A cerebellar cyst is a dangerous neoplasm that can lead to disruption of brain activity and paralysis of the limbs. This type of benign tumor requires mandatory treatment. The characteristics of the compaction determine whether the doctor will prescribe drug therapy or surgical intervention.
It threatens with disruption of brain activity and paralysis of the limbs.
Features of the pathology
A thickening is a cavity that appears in different parts of the cerebellum. It is filled with liquid contents and gradually increases in size. This cyst provokes consequences, so it must be treated immediately after diagnosis.
The pathology is located between the roof of the brain (blue arrow) and the pineal gland (red arrow).
The difficulty in prescribing therapy in a timely manner is that there are no symptoms, at least in the early stages of tumor development. As its size increases, signs appear, but by this time the capsule may already have grown significantly.
Causes
Cysts in the cerebellum can be congenital or acquired. Its causes depend on what type it belongs to. If the neoplasm is of the congenital type, it is formed during the period of embryonic development. This is due to developmental disorders during pregnancy or death of brain tissue. Necrosis may occur due to suffocation. This occurs during childbirth or in cases where the fetus, for certain reasons, lacks oxygen.
Risk factors that provoke the development of acquired pathology include:
Head injuries, concussions.
- acute foci of inflammation;
- hematoma in the brain area, which appeared due to mechanical impact;
- stroke;
- previous surgical interventions (related to the brain);
- concussions;
- injuries, blows, skull fractures;
- infections with parasites;
- multiple sclerosis.
Classification of cerebellar cysts and their treatment
Any brain pathology should not be ignored.
A deviation such as a cerebellar cyst is often diagnosed. This is the formation of a cavity filled with liquid. As a rule, this disease does not reveal itself in any way at the initial stages, and small formations are discovered completely by chance during magnetic resonance therapy. Symptoms appear as the size of the cyst increases.
Classification of pathology
All cysts localized in the cerebellum are usually divided into two large groups:
- primary – that is, congenital;
- secondary – acquired pathology.
There are several types of cysts. This classification is based on the causes and location of the pathological formation:
- Cystic-glial formations in the right half of the cerebellum. They arise as a result of previous TBI.
- Cystic-atrophic cysts in the right half of the cerebellum. This pathology is characterized by the presence of necrotic and atrophied areas.
- Cystic-glial formations in the left half of the cerebellum are characterized by severe symptoms.
- Lacunar cyst in the left half of the cerebellum. These are small formations, they are usually single. This form of the disease does not require treatment.
- A retrocerebellar cyst forms in the place where there is tissue necrosis.
- Cyst-like expansion in the subarachnoid space.
- Arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst.
- Pseudocyst is a congenital formation of the cerebellum.
Etiology
The causes of this pathology depend on which group it belongs to. The etiological factors for primary and secondary cysts are different.
Causes of primary formations:
- Anomalies of intrauterine development of the fetus.
- Asphyxia of the child during childbirth. In this case, necrotic areas of tissue are formed that have died from oxygen starvation.
Reasons for the development of secondary cysts:
- Traumatic brain injuries (skull fractures, concussion and bruises).
- Acute cerebrovascular accident (hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke).
- Inflammation in brain tissue.
- Surgical intervention.
- Tissue death as a result of stroke.
- Viral diseases of the brain (meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis).
- Hemorrhages from formed hematomas.
- Neuroinfections.
Clinical picture
Primary cysts most often do not manifest themselves in any way and do not interfere with a person’s life. As a rule, this pathology is not treated.
Symptoms of a secondary formation depend on its size and etiology. Small brain cysts do not have pathological symptoms; they are characteristic of large specimens. However, experts have identified several common signs of the disease:
- Severe pain in the head that is not relieved by painkillers.
- Dizziness, in some cases there is loss of consciousness.
- Bursting and pulsating sensations in the head area.
- Periodic nausea. Sometimes it ends in vomiting, which, in turn, does not bring relief.
- Disturbance of sleep and biological rhythms of patients.
- Cramps, tremor of fingers.
- Neurological symptoms.
- In children under one year of age, bulging and pulsation of the large fontanel and frequent regurgitation, in some cases vomiting, are observed.
- Coordination of movements worsens, gait changes.
- Partial or complete paresis and paralysis of the upper and lower extremities occur.
- Some areas of the skin may lose sensitivity.
- Pathological changes in hearing, vision, and speech are possible.
It is also necessary to note individual symptoms of cerebellar cysts depending on their type:
- hallucinations are characteristic of a retrocerebellar cyst;
- when the right half of the cerebellum is damaged, a person becomes quickly fatigued, both physical and mental;
- paralysis is more often observed with the development of pathology in the left half of the organ;
- hydrocephalus is a sign of cyst-like expansion of the subarachnoid space.
Diagnostics
When a patient seeks medical help, it is necessary to carry out a number of diagnostic measures to make an accurate diagnosis. First of all, anamnesis is collected (patient complaints, previous injuries, diseases). After which the patient is sent for diagnostic studies:
- Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound examination. These methods help to clarify the location and size of the formation, as well as to identify its nature. They should be carried out periodically to monitor the dynamics of the pathology.
- Electroencephalography. With its help, convulsive readiness is revealed.
- NSG (neurosonography). This study is only carried out on children under two years of age.
- Histology determines the nature of the formation (cyst, benign or malignant tumor).
- Laboratory examination of cerebrospinal fluid. The analysis is carried out to detect inflammation and infection.
Treatment
Treatment of this disorder is aimed at eliminating the cause and symptoms, and it is also necessary to stop the growth of the pathological formation.
In this case, two treatment methods are used:
- medicinal – in patients with small cysts;
- surgical – in the presence of large cysts.
Medicines are prescribed only by a doctor, therapy is carried out under the control of laboratory blood parameters:
- Medicines for resolving adhesions and scars (“Longidaza”).
- Antibacterial drugs to eliminate infection.
- Immunomodulators to restore the body's defenses.
- Nootropics provide better nutrition and gas exchange of brain cells.
- It is also necessary to take a number of medications, the action of which is aimed at reducing blood cholesterol, normalizing blood pressure levels and thinning the blood.
Indications for the operation:
- Development of hydrocephalus and hypertension.
- Worsening of focal symptoms.
- The presence of hemorrhage in the brain tissue.
- Cramps.
- Severe loss of coordination and balance.
In modern medicine, three types of operations are used:
- Endoscopic. This method is preferred by neurosurgeons. The operation is minimally traumatic and is performed under visual control. Complications are minimal and are not always detected. The outcome is favorable.
- Microneurosurgical operation.
- Shunting.
The last two types of surgical treatment are performed with mandatory craniotomy, which provides access to the brain.
Consequences
Any consequences are possible if the cyst grows rapidly or ruptures. That is why it is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of this formation and carry out timely therapy.
Consequences of the pathology:
- Impaired blood circulation and movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
- The appearance of tumors at the site of the cyst.
- Disorders of speech, movement, touch and vision.
- Patient death is extremely rare.
If the cyst bursts, quite dangerous complications arise:
- Blood poisoning (sepsis).
- The purulent contents of the cyst enter the cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to inflammation.
- Bleeding inside the skull.
- Complete paralysis.
- Death of the patient.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the severity of the pathology. If a formation in the cerebellum is detected in the early stages of development before its growth accelerates, then the prognosis is favorable. In this case, patients are cured, complications and cyst ruptures are not observed.
A fatal outcome is possible if the pathology is diagnosed too late or if proper treatment and control are lacking. Rapid growth and rupture of education occur, and pathological changes in the corresponding psychological functions are observed.
Preventive actions
Any unpleasant symptoms should not be ignored. Therefore, if the patient exhibits the above symptoms, it is necessary to seek advice from specialists (neurologist or neurosurgeon).
If a person is diagnosed with a cerebellar cyst, it is important to follow several recommendations that will help avoid complications:
- You need to visit your doctor periodically. This is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition and monitor the formation over time.
- Undergo diagnostic tests prescribed by a specialist.
- Carry out prevention against infectious diseases. You should increase the body's defenses: take vitamins, provide adequate nutrition, and healthy sleep.
- Prevent hypothermia of the body. A person should dress according to the season, avoid drafts, and keep his feet warm.
- Give up bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking).
- It is necessary to monitor blood counts. If cholesterol or platelet levels increase, you should take medications prescribed by the doctor (prevention of blood clots, ischemia of brain tissue, and so on).
- Monitor blood pressure levels. If hypertension is observed, then constant medication is needed. This will help avoid strong pressure surges.
- If your health worsens, it is important to inform your doctor about it in order to adjust your treatment.
Source: https://glmozg.ru/bolezni/kisty/kisty-mozzhechka.html
Types of cysts
Doctors have developed classifications that relate to the location and etiology of the tumor. There are the following varieties:
- Cystic-glial changes usually appear against the background of previous injuries in the head area. A cyst of the right or left hemisphere of the cerebellum has pronounced symptoms. These include worsening migraines, constant loss of strength, and dizziness. Subsequently, convulsions appear;
- A retrocerebellar tumor occurs where necrosis of gray matter cells occurs. This is often associated with a stroke, surgery in the skull, or blows. If it appears between the hemispheres, it is triggered by problems with the blood supply to tissues, with infections and with a source of inflammation. It provokes a severe migraine, which painkillers cannot cope with, as well as significant changes in consciousness and even hallucinations;
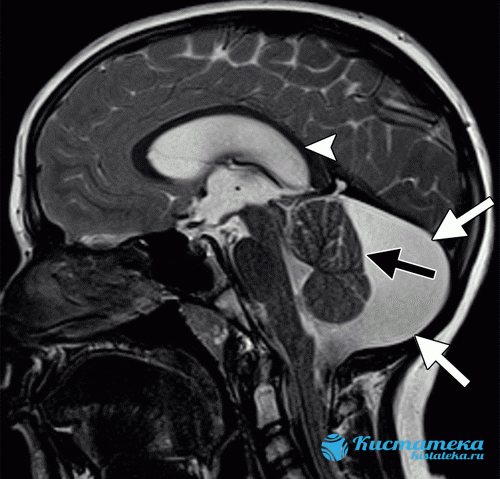
Occurs in the place where cell necrosis occurs. - An arachnoid cyst appears in the cerebellar space. The appearance of the capsule is facilitated by scars on the tissue, which are associated with problems with the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Signs appear depending on where the lump appears. An arachnoid cyst must be removed if it enlarges. When the capsule reaches a large size, it causes severe symptoms, such as seizures similar to epilepsy;
- the subarachnoid cavity is usually congenital. It is discovered after the baby is born during a standard examination. Less commonly, this type of neoplasm is acquired. Then the appearance is associated with infection with neuroinfections, with a stroke. Accompanied by pulsation in the brain tissue, convulsions;
- A pineal tumor appears in the pineal gland, which affects the production of hormones. An epiphysis cyst is characterized by loss of orientation in space and a constant desire to go to bed. The patient may experience double vision;
- pseudocyst is a congenital type of seal. They lack a lining of epithelial tissue.
Cerebellar cyst
A fairly common pathology is a cyst in the cerebellum of the brain; it is a hollow formation filled inside with mucus, a viscous liquid. The pathology requires timely detection by a doctor; in advanced cases, the disease seriously threatens a person’s health and life.
The danger of its occurrence lies in the long absence of symptoms; it is more often diagnosed during a routine medical examination or MRI. After diagnosing the disease, a person must receive qualified help and treatment.
Classification
Cysts in the cerebellum are: primary, secondary. A medical classification of formations has been developed.
- After a traumatic brain injury, a cystic-glial cyst can form, located on the right side of the cerebellum.
- In the right part of the cerebellum, a cystic-atrophic formation can be diagnosed, characterized by the presence of necrotic areas of tissue.
- Severe symptoms occur if there is a cystic-glial formation in the left side of the cerebellum.
- A small formation that does not require treatment is a lacunar cyst.
- A retrocerebellar cyst forms at the site of necrosis of the cerebellar tissue.
- A congenital formation is a pseudocyst.
- In the subarachnoid space, it is possible to diagnose cystic expansion, accompanied by hydrocephalus.
- Often, boys in early adolescence are diagnosed with an arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst. It requires timely treatment. This will avoid deterioration of your general condition.
What is the danger
The formation in the cerebellum is not dangerous for humans; it is not susceptible to malignancy. The risk of complications arises when the cyst actively increases, causing unpleasant symptoms and concomitant diseases.
A benign formation is dangerous if the impetus for its appearance was a chronic disease, an infection that affected brain tissue. Bacterial formation cannot be eliminated using traditional treatment methods; here we should talk about surgical intervention. In the absence of necessary therapy, the consequences can be fatal to a person.
What if it bursts?
In individual cases, a cerebellar cyst may burst. The consequences become:
- brain sepsis;
- inflammation of the cerebrospinal fluid;
- complete or partial paralysis;
- internal hemorrhage;
- death.
The methods used for diagnosing and treating education make it possible to exclude such a situation. It is possible to say that a cyst will burst in cases where a person did not go to the hospital, not knowing about the presence of a formation.
Treatment methods
The prescribed therapy depends on the size of the formation and the general condition of the person. If there is no worsening of the condition or pain symptoms, maintenance therapy is recommended. In case of abnormal enlargement of the cyst, surgery is recommended.
Many fear that the formation will later degenerate into a malignant tumor. This occurs only in 2-3% of cases from the total number of cysts diagnosed. Education responds well to medication.
Surgical treatment
The operation allows you to completely remove the cystic formation, but due to the complexity of the procedure, it is indicated only in a number of cases when:
- Coordination of movements is already impaired.
- Oncological disease is diagnosed.
- Convulsions similar to epileptic seizures are observed.
- Education is actively growing.
- There was a danger of internal hemorrhage.
The operation can be performed microneurosurgically, in which the skull is opened. The method is accurate, but there is still a risk of brain damage. There are practically no risks with endoscopy, and the recovery period is quite short. You can empty the cystic cavity using a shunt. If the catheter is left in place for a long time, there is a risk that an infection may develop.
ethnoscience
Proven recipes of alternative medicine allow you to stabilize and keep the body’s condition under control. It is necessary to select the optimal prescriptions with your doctor. Many herbs can have negative effects on humans if used incorrectly.
To resolve the cyst, spotted hemlock may be recommended. It combines with black elderberry and violet. The fee is applied if the formation begins to grow. The proportions, method of preparation and duration of therapy are determined by the doctor.
Drinking tea from viburnum, horsetail, and chokeberry allows you to control blood pressure, which is also important in this condition. The diet should be supplemented with celery, asparagus, vegetables, and fruits.
Alternative medicine can be used exclusively at the stage of remission, but not exacerbation.
Symptoms
It is quite difficult to determine the development of a cyst in the early stages. This happens because it does not manifest itself in any way and does not bother the person. Congenital tumors may not affect infants and sometimes resolve spontaneously.
If the acquired neoplasm increases in size or even provokes the appearance of adhesions, the following symptoms occur:
- there is a feeling of compression and pulsation in the area of the skull;
- Coordination gradually deteriorates, the patient experiences loss of orientation in space;
- tinnitus is accompanied by nausea. Possible partial hearing loss, bouts of vomiting;
- the pain in the head sometimes becomes very severe. Painkillers do not cope with it;
- the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness is disrupted, insomnia appears;
- in difficult situations, convulsions, trembling of hands and fingers occur;
- periodic fainting occurs;
- subsequently vision deteriorates, paralysis (partial or complete) cannot be ruled out;
- the person begins to limp and cannot relax the muscles that are cramped by tension or cramps.
If we talk about symptoms in newborns, we are talking about constant regurgitation and vomiting.
Signs
Several types of brain cysts with their own characteristics and symptoms have been classified. First of all, hollow formations of the primary (congenital) and secondary (acquired) types are distinguished.
If a formation does not produce symptoms and does not pose a threat to normal life, modern medicine considers it an anomaly. But usually this is typical for a primary – congenital cyst.
Small cysts of the secondary type also do not detect themselves, but overgrown ones can put pressure on neighboring areas, causing the following symptoms:
- feeling of pulsation, fullness in the head;
- headaches that do not improve with medication;
- disturbance of balance, coordination, spatial orientation;
- noises and ringing in the ears, hearing loss;
- nausea, attacks of vomiting, which does not alleviate the condition;
- circadian rhythm shift and sleep problems;
- movement disorders (uncontrolled limb movements);
- convulsive attacks (rarely), tremor (trembling of fingers);
- fainting conditions;
- blurred vision;
- partial paralysis of arms and legs;
- neurological disorders;
- increased or decreased muscle tone (weakness or, conversely, abnormal muscle tension);
- changes in gestures, gait, handwriting;
- loss of skin sensitivity;
- limping;
- pronounced pulsation of the fontanelle in infants, excessively frequent regurgitation, vomiting.
But since individual areas of the brain are responsible for certain functions, clinical signs are largely differentiated depending on the type of brain cyst, location and area on which it is capable of affecting.
The main types of cerebellar cysts and symptoms of the disease:
- Cystic-gliotic changes in the brain in the hemispheres
- In the right hemisphere: dizziness;
- physical and mental fatigue;
- convulsive phenomena;
- headaches.
- In the left hemisphere:
- movement disorders;
- paralysis of the limbs (partial or complete);
- speech disorders
- intense headaches that do not respond to analgesics;
- epileptic-type seizures;
- tissue atrophy, the appearance of foci of necrosis due to prolonged circulatory disorders;
- Intrauterine disorders - does not manifest itself and does not need to be removed;
What is the danger?
Small seals do not pose a danger to human life and health. The problem is that in most cases they continue to grow and begin to put pressure on the brain tissue. This provokes the following complications:

Complete or partial paralysis cannot be ruled out.
- blood circulation deteriorates, insufficient oxygen reaches the cerebellum;
- irreversible processes occur that affect speech, vision, hearing, and coordination of movements;
- complete or partial paralysis cannot be ruled out, in which it is impossible to restore lost functions;
- in the most severe cases, the pathology leads to the death of the patient.
Sometimes spontaneous rupture of the capsule membranes occurs, which leads to sepsis and a purulent inflammatory process in the cerebrospinal fluid. There is also a risk of internal bleeding, paralysis and death.
A cerebellar cyst in a newborn child (if it does not resolve) causes developmental disorders and delays in many functions.
Consequences
Health and life-threatening consequences occur if a cyst in the cerebellum begins to grow rapidly. Without active treatment, the following are possible:
- hearing, vision, speech disorders;
- convulsive attacks, fainting, mental disorders;
- problems with motor functions, balance, coordination;
- hydrocephalus (abnormally high accumulation of fluid in the ventricular system), in which complete restoration of many functions is impossible;
- disorders of the blood supply to certain areas with tissue death, disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF);
- encephalitis;
- retardation of infants in mental and physical development;
- degeneration of a hollow structure into a brain tumor;
- rupture of the cystic capsule, which is likely to result in: general blood infection, penetration of pyogenic microorganisms into the cerebrospinal fluid;
- paralysis of limbs;
- internal bleeding;
- death of the patient.
Diagnostics
During a visit, during which the patient complains of unpleasant symptoms, the doctor prescribes diagnostic measures to clarify the diagnosis. MRI is considered the most revealing examination method. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrates where the tumor is located and clarifies its size and structure. During the examination, you can find out how the tumor affected the surrounding tissues, whether deformation of the worm and other parts has occurred.
In addition to MRI, the following procedures are prescribed:
- puncture. Provides analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in order to exclude or confirm an inflammatory process in tissues;
- the contents can be sent for histological examination in order to clarify the nature of the compaction. If cancer cells are present, the treatment will be radically different than for a benign type of cyst;
- An electroencephalogram is designed to calculate convulsive contractions of the brain. The results of this manipulation also influence the prescribed treatment;
- if the patient is a small child who has not yet turned 2 years old, neurosonography is prescribed. This is a safe type of research that gives a complete picture of the processes occurring in the cerebellum;
- A blood test is necessary in order to exclude concomitant infectious diseases or foci of inflammation.
Treatment
This type of neoplasm requires a special approach. Doctors seek to remove most thickenings in order to improve the person’s condition. But brain intervention always carries serious risks, so it is prescribed only in the most severe cases.
Therefore, most often they try to limit the growth of the cyst and reduce the unpleasant symptoms experienced by the patient. Drug treatment is prescribed in most cases.
Drug therapy
After completing diagnostic measures, the doctor chooses treatment tactics. It is aimed at preventing the growth of the cyst. In addition, it contributes to the achievement of the following goals:
- resorption of adhesions that appear due to the progression of pathology;
- ensuring proper functioning of the circulatory system;
- saturation of brain cells with oxygen and necessary components;
- lowering cholesterol;
- normalization of blood pressure levels;
- maintaining blood clotting;
- combating pathogens of dangerous infections (if they are present);
- maintaining a high level of immunity;
- antioxidants should increase cell resistance to increased pressure.
The attending physician decides how long the rehabilitation will last. The patient should not independently discontinue medications or change the established daily dosage.
Surgery
Doctors put off surgical intervention until last. It is prescribed when medications do not cope with their tasks. The operation is associated with a high risk of damage to brain structures, so it is prescribed in specific cases:
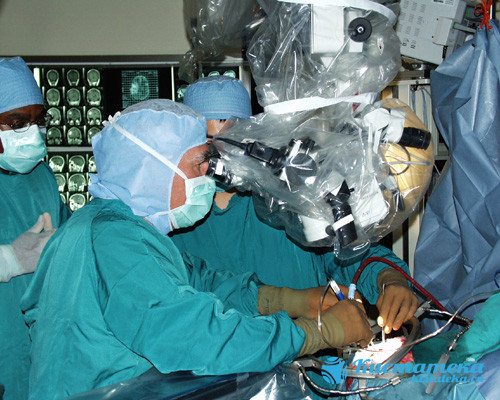
Microneurosurgery is used.
- coordination of movements is increasingly impaired;
- cancer cells have been identified;
- the patient suffers from severe cramps;
- the tumor is constantly increasing in size;
- there is a possibility of cerebral hemorrhage.
The intervention is carried out using one of three main methods. Microneurosurgery is used, which requires opening the skull. The accuracy of capsule removal is guaranteed, but the risk of damage to healthy tissue is also higher.
The endoscopic method minimizes the risk of complications and also shortens the recovery period. The third type of operation is bypass surgery. With it, a catheter is inserted into the cavity, through which the contents of the capsule are pumped out. However, it cannot be kept for a long time, otherwise there is a possibility of penetration of pathogenic pathogens.
Cerebellar cyst - what is it and how to treat it
A cerebellar cyst is a fluid-filled cavity that can lead to serious complications. The danger of the disease lies in the possibility of its asymptomatic course. The cyst has congenital and acquired forms.
Causes of pathology
A cyst in the cerebellum of the brain develops under the influence of primary and secondary factors. The primary ones are disturbances during the intrauterine development of the baby. If a child suffocates during childbirth, this becomes the cause of tissue necrosis and cyst development .
Secondary reasons are:
- Brain hematomas, which are accompanied by hemorrhages;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke;
- Viral tissue lesions;
- Circulatory disorders in the vessels of the brain.
The disease is diagnosed in patients after brain surgery. The pathology develops against the background of traumatic brain injuries, which are moderate to severe.
If the brain has pockets of dead tissue against the background of impaired blood circulation, this leads to the development of the disease. It is diagnosed in people with neuroinfections and parasitic lesions. If cerebral cells are replaced by cystic tissue, this leads to disease.
A cerebellar cyst develops in a patient due to exposure to various unfavorable factors and diseases that occur in the patient’s body.
Signs of the disease
Depending on the location and severity, cerebellar cysts share a variety of disease symptoms. With pathology, patients complain of pulsating movements in the head of a bursting nature.
A headache occurs that cannot be eliminated with the use of analgesic medications. With a long course of the disease, the patient's hearing and vision deteriorate. It is accompanied by disturbances in sleep and daily routine.
The disease causes noise and ringing in the ears. A common symptom of the pathology is fainting. Patients complain of cramps and trembling in the fingers. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, partial paralysis of the upper and lower extremities is diagnosed.
The patient cannot control the movements of his arms and legs. The disease is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief. The patient's orientation in space and coordination of movements becomes impaired. Patients complain of weakness and increased tension in the muscles.
Some patients limp during the course of the disease. The skin of patients is characterized by reduced sensitivity. Patients' gait and handwriting change. In newborns with the disease, the fontanel pulsates and excessive regurgitation is observed.
A cyst of the cerebellum of the brain is accompanied by a large number of symptoms. If several of them appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist who, after diagnosis, will prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnostic measures
After the patient contacts a specialist, he is examined and anamnesis is collected. This allows the doctor to make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm it, it is recommended to use instrumental research methods:
- Ultrasound examination and magnetic resonance imaging . These diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the location of the cyst in the cerebellum, its size and pressure level. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine the quality of treatment.
- Neurosonography . The diagnostic procedure is recommended for children under 2 years of age. This examination is characterized by safety and provides the opportunity to obtain detailed information about the condition of the brain and the location of the cyst.
- Electroencephalograms . Provides the opportunity to determine convulsive readiness and the possible outcome of therapy.
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe additional research methods. It is recommended to conduct a blood test , which can be used to determine diseases of an infectious and autoimmune nature.
Benign and malignant tumors are distinguished using histological examinations. The inflammatory or infectious process is determined by analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible to determine how much the cerebellum is affected by the tumor process and to develop an effective treatment regimen.
Treatment of the disease
For cysts, patients are prescribed medication or surgery. To resolve adhesions, patients are recommended to take Longidaza and Karipain. Restoration of blood circulation processes in the organ is ensured thanks to Cerebrolysin and Encephabol. The action of the drugs is aimed at enriching brain tissue with nutrients .
Normalization of cholesterol levels in the blood is ensured by Simvastin. To ensure normal blood and intracranial pressure, patients should take Corinfar.
Warfarin is prescribed to support blood clotting levels. Blood fluidity is maintained thanks to Cardiomagnyl. The resistance of brain cells to the effects of increased intracranial pressure is ensured with the help of antioxidants.
If the cause of the cyst is an infectious process, then it is necessary to take antibacterial drugs. To strengthen the functioning of the immune system, it is recommended to take immunomodulators.
If drug therapy is ineffective, patients are prescribed surgery. It is carried out in two ways - microneurosurgical method and bypass surgery.
The first of them is characterized by a high level of effectiveness and requires opening the skull, which increases the risk of complications. Some patients are recommended to undergo laser cyst removal, which is characterized by effectiveness.
Treatment of the cyst should be prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the degree of development of the pathology.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes help curb tumor growth. However, they should not be used thoughtlessly. Before using any product, you must obtain the approval of your physician. Otherwise, you may not improve the condition, but only provoke the development of complications.
Traditional recipes can be used during the recovery period, but not in the acute stage. They are used only in combination with medications prescribed by a doctor. To slow down the growth of a tumor, the following means are used:
- spotted hemlock. It is used alone or in combination with elderberry and violet;
- tea from viburnum, rowan or horsetail helps stabilize blood pressure, which has a positive effect on the patient’s condition;

Viburnum tea stabilizes blood pressure levels. - fresh vegetables (celery, asparagus, etc.) help strengthen the immune system and give strength to fight pathology.
Prevention
If we talk about the prevention of congenital neoplasms, then a pregnant woman should lead a correct lifestyle. You need to give up bad habits and avoid emotional stress. It's important to eat right. If the body does not receive enough nutrients with food, it is necessary to additionally consume vitamin complexes designed for pregnant women.
Secondary tumors can also be prevented. To do this, follow the general recommendations:
Monitor your blood pressure readings.
- diseases associated with the nervous system require prompt treatment. Their nature does not matter - infectious, vascular, etc.;
- undergoing a routine examination by a doctor. If you experience any disturbing symptoms, even minor ones, consult your doctor immediately;
- don't let yourself freeze. It's about the head - always wear a hat;
- monitor your blood pressure and take medications if it changes;
- watch your cholesterol;
- minimize the likelihood of developing infectious diseases, avoid contact with sick people;
- get rid of bad habits.
Neoplasms in the cerebellum usually require immediate treatment. In newborns, they can resolve spontaneously. But adults need to take medications under the supervision of a physician. In the most severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.