can determine the cause in the sternum yourself. If the pathology is caused by abnormalities in the functioning of the heart, after taking Validol or Corvalol, pain in the thoracic region weakens or disappears.
If the pain intensifies when sneezing, taking a deep breath, coughing or changing position, the pathology is of neurological origin. Such manifestations are not characteristic of heart disease. When the pain is caused by lesions of the vascular system, it passes quickly, but can worsen during stressful situations or excitement. This type of intercostal pathology often occurs as a result of overwork. The exact cause of the development of neuralgia in the thoracic area can be determined by a doctor based on hardware examination data.
Treatment of sternal neuralgia is aimed at 2 main goals:
- pain relief;
- elimination of the factor that provoked the pathological condition.
It is allowed to take painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To suppress spasms, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants. Preparations containing B vitamins help restore the nerve fibers located between the ribs.
Taking medications
To eliminate the symptoms of the disease in question, the following medications are taken:
- Ibuprofen has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects due to the suppression of prostaglandin biosynthesis and obstruction of the production of the enzyme cyclooxygenase. Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, concentrating in the blood after 2 doses. Processed and excreted by the liver. Contraindicated in ulcerative colitis, renal impairment, liver failure, hemophilia and diseases of the optic nerve. Individual intolerance is possible. Analogues: Diclofenac, Piroxicam, Voltaren, Indomethacin.
- Sedalgin has an analgesic, hypothermic effect. Effective by inhibiting the production of allogenes in the periphery. Stabilizes cell membranes. Has a stimulating effect on the nervous system. Contraindications: thrombocytopenia, acute allergic reactions, hypersensitivity to auxiliary components, hepatic porphyria. Analogues: Analgin, Spazgan.
- Clonazepam reduces the excitability of subcortical areas of the brain and disrupts their interaction with the cortex. Inhibits polysynaptic spinal reflexes. Contraindications: hypersensitivity, disturbances of consciousness and breathing (central origin), respiratory failure, glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, severe liver dysfunction. Analogues: Aklofen, Sirdalud.
Complementary therapy
To ensure successful treatment, the regimen must be followed. It is necessary to provide the patient with peace and comfort. It must be in a horizontal position. The use of hard mattresses is indicated. Recommended:
- Avoid stress and anxiety.
- Reduce physical activity.
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
If the development of neuralgia is caused by pathologies of the spine, it is advisable to use the following methods:
- manual treatment is a complex of various therapeutic techniques and techniques for diagnosing diseases (mainly in the field of orthopedics);
- therapeutic massage;
- acupuncture;
- a course of physiotherapy - the use of physical means (movement, heat, water);
- therapeutic physical culture (PT) is a treatment method based on the use of physical exercises;
- Laser therapy is one of the methods of physiotherapy. Therapeutic use of optical radiation, the source of which is a laser;
Alternative techniques
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia involves long-term use of various pharmaceutical drugs, which affects health. Nanoplast forte is a new generation product that allows you to reduce the chemical effect on the body, effectively relieving pain and inflammatory processes. It is valid for 12 hours.
It is easy to use and effective due to its unique composition. By stimulating blood circulation, you can reduce the amount of painkillers and NSAIDs you take. The patch is fixed in the area of the ribs, while avoiding the left side of the thoracic region. If osteochondrosis is present, the patch can be glued to the projection of the exit of the spinal nerves. Nanoplast can be used in the area of direct damage to the nerve and its projection (on the back, in the upper parts of the spinal column). The product is fixed in the morning and throughout the day, but its use during sleep is not excluded. Treatment lasts 10 days.
- Prevention of acute respiratory diseases.
- Periodic examinations by an orthopedist.
- Timely treatment of diseases of internal organs and systems.
- Limit alcohol consumption and quit smoking.
- Strengthening the immune system, taking vitamins, eating right and exercising.
How to recognize intercostal neuralgia: symptoms and diagnosis
Intercostal neuralgia (or “thoracic radiculitis”) is a pathology that occurs when the intercostal nerve is compressed or irritated and is manifested mainly by pain, and the intensity of the pain syndrome is very high. The main danger of this disease is that the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia can mimic a large number of diseases of internal organs, including very life-threatening ones, for example, myocardial infarction.
Often, even experienced doctors are misled by the signs of neuralgia: angina is diagnosed where there is none, or a heart attack is missed where it is present. Therefore, it is very important to study in detail the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the right and left, as well as learn about diseases that may be hidden under a neuralgic mask. This is exactly what will be discussed below.
The fact is that neuralgia of various intercostal nerves (there are 12 pairs in total) manifests itself in different ways. All intercostal nerves are an anatomical continuation of the thoracic nerves, which exit through the intervertebral foramina from the spinal canal. They are directed forward from the thoracic spinal column and pass through the thickness of each intercostal space on the right and left sides of the chest.
The lower pairs of intercostal nerve fibers reach the upper part of the anterior abdominal wall. Therefore, with neuralgia, pain can be localized not only in the chest area, but also in the abdomen, simulating diseases of the stomach, liver, and pancreas.
All intercostal nerves consist of 3 components:
- sensory fibers (innervate the skin);
- motor fibers (provide movement of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm, which directly affects the frequency and depth of breathing);
- vegetative fibers (manage the tone of blood vessels, the work of the sweat glands of the skin of the chest).
Depending on which part of the intercostal nerve is most affected, various symptoms of neuralgia develop. For example, when the motor fibers are compressed, the patient is concerned about shortness of breath, the sensitive fibers are worried about pain, and the autonomic fibers are worried about increased sweating of the skin of the chest. Sometimes the nerve is compressed evenly, which manifests itself in a complex of symptoms.
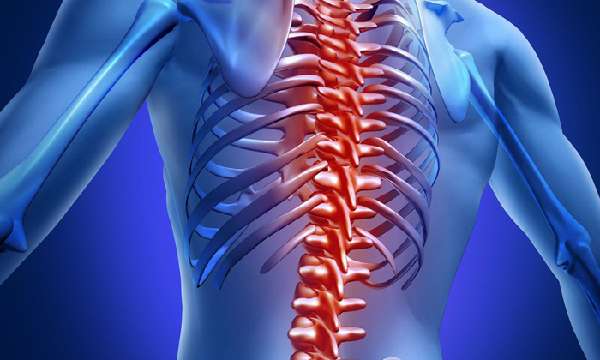
As a rule, only one intercostal nerve is affected, which leads to unilateral pain; very rarely, two or more nerve fibers can be affected simultaneously and the pathology can become symmetrical (if the inflamed nerves are on both sides of the body).
So, the leading sign of intercostal neuralgia is pain, without which there is no diagnosis. We have figured out the localization - this is any intercostal space of the chest on one side. The soreness does not extend beyond its limits (girdling nature), which is an important diagnostic sign.
The pain is intense and is assessed by patients on a visual analogue pain scale as severe. The nature of the pain is burning and piercing in the acute period, aching and dull in the subsequent period. The duration of pain is several hours or days.
The pain intensifies with physical movements and in an uncomfortable position. Also, coughing, deep breathing, sneezing, and sudden movements contribute to increased pain.
Characteristic is the presence of pain points, when pressed, the pain intensifies:
- paravertebral points (on both sides of the spinal column), which correspond to the affected intercostal space;
- on both sides near the sternum;
- along the path of the diseased nerve.
Intercostal neuralgia can occur as acute attacks that are repeated at regular intervals throughout the day. During such an attack, the pain is so severe that the person freezes in the position in which it arose and is afraid to even breathe, so as not to provoke a new wave of pain.
In women, you can observe stabbing pain in the mammary glands, which radiates to the nipple, which does not occur in men.
Other symptoms
In addition to pain, patients may complain of the following symptoms (but this is not necessary).
Causes
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles .
Thoracalgia is a secondary disease. Damage to nerve fibers is caused by long-term pathological processes in the body. Often intercostal neuralgia on the left occurs due to:
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- tumor growth on the spinal cord;
- constant poisoning with chemicals;
- inflammation;
- damage to the myelin sheath;
- deficiency of B vitamins;
- diseases of the spinal column;
- diabetes mellitus;
- infections (flu, tuberculosis);
- rib diseases;
- deformed sternum;
- aortic aneurysm;
- pleurisy;
- allergies;
- multiple sclerosis.
Some patients, before the onset of thoracic thoracalgia, are not aware of the presence of ailments that pose a serious threat to their health and life. Therefore, the doctor tries to understand not only the signs of neuralgia, but also to determine the reasons that caused it. Treatment gives positive results if the root cause of thoracic radiculitis and its symptoms are simultaneously eliminated.
The following are recognized as direct provocateurs of intercostal neuralgia:
- injury to the chest and spinal column;
- hypothermia of the thoracic spine;
- intoxication of the body (food, medicinal, alcohol, chemical);
- hormonal imbalance;
- age-related changes;
- overstrain of the back muscles, leading to muscle inflammation or spasm (prolonged stay in static positions, excessive physical exertion, jerking during movement);
- stressful situations;
- infection of nerve tissue;
- menopause in women.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left under the ribs, in the side, under the scapula - how to treat?
Pain and limited mobility are the main signs of thoracalgia. Pain surrounds the chest when intercostal neuralgia occurs. Symptoms on the left indicate a unilateral course of the disease. They are often confused with signs characteristic of cardiovascular disease.
The appearance of pain syndrome is provoked by pinching, irritation or inflammation of the nerves located in the intercostal spaces. Thoracic radiculitis does not develop independently; it is caused by diseases of the spine. Middle-aged and older patients are at risk. In children, thoracic radiculitis occurs in exceptional cases.
Causes
Some patients, before the onset of thoracic thoracalgia, are not aware of the presence of ailments that pose a serious threat to their health and life.
Thoracalgia is a secondary disease. Damage to nerve fibers is caused by long-term pathological processes in the body. Often intercostal neuralgia on the left occurs due to:
- tumor growth on the spinal cord;
- constant poisoning with chemicals;
- inflammation;
- damage to the myelin sheath;
- deficiency of B vitamins;
- diseases of the spinal column;
- diabetes mellitus;
- infections (flu, tuberculosis);
- rib diseases;
- deformed sternum;
- aortic aneurysm;
- pleurisy;
- allergies;
- multiple sclerosis.
Some patients, before the onset of thoracic thoracalgia, are not aware of the presence of ailments that pose a serious threat to their health and life. Therefore, the doctor tries to understand not only the signs of neuralgia, but also to determine the reasons that caused it. Treatment gives positive results if the root cause of thoracic radiculitis and its symptoms are simultaneously eliminated.
The following are recognized as direct provocateurs of intercostal neuralgia:
- injury to the chest and spinal column;
- hypothermia of the thoracic spine;
- intoxication of the body (food, medicinal, alcohol, chemical);
- hormonal imbalance;
- age-related changes;
- overstrain of the back muscles, leading to muscle inflammation or spasm (prolonged stay in static positions, excessive physical exertion, jerking during movement);
- stressful situations;
- infection of nerve tissue;
- menopause in women.
Symptoms
The pain syndrome with intercostal neuralgia is intense, long-lasting, and does not go away. It causes a burning sensation.
Due to the similarity of symptoms, intercostal neuralgia is often mistaken for other pathologies. When diagnosing, the doctor, by comparing the distinctive signs, differentiates thoracic radiculitis from: ulcers, pancreatitis, pleurisy, atypical pneumonia, cardiovascular diseases.
The pain syndrome with intercostal neuralgia is intense, long-lasting, and does not go away. It causes a burning sensation. With increased tone or spasms of muscle tissue, the pain increases when the patient bends the body, moves the shoulder or scapula.
In heart disease, the pain is short-term, paroxysmal. Their appearance is provoked by stressful conditions and overwork. When symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left arise and radiate to the heart, this does not pose a threat to life.
However, they can easily be confused with the pain syndrome that appears during myocardial infarction. The patient in this situation requires emergency hospitalization. Heart pain is distinguished by the following characteristics:
- the pain syndrome in neuralgia is constant and prolonged, movements increase its intensity;
- with thoracalgia, pulse and pressure are unchanged;
- nitroglycerin does not relieve pain caused by thoracic radiculitis;
- with myocardial infarction, pain is accompanied by an attack;
General signs
Symptoms of left intercostal neuralgia include:
- acute persistent pain on the left side;
- burning and tingling sensation;
- increase in pain when performing movements;
- increased pain causes sneezing, coughing;
- muscle tension;
- muscle spasms;
The skin on the left side becomes numb, loses sensitivity, turns pale or red. It is difficult for the patient to breathe deeply. He experiences dizziness and fainting due to oxygen deprivation.
The pain subsides when the patient takes a forced fixed position. The main symptoms include: sweating, sudden surges in pressure, pain in the lumbar spine.
The nerves are formed by sensory, motor and autonomic bundles. The symptoms are influenced by the degree of damage to these fibers:
- If the sensory bundles are damaged, the patient suffers from piercing pain that is neuralgic in nature.
- When the motor bundles are affected, the patient suffers from shortness of breath (they are responsible for the motor functions of the diaphragm and muscles and regulate the respiratory rhythm).
- If the vegetative bundles are irritated, a person sweats profusely (they regulate the functioning of the sweat glands and vascular tone).
- With uniform pressure on the nerve endings, a combination of various symptoms appears.
Symptoms associated with the underlying causes of the disease
Since left-sided intercostal neuralgia is considered a complication of prolonged pathologies of adjacent organs, it causes symptoms of concomitant ailments.
The disease is accompanied by symptoms inherent in:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic region;
- displacement of the vertebrae;
- intervertebral hernia;
- injuries of the musculoskeletal system;
- curvature of the spinal column;
- colds;
- herpes zoster;
- tumor tumors of the spine;
- ankylosing spondylitis.
If the patient has difficulty breathing, diagnose pleurisy, pneumonia, and bronchial asthma. If there is pain in the lumbar region, the doctor will prescribe an examination to detect kidney disease. If you complain of colic in the abdomen, tests are done to detect peptic ulcers, cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
Symptoms in men and women
Signs of thoracic radiculitis differ slightly between men and women. Men suffer from severe discomfort and piercing pain on the left side. But their duration is shorter.
Acute pain radiating to the mammary glands, severe muscle tension are signs of intercostal neuralgia in women. Men never experience pain in the mammary glands. Pain radiating to the lower back in women is sometimes mistaken for signs of gynecological diseases.
Treatment options
Intercostal neuralgia requires serious treatment. Only a doctor can determine the root causes, symptoms and treatment. If you do not treat the disease, it will become severe.
Elimination of pain is the primary goal of complex therapy. In acute cases of intercostal neuralgia, strict adherence to bed rest is necessary. The patient is placed in a bed with a hard surface. They recommend that he find a comfortable position in which the pain will subside.
Drug treatment
For pain on the left side, medications with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed. They quickly relieve pain in the hypochondrium and significantly alleviate the patient’s condition.
Medicines are prescribed taking into account the patient’s age, severity of the disease and pathology of the digestive system. For treatment the following is prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets or injections: Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Indomethacin, Rofecoxib;
- medications that relieve spasms: Tolperil, Mydocalm, Baklosan, Siralud;
- drugs with a sedative effect: Persen, Sedasen, motherwort extract, Novopassit;
- B vitamins: Neurorubin, Neurobion, Milgamma. (they restore nerve fibers).
Intercostal neuralgia is treated with local medications. To relieve symptoms the following is prescribed:
- drugs with anti-inflammatory effect: DIP-relief, Dolobene, Fastum-gel;
- ointments and gels that have an anesthetic effect: Capsicam, Voltaren, Menovazin, Finalgon;
Physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy
Helps fight intercostal neuralgia:
- acupuncture;
- exposure to ultrasound and laser;
- manual therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine helps treat the disease. Using them, they get rid of pain and relieve inflammation. Signs of intercostal neuralgia are eliminated using the following recipes:
- Place flaxseeds in gauze and steam them. Make an application on the left side.
- The juice is squeezed out of horseradish root. Apply the product to the affected side.
- Steamed wormwood is combined with sea buckthorn oil. Applications are made to the left side of the chest, at the location of the pain.
- The affected side is treated with alcohol, wiped dry, and a pepper plaster is fixed to the skin.
- Apply dry heat to the affected side: bags of heated salt or sand.
The disease quickly recedes if the patient takes medicinal baths. Warm water with herbal infusions eliminates pain and inflammation. Baths are prepared using a specific composition:
- Take 500 g of aspen branches, boil them for 30 minutes, and leave. The product is filtered and added to the bath. Bath in the medicinal solution for 15 minutes. After the procedure, fir oil is rubbed into the affected side.
- Brew 4 tbsp in 250 ml of boiling water. spoons of sage, leave for 1 hour, filter. Pour 100 g of sea salt into the bath and add sage infusion. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes.
- Add 5 drops of eucalyptus and lavender oil to a mixture of milk and honey (100 ml and 1 tablespoon, respectively). Pour the composition into the bath and bathe for 10 minutes. After the procedure, do not wash off the treatment solution, simply dry the skin with a towel. The procedure is performed every other day.
Prevention
The development of intercostal neuralgia is prevented by daily exercises, kneading the body, self-massage, and proper nutrition. It is necessary to give your body adequate physical activity every day. Do not be in a draft or be exposed to hypothermia. The diet should contain foods rich in B vitamins.
Comprehensive treatment recommended by the attending physician, moderate physical activity, and a balanced diet relieve intercostal neuralgia. Preventive measures prevent relapses from occurring.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left under the ribs, in the side, under the scapula - how to treat? Link to main publication
Causes of the disease
The causes of intercostal neuralgia and the accompanying symptoms are determined by the anatomical structure of the body. The thoracic region contains 12 pairs of nerves that arise from the spinal cord. These elements consist of sympathetic, sensory and motor fibers. A separate nerve runs in the space between the ribs in the area where the external and internal muscles are located. They provide the respiratory function of the body.
The nerves located in the intercostal space innervate the muscle fibers of the following areas of the body:
- breast;
- rib cage;
- costodiaphragmatic part of the pleura;
- anterolateral and anterior parts of the abdomen.
The spinal nerves are intertwined, which explains why intercostal neuropathy affects several areas of the body at the same time.
Shingles is one of the most common causes of the disease. The appearance of intercostal neuralgia can also be caused by:
- osteochondrosis of the spine;
- injuries and fractures of ribs;
- pleurisy;
- chronic vertebrogenic pain syndrome;
- arthrosis;
- chest deformation;
- pathologies of the spine.
In the absence of an inflammatory process caused by herpes zoster, intercostal neuralgia can be caused by irritation or compression of nerve fibers.
This condition develops against the background of:
- excessive physical activity leading to the appearance of muscular-tonic syndrome;
- inactive lifestyle;
- intervertebral hernia;
- thoracic spondylosis;
- neoplasms of various types that affect the thoracic region or pleura;
- aneurysms of the descending thoracic aorta.
In addition, intercostal neuralgia manifests itself due to a deficiency of B vitamins, which is often observed against the background of metabolic disorders. These same pathologies and a number of others can cause intercostal nerve pinching in women during pregnancy. In adults, this condition also occurs with excessive alcohol abuse. The appearance of intercostal neuralgia in children is explained by pathologies of the digestive system, diabetes mellitus, and hypothermia.
What is neuralgia and how to treat it
Neuralgia, the treatment of which must begin immediately and requires urgent intervention by specialists, is caused by damage to the peripheral nerve. Displaced spinal discs, ribs, or muscles pinching a nerve cause pain in the patient.
Specific pain occurs suddenly, causing a lot of inconvenience and discomfort to the patient. The most negative aspect of the disease is its treatment, which is poorly amenable to conventional pharmacology. When pain occurs, long-term use of painkilling injections and tablets is always required. There are several causes of neuralgia:
- hypothermia;
- injuries;
- consequences of viral infections;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx.
Trigeminal neuralgia and intercostal neuralgia can be caused by a herpetic infection. Treatment of neuralgia can only be carried out by a specialist. The correct selection of means and techniques ensures relief from neuralgic pain. In principle, a complete recovery is possible.
Since the branched nervous system has peripheral sections and tips of nerve endings, they can be pinched by nearby muscles or groups of muscles. This causes severe pain in the neck, face, intercostal space, hip, and leg. Thus, the following neuralgia are distinguished:
- cervical;
- trigeminal nerve;
- occipital;
- intercostal;
- sciatic nerve (sciatica);
- brachial plexus;
- lumbar plexus.
Treatment of neuralgia, any part of it, begins with an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to contact specialists and find out the exact segment of the lesion. To do this, they undergo tomography:
- computer;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Neck neuropathy
If the nerve is compressed by the connective and surrounding tissues, then very painful sensations occur in the neck area. Pain along the entire length of the neck occurs due to problems with the spine, or due to an occipital injury. Neck pain is also caused by hypothermia. Acute pain running from the back of the head to the neck most often occurs with intense movement. Painful symptoms of neuralgia in the neck can spread to the shoulders.
Neck neuritis causes discomfort and pain in the fingers. Sometimes neck pain starts from the back of the head and spreads to the entire head, especially to the temples and frontal part, and the eyes may suffer. Neck neuropathy is treated comprehensively. Since it is caused by several reasons, in particular, osteochondrosis, treatment of the cervical spine is recommended and prescribed not only with medication, but also with the help of massage, physical therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Cervical neuritis most often resolves with bed rest. If the cervical pain is acute, special ointments with a warming effect should be used. An attack of cervical pain is characterized by an intermediate state, with persistence of a dull, pressing pain in the occipital region. Painkillers for the relief of cervical pain are not prohibited. We should not forget about the prevention of cervical neuritis:
- swim more in the pool;
- do physical education;
- do morning exercises;
- lead an active lifestyle;
- avoid hypothermia.
Intercostal neuritis
The nature of the spread of pain in neuralgia can be radicular and nervous. With nerve distribution, pain occurs in the part of the arm adjacent to the body or its outer half. The whole arm may hurt if the roots are completely damaged. Neuralgia of the shoulder joint also leads to immobilization of the arm.
When pain occurs under the left shoulder blade, we can assume that it is intercostal neuralgia. It is difficult for an untrained person to determine the cause of pain under the shoulder blade. Aching or sharp pain under the left shoulder blade is not a sign of any specific disease. Most often, pain under the scapula is an occupational disease of people who keep the muscles of the subscapular region, tendons and ligaments in constant tension. Constant muscle fatigue causes spasm and pain under the left shoulder blade.
A pinched nerve in the intercostal space, which causes pain under the scapula, can result in intracranial pressure, hypertension, tachycardia, angina pectoris, and disturbances in heart rhythm. Pain under the shoulder blade can be cured if you consult a doctor in time. During its acute period, experts recommend spending at least 5 days in bed.
Dry heat, pepper plaster, mustard plasters help overcome the pain under the shoulder blade, and they treat it with other folk remedies. Neuralgia under the shoulder blade is relieved by warming ointments based on bee and snake venoms. For severe, prolonged pain under the scapula, blockades with painkillers and anesthetics are necessary.
Illness in pregnant women
The most unpleasant moment during pregnancy can be neuralgia during pregnancy. The third semester of pregnancy is the most dangerous and therefore, it is better to take preventive measures than to suffer from pain that affects some parts of the body leading to:
- severe discomfort;
- insomnia;
- lack of mobility;
- lack of appetite.
Neuralgia can occur at any stage of pregnancy. The nerve endings under the shoulder blade, the sciatic nerve, or the nerve in the neck may be pinched. It is not recommended to take medications during pregnancy. Therefore, one of the effective ways to avoid illness in the early stages of pregnancy is physiotherapy and physical therapy.
Experts prescribe strengthening the body’s protective functions during pregnancy in the form of B vitamins or vitamin therapy. Treatment of neuralgia during pregnancy is determined taking into account its position. For acute pain, local anesthesia is prescribed with ointments based on bee venom.
- rubbing;
- warming up;
- compresses;
- mustard plasters;
- pepper patch.
When does your back hurt?
Muscular neuralgia of the back manifests itself in several ways. Pinching of a peripheral nerve when compressed by ribs or displaced spinal discs leads to painful sensations in the lumbar plexus area. There is muscle neuralgia in the form of acute paroxysmal pain in the leg.
A pinched nerve can practically paralyze movement and literally put you to bed. Pain in the lumbar plexus area forces it to be anesthetized with strong medications, especially if it progresses from the stage of burning and paroxysmal. In this case, treatment is necessary and you cannot do without consulting doctors. Nerve damage can occur throughout the body.
Treatment of neuralgia of the back is carried out comprehensively. There are effective drugs that are prescribed by specialists for conservative therapy. Non-narcotic analgesics stop aching, sharp or dull pain, localizing it along the nerve. The initial degree of nerve damage is amenable to drug therapy, when B vitamins are used in addition to analgesics.
Muscular neuralgia of the leg of the corresponding branch is treated with novocaine blockade. The drug Milgamma is prescribed for inflammation of the sciatic nerve. These drugs are quite effective and efficient. Such drugs as ichthyol ointment and Menovazin for local anesthesia have proven themselves to be excellent. Doctors also suggest treating the disease with folk remedies, for example, acupuncture.
A disease such as neuritis can be treated with folk remedies. These are medicinal herbs with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. For example, peppermint, which contains menthol. The essential oil from this herb is part of menovazin. Mint in alcohol tincture is taken 10 drops as a painkiller for neuralgia at one time.
Despite the fact that neuralgia is a disease of our time, we should not forget that immunity and health always need to be stimulated, protected and strengthened with folk remedies. Take as many vitamins as possible, walk more in the air, lead an active lifestyle, especially for those who have been working too long.
Walking, jogging and especially swimming are the best advice for preventing neuralgia. Take care of your health, it is priceless, do not let illness take over your time. Use folk remedies at hand to prepare a vitamin cocktail. And then the disease and its symptoms will not take you by surprise, but the defense will work and the immune system will turn on. And if the disease cannot be avoided, then it will be much easier to endure it.
What is intercostal neuralgia?
The term “neuralgia” refers to pain that occurs at the location of the nerve. It follows that “intercostal neuralgia” is pain in the locations of the intercostal nerves.
Which is, in principle, accurate and correct, since pain occurs due to pinching and compression of the nerves located between a person’s ribs. As a result, the patient suffers from paroxysmal pain, which intensifies with every movement, coughing, and sneezing.
Causes of intercostal neuralgia
The reasons for the development of intercostal neuralgia may be different. People at risk include those who:
If you feel girdle pain under the ribs and in the sternum, you should not postpone your visit. It is urgent to diagnose the causes of such unpleasant sensations.
Symptoms of a pinched intercostal nerve
All the main symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the right are associated with various manifestations of pain. For a person who is not familiar with the specific manifestations of the pathology, it is easy to confuse intercostal neuralgia on the right with a heart attack. However, their main differences are actually quite clear. Unlike heart pain, a sign of intercostal neuralgia is:
- prolonged, almost unremitting pain, intensifying at night;
- discomfort does not disappear after taking nitroglycerin;
- the pain increases significantly when changing body position, coughing and deep breaths;
- heart rhythm is not disturbed.
In addition, pinching of the intercostal nerve on the right side is characterized by increased sweating in almost all patients. Often in the area of pain, the skin becomes pale or red, and muscle spasm occurs in the same place. At the same time, the strength of the manifestation of symptoms and the localization of pain in each patient is different, due to the individual characteristics of the body. However, intercostal neuralgia on the right has common symptoms. These include:
- prolonged pain that occurs suddenly;
- burning and tingling sensation on the right side in the side;
- short-term partial numbness of the chest on the right.
One of the most striking and reliable symptoms of this pathology is significantly increasing pain that occurs even with slight palpation of the spaces between the ribs.
Treatment tactics
Treatment in the presence of intercostal neuralgia on the right should be aimed at eliminating the main etiological factor. If the cause lies in osteochondrosis, the doctor may prescribe painkillers, chondroprotectors, physical therapy, and physiotherapy. If the cause of neuralgia is a herniated disc, surgery may be required.
Painkillers can be taken in the form of tablets, or the drugs can be injected. In case of severe muscle spasm, muscle relaxants should be included in the treatment regimen. These include Baclofen, Sirdalud. Apisatron can be used to improve blood circulation. To improve nutrition of the affected nerves, B vitamins (Kombilipen) are prescribed.
To ensure normal sleep and calm the patient, it is advisable to use drugs such as Deprim and Gelarium.
Physiotherapy is of no small importance in the treatment of intercostal neuralgia. UHF, iontophoresis, acupuncture, and magnetic therapy are often used. Along with general therapy, topical agents (gels, ointments) may be prescribed. They relax muscles, eliminate pain, and improve blood circulation. In the presence of space-occupying formations, surgical treatment is indicated. Treatment for neuralgia is selected by a doctor (neurologist).