Inflammation of the nerve manifests itself in the form of sensory disturbances and motor disorders in the affected area. If one nerve is inflamed, then this pathological process is called mononeuritis, if two or more - polyneuritis. This neuralgia may be associated with infectious diseases or hypothermia. Whatever the cause of the disease, in no case should you let it take its course or self-medicate. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the situation worsens; the disease becomes chronic, which is very difficult to treat.
What is
This pathology can occur for various reasons. If mononeuritis or polyneuritis appears, the following signs appear:
- changes in skin sensitivity
- pain at the location of the affected nerve;
- decreased muscle tone;
- muscle weakness.
On this topic
If these signs occur, you should immediately contact a specialist.
The most common neuritis occurs in the occipital, intercostal, and facial areas.
Classification
The disease can be classified according to different criteria.
The division occurs according to:
- location ;
- pathomorphological changes;
- the conditions of its occurrence;
- the number of affected nerves.
By localization they are divided into:
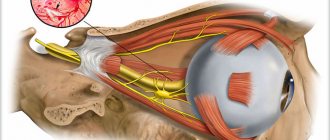
- Optic neuritis The cavity of the eyeball, the back of the orbit or the intracranial area is affected. If you do not go to the clinic in a timely manner, you can completely lose your vision.
- Vegetative. Any area of the human body is affected. Autonomic nerve fibers become inflamed, after which disturbances in blood circulation occur. A different shade of skin appears in the area of inflammation.
- Lesions of the cochlear nerve. Occurs after injuries to the skull, ear or infectious disease. If left untreated, deafness occurs, which later cannot be treated. A common symptom of this pathology is the appearance of noise and ringing in the ears.
- Trigeminal neuralgia, etc.
On this topic
According to pathomorphological changes, neuritis is as follows:
- Axial. Characterized by predominant damage to the axial cylinders.
- Adventitial. During the destruction of the upper outer sheath of the nerve, this type of neuritis occurs.
- Interstitial. Inflammation of the connective tissue structure of the nerve is observed
- Segmental. Individual small sections of nerve fibers along its entire length are affected.
- Rising. This is a process in which the lesion occurs in the distal part of the limb and spreads proximally.
- Parenchymatous. Inflammation of the nervous tissue itself occurs, involving axons and Schwann cells.
- Hypertrophic Gombo neuritis is characterized by segmental disintegration of the myelin sheath in limited areas of the nerve fiber with relative preservation of the axial cylinder; manifests itself in reversible dysfunction of the nerve fiber.
On this topic
If we take into account the conditions for the occurrence of neuritis, they are divided into:
- Infectious. Appear as a complication after infectious diseases (diphtheria, measles, scarlet fever, rubella). Toxic substances that spread throughout the body quickly give rise to new foci of the inflammatory process.
- Vibrating . If people's professions are associated with constant vibration, then they may suffer from such a disease. Oppression of the hand or foot occurs. In most cases, miners, drillers and construction workers suffer.
- Traumatic. Appear after accidents, bruises, falls, after which bone fractures occur. Another reason is prolonged compression of some part of the body.
- Toxic. The ulnar nerves suffer if heavy metal affects the body. Peroneal nerves, if affected by alcohol. Toxic poisoning can occur in the workplace when working with mercury or zinc.
- Endemic. Appears when there is a lack of nicotinic acid or B vitamins in the body. Frequent victims are patients with diabetes and pregnant women who have toxicosis.
On this topic
If we take into account the number of affected nerves, neuritis is divided into two types:
- Multiple lesions - polyneuritis.
- Single - mononeuritis.
Inflammation of nerve endings, symptoms and treatment
Inflammation of nerve endings or radiculopathy is perceived by a person as pain, which is a natural signal of the body to dangerous pathological processes that occur in it.
Pain sensations are ordinary electrical nerve signals, no different from signals caused by sounds, images or smells.
The irritating effect is caused by the brain's reaction to received information about danger.
Many people ignore such signals or consider it the height of masculinity to endure such inconveniences, when seemingly causeless pain, not associated with internal organ ailments or injuries, are symptoms of various dangerous diseases of the nervous system.
What's happened
Neuralgia and neuritis are inflammations of the nerves that occur for various reasons; sometimes inflammation occurs not of the nerves themselves, but of their endings or other parts.
Nerve endings are special tiny formations at the ends of neural processes that are responsible for receiving or transmitting information in the form of electrical nerve impulses.
There are several types of endings according to their area of specialization:
- Synapses that transmit impulses between neurons.
- Receptors or afferent endings that transmit information to a nerve cell from the external environment.
- Effectors – transmitting an information impulse from a neuron to tissue cells.
Inflammation of nerve endings is often called neuritis, when in addition to pain, paralysis, paresis, reduction or loss of sensitivity in the area of responsibility of the damaged area of the nervous system may occur.
Neuritis is a more dangerous disease than neuralgia, since the symptoms of neuralgia are caused only by the influence of something on the nerve, and not by its breakdown. With severe neuritis, which is a disease of the nerves themselves with a violation of their internal structure, the nerve may not recover, as well as the functions it performed.
It would be more correct to consider that inflammation of the nerve endings is a disease that is part of neuritis and its classification, and not directly by it, since with neuritis other parts of nerve cells or nerves can be affected.
What promotes inflammation
A variety of negative factors affecting the body or the nerve itself can contribute to inflammation of nerve endings:
- Drafts and hypothermia.
- Infection of the body with viruses, bacteria or fungi.
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues.
- Muscle spasms or compression of the nerve area.
- Bruises.
- Local infections in the form of an abscess.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Deficiency of certain substances, vitamins or minerals in the body.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- Toxic poisoning.
- Heredity or individual structural features of the body.
- Tumor processes and many other factors.
More often, inflammation of the nerves begins with prolonged negative irritating effects on the nerve or with infection.
Symptoms and types
The classification of inflammation of the nerve endings is based on the area of nerve damage, as well as their symptoms. There are the following main types, each of which has its own individual manifestations:
- Inflammation of the median nerve, also known as the ulnar, carpal, radial or ulnar nerve, which runs along the arm through the wrist. In this case, the work of the hand is disrupted or sensations arise in it in the form of numbness, tingling, pain or restriction of finger movement. The pain can shoot throughout the entire path of the nerve or be localized only at the site of inflammation.
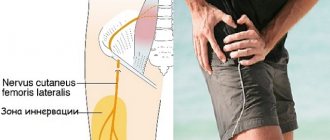
- Femoral nerve problems, where skin sensitivity or the ability to flex the hip joint are reduced, as well as pain along the surface of the leg, which can shoot down the entire leg.
- Inflammation of the nerve endings of the spine, which is one of the most dangerous types of neuritis and manifests itself in the form of severe pain in the back, chest or neck, depending on the affected area, which is called sciatica. Radiculitis also has its own classification, based on symptoms depending on the area of dislocation: radiculitis of the lumbosacral, cervical or thoracic region.
- Inflammation of the peroneal nerve is pain in the heel or lumbago from it, leading to the inability to fully lean on it.
- Damage to the nerve endings of the facial nerve is represented by disturbances in facial expressions, numbness of parts of the face or unpleasant sensations.
- A disease of the auditory nerve, when in addition to pain, hearing is lost or weakened, and problems with balance or nausea begin due to the fact that the auditory nerve is also responsible for the vestibular apparatus.
- Damage to the intercostal nerve causes more discomfort, since pain can occur not only when moving the body, but when breathing, which makes it difficult or unpleasant. In this case, the pain is truly hellish.
- Inflammation of the optic nerve is accompanied by loss or distortion of vision.
- Damage to the sciatic nerve endings manifests itself in the form of pain in the lower limb and impaired sensitivity and ability to move the leg. There are severe cutting groin and lumbar pains.
- Disease of the nerve endings in the occipital region provokes headaches, pain around the back of the head, pain from touching it, “twitching” of the nerve in the head, a negative reaction to light and lumbago in the ear or lower jaw.
In addition to the above, there are many more types of this disease: exactly as many as there are nerves in the body, each of which can become inflamed; other cases are extremely rare.
The concepts of primary inflammation of nerve endings are used - direct, and secondary, which develops against the background of any disease.
Diagnostics
To determine the presence of neuritis, a neurological examination and testing of nerve function using reflexes and testing motor functions, if possible, is performed.
To determine the extent of damage, instrumental examination methods are used:
- Electroneurography is a study of the speed of impulse transmission along a fiber and its conductivity. Allows you to determine the extent and area of damage.
- Electromyography – examines the boelectric activity of muscles and checks the functional state of neurons.
- Evoked potentials are a method similar to electroneuronography, but for deep nerves, such as the optic and auditory, where they are affected by sound or image and the conductivity is recorded by the activity of the corresponding parts of the brain.
- Ultrasound, X-ray, MRI or CT are diagnostic methods designed to identify the physical cause of damage to the nerve and its endings and prescribe the necessary treatment, rather than the disorder itself.
If an infection is suspected, laboratory tests of blood and other tissues are performed, including a biopsy of nerve tissue in extreme cases.
Consequences
Usually, neuritis of any origin is well treated, especially in young people whose regenerative abilities are high.
However, if neuritis is not treated, it can lead to a complete loss of the nerve’s functions, the capabilities it performed: vision, hearing, sensitivity, motor activity, secretion of any glands, as well as provoke the cessation of the work of any internal organ and etc.
Treatment
Treatment occurs by eliminating the cause of inflammation of the nerve endings, which may require the following procedures:
- Antiviral or antibacterial drug therapy.
- Surgical treatment with compression or physical impact.
- Anti-edematous therapy.
- Stimulation of blood circulation.
- Biogenic stimulation – stimulation of restoration processes with special preparations.
- Anticholinesterase therapy is treatment with drugs that inhibit nervous activity.
- Fortification and replenishment of deficiencies of minerals and other substances.
- Plastic or surgical suturing of the nerve, when a severely damaged area is removed.
- Local administration of drugs directly near the nerve.
- Physiotherapy treatment.
- stimulation of the nerve.
- Symptomatic treatment with anesthetics.
Treatment of inflammation of nerve endings is selected individually and depends on the specific type of neuritis and its location. With this disease, traditional methods selected with the help of a doctor are very helpful.
Conclusion
Diseases such as neuralgia or neuritis, which in addition to inflammation of the nerve endings has many other manifestations (radiculitis, funiculitis, plexitis, mononeuritis, polyneuritis) are similar in the method and names of classification, causes of occurrence, symptoms and treatment methods, may well lead the patient into confusion.
These ailments have a common essence and few differences:
- Neuralgia is a disease of the nerve for the same reasons without changing its structure, but only through its excessive excitation.
- Neuritis can be called a late or acute stage of neuralgia, when a disease of the nerve tissue itself occurs with its disorders.
- Varieties of neuritis differ from each other in the disease of specific parts of the nerve: nerve endings, nerve roots, peripheral nerves, etc. The causes and methods of treatment for all these diseases are the same. Plexitis can be classified as a separate category - a plexus of nerves or fusion.
A non-specialist does not need to understand all the terminology, classification of neuralgia and neuritis, the main thing is to remember that what seems from the outside a non-serious disease, which may not cause much suffering, only mild discomfort, can quickly lead to serious problems if the process is left to chance.
Nerve tissues are extremely difficult to restore, while the neurons themselves die forever, and the so-called restoration occurs by taking over the functions of dead cells by others.
If you have signs of neuralgia, you should definitely consult a doctor; no one wants to lose, for example, the ability to move a leg because of some stupidity, which could have been solved at one time by simply warming it up or a couple of injections.
Source: https://NashiNervy.ru/perifericheskaya-nervnaya-sistema/kak-lechit-vospalenie-nervnyh-okonchanij.html
Causes
The disease can occur due to external or internal reasons.
With internal causes, various diseases affect inflammation of the nerves. With external ones, the action comes from the environment.
These include:
- infectious diseases (influenza, scarlet fever, measles, herpes, polyarthritis, rubella, etc.);
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- various stages of obesity;
- osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia;
- disorders ;
- thyrotoxic goiter;
- poisoning (alcohol, drugs, mercury, zinc, drugs, etc.);
- lack of B vitamins
- various injuries (fractures, dislocations, wounds, unskilled injection, poorly performed surgery, etc.);
- last trimester of pregnancy (associated with excessive stress on the spine);
- hypothermia.
Regardless of what caused the inflammation of the nerve, only a highly qualified specialist should treat the disease.
Treatment of inflammation of nerve endings
What treatment can be given for inflammation of nerve endings? To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, medications are used: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, Nise, Movalis, etc.), glucocorticoid hormones (dexamethasone, prednisolone, etc.), B vitamins and other drugs. In addition, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, amplipulse, etc.). However, medications have many side effects and are not safe for our body.
Is it possible to cure inflammation of nerve endings without drugs? Our nervous system produces its own painkillers - endorphins and enkephalins; a person can initiate or enhance their synthesis. In addition, special gymnastics can relieve muscle spasms, improve blood supply to the source of inflammation and eliminate pain. There are also other methods and techniques to combat pain and inflammation. You can learn more about them at a special course at the M.S. Center. Norbekov "First health course." Wellness courses will teach you how to restore physical health, increase immunity, launch regeneration processes, and normalize your emotional background.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease will vary depending on the nerve affected. Common signs include:
- numbness of the affected area;
- feeling of goosebumps and tingling;
- poor sensitivity;
- pain while working or staying in one position for a long time;
- weakness and lethargy in the muscles (if left untreated, atrophy will occur);
- poor motor activity;
- poor functioning of the glands of the skin and organs.
On this topic
Swelling and discoloration of the skin where inflammation is localized may occur.
Most often it happens:
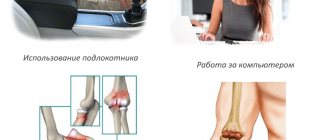
- Neuritis in the forearm (radial, ulnar and median). There is impaired mobility in the hand. It is difficult to bend your arm and move the phalanges of your fingers. My hand goes numb.
- Femoral neuritis. The knee and hip joints bend poorly. There is poor sensitivity on the front surface of the thigh below and inside the side of the shin. Muscle mass decreases in size and weakens.
- Peroneal neuritis. There is lameness due to the pain of standing on the heels. There is also shuffling and stumbling. When walking, a person lifts his feet strongly upward when he brings them forward.
- Facial neuritis. The affected part of the face immobilizes and relaxes. There is asymmetry. The eye cannot close, the forehead does not wrinkle. Pain behind the ear may occur, and half of the lips lose mobility.
The disease can be noticed immediately, since the signs of neuritis are very specific.
Diagnostics
With signs of an inflamed nerve, the patient is sent to see a neurologist. The doctor conducts an examination and functional tests. They determine movement disorders.
If a person has radial neuritis, then:
- when the hands are on the table surface with palms up, the thumb is not moved to the side;
- if the patient is in an upright position, with his arms down along his body, he is not able to turn the hand with the palm forward and move the thumb.
When a patient has median neuritis, then:
- impaired flexion of the hand and fingers in the interphalangeal joints,
- impaired sensitivity on the lateral surface of the palm and 1-4 fingers;
- It is not possible to make a contrast between the little finger and the thumb.
For ulnar neuritis:
- the patient is unable to spread the phalanges of the fingers when the palms are on the table surface;
- deformation of the hand like a “bird’s paw” as a result of paralysis and atrophy of the small muscles of the hand;
- pain and decreased sensitivity on the 5th and 4th fingers.
The patient may be referred by a doctor for a CT or MRI.
Electroneurography is used to measure the speed of transmission of a nerve impulse through peripheral nerve fibers. Using this technique, it is possible to identify pathology, discover where it is localized, and at what stage it is.
Electromyography is done to evaluate the bioelectrical activity of muscle tissue. This makes it possible to determine the functional state of the nerves and understand how far everything has gone.
Evoked potentials are a study of the bioelectrical activity of nerves. Neurologists use this method to study how the autonomic nervous system functions and evaluate the visual and auditory nerves.
Treatment
After a complete examination of the patient has been carried out, the causes of the disease and its degree have been determined, it is necessary to eliminate all the factors that provoked this pathology. This is done so as not to aggravate the situation and cause complications.
On this topic
The result and effectiveness of treatment depends on age, type of disease and therapy. All medications and physiotherapeutic procedures are used only after prescription by the attending physician:
- Bacterial mononeuritis and polyneuritis are treated with antibiotics and sulfonamides.
- Viral - “Gamma globulin” and “Interferon”.
- Traumatic - immobilization of the fracture, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are used. At the same time, you should drink B vitamins and drugs that improve neuromuscular transmission.
- Vascular – treated using vascular agents. If necessary, Hydrocortisone with Novocaine is administered.
If the neurosurgeon decides that surgery is inevitable, then surgery is performed. During it, the compressed nerve is released. Plastic surgery or stitching is done, so the functionality of the damaged area is restored.
Medicines for neuritis are usually anti-inflammatory. Physiotherapy, normalization of water-salt balance, and intake of vitamin complexes are required.
Anticonvulsants and antidepressants are prescribed if inflammation occurs in the area of the glossopharyngeal or trigeminal nerve, or the nature of the pain is neuropathic in nature.
Physiotherapy refers to the use of:
- ultrasound;
- pulse current;
- exposure to high-frequency currents;
- electrophoresis.
All of the above procedures can restore functionality to the damaged nerve.
If there are no contraindications, then massage therapy and exercise therapy are advisable. If recovery does not occur for a long time, then inductophoresis procedures, chamber hydrogalvanic sessions, mud and radon baths may be prescribed.
Inflammation of the nerve endings of the spine treatment
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
Neuralgia and neuritis are inflammations of the nerves that occur for various reasons; from time to time, inflammation occurs not of the nerves themselves, but of their endings or their remaining parts.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Nerve endings are special tiny formations at the ends of neural processes that are responsible for receiving or transmitting information in the form of electrical nerve impulses.
There are several types ( VIEW: Literally: That which is visible to the eye
) graduations in their area of specialization:
- Synapses that transmit impulses between neurons.
- Sensors or afferent endings that transmit information to a nerve cell from the external environment.
- Effectors – transmitting an information impulse from a neuron to tissue cells.
Inflammation of nerve endings is often called neuritis ( an inflammatory disease of the peripheral nerves, in which, along with pain, so-called loss is detected, that is, loss or decrease in sensitivity, as well as paralysis and paresis
), when, in addition to pain, paralysis, paresis, decreased or loss of sensitivity in the area of responsibility of the damaged area of the nervous system may occur.
Neuritis is a more dangerous disease than neuralgia, since the symptoms of neuralgia are caused only by the influence of something on the nerve, and not by its breakdown. With severe neuritis, which is a disease of the nerves themselves with a violation of their internal structure, the nerve may not recover, as well as the functions it did.
It would be more accurate to consider that inflammation of the nerve endings is a disease that is included in the composition of neuritis and its classification, and not specifically by it, since with neuritis the remaining parts of the nerve cells or nerves can be affected.
What promotes inflammation
Inflammation of nerve endings can be promoted by a variety of bad causes affecting the body or specifically the nerve itself:
- Drafts and hypothermia.
- Infection of the body with viruses, microbes or fungi.
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues.
- Muscle spasms or compression of the nerve area.
- Bruises.
- Local infections in the form of an abscess.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Lack of certain substances, vitamins or minerals in the body.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- Toxic poisoning.
- Heredity or personal individuality of the structure of the body.
- Tumor processes and almost all other causes.
More often, inflammation of the nerves begins with a prolonged negative irritant effect on the nerve or with an infection.
Healing
Healing occurs by eliminating the prerequisites for inflammation of the nerve endings, which may require the following procedures:
- Antiviral or antibacterial pharmaceutical therapy.
- Healing ( by faith (as well as healing by prayer, divine healing) is a doctrine that asserts the possibility of supernatural physical healing from an illness or congenital (acquired) defect of the body
) by surgical methods through compression or physical actions. - Anti-edematous therapy.
- Stimulation of blood circulation.
- Biogenic stimulation – stimulation of restorative actions with special products.
- Anticholinesterase therapy - treatment with products that inhibit nervous activity.
- Fortification and replenishment of deficiencies of minerals and other substances.
- Plastic surgery or suturing of the nerve using a surgical method, when a severely damaged area is removed.
- Local administration of pharmaceutical products specifically near the nerve.
- Physiotherapy healing.
- stimulation of the nerve.
- Symptomatic treatment with the use of anesthetics.
Healing inflammation of the nerve endings ( the smallest unit of language that has some meaning (as defined by American linguist Leonard Bloomfield in 1933)
) is selected individually and depends on the specific type of neuritis and its location. In case of advanced illness, folk methods selected with the help of a doctor are of great help.
Symptoms of inflammation of nerve endings
Before proceeding with diagnosis and prescribing treatment, the patient should describe his symptoms and feelings to the doctor in as much detail as possible. The main sign of inflammation is pain, the source of which cannot always be identified without the help of others. It can get worse at night, with all physical exertion, even walking, and from time to time in the cold.
The second more appropriate sign, indicating that there is inflammation of the nerve endings in the body, is a burning and tingling sensation in the affected area. Depending on the area of pathology, pain may appear even with minor skin irritations.
In general, all symptoms depend on the area of the body in which the lesion occurs. For example, when the nerve endings of the legs become inflamed, the sensitivity of the foot or lower leg is aggravated. Often movements in the knee area are severely limited and even the slightest change in position causes pain. In the case of eye disease, pain makes itself felt when moving the eyeballs, and vision often decreases.
Prerequisites
What conditions can cause inflammation of nerve endings and roots? Causes of radiculitis and vertebral neuralgia ( damage to peripheral nerves, characterized by attacks of pain in the area of innervation of a nerve
) there may be the following states:
- Infectious diseases of the spine.
- Injuries, tragedies, road accidents.
- Extra overload on the spine.
- Osteocondritis of the spine.
- Osteoporosis and calcium deficiency.
- Intervertebral disc herniation.
- Spondylolisthesis is a displacement of a vertebra.
- Narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Spondylitis.
- Spondyloarthrosis and bone osteophytes.
- Spinal tumors.
- Spinal osteomyelitis.
It is worth considering that inflammation can be caused by an infectious agent or a violation of anatomical interactions. In the second option, aseptic inflammation occurs, the treatment of which does not require the use of drugs, rather anti-inflammatory products.
The treating doctor will help you find the real cause of radiculitis.
Source: https://chelovek.asustav.ru/simptomy/vospalenie-nervnyh-okonchanij-pozvonochnika-lechenie/
Consequences and complications
If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, complications may arise in the form of motor disorders, paralysis, and complete muscle atrophy.
Rational treatment will help to avoid serious consequences and quickly return to a full life. In most cases, after quality treatment by a specialist, complete recovery and recovery occurs.
Nerve inflammation is a serious disease that requires early treatment. To avoid its occurrence, you should eat well, monitor your health, treat all infectious diseases in a timely manner, harden yourself, and avoid hypothermia. It is impossible to treat neuritis on your own, since without examination the treatment will not be beneficial.
Inflammation of nerve endings, symptoms and treatment – Neurology
Inflammation of nerve endings or radiculopathy is perceived by a person as pain, which is a natural signal of the body to dangerous pathological processes that occur in it.
Pain sensations are ordinary electrical nerve signals, no different from signals caused by sounds, images or smells.
The irritating effect is caused by the brain's reaction to received information about danger.
Many people ignore such signals or consider it the height of masculinity to endure such inconveniences, when seemingly causeless pain, not associated with internal organ ailments or injuries, are symptoms of various dangerous diseases of the nervous system.
Neuritis: main symptoms, causes, how to treat, complications
Inflammation of the nerve manifests itself in the form of sensory disturbances and motor disorders in the affected area. If one nerve is inflamed, then this pathological process is called mononeuritis, if two or more - polyneuritis.
This neuralgia may be associated with infectious diseases or hypothermia. Whatever the cause of the disease, in no case should you let it take its course or self-medicate.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the situation worsens; the disease becomes chronic, which is very difficult to treat.
Source: https://perinatal39.ru/tsns/vospalenie-nervnyh-okonchanij-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Expert commentary
The primary task for neuropathies is to eliminate the physical impact; currently, orthoses are successfully used for immobilization in the damaged area. To relieve pain, analgesics and NSAIDs are traditionally used in a short course; when the pain syndrome becomes persistent chronic pain, drugs aimed at relieving neuropathic pain are required: anticonvulsants, antidepressants. For tunnel neuropathies, a blockade with an anesthetic and hormone in the area of infringement is successfully used.