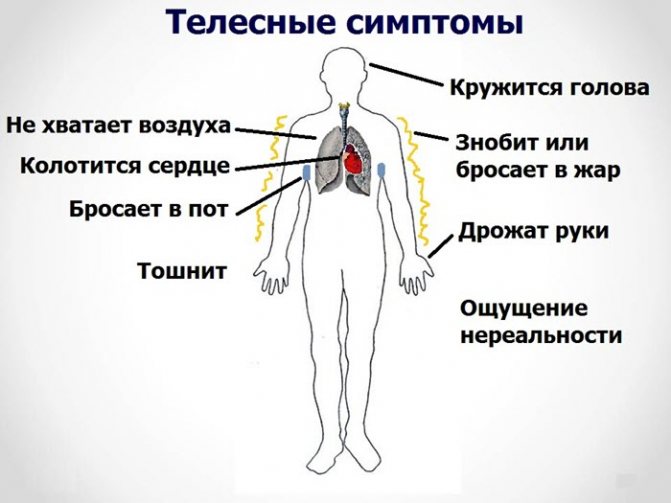
Psychovegetative syndrome is a painful condition characterized by cardiac ailments (a feeling of constriction, rapid heartbeat), headaches, heaviness in the stomach, urinary disorders, increased sensitivity to cold, sweating, nausea, dizziness, and irregularities in the monthly cycle. In addition, depression, various phobias, internal restlessness, anxiety, irritability, insomnia and apathy are often noted. Patients characterize all these symptoms as pronounced. However, after a thorough medical examination, it turns out that the internal organs (heart, stomach, intestines and bladder) of the patients are absolutely healthy.
...manifestations of psychovegetative syndrome are often mistakenly diagnosed as somatic pathology
Psychovegetative syndrome is a common variant of vegetative dystonia syndrome (VDS), which is most often associated with “anxiety”, “depression” and “adaptation disorders” (stress), identified by doctors at the syndromic level.
As can be seen from the structure of the term, it has two components: “psycho” and “vegetative”, the combination of which is due to the unity of the neurobiological process in case of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system with an emotional component that regulates the motivational and behavioral reactions of the individual, which are aimed at “stress-exclusion behavior” "
In other words, emotion is a signal for action, and vegetative reactions ensure this action and vice versa, the result of which is adaptive activity, that is, adaptation.
Factors contributing to the development of psychovegetative disorders
Undoubtedly, personality traits and the role of adrenergic regulation disorders, accompanied by sympathetic hyperactivity, are of primary importance. A significant role in the development of psychovegetative disorders is given to a decrease in the level of g-aminobutyric acid (or GABA), which is one of the main inhibitory mediators of the brain.
Most often, psychovegetative syndrome is a manifestation of an anxiety disorder, which at the emotional and behavioral level is manifested by a feeling of stiffness and tension, inability to relax, fussiness, irritability, inability to concentrate, difficulty falling asleep and disrupted night sleep, fatigue, fear, panic.
The appearance of psychovegetative syndrome is the following deviations in the functioning of various organs and systems:
- cardiovascular system: rapid heartbeat, tachycardia, extrasystole, discomfort or pain in the chest, increased blood pressure, hot or cold flashes, sweating, cold and wet palms;
- respiratory system: feeling of a “lump” in the throat, feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, uneven breathing, dissatisfaction with inhalation;
- nervous system: dizziness, headaches, tremors, muscle twitching, shuddering, paresthesia, muscle tension and pain, sleep disturbances;
- gastrointestinal system: dyspepsia, flatulence, appetite disturbances;
- genitourinary system: frequent urination, decreased libido, impotence.
Diagnosis of the disease
The difficulty in diagnosing psychovegetative syndrome lies in the fact that it does not have a clear clinical picture and often becomes only a syndromic manifestation of the main diagnosis. To identify this disorder, the patient's assessment includes:
- careful collection of medical history and exclusion of somatic pathologies;
- analysis of mental abnormalities that accompany psychovegetative syndrome - sleep disorder, depression, apathy, tendency to depression, lack of interest in what is happening;
- determining the connection between psychogenic situations and an increase in the severity of clinical manifestations of pathology.
Anxiety disorders are characteristic not only of psychovegetative syndrome, therefore, to carry out differential diagnosis and establish the severity of apathetic manifestations, a psychometric scale is used - the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Patients are required to undergo a blood test for hormones, an ECG or an ultrasound of the heart in order to distinguish pathology from cardiac disorders and disorders of the thyroid gland.
Principles of treatment of psychovegetative syndrome
Currently, alpha-blockers are used in the treatment of patients with SVD, along with ganglion blockers, angioprotectors, and vasoactive agents.
Effective for a very wide range of anxiety-neurotic disorders and psychosomatic pathologies, sleep disorders, vegetative-vascular dystonia is the alpha adrenergic blocker PROROXAN - the drug does not have a negative effect on psychomotor and cognitive functions, dependence, tolerance does not form, and withdrawal syndrome does not occur.
PROROXAN is not included in the list of medicines subject to subject-quantitative registration; it is prescribed on a standard prescription form.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
- Generalized anxiety disorder. This subtype of neurosis is based on persistent anxiety, which has become dominant in the patient’s life. Typically, chronic anxiety is accompanied by a number of somatic symptoms: headaches, nausea and dizziness, fussiness and nervousness, a vague expectation of some kind of misfortune and the inability to relax, to forget about disturbing factors even for a short time.
- Anxiety-depressive disorder. In psychiatry it is also called astheno-depressive syndrome. It is based on two cornerstones: anxiety and depression.
- Obsessive-compulsive anxiety disorder. With this type of neurosis, patients suffer from obsessive ideas and thoughts - so-called obsessions. The content of obsessions is gloomy and depressing. These are thoughts about death, catastrophe or the end of the world, about leaving the family or betrayal of a spouse, about miscarriage (in pregnant women).

Causes of occurrence and development
Psychovegetative disorders are in many cases diagnosed in children who belong to a group close in age to teenagers. Less common in young adolescents and young adults. And in rare cases, the syndrome manifests itself in older people. It is believed that there are “prone” groups of people who have a very high risk of developing or developing a psychovegetative syndrome:
- lack of a permanent job;
- meager wages;
- female;
- poor health of a person, low self-esteem;
- presence of traumatic events or situations;
- difficult family situation (divorced, widowed);
- advanced age;
- chronic neurological disease;
- regularly present in clinics and during hospitalizations.
The syndrome most often manifests itself in adolescents. This is explained by the inhibited development and formation of important hormonal systems in a young body, as well as the development and growth of the human body.
Psychovegetative syndrome is detected under the influence of heredity, human constitution, and disorders of the nervous system. Symptoms of this syndrome can also appear after changes in the body’s hormonal levels, various types of stress, disorders of the body’s nervous system, various occupational diseases, nervous breakdowns and mental disorders.
All of these factors contribute to the emergence and development of psychovegetative syndrome. It is necessary to begin timely treatment, otherwise the development of the disease may be complicated by the manifestation of more serious symptoms and complications, for example, panic attacks.
The syndrome manifests itself as a result of organic diseases of the brain, as well as in the presence of damage to the peripheral nervous system. However, the most common reason for the development of the syndrome is the process of development and restructuring of the endocrine system during adolescence and menopause in women. Another form of the syndrome is psychophysiological autonomic dystonia, which can manifest in a person after stress, panic situations, overwork, tiring physical activity and neurotic disorders.
Psychovegetative syndrome: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment features
Psychovegetative syndrome is characterized by the fact that it can include a large number of different symptoms arising from many systems and organs.
Such signs are so diverse that a person can go to doctors for a long time to find out the diagnosis.
But most often, numerous studies are not able to identify any pathology, and in this case, doctors recommend that the patient consult a psychoneurologist, suspecting the presence of a psychovegetative syndrome. So what is it?
Features of the manifestation of psychovegetative syndrome
This pathology is manifested by heart ailments, headache, increased sweating, nausea, dizziness, heaviness in the stomach, difficulty urinating, and sensitivity to cold.
Characteristic complex of symptoms
The symptoms are quite varied; with psychovegetative syndrome the following are observed:
- chest pain;
- increased heart rate;
- blood pressure disorders;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- heavy sweating;
- chilliness of the limbs;
- trembling of limbs;
- painful urination;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- lack of air;
- pale skin;
- sexual dysfunction;
- cystitis.
Signs of the syndrome are numerous. Their manifestation is individual and is associated with many characteristics of each organism.
Psychovegetative syndrome is the general name of the disease. Its particular manifestations are neurocirculatory dystonia and vegetative-vascular dystonia. They indicate specific disorders of the autonomic system, namely, disorders associated with the cardiovascular system.
Reflexology, physical therapy and massage are the main ways to treat the symptoms of the syndrome. Spa treatment and physiotherapy are used. Breathing exercises and antidepressants help relieve symptoms of the disorder. The whole body is strengthened. A healthy lifestyle and hardening are important.
There may be a need for psychotherapy, which will help to realize that the disease is in the past and there is no threat to life. Ion therapy and sedatives also help in the treatment process.
Psychovegetative syndrome does not have serious consequences as such, since most often no medications are used for its treatment. The only complication of the disorder can be considered the constant risk of development and recurrence of the disease.
- chest pain;
- increased heart rate;
- blood pressure disorders;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- heavy sweating;
- chilliness of the limbs;
- trembling of limbs;
- painful urination;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- lack of air;
- pale skin;
- sexual dysfunction;
- cystitis.
Causes
Psychovegetative disorders are often diagnosed in children of the older age group, as well as in adolescents and young adults. In more rare cases, the disease appears in people over 40 years of age. Neurocirculatory dystonia most often develops in young people. This is primarily due to the slow development of the neuroendocrine system in a young body, as well as the inconsistency between physical development and the functioning of the endocrine system.
Psychovegetative syndrome manifests itself under the influence of hereditary factors, constitutional characteristics, damage to the nervous system of an organic nature, somatic and mental disorders. Symptoms of the disease also appear due to hormonal changes in the body, psychophysiological changes (we are talking about stress - acute and chronic), psychosomatic diseases (heart disease, hypertension, bronchial asthma, etc.), diseases of the nervous system, some occupational diseases, mental disorders and neuroses.
All the described factors contribute to the manifestation of vegetative dystonia. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, it can be complicated by panic attacks.
Autonomic dysfunction often occurs as a consequence of organic diseases of the brain, as well as in the presence of damage to the peripheral nervous system. But one of the most common causes of autonomic disorders is the process of endocrine changes in the human body during adolescence, as well as in women during menopause. A separate form is psychophysiological vegetative dystonia, which manifests itself in humans as a consequence of stress, severe physical strain, overwork, and neurotic disorders.
What is special about a panic attack?
During an attack, a person experiences strong, unreasonable fear. This maintains the awareness that there is no threat, but this does not help stop the attack. The physical symptoms of an attack are palpitations, rapid shallow breathing, trembling, cold sweat, nausea, even loss of consciousness and convulsions.
Panic attacks worsen the course of anxiety neurosis, since a person is kept in constant tension by the fear of anticipation - the painful expectation of a new attack.
There are several reasons for the development of panic disorder:
- chronic stress - troubles at work and at home, constant overexertion and lack of rest;
- frightening incidents in a particular situation that are so embedded in the memory that a person tries with all his might to avoid their repetition;
- constitutional features - labile (mobile) nervous system, tendency to suspiciousness and anxiety.

Symptoms
Autonomic dystonia syndrome can be expressed by different symptoms, which are influenced by etiological factors. Symptoms of vegetative dystonia are manifested by a number of different syndromes, the treatment of which should only be carried out comprehensively.
Cardiac syndrome is the occurrence of pain of various types or discomfort in the precordial area. The pain is sometimes mistaken for angina, but it is not associated with physical activity, lasts longer and does not go away after taking nitroglycerin. Sometimes changes can be detected on an ECG.
Also, with pain, a person suffers from hyperventilation (fast breathing, feeling of lack of air), shortness of breath, which is psychogenic in nature, as well as coughing. Rapid breathing removes too much carbon dioxide from the body. As a result, processes occur in the body leading to the manifestation of muscle spasms and paresthesia in the distal limbs and perioral region. Hyperventilation can cause pre-fainting symptoms in the patient - his vision darkens, weakness and dizziness appear. But most often, hyperventilation is manifested by pain in the heart, as well as abdominal pain, in which there is a violation of gastrointestinal motility.
If there are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, the patient's appetite is disturbed and irritable bowel syndrome may occur. Sometimes vomiting, heaviness in the epigastrium, and upset stool appear.
With vegetative dystonia, sexual dysfunction may occur, in which men experience erectile dysfunction or ejaculation, and women experience vaginismus or anorgasmia. Another symptom is cystalgia (frequent, painful urination).
Psychovegetative disorders are also expressed by the presence of thermoregulation disorders. They are manifested by hyperthermia, hypothermia, chill syndrome. Hyperthermia can be permanent or paroxysmal.
Speaking about their own illness, patients who have been diagnosed with general psychosomatic syndrome note that the symptoms of the disease are very wide. In other words, sometimes a person feels like absolutely everything hurts. Consequently, the main feature of the symptoms of this disease is the variety of manifestations.
Psychovegetative syndrome (vegetative dystonia)
Psychovegetative disorders are often diagnosed in children of the older age group, as well as in adolescents and young adults. In more rare cases, the disease appears in people over 40 years of age. Neurocirculatory dystonia most often develops in young people. This is primarily due to the slow development of the neuroendocrine system in a young body, as well as the inconsistency between physical development and the functioning of the endocrine system.

Psychovegetative syndrome manifests itself under the influence of hereditary factors, constitutional characteristics, damage to the nervous system of an organic nature, somatic and mental disorders. Symptoms of the disease also appear due to hormonal changes in the body, psychophysiological changes (we are talking about stress - acute and chronic), psychosomatic diseases (heart disease, hypertension, bronchial asthma, etc.), diseases of the nervous system, some occupational diseases, mental disorders and neuroses.
All the described factors contribute to the manifestation of vegetative dystonia. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, it can be complicated by panic attacks.
Autonomic dystonia syndrome can be expressed by different symptoms, which are influenced by etiological factors. Symptoms of vegetative dystonia are manifested by a number of different syndromes, the treatment of which should only be carried out comprehensively.
Cardiovascular syndrome in a patient is manifested by changes in heart rhythm (both tachycardia and bradycardia), increased blood pressure, changes in skin color (pallor, cyanosis), hot flashes, and chilliness of the extremities.
Cardiac syndrome is the occurrence of pain of various types or discomfort in the precordial area. The pain is sometimes mistaken for angina, but it is not associated with physical activity, lasts longer and does not go away after taking nitroglycerin. Sometimes changes can be detected on an ECG.
Also, with pain, a person suffers from hyperventilation (fast breathing, feeling of lack of air), shortness of breath, which is psychogenic in nature, as well as coughing. Rapid breathing removes too much carbon dioxide from the body. As a result, processes occur in the body leading to the manifestation of muscle spasms and paresthesia in the distal limbs and perioral region.
If there are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, the patient's appetite is disturbed and irritable bowel syndrome may occur. Sometimes vomiting, heaviness in the epigastrium, and upset stool appear.
With vegetative dystonia, sexual dysfunction may occur, in which men experience erectile dysfunction or ejaculation, and women experience vaginismus or anorgasmia. Another symptom is cystalgia (frequent, painful urination).
Psychovegetative disorders are also expressed by the presence of thermoregulation disorders. They are manifested by hyperthermia, hypothermia, chill syndrome. Hyperthermia can be permanent or paroxysmal.
Speaking about their own illness, patients who have been diagnosed with general psychosomatic syndrome note that the symptoms of the disease are very wide. In other words, sometimes a person feels like absolutely everything hurts. Consequently, the main feature of the symptoms of this disease is the variety of manifestations.
Types of neurocirculatory dystonia
Today, experts define three different types of neurocirculatory dystonia: hypertensive, cardiac, hypotensive. Symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type are expressed by insignificant changes in blood pressure. However, in this case, the person suffers from increased heart rate, interruptions in cardiac activity, and shortness of breath.
With neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotensive type, the patient experiences symptoms of heart failure. We are talking about decreased systolic pressure, decreased symptomatic activity and cardiac index. A person suffers from a headache, he gets tired very quickly, feels weak in his muscles, his limbs are cold, his skin turns pale. As a rule, this form of dystonia affects people who have an asthenic physique.
Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type is characterized by transient increases in blood pressure. But at the same time, most people do not feel a deterioration in their health. As a result, the disease is diagnosed late, and in most cases this occurs during routine examinations. In addition to increased blood pressure with dystonia of this type, patients experience severe fatigue, headaches, and rapid heartbeat.
In addition to these forms of the disease, mixed-type dystonia is also diagnosed, in which the patient experiences fluctuations in blood pressure.
A diagnosis of “vegetative dystonia” (psychovegetative syndrome, autonomic neurosis) can only be made if a comprehensive examination is carried out. Initially, it is necessary to exclude all somatic diseases that could provoke the manifestation of certain symptoms. It is especially important to do this if there are only violations in the operation of one of the systems.
To conduct a high-quality diagnosis, consultations with several doctors - specialists in different fields - are often necessary. Interviewing the patient is very important. The specialist needs to ask the patient in detail about his feelings and learn in detail about the subtleties of all manifestations.
During the examination, if psychovegetative syndrome is suspected, an electrocardiogram, MRI and computed tomography, and vascular Dopplerography are often prescribed. Treatment is prescribed on an individual basis, taking into account all the characteristics of the manifestations of the disease.
If possible, treatment of psychovegetative syndrome is carried out without the use of medications. The patient is prescribed reflexology, massage, and physical therapy sessions. Physiotherapy methods and spa treatment are also practiced. Breathing exercises help reduce the severity of hyperventilation.
If you have an anxiety-depressive state with sleep disorders, it is advisable to take antidepressants that have a sedative effect. Drugs - beta blockers are used for heart pain, arterial hypertension, tachycardia. If vegetative dystonia is manifested by arterial hypotension, the patient is recommended to undergo treatment with tinctures of ginseng, lemongrass, and eleutherococcus.
Due to the variety of symptoms, other medications are also used in treatment, which are prescribed on an individual basis. A correct lifestyle, hardening, and treatment aimed at overall strengthening of the body are also important.
In some cases, the use of rational psychotherapy has a clear positive effect, during which the patient realizes that he does not have a life-threatening disease.
Sanitary-resort treatment is also practiced, which works effectively due to the impact of climate change on the patient’s body. Under the influence of changed climatic conditions, the patient’s cardiovascular system functions in adaptation mode and adapts to all other systems of the body.
In addition, treatment with ionotherapy is practiced, the course of which lasts about 30 days. For vegetative dystonia, it is symptomatic to take sedatives.
Considering the tendency to high or low blood pressure, it is possible to take medicinal herbs, as well as drugs made on their basis. For high blood pressure, it is recommended to take preparations of motherwort, valerian, and oregano. It is useful to consume bee honey before bed. For low blood pressure, it is worth using an infusion of Eleutherococcus and Chinese Schisandra.

Smoking and alcoholic beverages are contraindicated in patients with vegetative dystonia. But playing sports and daily water procedures using a contrast shower will ensure improved well-being. Swimming in open water, jogging, and walking in the fresh air are beneficial for the health of patients with psychovegetative syndrome.
As a preventive measure, it is important to use all the measures described above aimed at normalizing a person’s lifestyle. In addition, special attention should be paid to rest and sleep patterns. A person should sleep at least 8 hours every day.
An important factor is the correct approach to the daily diet. All meals in the diet should be high in vitamins and minerals. At the same time, it is better not to consume foods that excite the nervous system. We are talking about coffee, tea, chocolate, spices, smoked meats, and pickles.
In addition, doctors strongly recommend trying to receive as many positive emotions as possible and strive for a positive perception of life in general.
With neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotensive type, the patient experiences symptoms of heart failure. We are talking about decreased systolic pressure, decreased symptomatic activity and cardiac index. A person suffers from a headache, he gets tired very quickly, feels weak in his muscles, his limbs are cold, his skin turns pale. As a rule, this form of dystonia affects people who have an asthenic physique.
Types of neurocirculatory dystonia
Today, experts define three different types of neurocirculatory dystonia: hypertensive, cardiac, hypotensive. Symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type are expressed by insignificant changes in blood pressure. However, in this case, the person suffers from increased heart rate, interruptions in cardiac activity, and shortness of breath. People who suffer from this type of dystonia tend to experience periodic tachycardia, changes in heart rate, and other changes in cardiac activity.
With neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotensive type, the patient experiences symptoms of heart failure. We are talking about decreased systolic pressure, decreased symptomatic activity and cardiac index. A person suffers from a headache, he gets tired very quickly, feels weak in his muscles, his limbs are cold, his skin turns pale. As a rule, this form of dystonia affects people who have an asthenic physique.
Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type is characterized by transient increases in blood pressure. But at the same time, most people do not feel a deterioration in their health. As a result, the disease is diagnosed late, and in most cases this occurs during routine examinations. In addition to increased blood pressure with dystonia of this type, patients experience severe fatigue, headaches, and rapid heartbeat. Considering these symptoms, we can say that the signs of this form of neurocirculatory dystonia are similar to the symptoms of hypertension. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis requires a thorough examination by a specialist and the appointment of further examination.
In addition to these forms of the disease, mixed-type dystonia is also diagnosed, in which the patient experiences fluctuations in blood pressure.
Symptoms of panic disorder
Let me remind you that panic disorder is the repetition of panic attacks on a regular basis, which is accompanied by all the inconveniences of a person’s life, subject to constant fear of new attacks. There are people for whom panic attacks are reduced to isolated incidents in their lives. For example, one person told me that the attack happened a long time ago when he was riding in a minibus. But it never happened again. Therefore, it cannot be said that such a person suffers from panic disorder; nevertheless, he had a panic attack.
For such people, this is expressed in isolated episodes, so they are unlikely to turn to specialists or read articles on the Internet. Therefore, with a high degree of confidence, we can say that patients of psychiatrists and psychotherapists, readers of this article, are faced with panic disorder (which may be accompanied by symptoms of anxiety disorder, depression, obsessive thoughts, etc.), because it is this disorder that causes problems in life, and, one might even say, is characterized by the presence of these problems. Although, of course, everyone is accustomed to saying “panic attacks,” since this is the most striking symptom of this illness. But such a definition should not be misleading. It should be clear that a person experiencing panic disorder may experience more than just the symptoms of panic attacks per se.

Diagnostics
A diagnosis of “vegetative dystonia” (psychovegetative syndrome, autonomic neurosis) can only be made if a comprehensive examination is carried out. Initially, it is necessary to exclude all somatic diseases that could provoke the manifestation of certain symptoms. It is especially important to do this if there are only violations in the operation of one of the systems.
To conduct a high-quality diagnosis, consultations with several doctors - specialists in different fields - are often necessary. Interviewing the patient is very important. The specialist needs to ask the patient in detail about his feelings and learn in detail about the subtleties of all manifestations.
During the examination, if psychovegetative syndrome is suspected, an electrocardiogram, MRI and computed tomography, and vascular Dopplerography are often prescribed. Treatment is prescribed on an individual basis, taking into account all the characteristics of the manifestations of the disease.
Diagnostic stages
The diagnosis should be made only after a detailed questioning of the patient about the nature of the manifestation of pain, as well as after examining various organ systems.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by excluding a number of other ailments. First of all, a comprehensive diagnosis of the patient’s body is carried out. As a result of a thorough examination, it is necessary to exclude all types of somatic diseases that have the same symptoms as autonomic neurosis. It is mandatory to examine the patient by specialists in various fields. The patient is interviewed about the characteristics of pain, symptoms and their manifestations.
In most cases, an electrocardiogram, MRI, vascular Doppler sonography and computed tomography are performed.
When prescribing treatment, the doctor must take into account all the individual characteristics of the patient and his disease.
Treatment
If possible, treatment of psychovegetative syndrome is carried out without the use of medications. The patient is prescribed reflexology, massage, and physical therapy sessions. Methods of physiotherapy and spa treatment are also practiced. Breathing exercises help reduce the severity of hyperventilation. But if acute manifestations of the symptoms of the disease occur, then patients may be prescribed benzodiazepine drugs for a certain period of time. If a person is bothered by constant pain, he is prescribed a course of treatment with antidepressants.
If you have an anxiety-depressive state with sleep disorders, it is advisable to take antidepressants that have a sedative effect. Drugs - beta blockers are used for heart pain, arterial hypertension, tachycardia. If vegetative dystonia is manifested by arterial hypotension, the patient is recommended to undergo treatment with tinctures of ginseng, lemongrass, and eleutherococcus.
Due to the variety of symptoms, other medications are also used in treatment, which are prescribed on an individual basis. A correct lifestyle, hardening, and treatment aimed at overall strengthening of the body are also important.
In some cases, the use of rational psychotherapy has a clear positive effect, during which the patient realizes that he does not have a life-threatening disease.
Sanitary-resort treatment is also practiced, which works effectively due to the impact of climate change on the patient’s body. Under the influence of changed climatic conditions, the patient’s cardiovascular system functions in adaptation mode and adapts to all other systems of the body. Climatic conditions also make it possible to train the body's defenses, therefore, it becomes much easier to fight diseases.
In addition, treatment with ionotherapy is practiced, the course of which lasts about 30 days. For vegetative dystonia, it is symptomatic to take sedatives.
Considering the tendency to high or low blood pressure, it is possible to take medicinal herbs, as well as drugs made on their basis. For high blood pressure, it is recommended to take preparations of motherwort, valerian, and oregano. It is useful to consume bee honey before bed. For low blood pressure, it is worth using an infusion of Eleutherococcus and Chinese Schisandra.
Post-alcohol syndrome: treatment methods
Treatment of alcohol withdrawal is possible at home and in the clinic. According to survey data, most patients prefer to be treated at home, seeing a doctor only as a last resort.
Therapy is carried out comprehensively using psychological correction, traditional medicine recipes, and pharmacological agents. The primary task during a panic attack is the ability to act in the current situation.
First aid
If you need help for a person experiencing severe fear, it is advisable to follow a number of recommendations:
- attract attention;
- take hands, reassure him in a confident tone that there is no danger and he will not be left alone;
- try to meet the person’s gaze and hold his attention;
- Carry out breathing exercises together, consisting of deep breaths and slow exhalations.
After a few minutes, when the symptoms subside, you can let go of your hands and invite the person to dialogue.
Psychotherapy sessions
The psychotherapist conducts an individual conversation with the patient to find out the nature of fears, the frequency and degree of manifestation of paroxysms. The main direction in correcting the condition is to teach a person to manage emotions. The following techniques are used:
- cognitive-behavioral for the patient’s acceptance of the problem and reassessment of attitude towards it;
- cognitive-behavioral, including breathing exercises, influencing the subconscious through hypnosis. The doctor finds out the cause of fears, gives an attitude towards them;
- Gestalt therapy teaches an individual to analyze in detail the situation of a panic attack and independently find a way out of the crisis.
An innovative method in the treatment of the disease is neurolinguistic programming. It is carried out by simulating the situation that provokes the syndrome. The psychotherapist helps the patient cope with a panic attack, then the actions are analyzed step by step, which helps the person rethink the attitude towards the sensations being tested and the ability to independently manage them.
Drugs
Prescription of medications for panic attack syndrome is included in the course of treatment; medications are selected in accordance with the clinical picture. Therapy is based on the use of the following drugs:
- Antidepressants - Melipramine, Anafranil, Desipramine.
- Tranquilizers to eliminate an attack - “Valium”, “Dormikum”, “Signopam”, “Lorazepam”, “Afobazol”.
- Serotonin reuptake inhibitors - Fluoxetine, Zoloft, Fevarin, Citalopram.
- Atypical antidepressants - Trittico, Bupropion, Mirtazapine.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors - Moclobemide, Pyrazidol
- Beta blockers - “Anaprilin”, “Egilok”.
- Nootropics – “Pyritinol”, “Glycine”, “Mexidol”.
Diet is recommended. The menu should not contain products containing thiamine: alcohol-containing drinks, smoked sausages, legumes, cheese.
Folk remedies
Medicinal plants with a calming effect help reduce the intensity of paroxysm. To prepare the product, you will need a herbal mixture consisting of valerian, motherwort, peony, and Rhodiola rosea in equal parts. For 0.5 liters of water, take 4 tablespoons of the ingredient, place it in a steam bath (15 minutes), and strain.
Possible reasons
The occurrence of psychovegetative disorders is inherited, is associated with the structure of the body, and is also formed as a result of a disorder of the nervous system. In children, the disease manifests itself at an early age. As you get older, the condition stabilizes. But with increased physical stress (stress, strain, climate change, harmful work conditions, hormonal imbalance, somatic diseases), well-being worsens.

Factors that increase the risk of pathology:
- lack of permanent work;
- low salary;
- breakdown of family relationships, loss of a loved one;
- the presence of situations affecting the psyche;
- low self-esteem;
- neurological diseases of a chronic nature;
- female;
- old age.
Children close to transitional age (puberty) and young people with an immature neuroendocrine system are susceptible to the manifestation of psychovegetative syndrome. In women during pregnancy, breastfeeding and menopause, hormonal imbalance occurs, which can lead to the development of the anomaly in question.

Psychotherapy for panic attacks
The correct choice of a psychologist who will conduct psychotherapy is very important. Panic disorder is a complex problem, so it is necessary for a psychologist to have positive experience in this area. And accordingly, the more this experience, the better. To find out whether a psychologist has such experience, you can read reviews from his clients.
Work with a psychologist can be done via Skype. This is absolutely as effective as a face-to-face appointment, but there are a number of serious advantages.
- You can choose any psychologist, not limited to your city. This is very important if you have a small city and do not have psychologists with experience in panic attacks.
- You don’t need to go anywhere, you are in a cozy, protected environment, this is especially true for people with agoraphobia
- Working via Skype is cheaper than face-to-face, because you don’t have to spend money on renting an office.
- If necessary, sessions can be carried out early in the morning or late in the evening

Clinical signs
An important feature of the psychovegetative syndrome is the multiplicity of autonomic disorders. In this case, patients indicate the following disorders:
- feeling of tightness in the chest, changes in heartbeat;
- stomach ache;
- frequent vomiting;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- neuralgia of various localizations;
- problems with urination;
- increased sweating;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- feeling of cold.
Typically, psychovegetative syndrome with anxiety manifestations is characterized by the following symptoms:
- tension in the body, muscles are stiff;
- there is no opportunity to relax;
- fussy movements;
- irritation;
- impatience;
- excited state;
- forgetfulness;
- rapid onset of fatigue;
- absent-mindedness;
- poor night sleep;
- problems falling asleep;
- fears.

Symptoms of psychovegetative syndrome are varied and may indicate the presence of other syndromes:
- Cardiovascular – heartbeat disturbance (tachycardia, bradycardia), arterial hypertension, feeling of cold hands and feet, flushing of the face, pallor.
- Cardialgic - the appearance of pain of various types in the heart area, which is confused with angina pectoris, but Nitroglycerin does not help.
- Hyperventilation – shortness of breath, cough, as if there is not enough air. With frequent breathing, the ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs is disrupted, the airways spasm, and pain similar to heart pain appears. Due to lack of air, a pre-fainting state occurs (the eyes become dark, the ears are noisy, the head is dizzy).
- Irritable bowel syndrome - disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal upset, vomiting, heaviness in the epigastric region, decreased appetite.
Sexual disorders associated with erection and ejaculation in men are possible; in women, painful sensations appear in the vagina due to muscle spasms, and anorgasmia develops.
With psychovegetative syndrome with cerebrovascular disorders, a person experiences pain and dizziness, noise in the ears, and a state close to fainting occurs. This situation is caused by changes in the blood vessels of the brain. The narrowing of the lumen of the arteries reduces cerebral blood flow, resulting in the development of atherosclerosis and increased blood pressure.
A certain category of patients is concerned about the appearance of panic disorders. The feeling of fear and panic occurs unexpectedly, but is always characterized by a certain state:
- breathing problems, feeling of lack of air;
- pain in the heart area;
- increased heart rate;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased sweating.
The patient develops a fear of cardiac arrest and stroke. The patient thinks that he will go crazy and die. Such symptoms are called psychovegetative syndrome with panic attacks.

Diagnosis of panic disorder
Every person with panic disorder experiences panic attacks. But panic attacks do not always indicate panic disorder. Some people experience panic attacks as a response to certain situations. For example, a person may have a phobia (overwhelming fear) of closed spaces (claustrophobia) and experience panic attacks when they are in such a place.
For most people with phobias, attacks occur only when confronted with something that triggers their fear, but for people with panic disorder, panic attacks usually occur without warning and for no apparent reason. Therefore, a diagnosis of panic disorder is made only if a person has repeatedly experienced unexpected panic attacks, after which he experienced anxiety or fears about the next attack for at least a month.
Panic disorder and panic attacks are usually diagnosed by a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. The doctor will ask you to describe your symptoms, how often they occur and in what situations. Discussing your feelings, emotions and personal life with a stranger can be difficult, but there is no need to feel anxious or ashamed. The doctor needs to understand the existing symptoms in order to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment.
After the conversation, the doctor may order a physical examination to check whether the symptoms are caused by any internal disease. For example, an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) sometimes causes symptoms similar to a panic attack. By excluding possible chronic diseases, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis.

Diagnostic methods
Determining the disease requires consultation with doctors of various specializations, as well as a thorough examination of the patient. What events are held:
- Autonomic disorders are determined in conversation with the patient using a special questionnaire.
- Somatic diseases are excluded based on patient complaints.
- Find out how difficult life situations and the occurrence of vegetative symptoms are connected.
- Clarify how autonomic disorders occur.
- Determine whether there are mental symptoms: sleep disturbances, deterioration in emotional mood, changes in appetite, fatigue.
For examination the following is prescribed:
- ECG;
- MRI;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels;
- computed tomography;
- blood test for hormones;
- Ultrasound of the heart.
Differential diagnosis is aimed at excluding diseases with similar symptoms. For example, anxiety states appear with increased thyroid function, and cardialgia syndrome is confused with angina pectoris.
If the heart malfunctions, the patient undergoes a specialized examination. This is a necessary measure when diagnosing this syndrome. At the same time, the examination should be understandable and uncomplicated for patients. Otherwise, patients will worry and come up with a catastrophic diagnosis.
Generalized anxiety disorder
The main thing is that anxiety in the case of generalized anxiety disorder is constant, it is not determined by any external situation, the person is anxious regardless of the presence or absence of a reason for this. This is the so-called “floating” or floating alarm. The degree of anxiety can be so high that a person begins to experience the fear that he is “going to go crazy.”
Against the background of anxiety, there may be a feeling that a person “does not recognize” things that are familiar to him, the environment, it seems “changed”, alien. This is how the symptom of derealization manifests itself. Even to himself such a person may seem “changed,” “as if he sees himself with different eyes, from the outside.” This is a symptom of derealization.
Like any other anxiety disorder, generalized is accompanied by pronounced muscle, autonomic and autonomic pain reactions, sleep disturbances, and fears. If anxiety is present continuously for several months (from 3 to 6), then it may be a generalized anxiety disorder.