Main symptoms of the disease:
- headache,
- insomnia,
- mental disorders,
- noise in ears,
- loss of consciousness,
- lack of coordination
- convulsions,
- loss of skin sensitivity,
- nausea,
- vomit.
The causes of cysts include bruises and hematomas, congenital disorders, parasitic infections, meningitis, dystrophic transformations, problems with blood circulation in the brain. It is impossible to perform an operation to remove a brain cyst without finding out the true cause of the disease. Even the slightest mistake in making a diagnosis will lead to further inflammation of the meninges and the emergence of new lesions.
Small cysts that are not accompanied by any symptoms are most often discovered during the diagnosis of other diseases. In some cases, they do not require surgical intervention, especially if they do not increase in size over a long period of time. It is enough to monitor your blood pressure, avoid hypothermia, avoid viral infections, and do not abuse smoking and alcoholic beverages.
Leading clinics in Israel

Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv

Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv

Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
In its structure, neoplasia is similar to other malignant neoplasms that originate in tissues of neuroectodermal origin: medulloblastoma, retinoblastoma. The cancer process originates in the cells of the pineal gland, a gland that produces melatonin (it regulates the cycles of wakefulness and sleep). The pineal gland synthesizes several bioactive substances - hormones that affect human biorhythms and participate in the activity of the endocrine, nervous and digestive systems.
This disease occurs in only 0.1% of cases of the total number of intracranial tumors; according to ICD10, pineoblastoma has code C75.3.
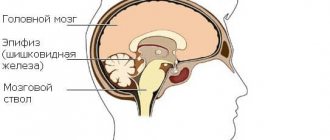
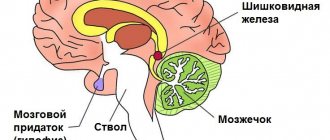
The pineal gland, or pineal gland, has minimal dimensions and is located between the hemispheres of the brain behind the 3rd ventricle. Next to it is the “Sylvian aqueduct” through which cerebrospinal fluid circulates. This complex anatomical zone where pineoblastoma develops is called the pineal region.
Macroscopically, pineoblastoma is a densely elastic formation of a brown hue; microscopically, this tumor is a collection of small monomorphic cells with hyperchromatic nuclei.
Several features of pineoblastoma can be distinguished:
- Aggressive growth. This leads to the appearance of a pronounced clinical picture in just a few months.
- Increased production of melatonin, a hormone that is responsible for normal falling asleep and waking up.
- Blockage of the ventricles of the brain during tumor growth, which leads to hydrocephalus.
- Spread of the tumor to the spinal cord.
- The predominant diagnosis of this neoplasia is in children and adolescents up to approximately 18 years of age.
Causes of pineoblastoma formation
This malignant neoplasm appears as a result of mutation of individual pinaeocytes, which begin to multiply intensively. Mutations are sporadic, which does not exclude a hereditary predisposition.
The obvious causes of tumor modification of pinaeocytes have not been established, but the influence of the following factors is possible:
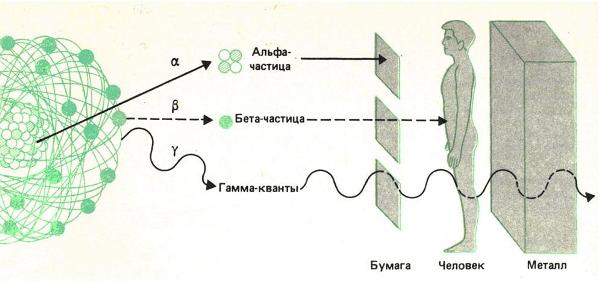
- ionizing radiation. High background radiation and radiation therapy in the treatment of cancerous tumors can provoke the appearance of a cerebral tumor;
- complicated pregnancy. Fetal hypoxia, intrauterine infections of the fetus, toxic effects lead to disruption of differentiation and transformation of the genome of some cells. The cells remaining in the pineal gland that have not undergone differentiation after gestation can become the basis for the formation of a tumor;
- carcinogens. Substances found in household chemicals, food products (dyes, preservatives, flavors) and other products can have a carcinogenic effect. Carcinogens that enter the body of a pregnant woman affect the child during intrauterine development, when the body is most vulnerable.
Provoking factors include: genetic predisposition to malignant diseases, central nervous system injuries, surgical interventions.
Symptoms of pineoblastoma
Symptoms of the disease include:
- symptoms of intracranial hypertension: deterioration of visual function, intense headache, nausea that resolves after vomiting.
- increase in body temperature.
- convulsive syndrome.
In infants, pineoblastoma can manifest as anxiety and moodiness. As the tumor grows and invades surrounding tissue, other signs appear:
- when the tumor grows in the upper parts of the midbrain, strabismus, double vision, and bilateral ptosis appear;
- changes in melatonin production explain disruptions in the sleep process: difficulty falling asleep may occur or hypersomnia may develop;
- damage to the cerebellum forms cerebellar ataxia: loss of coordination, unsteadiness of gait, disproportion of movements;
- hemiparesis, behavioral disorders, and decreased sensitivity of half the body may occur.
Important! Due to the fact that the pineal gland is responsible for the synthesis of sex hormones, with the development of pineoblastoma in children, rapid and earlier puberty may be observed.
Pineoblastoma is also characterized by other changes in well-being. This may include apathy, weakness, unexplained fluctuations in weight down or up, lethargy, and a pathological change in behavior and personal qualities becomes noticeable.
There are no obvious symptoms indicating the development of a malignant tumor of the pineal gland, since the listed signs can also be present in other diseases of the internal organs and the central nervous system.
Remember! The symptoms of pineoblastoma in children are varied and often depend on the age of the child, location and size of the tumor.
Prevention
A pineal cyst of the brain can occur in any person; the reasons for its appearance are not fully understood. However, there are some methods that can significantly reduce the risk of its occurrence . Such measures include:
- Regular preventive examinations by a neurologist, especially if you have symptoms such as headaches, poor coordination, or depression.
- Refusal to self-medicate in the presence of any type of ailment.

- Lead a healthy lifestyle: exercise regularly, spend enough time outdoors, give up bad habits.
- Children should have adequate sleep and rest.
- You should refrain from outdoor activities and sports where there is a high risk of head injury.
- The diet must contain the trace element tryptophan. It is found in high protein foods, nuts, fatty fish, and oatmeal.

- Be sure to follow a daily routine, go to bed and wake up at approximately the same time.
- Do not perform frequent x-ray examinations of the head unless absolutely necessary.
- Maintain good personal hygiene to protect yourself from parasites.
All these precautions will help not only reduce the risk of developing a disease such as cystic transformation of the pineal gland, but also strengthen the body's defenses and improve well-being.
Thus, a pineal gland cyst is, although rare, a relatively harmless disease. However, when such a compaction is detected, monitoring by a neurologist and undergoing preventive examinations every six months is extremely important. In this case, the patient's condition will be under control, and if there is a significant deterioration in the condition, emergency measures can be taken.
Complications of pineoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is characterized by a rapid increase in intracranial pressure due to occlusion of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways. A strong enlargement of the ventricles in a narrow space inside the skull leads to compression of the brain.
The predisposition of pineoblastoma to metastasis explains the formation of secondary tumor foci in different areas of the brain and spinal cord. A dangerous complication is hemorrhage into the tumor body with blood entering the ventricles. As it develops, the neoplasm compresses the tissues of the medulla oblongata and grows into the locations of the vital centers of cardiovascular and respiratory regulation. Their involvement in the cancer process can be fatal.
4. Treatment of tumors and cysts of the pineal gland
The main method of treating tumors is surgery
.
Most often, a neurosurgeon is faced with the need to choose a complex treatment method (a combination of radiation, surgical and drug therapy)
. The main difficulty of treatment is associated with the histological diversity of neoplasms and their dangerous proximity to large blood vessels.
As for cysts, in most cases they cannot be removed - they are under constant medical supervision
. The exception is when the cysts reach a large size and are removed through surgery.
If hydrocephalus develops, drainage operations are performed to ensure the outflow of excess fluid.
Diagnosis of pineoblastoma
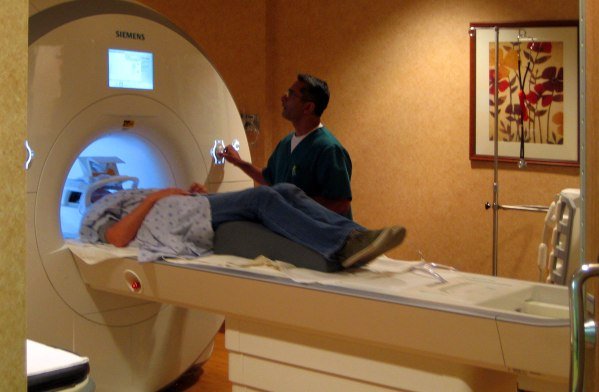
To make a diagnosis, anamnesis is first collected in order to have an idea of the course of pregnancy, the process of childbirth, the postpartum period, early symptoms and the time of onset of the disease. Further examination of the patient consists of:
- biochemical blood test (an increase in ALT, AST, a decrease in protein concentration is determined);
- general blood test (signs of leukocytosis and anemia may be noticeable);
- blood tests for tumor markers;
- examination by an ophthalmologist. If swelling of the optic nerve head is detected, conclusions can be drawn about increased intracranial pressure.
- cerebrospinal fluid studies. This helps eliminate the effect of infection on the central nervous system. Significant cytosis, increased protein concentration, and the presence of cancer cells are also diagnosed. Red blood cells can be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid during hemorrhage.
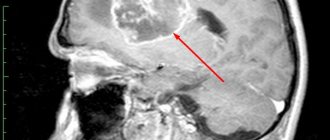
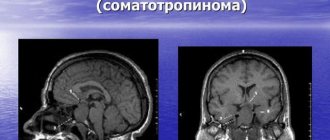
- neuroimaging. Most often this is an MRI of the brain; in older people (if there are contraindications to MRI), a cerebral CT can be performed. This helps to identify neoplasia, establish the growth pattern, the extent of the process and its location.
- stereotactic tumor biopsy. It is used when deciding whether neurosurgical treatment is necessary.
- histological examination of the biopsy specimen.
In addition to the above examination methods, before surgery, neurosurgeons often conduct the following studies: cerebral angiography or MR angiography, ventriculography.
It is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis with benign pineocytoma, encephalitis, other intracranial space-occupying formations (abscess, cerebral cyst, tumors), and traumatic injuries. In the first year of life, congenital brain pathologies are excluded. In young children, some symptoms (fever, nausea or vomiting) may be mistaken for symptoms of an intestinal infection.
Therapy for pineoblastoma
If previously conservative treatment of patients was most often carried out, the use of microsurgical equipment today allows doctors to increase the radicality of tumor removal and increase the list of indications for surgical intervention. The modern treatment regimen is divided into 3 basic stages:
Surgery . Contraindications to surgical intervention are: involvement of the brain stem and choroid plexuses in the oncological process with the risk of massive bleeding during the operation. Bypass surgery is used as a palliative method and to stabilize the patient’s health before radical surgery.
Radiation therapy . Due to the high malignancy of pineoblastoma, general irradiation of the spinal cord and brain and additional irradiation of the tumor bed are performed. The use of capsules with radioisotopes for injection into the brain is the most effective method of radiation therapy with minimal risk of side effects.
Polychemotherapy . It is carried out in conjunction with radiation therapy after neurosurgery or as palliative treatment of inoperable tumors. Chemotherapy can be administered in several ways - when the drug is taken orally or injected into a muscle or vein, in this case it enters the bloodstream and affects tumor cells throughout the body (this method is called systemic chemotherapy). When the drug is injected directly into the organ, the spine, the drug affects the tumor cells in these areas (this is called local chemotherapy).
Combination chemotherapy involves the use of more than one antitumor agent. The choice of chemotherapy administration method and type of chemotherapy depends on the form and stage of the cancer. Most often, polychemotherapy is used, which consists of a combination of 2-3 cytostatic drugs (Etoposide, Vincristine, Carboplatin). The side effects of chemotherapy that occur require additional symptomatic treatment.
Would you like to receive an estimate for treatment?
*Only upon receipt of data on the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate an accurate estimate for treatment.
The choice of treatment methods depends on the following points:
- localization of the tumor in the brain;
- the patient's age at the time of diagnosis of the tumor;
- the number of tumors remaining after the operation;
- spread of cancer to other parts of the central nervous system: spinal cord and meninges, other organs - bones and lungs;
- whether it is a primary tumor or a relapse of the disease.
The most effective method of treatment is surgery, but if the tumor is very widespread, it is almost never performed.
The main goal of surgery is the absolute removal of pineoblastoma . Brain surgery is characterized by its complexity; the neurosurgeon must cut off the modified tissue so that healthy and functioning brain structures are not affected.
Some cancer treatments can cause side effects that may appear months or years after treatment in patients who have recovered. Such consequences are called long-term. These types of consequences of disease therapy include:
- various physical disorders.
- transformation of thinking, learning abilities, changes in memory, changes in mood, emotional state.
- The emergence of secondary cancer (new types of cancer).
Some long-term consequences can be cured or their symptoms reduced.
Video on the topic:
Surgery for a brain cyst
In the neurosurgical department of the city clinical hospital named after. A.K. Eramishantsev will offer you cyst removal at an affordable price. The type of operation is selected after diagnosing the disease and carefully studying the general condition of the patient. Today there are three main technologies in use:
- Shunting is the emptying of a cavity using a special drainage tube. A possible negative consequence of this procedure is the risk of infection.
- Endoscopy - removal of a tumor as a result of puncture. There are practically no complications in this case, but this solution to the problem is not suitable for all types of brain cysts.
- Cranial trephination is a fairly effective method of removing a cyst, but there is a risk of brain injury. To prevent this from happening, you need to take a responsible approach to choosing a specialist.
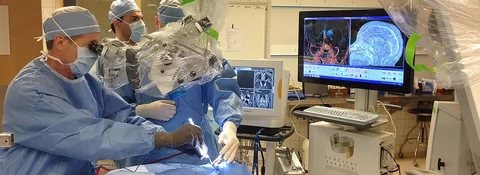
To minimize negative consequences and maximize the effectiveness of intervention, doctors conduct computer monitoring. The operation may be delayed due to an active inflammatory process in the body. The consequences of an operation to remove a cyst with an unprofessional approach can be: problems with vision and hearing, impaired motor functions, and the appearance of new cysts.
Prognosis of pineoblastoma
The prognosis for survival of the disease depends on the following factors:
- the size and prevalence of the tumor before surgery;
- presence of residual cancer cells after surgery;
- patient's age.
The lethal outcome is caused by compression of the brain, hemorrhage into the ventricles, and the involvement of the vital centers of the medulla oblongata in the process. Combined 3-stage treatment helps to increase the life expectancy of patients. The predisposition of the tumor to implantation spread and metastasis explains the high rate of relapses.
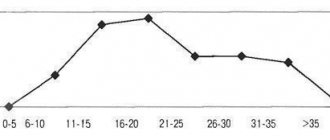
Pineoblastoma in children under 5 years of age has a more malignant course; 5-year survival can be only in 15% of cases; in children over 6 years of age, the prognosis is much more favorable. If the tumor disseminates, patients die within a year from the onset of clinical symptoms. Operated patients survive to the five-year mark in 60-70% of cases. Premature death is possible if the tumor is inoperable.
Epidemiology
Tumors of the pineal parenchyma, according to various authors, account for 15 to 32% of all tumors of the pineal region.
According to SESchild, these tumors are dominated by: pineoblastoma - 50%, pineocytoma-pineoblastoma - 6%, pineocytoma with intermediate differentiation - 14%, pineocytoma - 30%. MKHerrick, on the contrary, notes the predominance of pineocytomas over pineoblastomas - 60%. Tumors of this group are more common in men. In our series of observations, tumors of the pineal parenchyma accounted for 27% (75 observations). Among them, pineocytomas - 21 (41%), anaplastic pineocytomas - 19 (37%) and pineoblastomas - 11 (22%). Tumors of the pineal parenchyma were more common in women with a f/m ratio of 1.6:1. Malignant tumors made up the majority - 50 observations (64%). In children, malignant tumors of the pineal gland were detected more often (20 out of 23 observations) - 87%, than in adults - 60% (30 out of 51 observations). The average age of patients with pineocytomas is 27 years, and with pineoblastomas - 16 years.