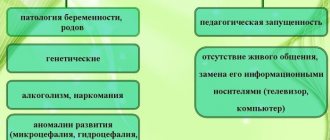
SURVEY OF THE VOCABULARY AND GRAMMARICAL STRUCTURE OF THE LANGUAGE
Formation of the grammatical structure of students' speech during speech development lessons. Overcoming impressive and expressive agrammatism.
The objectives of correctional pedagogical work are: 1) consolidation of articulation skills; 2) overcoming literal paraphasia; 3) stimulation of expressive speech, overcoming defects in sound-letter analysis of word composition and literal paragraphs when writing words; 4) overcoming expressive and impressive agrammatism: understanding the meanings and use of prepositions that convey the spatial relationship of objects.
expressive agrammatism - characterized by errors in the grammatical construction of active speech; 2) impressive agrammatism is characteristic ...
1) expressive agrammatism - characterized by errors in the grammatical construction of active speech;
2) impressive agrammatism - characterized by difficulties in understanding the meaning of grammatical structures, primarily those expressing relationships (connectives, prepositions, conjunctions, word order).
In the preparatory class, speech development (work on words).
Accumulation of the vocabulary necessary for full communication based on expanding children’s orientation in their environment, familiarization with the natural environment, and with some aspects of social life. Naming objects and actions that children directly perceive in the reality around them. Naming details, parts of an object. Correct understanding of the meanings of the words used. Their exact relationship with the objects of the surrounding world. Distinguishing similar objects based on essential characteristics.
Understanding and using words with meaning in colloquial speech:
diminutives-endearments (nouns with the suffixes -ik, -ok, -k: table, fungus, machine);
spatial arrangement of objects (here, there, here, left, right, there, here),
and also through prepositions in, on, denoting location, direction of action, movement;
attribute of an object by color, size, shape, taste, condition (red, large, round, sweet, clean)
and a sign of action
(write beautifully);
temporary relationships (now, in the morning).
Personal and demonstrative pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, this, that).
Working on a proposal
Writing simple, common sentences. Highlighting words in a sentence that denote an object and an action, based on questions (who? what? what is he doing? what did he do?).
Grammatical signs of number in nouns and in verbs of the present and past tense of the 1st and 3rd person, masculine and feminine, in combination of nouns with numerals one, one
or pronouns
mine, mine,
in past tense verbs.
Compiling a simple common (three-term) sentence, where the third member refers to the verb and denotes the transitivity of the action to the object (an inanimate noun in the accusative case of the feminine and masculine gender: eats a cutlet, draws a house).
Spatial relationships indicating the directions of movement, movement of objects, answering the question where? (noun in the accusative case with prepositions in, on, under: put in the desk, on the desk, under the desk).
Location of objects that answer the question where? (noun in the prepositional case with prepositions in, on: lies & desk, on the desk).
Mastering the meaning of prepositions. The ability to discriminate. them and answer questions where? Where?
Tools or means of action (noun in the instrumental case, masculine and feminine: draws with a pencil, saws with a saw).
The ability to answer a question makes what?
Signs of action (adverb: Vova writes beautifully).
Extension of a three-term sentence through words denoting the characteristics of the subject (adjective and noun of the feminine and masculine gender in the nominative case).
Compiling sentences with combinations denoting temporary relationships.
Verbs of the present and past tense of the 1st and 3rd person. Distinguishing and composing sentences with combinations of verbs expressed in the complex future tense.
Correctly matching questions does what? what did you do? what will it do? with time of action.
Formation of the ability to establish connections between words in a sentence and questions.
I CLASS
SPEECH DEVELOPMENT (128h)
Working on the word
Understanding and using in speech words expressing instructions, orders. Words are the names of objects, actions, signs of objects, signs of actions, time of actions that children constantly encounter in everyday life, in school, when getting to know nature, and social phenomena. Understanding the general meanings of words. One object in different situations (a toothbrush, for cleaning clothes, shoes, for sweeping floors; folding - numbers, clothes, school things).
Understanding and correct use of words with the meaning of diminutive-affectionate, augmentative (nouns with the suffixes -ik, -ok, -k, -chek, -ochk, -echk, -its);
words denoting animals (nouns with the suffix -onok, enok);
persons by the type of their activity (nouns with the suffixes -ist, -schik, -chik, -nits(a), -tel, -ar);
movement, signs of objects in color, shape, size, taste, weight, temperature Properties, quality and their opposite meaning (hard - soft);
signs of action
(fast, fun, good);
time of action
(morning, evening, today):
Isolation and naming of parts of individual objects. Distribution of names of objects into groups. Knowledge and use of species and generic designations.
Developing the ability to use words and the correct grammatical form depending on its meaning in sentences.
Working on a proposal
Understanding and using imperative sentences, declarative non-common sentences and common sentences (consisting of 3-5 sentence parts). Compiling sentences using models: a simple sentence with verbs in the present and past tense in the singular. Isolating the subject and actions on the questions who? What? what is he doing? what did you do? and the distinction between these questions (about an object, about an action or a state). Distinguishing questions who? What? as questions about an animate or inanimate object; questions what does it do? what did you do? as questions about action expressed in the present or past tense.
Formation of the plural form of nouns (with the ending - ы(-и),
a(s) and verbs (present and past tense).
Compiling and using simple sentences with singular and plural nouns and verbs.
Identification of grammatical features of the gender of nouns in phrases with numerals and pronouns. Practical mastery of the meaning and methods of using gender characteristics of nouns with past tense verbs in sentences.
Compiling and using in speech sentences (three to five terms) with phrases denoting the transitivity of an action to an object (washes a cup, the floor).
Distinguishing the ending of the accusative case depending on the gender of nouns and the designation of animation and inanimateness
(sees a boy, a girl).
An instrument or means of action (draws with a pencil, sweeps with a broom).
Distinguishing the ending of the instrumental case depending on the gender of the noun.
Spatial relationships in the meaning of direction and place and action. Collocations of a verb with a noun in the accusative case with prepositions in, on, under (put in (on, under) the table, put in (on, under) the book);
in the prepositional case with prepositions in, on
(lies in the table, on the table);
in the instrumental case
with
the prepositions under, above, -for
(hid under (behind) a bush);
in the genitive case with prepositions from, with, from, about in the sense of the place from where the action is performed
(left the house, got off the train, drove away from the store, stands near the kiosk);
in the dative case with the preposition to in the meaning of the person or place to which the action is directed
(approached a friend);
in the instrumental case with the preposition s in the meaning of togetherness or accompaniment
(goes with mother);
in the dative case in the meaning of the addressee.
Noun phrase in genitive case with
with the preposition y, and without a preposition in the meaning of belonging to an object or its negation
(at a goat, there is no goat).
Isolating words from sentences that denote attributes of objects based on questions. Distribution of phrases and sentences on questions of what? which? which? which? Agreement of an adjective with a noun in the nominative, accusative and instrumental cases of the singular and plural.
Practical mastery of sentences with combinations denoting temporal relations (verbs in the present, past and future tense).
Combination of pronouns with 1st and 2nd person verbs.
Combinations of numerals with nouns. Quantitative relationships and characteristics of an object by counting.
II CLASS
» ‘ > •
Speech development (104 h)
Working on the word
Clarification, enrichment and activation of the vocabulary denoting the names of objects, signs, actions. The ability to pose questions to words.
Correct use of specific and generic words-names; words ,
denoting proper names, having only singular or plural
(milk, cream),
indeclinable
(coat, metro),
united by a common characteristic, indicating persons by their type of activity, profession.
Correct use of words denoting characteristics of objects by “quality” (soft, hard);
by weight
(light, heavy);
but seasonality
(winter, autumn);
by the material from which it is made
(rubber, metal);
by affiliation
(fox, bear);
by the degree of comparison of the qualities of objects
(white, whiter);
by the diminutive name of the qualities of objects (
new, blue).
Correct use of words denoting the actions of objects, with the most common prefixes: in-, in-, you- in the meaning of movement inside or from within; at-,
y-, from-, sub- in the meaning of removal or absence; re-, pro-, do- - in the meaning of movement; raz-(ras-), s-(co-), for- - in the meaning of the direction of action in different directions, rapprochement, connection; on-, up- (vs-), s- - and the meaning of movement down, up, along the surface of an object; o-(from-) - in the sense of movement around an object.
Understanding the semantic nuances of words. Comparison of words denoting an unfinished action and a completed one (verbs with prefixes na-, vy-, po-, s-). Correlating action words with animate and inanimate objects. —
The use of reflexive verbs and possessive pronouns. Correct use of the word in different contexts (go
Where? Where? in what? with whom? (with what?).
Comparison and grouping of words with a common root, prefix, suffix, similar and opposite in meaning. Distinguishing the simplest cases of polysemy of words.
The ability to quickly find the right word that most accurately expresses a thought, bringing it into a grammatically correct combination with other words.
Working on a proposal
Improving the speech skills acquired by children in the first grade. Using sentences with phrases that have meaning in your answers; accessories (without a preposition and with a preposition y regarding the questions of whom? h him?) (book of a brother, sister; a goat has a kid)
;
denial or absence (no book, comrade)
;
lack of sharing or accompaniment (bread without cheese, came without brother);
quantity or quality of the whole
(kilogram of bread, liter of milk);
denoting an indirect object
(tea without sugar);
target orientation with the preposition for
(a book for a friend);
temporary relationships with prepositions before, after, in, through
(came in before (after) lunch, meeting);
spatial relations with prepositions at, from, with, with, because of, from under
(a boat near the shore, sailed away from the shore, took it off a hanger, from a wall, drove around the corner, crawled out from under a closet);
presence of compatibility or accompaniment with the preposition with on issues with whom?
with what? (came with my brother, bread and butter),
target orientation with the preposition for
(came for my brother, for a book),
spatial relations with prepositions for, in, in front of, between
(stands behind (in front of) a tree, lies between the closet and the table !
and without prepositions; characterizing an object by materials and purpose
(wooden mug, paper folder);
denoting causal relationships with prepositions from, because of
(trembled from the wind, did not come because of the rain).
Practical mastery of all case forms adjectives, their agreement with nouns in gender, number, case and with personal pronouns without prepositions and with prepositions (her, to her, from her
etc.). Function and place of adjectives in a sentence.
Correct expression of temporal relations, use of perfect and imperfect verbs in speech in all tense forms with nouns and pronouns (1st, 2nd, 3rd; singular and plural persons).
Establishing connections between words in a sentence and analyzing sentences on questions in accordance with its composition. Expanding sentences through questions.
Class
Working on a proposal
Using a simple common sentence in speech. Using sentences with phrases consisting of a noun as the subject and an adjective as the attribute (a fun game);
from a verb as a predicate and nouns in indirect cases as an object (draw a house, make it out of paper);
from a verb in the role of a predicate and a noun in the role of an adverbial (left Moscow, arrived in the village)
;
from a verb in the role of a predicate and an adverb in the role of an adverb of action, place, time (wrote carefully, runs to the right, let's go in the evening);
from a noun in the role of circumstance and an adjective agreed with Him in the role of a definition (with great appetite).
Practical mastery of the grammatical forms of words depending on their meaning in a sentence.
Isolating words from a sentence that are related in meaning and grammatically (word combinations with and without prepositions). The connection of words in a phrase, in a sentence on questions.
Extending sentences using words related to verbs and asking questions about them.
Clarification of the grammatical concept of words denoting objects, grouping words according to the questions who? What? Generalization of knowledge about words denoting objects.
Determining the gender of nouns by their initial form. Distinguishing between singular and plural, endings of nouns in all case forms. Finding the initial form of nouns used in any case form.
Formation of the grammatical concept of “verb”. Clarification of its semantic meaning. Changing verbs by numbers and questions.
Recognizing present, past and future tenses of verbs using the questions what' does? what are they doing? what did you do? What they were doing? what will it do? what will he do? What will they do?
Formation of tense forms of perfective and imperfective verbs.
General practical acquaintance with complex sentences consisting of two simple ones.
Previous13Next