Encephalitis or inflammation of the brain is a very dangerous disease, the causes of which are usually infectious, i.e. viruses, protozoa and bacteria. Allergic and toxic factors can aggravate the situation. Depending on the provoking factor, the disease can be very unexpected and occur very rapidly, or it can occur slowly, in a latent form. Often, brain inflammation occurs as an independent disease or develops as a complication of another pathology. As a result, it is usually customary to talk about primary and secondary encephalitis.
The causes of primary inflammation, as a rule, lie in the pathogenic action of viruses, which, due to their simple structure, can easily overcome the blood-brain barrier on their way to the medulla. Some protozoa, bacteria and other microorganisms have the same ability. Inflammation can affect the gray matter, and in this case they speak of polyencephalitis, and such a disease can also affect the white matter, which means leukoencephalitis.
Meningitis ↑
One of the subgroups of brain inflammation is meningitis, which affects the membranes of the brain. The disease can be caused by viruses, fungi or bacteria. Pathology has an extensive classification; according to the nature of the disease, purulent and serous meningitis are distinguished. The pathology can be primary, when inflammation arose directly in the lining of the brain, and secondary, in this case the process moved to the cerebral cortex as a result of insufficient treatment of infectious diseases, for example, purulent otitis media.
According to the type of disease, there are three stages:
- acute;
- subacute;
- chronic.
Symptoms of encephalitis
Clinical signs that indicate the presence of brain inflammation are varied. Symptoms primarily depend on the cause of encephalitis, the phase of the disease and the location of the source of inflammation. Usually,
determine several stages of the disease, which correspond to certain signs. Primary symptoms are characteristic of any infectious diseases. So, in the period from two hours to several days there is elevated temperature, chills, nausea and other gastrointestinal problems. You can learn about purulent inflammation of the brain in this article.
The next stage demonstrates general cerebral symptoms:
- drowsiness and other symptoms of confusion;
- psychosensory disorders;
- soreness in the forehead area;
- high excitability;
- photophobia;
- apathy.
In addition, a sick person may experience stiff neck muscles, that is, the so-called Brudzinski symptoms. These usually include a cervical symptom, which consists of an involuntary bending of the head towards the chest, as well as zygomatic signs, which appear when pressing on the cheek just below the zygomatic arch. In this case, the patient reflexively bends his elbows and raises his shoulders.
In addition, the pubic symptom is quite indicative. It is so called because pressure is exerted on a person’s pubis, as a result of which, when the brain is inflamed, he cannot help but bend his legs at the knee and hip joints.
Also important are focal symptoms of central nervous system malfunctions, which can be a clue in determining the form and location of inflammation. Such symptoms usually include paresis of the limbs, aphasia or epileptic seizures. However, the usual and characteristic symptoms can be supplemented by others if the disease occurs in an abortive or fulminant form.
They have their own specific symptoms. So, for example, when an abortive form of the disease occurs, there are no neurological symptoms, but it has signs of an acute respiratory or gastrointestinal infection. The fulminant form of the disease is very dangerous, since it often ends in the death of the sick person.
Clinical picture ↑
All symptoms of meningitis are divided into three groups:
- meningeal;
- infectious;
- general cerebral.
Infectious symptoms include:
- a sharp increase in body temperature, accompanied by chills and fever;
- earthy skin tone with blue discoloration in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- tachycardia and increased sweating;
- weakness and increased anxiety.
Depending on the form of the disease, symptoms can appear at lightning speed, within a few hours due to swelling of the brain and be accompanied by convulsions and confusion. A similar picture can be observed with the primary form of meningitis. The secondary form develops less rapidly, and the symptoms are intertwined with the manifestations of the primary pathology.
General cerebral signs include:
- very intense headache, often localized in the forehead and temples;
- fear of light and sharp sounds;
- vomiting, especially frequent when changing the position of the head, it is not associated with food intake, intense, sudden, and is not preceded by nausea;
- discomfort when touching the patient’s skin;
- disorders in joint mobility.
Meningeal symptoms are as follows:
- increased tone of the neck muscles;
- Kernig's sign;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- acute hydrocephalus.
Examination of cerebrospinal fluid helps to accurately establish the diagnosis. The results of a puncture of this fluid show a complete picture of what is happening, the form of the disease, the degree of its course, the intensity of inflammation, etc.
Reasons ↑
Most often, the disease develops as a result of infection by viruses or bacteria, less often by fungi, or due to injuries and hypothermia. The most common bacteria that can provoke an inflammatory process are meningococci, streptococci, salmonella, pneumococci, hemophilus influenzae, and staphylococci. Of the fungi, candidiasis most often affects others.
Pathologies that can lead to secondary purulent meningitis:
- sinusitis, sinusitis;
- abscesses of different localization;
- otitis;
- fistulas;
- pneumonia;
- conjunctivitis;
- furunculosis.
Serous meningitis can be caused by: chickenpox, measles, mumps, mumps, rubella.
Complications of meningitis ↑
The duration of the disease depends on its form and timeliness of treatment. If we do not consider the lightning-fast form, when symptoms increase over several hours, on average, treatment of the pathology lasts from two weeks to one and a half months. In the chronic form, relapses often occur, and therapy can be protracted.
Meningitis is fraught with many dangers; even after treatment is completed, various complications often occur, these include:
- hearing or vision loss;
- development of mental retardation;
- epilepsy attacks;
- strabismus;
- paralysis of limbs;
- development of renal or liver failure;
- additional stress on the work of the heart and lungs.
But the main danger remains death. If timely therapy is not started, the patient dies on days 5-7 of illness. According to statistics, with timely treatment and adequate treatment, death occurs only in 10% of cases. For late applications, this figure increases to 50%.
Inflammation of the human brain
Brain inflammation is a dangerous disease during which cells gradually begin to die. Developing damage to the central nervous system is also observed. Pathology is usually caused by infections. The development of the inflammatory process occurs as an independent pathology, but in some cases, inflammation in the head becomes a consequence of another disease.
If correct and timely diagnosis is carried out, doctors prescribe adequate treatment, then the disease can be completely eliminated without serious consequences and complications for the person.
It is customary to distinguish between two main types of inflammatory processes in the brain. They are called meningitis and encephalitis. It all depends on the location of the inflammatory focus.
- Meningitis. With the development of this pathology, inflammation in the meninges is observed. The disease can be provoked by bacterial, viral, fungal pathogenic microorganisms.
- Encephalitis. With the development of this disease, inflammation of the white matter occurs. The course of the disease can be mild or severe (in the latter case, the likelihood of death increases significantly if drug or surgical treatment is not prescribed in a timely manner).
According to statistics, encephalitic inflammation of the brain is usually diagnosed in patients under the age of 14 years (more than 60% of cases). It is customary to distinguish between two types of encephalitis: primary and secondary.
- Primary encephalitis develops as a consequence of an encephalitis tick bite, or against the background of a severe form of influenza or herpes.
- Secondary encephalitis is always a complication of various pathologies (for example, measles, malaria, chickenpox, rubella). In recent years, secondary encephalitis has been repeatedly recorded after children were vaccinated with low-quality vaccines.
Pathology can develop in three forms: acute, chronic, subacute.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Regardless of the statistics, a person at any age can develop inflammation of the cerebral cortex, white matter, or membrane. But in more than 70% of cases, pathologies of this type are observed in children (under the age of 14 years) and in men aged 20 to 45 years.
The disease can begin to develop as a result of various factors. By and large, the trigger for the disease can be not only infectious lesions of the brain, but also, for example, back injuries, diseases of other organs, a stroke, etc.
The main reasons for the development of inflammation in the head include:
- Hypothermia (of the whole body and head in particular).
- Infectious pathologies (in 90% of cases this is encephalitis due to a tick bite).
- Chronic colds and diseases of the ear, nose and throat area (for example, rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis), which are not treated at the proper level.
- Previous severe pneumonia (pneumonia).
- Chickenpox (in children, chickenpox cannot cause inflammation of the brain - only in adults).
- Conjunctivitis (under certain circumstances).
- Untreated encephalitis or meningitis.
Inflammation begins due to the penetration of various pathogenic microorganisms (usually in large quantities) through the vessels into the brain. They enter the human body through airborne droplets, through the digestive system, and through direct contact with a sick person. Of particular danger are the bites of various insects that carry tick-borne encephalitis (this can be not only ticks).
Inflammation of the brain is a very common disease in cats and dogs, the treatment of which is routine practice in the veterinary field.
Diagnosis of the disease
Due to the fact that the inflammatory process in the brain (in the membrane, in the cortex, in the trunk) can develop rapidly, timely diagnosis of the pathology is extremely important. Therefore, at the first symptoms, it is recommended to contact a doctor directly at the clinic or call an ambulance, which will take the patient to the hospital.
High accuracy of establishing the correct diagnosis is possible already at the first symptoms of the disease. During diagnostic procedures, doctors examine the patient, study his medical history, and clarify the signs of pathology.
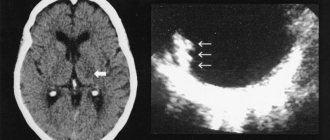
Diagnosis of the disease in young children is difficult. In a newborn child, it is not easy to differentiate the symptoms, so in such cases, adequate treatment begins only after specific diagnostics (CT, MRI, etc.).
The patient is required to be sent for additional examinations. According to the doctor's decision, they can be as follows:
- Blood and urine tests. First you need to establish that it is inflammation that develops in the body, and nothing else. The results of a standard blood test may indicate an excess of leukocytes and lymphocytes, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and also provide other important indicators indicating the presence of an inflammatory process (the location of its localization is not specified).
- Analysis of fluid from the spinal cord. If an inflammatory process in the brain is suspected, a puncture of fluid from the spinal cord must be taken from the patient (the spinal cord canal in the lumbar area is pierced). If there is inflammation of the head, then in the analysis results doctors will see a significant increase in the volume of immune cells and an excess of standard protein indicators, and a low glucose content. Also, when infected, the cerebrospinal fluid will have a yellowish tint and noticeable turbidity (the same thing is recorded with inflammation of the spine).
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Using MRI, the exact location of the inflammatory focus in the human brain can be quickly established.
Possible complications
The presence of an inflammatory process in the brain (regardless of the type of disease and the stage of its development) is an extremely dangerous condition for human health. Even after a completely cured pathology, the patient may encounter various unpleasant consequences and complications:
- Hearing problems.
- Problems with remembering new information and reproducing old information.
- Strabismus (in various forms), progressive deterioration of vision (usually myopia).
- Decreased intellectual abilities.
- Development of various forms of epilepsy.
- Malfunction of the thyroid gland and other internal organs.
- Problems with coordination of movements.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
When there is inflammation in the brain, there is almost always a possibility of death. If adequate treatment is not carried out, the patient may well die within 4-7 days after the first symptoms of the disease appear.
Source: https://vsepromozg.ru/oslozhneniya/vospalenie-mozga
Treatment ↑
When the first signs of illness appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. If meningitis is suspected, the patient is sent to the neuroinfectious department. Until transport to the hospital, the emergency doctor can administer aminophylline, glucocorticosteroid drugs and diuretics, such actions will help temporarily relieve brain swelling.
After hospitalization for purulent forms of the disease, approximately the following therapy is prescribed:
- antibacterial drugs for ten days, in the form of injections. The choice of medications depends on the causative agent of the disease;
- sulfonamide drugs in parallel with antibiotics;
- diuretics to reduce brain swelling;
- glucocorticosteroids, also to reduce swelling;
- against seizures or for the purpose of preventing them;
- aminazine, chloral hydrate, pipolfen;
- to reduce intoxication of the body - albumin or isotonic solution.
If the causative agent is a fungus, antibiotics are usually not strong and the use of antifungal drugs is required.
Encephalitis ↑
A pathology in which the substance of the brain becomes inflamed. The disease is characterized by a severe course and a high mortality rate of 20% of diagnosed cases; it is rare, with an average of 1.5 cases per hundred thousand inhabitants. Most often, cerebral encephalitis is viral in nature and in 75% of cases occurs in children. Just like meningitis, primary and secondary encephalitis are distinguished. In the first case, the damage occurs directly to the medulla of the viruses; the secondary process occurs as a result of cross-reaction with other infectious diseases.
Inflammation of the brain: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment tactics
Brain inflammation is a very serious pathology, which is characterized by the death of nerve cells and damage to the nervous system.
The disease may be infectious or allergic in nature. In most cases, it develops as an independent disease, but can be the result of a previously suffered pathology.
It is possible to defeat the disease with a timely diagnosis and competent immediate treatment.
Types of brain inflammation
Depending on the location of the lesion, there are two types of inflammation of the brain - encephalitis and meningitis.
Inflammation of the cerebral cortex can manifest itself in acute, subacute and chronic forms.
Each of them has its own specific manifestations and, accordingly, different treatment tactics.
Meningitis
With this disease, an inflammatory process of the lining of the brain develops; it can be provoked by:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungi.
It is very important to recognize the first symptoms of meningitis in children in time - this can save the child’s life!
Encephalitis
With this pathology, the substance of the brain becomes inflamed. Depending on the form of the disease, it can be severe and lead to death or mild.
According to medical statistics, the disease is more often observed in childhood.
There are primary and secondary encephalitis. In the first case, the disease can develop after a tick bite, influenza or herpes.
The secondary form develops as a complication of certain diseases, namely:
- rubella;
- chicken pox;
- malaria;
- measles
Also, a secondary form of encephalitis can become a complication after vaccination.
Causes of brain inflammation
A person can experience brain inflammation at any age. According to medical statistics, children and middle-aged men are more likely to suffer from inflammatory brain disease. The development of this disease can be caused by a number of factors - from back and head injuries to certain types of infection.
Among the main reasons are:
- severe hypothermia;
- infectious diseases, including tick-borne encephalitis virus.
A secondary form of brain inflammation can occur for the following reasons:
- chronic ENT diseases – sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis;
- severe form of pneumonia;
- conjunctivitis;
- chicken pox suffered in adulthood;
- previously suffered meningitis or encephalitis, not completely cured.
As a rule, the inflammatory process develops as a result of various pathogens entering the brain tissue through the circulatory system.
The pathogen can penetrate through the air, the digestive system, or through contact with a sick person. An insect bite (tick bite, for example) that transmits tick-borne encephalitis is also dangerous.
Main symptoms
Symptoms indicating inflammation of the brain are quite varied. Signs of brain inflammation depend on the type of pathology, stage of the disease and localization of the source of inflammation. Most of the symptoms are the same for both meningitis and viral encephalitis.
Among the external visible first signs:
- general weakness and constant malaise;
- regular and prolonged attacks of severe headaches;
- vomiting attacks; high body temperature and hallucinations;
- pain in muscles and joints, cramps.
The manifestation of neurological symptoms is expressed as follows:
- stiffness in the joints and loss of coordination of movement;
- change in consciousness;
- violation of the swallowing process;
- problems with articulation;
- eye movement disorders.
The manifestation of symptoms in the mental sphere is expressed in the following:
- increased anxiety;
- the appearance of insomnia;
- frequent mood changes;
- the occurrence of hallucinations.
Mental disorders arise suddenly and manifest themselves in the form of delusions and psychoses. The patient may experience a psychomotor agitated state in which he behaves inappropriately and cannot independently control his actions.
In the case of a secondary type of pathology and the development of complications, the disease develops rapidly, and the symptoms manifest themselves much more strongly. In this case, the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- pain becomes stronger, almost unbearable for the patient;
- intracranial pressure increases;
- the complexion becomes darker;
- there is acute sensitivity to bright light and smells;
- small rashes and red spots appear on the skin;
- sweating increases.
Similar symptoms can develop within a day, the patient experiences delirium and convulsions.
Diagnostics
You should consult a doctor and undergo the necessary diagnostic examination immediately after the first signs and unpleasant symptoms appear.
Diagnosis of the disease includes, first of all, a physical examination and study of the patient’s medical history and symptoms of the disease. Additional examination is required, which includes:
- lab tests. The following indicators will indicate the inflammatory process in the body: an increase in the number of leukocytes, lymphocytes, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an increase in the content of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein;
- cerebrospinal fluid examination. The puncture is taken by puncturing the spinal canal in the lumbar region. When the disease occurs, there is an increase in the number of immune cells, protein, and a decrease
- amount of glucose. In appearance, during the inflammatory process, the liquid is cloudy and yellowish;
- MRI. The procedure helps to accurately determine the location of the source of inflammation.
In addition, it is worth noting that MRI can detect a number of dangerous pathologies, such as, for example, a cancerous brain tumor at an early stage.
Treatment
When the first symptoms of a brain disease appear, you should contact an ambulance, whose doctor should refer the patient to hospitalization and administer appropriate medications that will help temporarily reduce swelling of the brain.
The treatment course depends on the diagnostic results and the diagnosis made. Symptoms of brain inflammation may be similar to those of other diseases, as a result of which proper treatment is prescribed and begins much later.
The course of therapy includes the following methods of treating inflammation:
- etiotropic therapy - intended to eliminate the causes of the inflammatory process;
- pathogenetic direction - the use of drugs that stop processes leading to damage to brain tissue;
- Symptomatic therapy can reduce the manifestations of the disease.
The following drug therapy may be prescribed:
- To combat the pathogenic infection, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. As a rule, the course lasts at least 10 days, and the drug is administered as an injection;
- if the disease is of viral origin, it is necessary to take antiviral medications;
- taking antibiotics will be ineffective in case of a fungal disease. In this case, it is recommended to take antifungal drugs;
- Diuretics may be prescribed to relieve swelling;
- in case of seizures, anticonvulsant medications are prescribed;
- When the temperature rises and a febrile state, antipyretic drugs are prescribed.
The patient is recommended to be hospitalized in a specialized medical facility to ensure constant monitoring of breathing and the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
It is very important to start proper treatment on time and as quickly as possible; every minute counts, since the consequences of brain inflammation are serious. Incorrect treatment can worsen the situation and lead to death.
In children, the disease is more severe than in adults; their bodies are not yet strong enough to fight such a terrible pathology.
Treatment of brain inflammation depends on the patient’s condition, symptoms and course of the disease. In any case, treatment should be comprehensive and under constant medical supervision.
After the course of treatment has been completed and the patient’s condition has improved, the patient needs rehabilitation measures. This will help reduce the effects of damage to brain tissue. During the recovery period, auxiliary rehabilitation measures are recommended: physical therapy classes, a massage course, physiotherapeutic procedures.
Possible complications
Inflammation of the brain in any of its manifestations is a very dangerous disease, especially its secondary form, which can lead to serious consequences and complications. The following possible consequences may occur with cerebral edema:
- hearing impairment;
- vision problems and development of strabismus;
- mental development disorder;
- memory impairment;
- the occurrence of epileptic seizures;
- problems with coordination of movements;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- coma.
The main danger is death. If left untreated, the patient may die within a week. There is also a possibility of such an outcome if you seek medical help late.
Inflammation of the brain can be mild, but there is still a risk of complications, so it is important to promptly pay attention to the appearance of symptoms and consult a doctor promptly.
Prevention
To prevent brain inflammation in any manifestation, special vaccines have been developed that produce immunity against viruses.
It should be borne in mind that it is impossible to completely protect yourself from the development of an inflammatory process in the brain, but you can reduce the risk of getting sick. To do this you need:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle - give up bad habits, eat properly and nutritiously;
- exercise;
- prevent chronic forms of the disease - cure diseases on time and completely;
- try to avoid going out into nature during times of likelihood of an outbreak of encephalitis and tick activity.
Finally
Despite the fact that the inflammatory process in the brain is considered a fairly rare pathology, unfortunately, it can affect anyone.
It should be borne in mind that with a weakened immune system, the likelihood of developing any disease increases. Watch your health and take care of yourself!
Source: https://golovnie-boli.com/bolezni-golovnogo-mozga/vospalenie-mozga.html
Reasons ↑
Viruses such as herpes, influenza, Coxsackie and others can provoke the development of pathology. The disease can also be caused by bites of infected insects, such as ticks or mosquitoes.
Secondary types can be caused by:
- measles;
- malaria;
- rubella;
- toxoplasmosis;
- smallpox;
- complications after vaccination.
The virus can be transmitted by airborne droplets, and also through insect bites, moving through the bloodstream and entering the brain.
Diagnostics
The following procedures help confirm the diagnosis:
Blood and urine tests.
A study of the brain fluid is carried out, which reveals the stage of the disease, its form and cause.
Treatment of inflammation of the meninges is always developed individually for each patient and depends on the type of infection, causes and form of progression.
Treatment ↑
Regardless of the severity of the pathology, the patient is hospitalized in the neuroinfectious department, where a complex of all necessary procedures is carried out. Diuretics and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed to relieve cerebral edema. The basis of treatment is etiotropic therapy. Gamma globulin is the main drug that has a pronounced therapeutic effect; it is administered intravenously for three days. Additionally, antiviral drugs are prescribed, for example, cytosine arabinosis, which delays the replication of the virus. To relieve symptoms, antipyretics, sedatives, and anticonvulsants are used. To prevent bacterial complications, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
Important! Meningitis and encephalitis are serious pathological processes that require constant monitoring by medical personnel. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate; all medications must be selected only by a specialist.
Despite the fact that inflammatory processes in the brain are a fairly rare pathology, they still occur and, unfortunately, take people’s lives due to untimely treatment and neglect of their health. Any disease is curable at the first stage; remember that attempts to relieve the symptoms of the disease on your own will only worsen the situation. Seek help on time, be healthy!
Author: Yulia Skladanaya
Treatment of vascular inflammation
Having discussed the causes of vasculitis and their symptoms, it is necessary to remember about the features of treating the inflammatory process in blood vessels. It should be remembered that the brain is the most important and most vulnerable organ, so self-medication is extremely dangerous and can lead to serious negative consequences. It is extremely important to see a doctor if you experience symptoms of any type of vasculitis.
Treatment of infectious inflammation
Treatment of infectious vasculitis will not be complete without antibiotics, which will help the body cope with pathogenic bacteria. Before prescribing a drug, the doctor must conduct a blood plasma analysis and determine the type of pathogen. There is no need to select antibiotics yourself - not all of them can cope with different types of bacteria.
After the analysis is carried out, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment, which is most often carried out in a hospital under the constant supervision of medical personnel. In addition to antibiotics, the patient is often prescribed droppers that cleanse the blood of toxic bacterial metabolites, vitamin-mineral complexes and anti-inflammatory drugs containing ibuprofen, which also help with severe headaches.
Treatment of non-infectious inflammation
If non-infectious inflammation is detected at an early stage, and the analysis does not reveal life-threatening pathogens, treatment can be carried out at home. The patient must be given complete rest and bed rest. Treatment consists of taking anti-inflammatory drugs based on ibuprofen, vasodilators to improve the outflow of fluid from the cerebral sinuses and vessels, and if a blood test reveals a small number of microorganisms, weak antibiotics are prescribed.
Treatment of tumor inflammation
Treatment of tumor inflammation of cerebral vessels is complicated by many factors. Firstly, analysis and x-rays are not always able to detect a tumor the first time, because in the photographs it looks like a slight darkening in the initial stages. Secondly, malignant or benign tumors cannot be removed from the brain through surgery, because any violation of the integrity of this organ will kill the person.
The inflammation caused by tumors can only be stopped, its bright symptoms removed with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs, strong painkillers and sedatives.
Inflammation of the circulatory network of the brain is dangerous for humans, because without the necessary treatment it will cause irreversible pathologies of brain tissue. Having discovered symptoms of vasculitis, a person should definitely consult a doctor, get an x-ray and the necessary brain analysis to establish a diagnosis and undergo treatment.