Reasons for violations
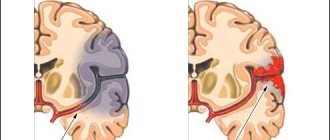
Among the most common causes of the onset of the disease, experts cite trauma to the brain stem area, resulting from concussions, bruises, as well as exposure to pathogenic microflora. In children, a separate group includes dysfunctions of brain stem structures resulting from severe pregnancy, caused by prolonged consumption of alcohol, maternal smoking, or as a result of birth trauma.
If there are suspicious signs, the cause of the pathology is determined. After describing the symptoms of the disease to the patient, the doctor prescribes a computed tomography scan, in which deviations from the normal functioning of the brainstem trunk are detected as a result of layer-by-layer scanning. Magnetic resonance or computed tomography will identify and evaluate the size of pathological neoplasms and detect displacement or deformation of the organ.
Note! Computed tomography is not recommended in the absence of signs indicating organ trauma.
An electroencephalogram is also prescribed, the essence of which is to record the electrical signals of the brain and their subsequent evaluation. The goal of the test is to find the source that is causing the brain stem irritation. Depending on the location of the area of deformation or damage to the organ structure, experts identify the following types of deviations of the brain stem.
Minimal dysfunction
In percentage terms, this type of disease affects 1/5 of the patients. Most often, deviation occurs due to oxygen deficiency, injuries received during pregnancy or during childbirth. Experts define this form of pathology as a mild degree of damage to structures, causing a minimal number of consequences, among which the most common are memory impairment, decreased or increased activity of the child, decreased ability to concentrate, fatigue, and developmental inhibition.
Note! Hyperactive children with damage to the brainstem are characterized by excessive impulsiveness, have difficulties with learning, concentrating and remembering the material covered, often cannot write correctly, and are characterized by impaired orientation in space.
Children with reduced activity seem lethargic and apathetic; they may have problems with the functioning of the speech apparatus and pathologies in the functioning of the nervous autonomic system. Such teenagers have a high risk of becoming antisocial citizens, they develop early cravings for alcohol and drugs, and they begin to be sexually active earlier than their peers.
Dysfunction of midline structures
This variant of pathology manifests itself in the form of sleep disturbances, emotional disorders and deviations in the functioning of the nervous system. Signs of dysfunction of the mid-stem structures of the brain are expressed as follows:
- Deviations of the endocrine system, which, depending on the location of the damage, make themselves felt by an increase or decrease in the patient’s pressure and body temperature.
- A decrease in sensitivity, especially clearly manifested in the area of the patient’s face and torso.
- Pathologies in the epiphyseal region of the brain, leading to early onset of sexual activity.
- Unnatural character of the patient's laughter or crying.
- Impaired fine motor skills and involuntary trembling of the limbs.
- Lowering the pain threshold, increasing sensitivity to discomfort.
Note! Dysfunction of the mid-stem structures occurs as a result of TBI in the brain stem associated with the consequences of an accident, falls, or bruises.
Lesions of cortical fields
Irritation of the cerebral cortex often leads to the appearance of epileptic seizures and other disorders, the specifics of which will depend on the location of the irritation. Irritation in:
If no local signs of irritation are found, it is said to be diffuse.
Irritation of diencephalic (trunk, median) structures can also lead to epileptic seizures. In addition, there are signs of cognitive, emotional, speech, and autonomic disorders.
Irritation of the lower stem sections leads to disorders:
- consciousness;
- changes in sleep and wakefulness;
- attention, memory.
Irritation of the central parts of the hypothalamic structures leads to the appearance of diencephalic syndromes, which suggest the presence of:
Irritation of the thalamus can lead to various cognitive and speech disorders of a reversible nature, changes in the perception of the body diagram.
Irritation of the hypothalamus in the area of the gray tuberosity causes general disturbances in cognitive processes, disorientation in time and space, as well as depersonalization (a phenomenon in which a person’s own actions are perceived from the outside).
Irritation of the ventrolateral nuclei of the thalamus leads to impairments in recognition and naming of surrounding objects, some speech disorders, as well as short-term memory (for example, for unfamiliar faces).
This division of structures (median and stem) is quite arbitrary (for example, the hypothalamus belongs to both areas), and was introduced together with the practice of EEG, designed to determine signal deviations in one direction or another during the development of a pathological process.
Treatment, which is prescribed after registering signs of brain dysfunction, should be prescribed after establishing the cause of this phenomenon: additional instrumental diagnostics are carried out and the underlying disease is determined.
So, irritation is a term that is used in neurology when deciphering EEG, and means painful irritation of the cortical and diencephalic (stem, median) structures of the brain. Dysfunction is most often a secondary disorder - the doctor is faced with the task of identifying the primary disease and prescribing treatment that specifically affects it.
Irritative changes in the EEG are a form of general disturbances in biopotentials. They are more often observed in meningovascular neoplasms, which are intimately connected to the vessels of the meninges. To record the electrical activity of the brain, neurophysiologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform EEG using the latest equipment from world manufacturers.
The results of the study are deciphered by candidates of medical sciences. Leading experts in the field of neurology and neurophysiology analyze EEG data using a computer program. If there are EEG changes that can be interpreted ambiguously, at a meeting of the expert council, professors and doctors of the highest category discuss the results of the study and collectively make a decision regarding the diagnosis and treatment tactics of the patient.
Diencephalic disorders
Dysfunction of the diencephalic-stem structures is a disorder in the diencephalon, which has the potential danger of spreading the pathology to other parts of the brain, as a result of which symptoms of disorders characteristic of each of the damaged areas are added to the signs described above. Evidence of dysfunction of the diencephalic-stem structures of the brain manifests itself in the form of disorders of appetite, sleep, metabolism and thermoregulation in the patient.
Such disorders appear as a result of irritation of the cortex or other areas of the brain, which occurs due to failures of metabolism or blood supply, the presence of an infectious lesion or neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
Find out what asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is and what it means.
All about the basal ganglia: anatomical structure and physiological role.
Bioelectric activity of the brain
Bioelectric activity of the brain according to EEG is a complex descriptive characteristic that concerns the rhythms of the brain. Normally, the bioelectric activity of the brain should be synchronous, rhythmic, without foci of paroxysms. Moderate changes in the EEG of a regulatory nature indicate the presence of a region in the brain tissue where excitation processes exceed inhibition. This type of EEG is found in migraines and headaches. If doctors do not detect any other abnormalities, diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain may be normal.
With moderate changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain in combination with paroxysms or foci of pathological activity, neurophysiologists determine the presence of epilepsy or a tendency to seizures. Reduced bioelectrical activity of the brain is detected in depression. Dysfunction of midbrain structures is a subtle disturbance in the activity of brain neurons that often occurs in healthy people. It may indicate functional changes after stress.
Venous disorders
They appear as a result of circulatory failure due to heart failure, due to pressure exerted on the veins by a growing tumor, or due to head injuries as a result of trauma and childbirth.
Symptoms of this type of disorder may include the following:
- the appearance of a bluish tint to the skin of the face;
- the formation of edema in the area of the soft tissues of the face;
- the occurrence of pre-syncope and fainting;
- migraines that are pulsating in nature and manifest as a result of pressure surges associated with changes in weather conditions;
- increased incidence of darkening of the eyes;
- migraines that are dull in nature and occur in the morning;
- urge to nausea and vomiting;
- minimal activity occurring in the first half of the day.
Note! If there is a suspicion of spasm of the arteries or veins of the brain, it is necessary to consult a specialist who will prescribe a transcranial examination using ultrasound.
On the issue of treatment
The choice of treatment regimen is made by the doctor, taking into account a visual examination, medical history and life of the patient (for a child - the course of pregnancy in the mother and the nature of childbirth), the results of instrumental research methods, often prescribed over time.
In addition, neuropsychological diagnostics are important for the doctor (especially if there are speech disorders). The chosen treatment methods are individual in nature and include neuropsychological and pedagogical areas.
If the initial stages of treatment do not produce a positive result, medications are prescribed, the main ones of which are tranquilizers, psychostimulants, and nootropics. Amphetamines (Ritalin, amitriptyline) have proven themselves well in treatment.
Treatment of children should be carried out against the background of a full fight against the disease in the family. These are routine moments, being in the fresh air, communication, educational activities, interesting and educational leisure. In case of accompanying complaints, the doctor may prescribe symptomatic treatment. However, it is possible that such symptoms will subside as the underlying cause is treated.