Causes
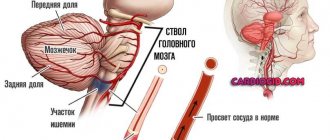
The cause of ischemic stroke is the development of local ischemia of brain tissue due to blockage of an artery. Most often, blockage occurs against the background of widespread atherosclerosis, when an atherosclerotic plaque closes the lumen of the vessel, making it impossible to adequately nourish the brain (atherothrombic ischemic stroke).
Ischemia can also occur due to thromboembolism of the arterial bed. In most cases, the clot is located in the chambers of the heart and travels through the bloodstream to the brain, leading to obstruction (cardioembolic stroke). Such blood clots often occur with atrial fibrillation, mitral valve stenosis, infective endocarditis and other pathologies.
In more rare cases, an ischemic stroke can be caused by a sharp drop in blood pressure, which causes a decrease in cerebral blood flow and insufficient blood circulation to the brain tissue (hemodynamic stroke). The causes of a sharp drop in blood pressure may be an overdose of antihypertensive drugs, orthostatic hypotension, myocardial infarction, etc. Hemodynamic stroke often occurs in combination with severe atherosclerosis.
Increased blood pressure is the main cause of hemorrhagic stroke. Long-term arterial hypertension contributes to damage and thinning of the vascular wall. At high blood pressure values, vessel rupture and the formation of an intracranial hematoma are possible. The risk increases in the presence of angiopathy (aneurysms, vascular malformations). There are also more rare causes of hemorrhagic stroke: coagulopathies, fibromuscular connective tissue dysplasia, vasculitis, etc.
A transient ischemic attack develops with reversible obstruction of an arterial vessel. In this case, there is an independent restoration of the perfusion of nervous tissue and a complete regression of neurological symptoms (minor stroke).
Cerebral hypertensive crisis also refers to stroke. Hemodynamic disturbances occur with a critical increase in blood pressure. This is caused by a long and malignant course of hypertension and can be provoked by various factors (withdrawal of antihypertensive therapy, emotional stress, physical stress, etc.).
Oncology of ischemic type: diagnosis, treatment, features – Izvilina
Ischemic stroke is also called cerebral infarction.
This is due to the fact that this type of stroke is based on the cessation of blood flow through the vessels, leading to the death of nerve cells (“infarction” translated from Latin means “death”). ACVA of ischemic type
This disease is extremely dangerous, because it often ends in death or persistent functional disorders. However, early diagnosis and treatment improve the prognosis. This is why knowing the signs of ischemic stroke is so important.
Why does ischemic stroke occur?
The death of neurons in this type of stroke occurs due to cessation of blood supply. The reasons that make this situation possible are:
- Obstacles that arise directly in the vessels of the brain: atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots.
- Emboli brought from outside and blocking the lumen of the vessel: blood clots from other parts of the circulatory system.
- Pathology of the vascular wall: hypertrophy and stenosis, for example, in hypertension.
- Changes in the rheological properties of blood: increased viscosity and tendency to thrombosis.
Features of female stroke
According to statistics, men are more susceptible to cerebral blood flow disorders. ACVA is diagnosed in them more often than in women. However, the stroke that affects the fair half of humanity has some peculiarities. Women sometimes suffer strokes much more severely than men. Serious complications, disability and death are common consequences of a cerebral infarction.
Women who use COCs have an increased risk of strokes
In women, cerebral blood flow disorders are more common in old age, while in men the risk of stroke is very high after 40 years. This, however, does not mean that stroke is not diagnosed in young girls.
This is also possible, because it is at the age of 18-40 that women often take COCs (combined oral contraceptives).
One of the complications that develops while taking this drug is thrombosis, because COCs increase blood platelet aggregation.
Women are much more likely than men to suffer from transient disturbances of cerebral blood flow. A distinctive feature of ischemic attacks in them is the vagueness of the clinical picture and the vagueness of symptoms. The disease is often disguised as other pathologies, making diagnosis much more difficult.
Pregnancy, by the way, is also a factor that increases the likelihood of developing a stroke. Changes in hormonal levels in women during pregnancy contribute to the occurrence of blood clotting disorders, and this, in turn, can serve as the onset of vascular disorders.
ACVA in women occurs less frequently and at an older age than in men, but is sometimes much more difficult to tolerate, often ending in disability and death.
Main manifestations of stroke
Doctors distinguish focal and cerebral symptoms of ischemic stroke
ACVA of the hemorrhagic or ischemic type has a characteristic clinical picture, which includes the following groups of symptoms:
- Signs due to cerebral edema.
- Symptoms of meningeal irritation. This group will not be considered in this article, since it is a characteristic manifestation of hemorrhage under the meninges and is more characteristic of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Focal symptoms. Its signs are varied and indicate which part of the brain is affected.
General cerebral symptoms
They are the first signs of developing cerebral edema. This group includes:
- Depression of consciousness.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Convulsive seizure.
The degree of depression of consciousness is assessed using the Glasgow scale
Depression of consciousness manifests itself in different ways: from mild stupor to terminal coma. At the very beginning (stunning), the patient is lethargic and inhibited, but reacts to stimuli and can answer simple questions, although with some delay.
As stunning progresses, the patient's interaction with the outside world is gradually lost. Already in a state of stupor, speech contact becomes impossible, only reactions to painful stimuli remain.
When coma develops, reflexes begin to fade, including protective ones, and at the last (fourth) stage, vital functions (breathing, blood circulation) suffer.
Headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting are nonspecific symptoms. Their presence does not yet indicate the development of cerebral edema. They can be signs of other diseases. When diagnosing stroke, you cannot take them into account alone; symptoms must be present that clearly indicate neuronal damage.
Headache can be a symptom of various pathologies
Seizures can occur both with cerebral edema and indicate local damage to an area of brain tissue. They are characteristic signs not only of stroke, but also of some other conditions (intoxication, epilepsy).
General cerebral symptoms are often the first signs of stroke. Their appearance means the development of cerebral edema. As the latter decreases, they give way to focal symptoms.
Signs of local damage to the central nervous system
This group of symptoms includes:
- Sensory disturbances (numbness of any part of the body).
- Movement disorders (paresis, paralysis).
- Visual impairment (blindness, loss of visual fields).
- Speech disorders (misunderstanding of the question asked, inability to repeat a simple phrase).
- Pathology of movement coordination (unsteadiness of gait).
- Memory losses.
- Cortical deafness.
- Cramps.
An ischemic stroke is characterized by the death of neurons, which leads to dysfunction of those organs for whose vital functions the affected area is responsible.
However, it should be noted that in the first few days, focal symptoms are sometimes obscured by general cerebral signs. Symptoms specific to the damage to a particular group of nerve cells can only become apparent after cerebral edema has decreased.
Based on which of these signs predominate, one can judge the location of the area damaged by an ischemic attack.
What to do if stroke occurs?
- Call an ambulance immediately. Treatment started in a timely manner significantly improves the prognosis of the disease.
You can call an ambulance in Russia by calling 103
- If the patient is conscious, calm him down and place him on the bed. The head and shoulder girdle should be raised with pillows. This simple action will slow down the development of cerebral edema.
- If the patient is unconscious, it is necessary to urgently assess the presence of vital functions (pulse and breathing). Their absence is a sign of clinical death. In this case, resuscitation measures must be started immediately.
- If the patient is alive, but does not come to his senses, before the doctors arrive, he needs to be placed on his side so that the airway does not close with the root of the tongue or vomit. Be sure to periodically check for pulse and breathing. Clinical death can occur at any time.
- Do not leave the patient unattended. Be prepared to initiate resuscitation if necessary.
Let's sum it up
An ischemic stroke occurs as a result of cessation of blood flow in one or more cerebral vessels. In the first days of the disease, signs of cerebral edema sometimes predominate, then focal symptoms begin to appear. The features of the latter help to understand which part of the brain tissue is affected, which centers were subjected to an ischemic attack.
Stroke in women and men has some differences
Most often, stroke is diagnosed in men, but in women it is sometimes more severe and with more serious consequences, especially in the presence of concomitant diseases.
The mortality rate from cerebrovascular disorders is lower among women. The signs of stroke in them are often nonspecific and mimic other diseases, which can cause late diagnosis.
This is why strokes in women are so dangerous and can lead to death or disability.
The onset of an ischemic attack can be rapid or gradual. But if there are signs indicating that a stroke has occurred, the patient should be transported to the hospital as soon as possible. Early treatment promotes a more complete restoration of the affected neurons and the return of lost functions.
Source:
ONMK: what is it?
- ACVA of ischemic type.
- Many people ask the question of what an acute stroke is and what consequences there are after it. This article will examine the main causes of stroke and consequences.
- ONMK - what is it?
Many people who have nothing to do with medicine probably do not know what stroke is.
So, an acute circulatory disorder in the brain is a stroke, which causes damage and death of brain cells.
The cause of this disease is the formation of a blood clot in the blood vessels of the brain or the rupture of some blood vessels, which causes the death of a huge number of nerve cells and blood cells. According to statistics, acute stroke ranks first among diseases that cause human death. Every year around the world, as the federal register of patients with acute stroke indicates, 14 percent of people die from this disease, as well as 16 from other types of diseases of the circulatory system.
Reasons why stroke may occur.
In order to prevent the occurrence of this disease, it is necessary to pay attention to your lifestyle from an early age. For example, constant exercise can significantly reduce the possibility of developing stroke. You already know what it is; some of the causes of this disease will be discussed further.
As a rule, this disease does not come suddenly; very often the diagnosis of stroke can be established as a consequence of certain diseases.
Often the cause of this condition can be:
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- high cholesterol;
- heart disease;
- alcohol and smoking;
- various types of medicines;
- high hemoglobin level;
- age;
- traumatic brain injury;
- genetic predisposition and so on.
Now it’s clear what ONMC is. These are the consequences of an incorrect lifestyle. Therefore, it is very important to monitor your health and physical condition.
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke is a stroke caused by damage to brain tissue and disruption of blood flow to one or another part of it.
Most patients with stroke of ischemic type have common diseases of the cardiovascular system. Such diseases also include arteriosclerosis, heart disease (arrhythmia, rheumatic disease), and diabetes.
This type of stroke is characterized by sharp and frequent manifestations of pain, the consequence of which is a deterioration of blood circulation in the cerebral cortex.
As a rule, such attacks can occur several times an hour and last for 24 hours.
Causes of ischemic stroke ACVA
The main reason for the manifestation of ischemic stroke is a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Very often, this is why the cause of death of a person is ischemic stroke. So, we found out the features of ischemic stroke, what it is and what its symptoms are.
Source: //fiz-disp.ru/lekarstva/onmk-po-ishemicheskomu-tipu-diagnostika-lechenie-osobennosti.html
Who's at risk
The following factors increase the risk:
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- diabetes;
- smoking;
- cardiac ischemia;
- high cholesterol;
- excess body weight;
- low level of physical activity;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- vascular malformations;
- stenosis of the carotid arteries;
- fibromuscular dysplasia of the arteries;
- diseases of the blood system;
- alcohol abuse.
How often does it occur?
Every year in Russia, 400-500 thousand people suffer strokes, of which 200-230 thousand die. In the most acute period (the first 3 days), the mortality rate is 35%, another 15% die within a year.
In more than half of the patients, their usual work activities are disrupted, and 25% require constant specialized care. A third of patients are of working age, of which less than 10% return to their usual work. 80% of stroke patients are assigned a disability group.
In the structure of the acute stroke disease, ischemic stroke is recorded in 75% of cases, hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack and cerebral hypertensive crisis are recorded in 25% of cases.
Transient ischemic attacks are precursors of stroke
In addition, there are transient disorders of cerebral circulation, the occurrence of which causes minor damage to brain activity and does not affect its vital functions. Most often they are caused by arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, or a combination of both. Such short-term disorders are called transient ischemic attacks. The patient's condition then normalizes within 24 hours.
Depending on the location of the ischemic focus, transient cerebrovascular accident manifests itself with various symptoms. When the pathological process is located in the basin of the carotid vessels, the patient experiences numbness on the side of the body opposite to the lesion, and the sensitivity of the part of the face in the mouth area is lost. In some cases, temporary paralysis of the limbs occurs. Speech disturbances are noted, and there is a high probability of an epileptic seizure.
Damage to the vertebrobasilar area causes weakness of the upper and lower extremities, dizziness, and a decreased swallowing reflex. Vision problems may occur: the patient sees luminous points, flashes, sparks, objects split into two. There is a loss of space, accompanied by memory lapses.
During transient disorders, a sudden severe pain syndrome occurs in the head area, radiating to the eyeballs, accompanied by drowsiness, stuffy ears and attacks of nausea. There is hyperemia of the skin on the face and increased sweating.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms, their duration and intensity depend on the specific lesion. All symptoms encountered in stroke can be divided into general cerebral, focal neurological and autonomic.
General cerebral symptoms:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- disturbance of consciousness (stunning, stupor);
- loss of orientation in time and space;
- psychomotor agitation.
Focal neurological symptoms:
- Motor disorders - limitation of motor function in one half of the body (for example, the left arm, left leg, left side of the face) is often combined with weakness and clumsiness in the limbs. The affected side is characterized by a gradual increase in the tone of the flexor muscles and an increase in deep reflexes. The disturbances occur on the side opposite to the lesion.
- Speech disorders - difficulties appear in choosing words and constructing phrases. Speech becomes slow, slurred, and it is difficult to pronounce even basic words. Patients may also experience difficulty understanding spoken speech.
- Impaired sensitivity manifests itself in the form of paresthesia (unpleasant tingling on the surface of the body), decreased pain and tactile sensitivity. Sensitivity is impaired on the side opposite to the side of the lesion, and is often combined with motor disorders.
- Visual impairment - blurred vision, double vision, the appearance of spots and spots before the eyes, and loss of visual fields may occur. In some cases, blindness in one eye occurs.
- Coordination disorders - unsteadiness of gait is observed, voluntary coordinated movements in the limbs are impaired. Patients are clumsy, unstable in an upright position, and often fall towards the affected side.
Autonomic symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- rapid breathing;
- strong heartbeat;
- dry mouth;
- increased sweating;
- increased body temperature;
- feeling of a rush of heat.
Epileptic seizure - convulsive seizures occur with extensive hemorrhagic strokes and subarachnoid hemorrhages. Convulsions are strong muscle contractions, lasting on average 2-3 minutes, after which a relaxation phase begins, during which there is a clouded consciousness, disturbance in spatial orientation, and incoherent speech.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of chronic cerebrovascular accident is made based on a combination of examination data, symptoms, neurological signs, results of brain neuroimaging (MRI, CT or MSCT), angiography of cerebral vessels.
The doctor may detect the presence of certain neurological, motor, and sensory deficits, such as changes in vision or visual fields, abnormal reflexes, abnormal eye movements, muscle weakness, decreased sensation, and other changes. In addition, certain tests help determine the presence of intellectual-mnestic disorders.
Laboratory research methods are prescribed for the diagnosis of somatic diseases.
Concepts and reasons
Disruption of brain activity as a result of the development of pathological changes in cerebral circulation can be caused by:
- Damage to large extracranial or intracranial vessels, which occurs as a result of the development of atherosclerotic phenomena.
- Not atherosclerotic vascular lesions (aneurysm, diseases of the blood system, impaired blood clotting ability, etc.).
- Thrombosis of the venous sinuses.
- Heart disease - cardiogenic embolism.
An acute cerebrovascular accident that causes permanent neurological damage to the brain is called a stroke. There are two types of this violation:
- An ischemic stroke develops when there is insufficient or no blood flow to a certain area of the brain. As a result, hypoxia occurs, a focus of brain tissue necrosis develops, and a cerebral infarction occurs.
- Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to decreased elasticity of the vascular wall. The vessel ruptures, which leads to the formation of a hemorrhage area, or hematoma. Blood penetrates either into the brain tissue (intracerebral hemorrhage) or under its membranes (spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage).
Circulatory disorders can be caused by a number of reasons, in the presence of which there is a high probability of developing cerebrovascular accidents of varying severity:
- hereditary predisposition;
- obesity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- bad habits: smoking and alcoholism;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- head injuries.
Treatment
If there are diseases such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus or other diseases, then, first of all, it is necessary to compensate for the underlying disease.
To treat chronic cerebrovascular accidents, various medications are used - vascular drugs (Trental, Cavinton, Sermion, etc.), nootropics, metabolic drugs, antioxidants. To prevent the formation of blood clots, antiplatelet agents such as aspirin, dipyridamole are prescribed. For high cholesterol levels in the blood Statins may be used.
Sometimes surgical treatment is required to eliminate the blood flow disorder - for example, carotid endarterectomy. Treatment methods such as carotid angioplasty and stenting are also used.
Clinical picture
Symptoms during the development of acute cerebrovascular accident have varying degrees of severity, which largely depends on the damage to a specific area of the brain.
As a result of the development of a stroke, the following appear:
- General cerebral symptoms - pain in the head, attacks of nausea and vomiting, impaired consciousness.
- Meningeal symptoms - photophobia, Kernig's sign, etc.
- Focal symptoms - neurological changes are observed depending on the focus of the brain lesion, paralysis of the limbs, impaired tactile sensitivity, the function of the speech apparatus, and loss of vision in one eye occur.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before hospitalization, it is extremely important to suspect the presence of stroke in time. The patient is asked to do the following:
- Pronounce a phrase - evaluate the clarity of pronunciation of individual sounds and words, the correct order of phrase construction.
- Raise your arms in front of you - they look at whether a person can raise and hold his arms in front of him, whether the strength in the limbs is the same.
- Try to smile - check whether the face is symmetrical during facial contractions, whether there is sagging of one half of the face, whether the movement of the facial muscles is difficult when smiling.
If there are difficulties in performing at least one point, immediate hospitalization in a hospital with suspected stroke is indicated.
At the hospital stage, diagnosis begins with anamnesis and objective examination. The doctor evaluates vital signs (the presence of consciousness, respiratory rate, degree of blood oxygen saturation, pulse rate and characteristics), conducts an examination, and also excludes other possible causes of a clinical picture similar to that of stroke (examination of the soft tissues of the head to exclude TBI, determination of glucose levels to exclude hyperglycemia, etc.).
A neurological examination may reveal the following pathological symptoms:
- Kernig's sign - the doctor bends the patient's limb, and then asks the patient to try to straighten it. This turns out to be impossible due to high muscle tone.
- Stiff neck - increased tone of the neck muscles makes it impossible to bring the chin to the chest.
- Brudzinski's superior sign is an involuntary bending of the leg when trying to bring the chin to the chest.
- Brudzinski's symptom is moderate - when pressing on the pubic bone, the patient's legs bend at the hip joints and are pulled towards the body.
- Brudzinski's lower sign - an attempt to straighten a previously bent leg leads to the other leg being pulled up towards the body.
Laboratory research
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemical blood test (ALT, AST, glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides).
- Coagulogram (APTT, fibrinogen, INR) is a method for studying the coagulation system and fibrinolytic activity of the blood.
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis is performed if a hemorrhagic stroke or subarachnoid hemorrhage is suspected. The material is taken through a lumbar puncture. In this case, a large number of red blood cells and a moderate number of lymphocytes will be present in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Instrumental examination
- CT (computed tomography) is a neuroimaging method based on layer-by-layer examination of the brain using X-rays. It is used to differentiate ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, assess the affected area, its size and location. Using CT, vascular malformations, aneurysms and stenoses, as well as other brain pathologies (tumors, infectious-inflammatory process, brain injury) are excluded.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a method also used in diagnosing stroke. It has the same diagnostic value and is used to assess structural disorders of brain tissue. More accurately than CT, it detects lesions in the brain stem. Less commonly used due to the duration of the examination (30-45 minutes).
- Ultrasound of neck vessels makes it possible to assess the condition of extra- and intracranial vessels (pathologies of vascular development, hemodynamically significant stenoses, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, blood flow velocity).
- EchoCG - ultrasound examination of the heart is performed if a cardioembolic nature of a stroke is suspected.
- An EEG (electroencephalogram) is used when a patient is having a seizure to rule out epilepsy.
- Cerebral angiography is used to detect aneurysms of cerebral vessels, as well as subarachnoid hemorrhages. In most cases, it is performed when CT and MRI are technically unavailable.
Treatment Goals
- Surgical correction of disorders of vital functions and organs;
- minimization of organic defect;
- prevention of possible complications;
- partial or complete restoration of lost functions.
Lifestyle and aids
If stroke is suspected, the patient should take a horizontal position with the head of the body raised. It is necessary to ensure the flow of oxygen, free the airways from foreign objects and prostheses, and monitor possible retraction of the tongue in case of impaired consciousness.
At the hospital stage, patients must be shifted from side to side every 3-4 hours to avoid bedsores. The use of elastic bandages and stockings on the lower extremities is indicated to prevent thrombus formation in the veins of the lower extremities and the development of complications - pulmonary embolism (PE).
Medicines
- Thrombolytic therapy is prescribed for ischemic stroke, when arterial occlusion is caused by a thrombus or embolus. Can be used in the first 6 hours from the onset of the disease. The following drugs are used for these purposes: alteplase, prourokinase, tenecteplase, etc.
- Antihypertensive drugs - in clinical practice, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists are used. The decrease in blood pressure should not be very rapid to avoid cerebral hypoperfusion.
- Neuroprotective drugs are drugs that have a protective effect on nerve cells in conditions of structural damage. Antioxidants, calcium channel blockers, nootropics, postsynaptic glutamate inhibitors, etc. are used.
- Antiplatelet drugs reduce the ability of platelets and red blood cells to stick together, preventing the formation of clots and leading to the disintegration of existing blood clots. They are used as a treatment for ischemic stroke, as well as to prevent the development of thromboembolic complications.
- Anticonvulsants are used in cases of epileptic seizures.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used when body temperature rises to febrile levels (more than 38 degrees).
- Antiemetic drugs - for prolonged and persistent dyspeptic symptoms (nausea and vomiting).
Procedures
- Oxygen therapy is the inhalation of a gas mixture with a high percentage of oxygen. Used to normalize the patient's external respiration function.
- Passive gymnastics and massage are carried out to maintain normal tone and prevent muscle atrophy.
Surgical operations
- Puncture aspiration of a hematoma - the method is used for subacute or chronic intracranial hematoma in a relatively satisfactory condition of the patient. Allows you to remove only the liquid part of the hematoma, without removing clots.
- Local fibrinolysis of the hematoma is carried out as the next stage of puncture aspiration. A special fibrinolytic drug is injected into the hematoma cavity, which dissolves the clots, after which the contents are aspirated.
- Open hematoma removal - removal of a hematoma using an open method. In one operation, complete removal of the hematoma can be performed. At the same time, open surgery increases the risk of complications.
- Videoendoscopic hematoma removal is a minimally invasive method of hematoma removal using modern endoscopic equipment. Allows you to completely remove the hematoma and reduce the risk of intra- and postoperative complications.
- Thrombendarterectomy - mechanical removal of a blood clot using a special catheter. Used for ischemic stroke.
Restoring and improving quality of life
Rehabilitation after stroke should begin as early as possible and have an integrated approach (with the involvement of a large number of specialists). Patients are recommended to be hospitalized in a specialized neurological department for patients who have suffered a stroke.
Household rehabilitation is carried out, patients are trained in the use of special devices that facilitate self-care. For speech disorders, classes with a speech therapist are indicated; for movement disorders, physical therapy, in particular kinesiotherapy, therapeutic massage, electrophysiotherapy, acupuncture, and individual psychotherapy.
During the rehabilitation period, drug therapy is used aimed at preventing long-term complications, restoring nerve cells and improving the patient’s cognitive functions:
- neuroprotective drugs;
- nootropic drugs;
- antidepressants;
- muscle relaxants;
- acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Consequences of stroke
Our clinic successfully treats stroke and eliminates the consequences of the disease. For this purpose, we use modern techniques, rich experience and a high level of qualification of our neurologists, and an individual approach. Based on this, patients who turn to us for help are confident in their recovery.
What are the consequences of stroke
An acute cerebral circulatory disorder can have both mild and severe consequences. Every year, about half a million cases of stroke are recorded worldwide.
Of the victims, 75% survive, but many remain with functional impairments, which are grounds for disability. According to WHO forecasts, by 2020 the number of cases will increase by 30%.
Therefore, it is important to know why the disease is dangerous and how to effectively fight it.
The most common consequences of stroke are:
- Sudden fainting.
- Involuntary urination.
- Loss of ability to move independently.
- Impaired ability to recognize individual body parts.
- Frequent dizziness, noises in the head, double images before the eyes.
- Speech dysfunction: confusion, difficulty finding words and pronouncing them.
- Frequent loss of balance, impaired ability to navigate in space.
- Partial dysfunction or complete paralysis of some limbs, part of the body, one of the sides.
- Loss/impairment of vision, hearing, touch, smell, sensitivity of nerve endings.
The majority of patients treated in the neurology department of our clinic are people who have suffered a stroke. During their treatment, doctors solve two strategic problems:
- Secondary prevention of recurrent stroke.
- Treatment (drug, non-drug) and correction of neurological disorders.
Preventing recurrence of attacks
25% of patients who have had an ischemic stroke are at risk of experiencing a recurrence. The greatest likelihood exists within the next year.
In this regard, it is important, after taking emergency measures to save the patient, to engage in secondary prevention.
Let us note that AI is not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This determines the set of preventive measures:
- Drug therapy aimed at eliminating cardiovascular diseases and rapid regression of neurological disorders.
- Lifestyle modification: getting rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), correcting body weight (bringing it to normal), performing special physical exercises, following the principles of proper nutrition, including reducing the amount of animal fat consumed.
Recovery process
Stroke is the No. 1 cause of chronic disability in the world. 40% of people unwittingly develop physical and psychological dependence on loved ones, doctors, nurses. However, neurological disorders tend to regress naturally. The task of specialists is to speed up this process.
The body's ability to recover is based on the mechanism of neuroplasticity:
- Departments of the central nervous system may be reorganized.
- Neurons have the ability to undergo structural and functional changes.
The recovery process has three stages:
- Spicy. Spontaneous recovery.
Immediately after AI (within a week), many body functions resume:
- cerebral edema decreases;
- blood circulation improves in areas bordering the lesion.
- Subacute. Full recovery.
During treatment the following changes occur:
- Brain tissues are functionally reorganized.
- The tissue around the lesion increases its activity.
- Synaptogenesis is activated.
- Chronic. The compensation is improved coordination and increased muscle mass.
This is the first important task of rehabilitation.
Loss of coordination and loss of mobility occurs in 80-90%, of which only 30% of patients remain able to move independently immediately after an attack. In this area, research is continuously being conducted and methods with a high level of efficiency are being developed. Today, three of them are most often used:
- A method for learning a specific skill. A rehabilitation specialist helps the patient set a specific task and solve it. As a result, the patient develops and learns the most productive movement strategy.
- Forced movement therapy. In this case, the limb that was not damaged at the time of the stroke is deliberately immobilized. As a result, the entire load falls on the injured leg/arm. Daily household activity helps restore the functionality of the organ.
- Bilateral training. In this case, motor tasks are performed simultaneously by both the healthy and the injured limb.
Speech restoration
This is the second important task of rehabilitation.
There are several rehabilitation programs. The choice is influenced by the period and stage of rehabilitation, the nature and degree of speech dysfunction. The main difference between the early stage and the late stage is the degree of patient participation: from passive to active.
What does the doctor do:
- Stimulates listening comprehension.
- Works with the expressive side of speech through the use of proverbs, songs, elementary speech patterns, and so on.
- Helps the patient complicate his speech with verbal vocabulary, which prevents agrammatism (telegraphic style).
- Engages the patient in reading and writing.
It is worth noting that restoration of speech function to its previous state is impossible. During treatment, the patient's speech changes its structure.
Possible complications
- Occlusive hydrocephalus is a hematoma that occurs during the development of a hemorrhagic stroke and can compress the cerebrospinal fluid outflow tract. This leads to the accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the ventricles of the brain and increased intracranial pressure.
- Infectious complications - patients who lie down for a long time have an increased risk of developing infectious complications such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, etc.
- Venous thrombosis of the lower extremities - in patients with forced bed rest, the risk of developing blood clots in the venous system of the lower extremities increases, which can be a source of thromboembolic complications, incl. pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Bedsores are necrosis of soft tissues due to prolonged mechanical pressure on tissues and disruption of local blood circulation and trophism. More often they occur on the back, the back surface of the upper and lower extremities, buttocks, and sacrum.
To prevent stroke, it is recommended:
- control blood pressure;
- monitor body weight;
- follow a diet and control cholesterol levels;
- give the body regular moderate physical activity;
- monitor blood sugar levels;
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- consult a specialist about taking oral contraceptives.
In case of identified vascular pathologies of the brain (vascular malformations, aneurysms, angiomas), specific prophylaxis is carried out to reduce the risk of stroke (balloon angioplasty, aneurysm clipping).
Vasoleptin
Vasoleptin is a biologically active drug containing a set of exclusively natural components. This complex smoothly and effectively reduces elevated blood pressure and stabilizes it, normalizes cholesterol levels, stimulates metabolism and cerebral circulation. It contains propolis derivatives, extracts of medicinal plants black rowan, rose hips, marigold, St. John's wort and leuzea. In combination, they have a pronounced antioxidant effect, reduce the level of the most atherogenic lipoproteins, are vasoprotectors, and normalize blood pressure. Additionally, propolis improves blood rheology and has an immunomodulatory effect. In addition, extracts of St. John's wort, marigold and leuzea increase the body's adaptive abilities to stress factors that can trigger the development of stroke.
Treatment and prevention
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, control diet and work habits, not overuse physical activity, and study and apply various methods of relieving psycho-emotional stress. Prevention of chronic cerebrovascular accident also involves regular medical examinations.
To treat dyscirculatory encephalopathy, drug therapy is used in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as acupuncture, massage, and therapeutic exercises.
| Make an appointment | Make an appointment by phone or by filling out the online form - the administrator will contact you to confirm your appointment |
UNION CLINIC guarantees complete confidentiality of your request.
Prevention
It is quite difficult to achieve complete regression of the neurological deficit after stroke (with the exception of PNMK). Therefore, it will be more competent to prevent the development of acute vascular accidents.
Prevention of stroke is understood as a set of measures aimed at identifying and eliminating correctable risk factors. Basically, they come down to the prescription of medications, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, diet optimization, psychotherapeutic correction, herbal medicine and the use of biologically active substances. It is considered ideal if the drug is completely natural, effective, has no side effects and affects several etiological links at once.
What questions should you ask your doctor?
- What types of stroke are there?
- What causes acute cerebrovascular accident?
- Who is at risk for developing stroke?
- How can one suspect an acute cerebrovascular accident?
- What to do if you suspect stroke?
- How is a transient ischemic attack different from a stroke?
- What treatment methods are there for stroke?
- How can you change your lifestyle to avoid stroke?
- What rehabilitation methods are used for strokes?
After 40-50 years, a burden of problems and diseases gradually accumulates. Some of them can be easily eliminated by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, changes in diet and exercise, but when blood circulation to the brain is impaired, treatment should be specific, depending on the type of pathology (acute or chronic disorders), as well as the severity and presence of certain symptoms and complications.
According to WHO data, pathologies associated with blood vessels, especially acute ones, are the leading cause of disability and death in relatively young patients.
Progressive symptoms of a chronic disorder without medical intervention gradually, over several years, lead to progressive dementia as a result of the formation of DEP (dyscirculatory encephalopathy), with disorders of both mental activity, cognitive functions, and motor acts, sensitivity and coordination. In this regard, the question of how to treat this disease in the presence of acute disorders or chronic, gradually progressive abnormalities becomes important. These issues are addressed by neurosurgeons, neurologists and therapists who deal with such patients.
Clinical guidelines for recovery
After the ambulance arrives, the patient is sent to the neurological department. He receives drug treatment depending on the symptoms and their severity.
Medicines
Medicines for each patient are selected depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of certain signs.
The treatment regimen may include drugs from different groups:
- Actovegin is considered the best remedy for improving nutrition and metabolic processes in the tissues of the whole body. It improves the condition, prevents the progression of the disease and stimulates cell restoration. The drug is administered intravenously at 10 ml per day for 10-14 days. At the same time, it is diluted with 10 ml of sodium chloride. In severe cases of the disorder, the daily dosage of the solution is increased to 20 ml.
- Cavinton is indicated to improve cerebral circulation and normalize blood pressure. The patient undergoes courses of 10 days with daily administration of 2-4 ml of solution, which is previously added to 200 ml of sodium chloride 0.9%. If necessary, the course is extended to 2-3 weeks.
- L-lysine helps eliminate cerebral edema and slightly reduces blood pressure; it is used in patients with a history of pathologies of the spinal column. 10 ml of solution is administered intravenously to the patient per day using a dropper after first adding 200 ml of sodium chloride. Treatment lasts up to 2 weeks.
- Magnesium sulfate is indicated for critical increases in blood pressure, when tablet medications do not help normalize them. The drug is administered intravenously in a stream very slowly in a dosage of 5-10 ml of solution. The product must be mixed with sodium chloride. The drug is rarely used in courses; usually a single administration is sufficient, but in an acute condition it may require administration from 3 to 10 days in a row.
- Atorvastatin helps lower the level of bad cholesterol in the blood and is used when the patient is able to swallow the pill. The patient takes 1-2 tablets per day, treatment lasts from 10 to 30 days, depending on the severity of the manifestations.
- Cardiomagnyl is prescribed to thin the blood and ease the work of the heart. Tablets are taken at 75-150 mg per day. Therapy lasts from 2 to 4 weeks.
- Lasix is a diuretic to eliminate swelling and lower blood pressure. 2-4 ml is administered intravenously or intramuscularly in the morning for 2-5 days.
- Neuroxon helps improve the nutrition of brain tissue and shortens the rehabilitation period. It is administered intramuscularly at 500-1000 mg per day for 10-20 days. The drug is effective and significantly increases the effectiveness of therapy.
- Nifedipine is used to lower blood pressure when the patient is conscious. Tablets are taken in the morning or evening, 1-2 pieces, depending on blood pressure readings. The drug can be used in courses or on an ongoing basis.
- Ceftriaxone is often prescribed to patients to prevent the development of severe bacterial complications. The drug is administered intravenously after preliminary dissolving the powder in 10 ml of sodium chloride. The course of therapy lasts 10 days. The daily dosage for the patient is 2-4 g.
- Propranolol helps normalize heart rhythm in patients with arrhythmia by reducing myocardial oxygen demand. Prescribed in courses of 2-4 weeks with daily use of 1 tablet. Correction of dosage and duration of use is determined by the doctor.
- Rheosorbilact is prescribed if necessary to relieve intoxication. The product helps prevent dehydration and improves blood circulation. Every day for 1-2 weeks, 200-400 ml of solution is infused intravenously into the patient using a dropper.
All remedies are not used at the same time; in each case, the specialist selects several of the most effective medications.
Traditional methods of treatment
Acute cerebrovascular accident cannot be cured using alternative medicine recipes. But many patients during the recovery period use herbal medicines, which somewhat alleviate the condition, lower blood pressure and help prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Motherwort tincture helps lower blood pressure and has sedative properties. You can prepare it from 20 g of crushed plant rhizomes and 100 ml of vodka. The product is infused for 2 weeks, after which the filtered composition is allowed to be taken orally. A single dosage is 30 drops, repeating the dose is allowed 2 times a day. The course lasts 10-14 days.
A decoction based on hawthorn fruit improves heart function and has a positive effect on the vascular wall. You can get the medicine by boiling 50 g of crushed fruits in 1 liter of water for 5 minutes. Take 150 ml of the filtered and cooled medicine 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
Propolis tincture has a positive effect on the entire body and improves general condition. You can get the medicine by infusing 20 g of raw material in 100 ml of alcohol for 2 weeks. Take the finished product 20 drops 2 times a day for 10 days.
Do not use the products in the acute period and without a doctor’s prescription. Otherwise, the risk of complications increases.
CNMK: treatment
In the presence of permanent or transient symptoms of chronic cerebrovascular accident, treatment will be long-term, lifelong and aimed at slowing down progressive changes in the skull associated with hypoxia and cell nutrition deficiency. It is important to take all measures to protect neurons from free radicals and hypoxic lesions, activate metabolic processes at the level of the cortex and subcortical, stem formations, and normalize blood flow through the vessels. The doctor selects the medications individually and takes them strictly under the control of vital signs.
In addition to basic therapy, for patients with poor, insufficient blood circulation to the brain, treatment can be supplemented (only in consultation with the doctor or in accordance with his prescription) with the use of traditional medicine and herbal medicine. Herbal medicines are recommended with basic medications - herbal teas to normalize vascular tone and blood flow, natural products - beekeeping products.
A diet with reduced calorie intake is indicated to combat excess weight and measures to reduce total cholesterol and atherogenic fats (low and very low density lipoproteins). If nutritional correction alone is ineffective, special statin drugs prescribed for a long period of time are indicated.
Indications for thrombolysis
Acute cerebrovascular accident requires urgent medical care, and this will not only save the patient’s life, but also increase the chances of rehabilitation in the future. Thrombolysis is used as an emergency measure when the first signs of acute cerebrovascular accident appear. The essence of this treatment method is the dissolution of blood clots that cause impaired blood flow in the brain.
Thrombolysis must be applied in the first 3 hours of stroke development, the maximum allowable time for administering the drug is 6 hours. After this period, the technique becomes useless and, in some cases, dangerous.
Thrombolysis is indicated for ischemic stroke. It is carried out by systemic and local administration of drugs. With systemic intravenous administration, the location of the thrombus is not important. When applied locally, the drug is administered at the site of its localization.
The use of this technique is contraindicated in the following cases:
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- stomach ulcer;
- predisposition to bleeding due to high blood pressure;
- liver diseases;
- brain surgery;
- pregnancy;
- arterial hypertension;
- aortic dissection.
Rehabilitation methods and restorative treatment of cerebrovascular accidents
Medicines can stop the progression of the disease, but they cannot restore movement or cognitive function. Therefore, it is important to carry out a course of rehabilitation that will help eliminate or reduce the severity of problems with limbs, movement and muscle atrophy.
Physiotherapeutic procedures play a major role in the rehabilitation of patients with stroke: magnetic therapy to improve blood flow in the vessels of the brain and neck, electrical myostimulation to restore lost muscle tone, hyperbaric oxygenation (pressure chamber) to increase oxygen access to brain cells.
During recovery, the return of lost body functions requires patience and perseverance of the person himself and his family, who will have to conduct special courses of massage and gymnastics for several months.
There is a classic system of exercises performed with the help of human hands or simulators, which helps in learning new movement patterns, forming new conditioned reflex connections in the brain. In essence, a person learns to move again, maintain balance and tone muscle groups. Rehabilitation doctors, kinesiotherapists, massage therapists and neurologists participate in the development of rehabilitation treatment.
Specialists select an individual program, monitor its tolerability and progress in restoring functions.
Consequences
The development of a stroke has serious consequences for the body and human health. As a rule, even with a favorable outcome of the disease, a long time is required for rehabilitation and restoration of normal motor, speech, and psychomotor functions.
In more severe cases, paralysis occurs, up to complete immobilization. In addition to problems with motor activity, disturbances in speech reproduction and speech understanding are observed.
Stroke is a disease that requires the mandatory participation of loved ones and relatives in the process of treatment and rehabilitation. Loss of the ability to move independently, speech problems lead to severe psycho-emotional distress on the part of patients; Depression and lack of desire to take any action are often observed.
To fully participate in the treatment and rehabilitation process, the person caring for the patient must take a course in massage and gymnastics or receive recommendations from a doctor or exercise therapy instructor. Such techniques are easy to learn. No special knowledge is required to perform them.
Despite all the achievements of modern medicine, acute cerebrovascular accidents do not go away without leaving their mark on health and in most cases have serious consequences. Timely seeking emergency medical help can increase the chances of minimizing them.
Additional rehabilitation measures
As acute symptoms are eliminated, therapy is supplemented with breathing exercises performed directly in bed as the patient’s condition improves. The set of exercises is aimed at improving tissue oxygenation, including muscles, relieving muscle tension after gymnastics and massage, and improving overall emotional tone.
In the presence of prolonged bed rest, the drugs complement the full-fledged care measures necessary to prevent serious complications - congestive pneumonia, joint contractures and bedsores. It is important to constantly change the patient’s position, including turning over onto the stomach, and it is also necessary to place bolsters and pillows under the legs and back. The use of special hygiene products, cosmetics, and medical devices during the care process allows you to keep the skin of a bedridden patient in good condition.
List of used literature
- Kothari RU, Pancioli A., Liu T., Brott T., Broderick J. Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale: reproducibility and validity.
- Guidelines for Management of Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack. The European Stroke Organization (ESO).
- V.G. Dashyan, I.M. Godkov, V.V. Krylov. Endoscopic surgery for hemorrhagic stroke.
- Neurology: national guide / Edited by E.I. Guseva, A.N. Konovalova, V.I. Skvortsova, A.B. Gekht., 2020.
- Association of General Practitioners (Family Doctors) of the Russian Federation.” Clinical recommendations “Diagnostics and tactics for stroke in general medical practice, including primary and secondary 1. prevention”, 2013.
- All-Russian Society of Neurologists. Clinical guidelines “Ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in adults”, 2018.