If a head injury occurs, it is important to immediately begin rehabilitation measures at home, which will help prevent serious complications - intracranial hemorrhages, swelling and dislocation of brain structures. If a person falls and hits their head hard, the consequences can range from a mild concussion to coma and death. Statistics show that the prevalence of head injuries is about 200 cases per 100 thousand population annually. For 30% of patients, brain damage is fatal. Every year, severe head injuries and associated disorders of vital and brain functions lead to the death of 1.5 million people in the world. Another 2.5 million people become disabled.
Definition
A head injury occurs when a person falls or hits the skull with a hard object; the condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Even weak blows to the skull area lead to an increase in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, the development of autoimmune reactions in the tissues of the central nervous system, and neurodegenerative changes.
If you hit the back of the head, forehead, or temple hard, the tissues of the brain and skull will be damaged, which can be hidden from view during a visual inspection when there are no violations of the integrity of the skin. A fracture of the bone structures of the skull is a life-threatening disorder, which is always accompanied by a change in the morphological structure of the brain matter.
A dent on the forehead, crown or back of the head after a blow is a reason to suspect a fracture of the cranial bones. Other signs to look out for include softening of the bone structures of the skull, progressive loss of motor coordination and other reactions. If you shake your head, it is important not to make sudden movements, which can aggravate the dysfunction of the brain.
If struck, a person may be seriously injured. As a result of a skull fracture, pneumocephalus (air entering the cranial cavity) often develops. A common complication of head injury is damage to the cranial nerves. The condition is accompanied by paresis of the facial muscles and visual impairment.
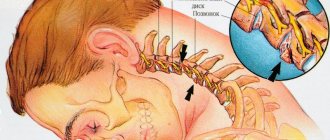
Often the pathology is combined with damage to the spinal column in the cervical region. Airway obstruction (obstruction) is a common cause of early death in TBI. Head injuries in 90% of cases are accompanied by loss of consciousness, which correlates with a decrease in the tone of the muscles located in the pharynx. A decrease in tone leads to a displacement of the tongue and soft palate, which causes a violation of the patency of the respiratory system.
Complications of a concussion
The main complications are associated diseases that result from the concussion - cerebral hemorrhage, disruption of brain function, fractures of the skull or spine (especially the cervical spine) or damage to the spinal cord leading to paralysis.
Intracranial hemorrhage can have serious consequences in the form of brain damage. The first signs may include changes in the pupils, severe headache, incipient paralysis of the limbs, repeated unconsciousness, and motor disorders.
An actual complication of concussion is post-concussion syndrome, which affects up to half of patients. This condition is defined by various symptoms associated with a concussion and can appear either immediately after the injury or several days or weeks later. Symptoms disappear on their own within one year. They include the following signs:
- Headache (migraine - may occur due to damage to the cervical spine).
- Feeling tired.
- Anxiety.
- Dizziness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Decreased performance (both mental and physical stress).
Types of injuries
Taking into account the nature of the damage, concussion, contusion of brain tissue or compression of the brain are distinguished. Considering the severity of the injuries received, a distinction is made between concussion of the brain (mild contusion), moderate contusion of brain tissue, and severe trauma. A wound that appears on the head when you fall, get knocked, or are attacked occurs:
- Open (damaged skin).
- Closed (skin without damage; subcutaneous soft tissues, bone and medulla undergo pathological changes in morphological structure).
- Penetrating (characterized by a violation of the integrity of the meninges).
Depending on the location of the pathological focus, contusion of the occipital area, frontal, temporal, parietal lobe is distinguished.
Hit my head, headache and nausea
If a head injury occurs, it is important to immediately begin rehabilitation measures at home, which will help prevent serious complications - intracranial hemorrhages, swelling and dislocation of brain structures.
If a person falls and hits their head hard, the consequences can range from a mild concussion to coma and death. Statistics show that the prevalence of head injuries is about 200 cases per 100 thousand population annually. For 30% of patients, brain damage is fatal.
Every year, severe head injuries and associated disorders of vital and brain functions lead to the death of 1.5 million people in the world. Another 2.5 million people become disabled.
Definition
A head injury occurs when a person falls or hits the skull with a hard object; the condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Even weak blows to the skull area lead to an increase in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, the development of autoimmune reactions in the tissues of the central nervous system, and neurodegenerative changes.
If you hit the back of the head, forehead, or temple hard, the tissues of the brain and skull will be damaged, which can be hidden from view during a visual inspection when there are no violations of the integrity of the skin. A fracture of the bone structures of the skull is a life-threatening disorder, which is always accompanied by a change in the morphological structure of the brain matter.
A dent on the forehead, crown or back of the head after a blow is a reason to suspect a fracture of the cranial bones. Other signs to look out for include softening of the bone structures of the skull, progressive loss of motor coordination and other reactions. If you shake your head, it is important not to make sudden movements, which can aggravate the dysfunction of the brain.
If struck, a person may be seriously injured. As a result of a skull fracture, pneumocephalus (air entering the cranial cavity) often develops. A common complication of head injury is damage to the cranial nerves. The condition is accompanied by paresis of the facial muscles and visual impairment.
Often the pathology is combined with damage to the spinal column in the cervical region. Airway obstruction (obstruction) is a common cause of early death in TBI.
Head injuries in 90% of cases are accompanied by loss of consciousness, which correlates with a decrease in the tone of the muscles located in the pharynx.
A decrease in tone leads to a displacement of the tongue and soft palate, which causes a violation of the patency of the respiratory system.
Types of injuries
Taking into account the nature of the damage, concussion, contusion of brain tissue or compression of the brain are distinguished. Considering the severity of the injuries received, a distinction is made between concussion of the brain (mild contusion), moderate contusion of brain tissue, and severe trauma. A wound that appears on the head when you fall, get knocked, or are attacked occurs:
- Open (damaged skin).
- Closed (skin without damage; subcutaneous soft tissues, bone and medulla undergo pathological changes in morphological structure).
- Penetrating (characterized by a violation of the integrity of the meninges).
Depending on the location of the pathological focus, contusion of the occipital area, frontal, temporal, parietal lobe is distinguished.
Features of head injury in childhood
The bone tissue of a child under 12 years of age contains a large amount of water, has a fibrous structure, and is characterized by a low content of calcium salts. The bones of the skull in childhood are soft and flexible. After a blow, a dent may appear on the child’s head; the brain matter is damaged more often due to strong mechanical impact on the skull than in adult patients.
If a child falls and hits his head, he may have a headache, an increase in body temperature, and vomiting, which suggests the need to urgently take the following actions: lay the child in a horizontal position and call a doctor. Even if the baby remains conscious, it is important to pay attention to changes in his behavior.
Affected children usually lose their appetite. They become inactive and complain of double vision. If a child feels sick after hitting his head, and signs such as apathy, lethargy, weakness, drowsiness and dizziness appear, he needs urgent medical attention.
Causes
If you have a headache after a fight, it is better to immediately seek medical help. Contusion of the brain and bone structures of the skull occurs due to a direct blow to the skull area, mechanical impact with acceleration, and compression of the cranial structures. Common situations associated with injury:
- Road accidents.
- Falling from height.
- Industrial injuries.
- Traumatic injuries as a result of a fight or attack.
- Sports activities.
Depending on the strength of the traumatic impact, damage of varying degrees of severity occurs - reversible disorders (concussions of the brain) and irreversible (foci of crushed brain structures).
The crush site is a variable area of the cerebral hemispheres, in the area of which the meninges are ruptured and particles of alternative brain matter are present.
The crush site is characterized by a functional and structural change in the nervous tissue (neurons, gliocytes, nerve fibers, synapses) and elements of the vascular system, in the area of which multiple hematomas appear. Bruises of the skull are usually accompanied by the formation of foci of hemorrhage.
The crush site in the acute period of TBI manifests itself clinically as an intracranial space-occupying process (hematoma, tumor) and contributes to the progression of hypertensive-dislocation syndrome. As a result, life-threatening conditions associated with pinching and compression of the brain stem may develop.
Symptoms
Injuries in the skull area are differentiated based on severity. In accordance with this classification, they are divided into mild, moderate and severe forms. Symptoms depend on the severity of the damage. A mild form, known as a concussion, is accompanied by symptoms:
- Darkness, loss of consciousness (lasts several seconds, minutes).
- Disorientation in space and time, confusion of thoughts.
- Amnesia (memory loss) of retrograde or anterograde type.
- Pain in the head area (intense, bursting, acute), dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Noise, buzzing in the ears.
- Pain in the eye orbits.
Neurological deficit of focal type is absent or mildly expressed. A strong blow to the back of the head during a fall or as a result of mechanical impact from the outside in adults and children is associated with serious consequences. Moderate injuries are accompanied by symptoms:
- Prolonged loss of consciousness (lasts several minutes or hours).
- Lethargy, inability to adequately navigate time and space.
- Amnesia of retrograde and anterograde type.
- Diffuse type headache.
- Meningeal symptoms (muscle rigidity in the occipital region, pathological reflexes of Brudzinsky, Kernig, state of stupor, stupor, paresis and paralysis, paresthesia - sensitivity disorder, numbness, tingling in the area of the limbs, face).
- Psychomotor agitation.
Additional signs of damage to nervous tissue depend on the localization of the site of impact during a head injury; taking into account the focal symptoms, the doctor decides what to do.
Focal symptoms include impaired motor coordination, pyramidal signs (pathological foot and hand reflexes, reactions of oral automatism, clonus - rapid, involuntary contractions of muscle groups, synkinesis - involuntary friendly contraction of a limb in response to voluntary movement of a symmetrical limb).
Source: //moy-zheludok.ru/simptomy/udarilsya-golovoj-bolit-golova-i-toshnit
Features of head injury in childhood
The bone tissue of a child under 12 years of age contains a large amount of water, has a fibrous structure, and is characterized by a low content of calcium salts. The bones of the skull in childhood are soft and flexible. After a blow, a dent may appear on the child’s head; the brain matter is damaged more often due to strong mechanical impact on the skull than in adult patients.
If a child falls and hits his head, he may have a headache, an increase in body temperature, and vomiting, which suggests the need to urgently take the following actions: lay the child in a horizontal position and call a doctor. Even if the baby remains conscious, it is important to pay attention to changes in his behavior.
Affected children usually lose their appetite. They become inactive and complain of double vision. If a child feels sick after hitting his head, and signs such as apathy, lethargy, weakness, drowsiness and dizziness appear, he needs urgent medical attention.
Head injury: symptoms, first aid, consequences
Head contusions are injuries that most often result from a fall or blow from a blunt object. Often such injuries occur in young people.
Even when there are no symptoms, it is not recommended to ignore head injuries, since they can pose a danger to human health and life.
Injuries can cause a fracture of the base of the skull, concussion and other unpleasant complications, which is why it is necessary to know what to do in case of a head injury and, if necessary, provide first aid.
Classification
The injury can be open, that is, damage to the skin is observed, and blood vessels are also affected. If the injury is penetrating, then the dura mater of the brain is affected, sometimes a fracture of the base of the skull is diagnosed - one of the most dangerous injuries.
With closed injuries, the skin is not injured. The following groups of brain damage have been identified:
- A concussion is a mild degree of traumatic brain injury, the manifestations of which disappear after a few days, there are no symptoms of vascular damage, and functional disorders are reversible. A bruise is a more severe injury and may cause brain damage. Manifested by such symptoms as nausea, vomiting, pale skin, tissue swelling, pain.
- compression of the affected area of the brain (foreign object, hematoma, air, bone fragment);
- hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space (the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater);
- diffuse damage.
A severe brain contusion can result from a combined injury.
With a head injury, there are 2 types of bruises:
- Brain contusion.
- Contusion of the soft tissues of the head.
Sometimes the injury is accompanied by hemorrhage. This is often accompanied by fractures of the bone tissue of the skull.
Types of damage are identified depending on location:
- contusion of the back of the head;
- damage to the temporal region;
- bruise of the frontal part of the head;
- damage to the parietal lobe.
Changes that occur in the brain as a result of a bruise are divided into primary and secondary. Primary ones are caused by the injury itself, and secondary ones are caused by deterioration of tissue nutrition and increased intracranial pressure, the appearance of edema, and hematomas.
In case of serious injuries, contusion of several areas of the brain is sometimes diagnosed.
When a child bruises the soft tissues of the head, a lump appears. However, as a result of the blow, brain injuries are also possible, the consequences of which can appear in adulthood, after 40 years or later. Therefore, even if a lump simply appears after a blow, it is recommended to seek medical help.
Symptoms
What can happen to the brain after a stroke? The brain, by inertia, sharply shifts in the opposite direction, so it is damaged not only at the site of the impact, but also on the opposite side, this causes vascular spasms and swelling. Due to edema, intracranial pressure increases.
A severe head injury is often accompanied by fractures of the skull bones, which worsen the person’s condition; the risk of developing an infection in the affected area also increases. In any case, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Symptoms of a head injury are determined by the location and force of the blow:
- A mild bruise is characterized by pain that subsides after a few hours. When the subcutaneous vessels are damaged, a hematoma forms. The victim complains of constant drowsiness, double vision and darkening of the eyes, and sometimes fainting occurs. Symptoms disappear after a few weeks;
- moderate injuries are accompanied by prolonged fainting (several hours), severe headaches, inhibited reactions and impaired awareness of what is happening. Speech is unclear and slow;
- for fractures of the skull bones, the main clinical symptoms are dizziness, vomiting, and nosebleeds;
- contusion of the back of the head is manifested by blurred vision, dizziness, loss of consciousness and general weakness.
In case of serious injury, patients are unconscious for a long time (up to several days), and coma may occur. There is a disturbance in speech, breathing and swallowing, and the pupils may vary in size. Partial or complete memory loss cannot be ruled out.
First aid for head injury
For a head injury, first aid consists of the following:
- put cold on the site of the impact, this will make it possible to reduce pain and swelling, keep it for several hours, but avoid hypothermia.
- the victim must be laid on a horizontal surface, which will make it possible to avoid another fall due to weakness and dizziness;
- regardless of the severity of the condition, take the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance; exclude the intake of water, food and medications;
- in case of hematoma, apply a compressive bandage;
- Warming compresses with alcohol can only be used after a few days.
First aid for a head injury can be provided by anyone, but qualified medical assistance will still be required.
If a child suffers a head injury, first aid must be provided; it must also be taken into account that the symptoms in children may not appear as pronounced as in adults.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment are prescribed by a neurologist. If head contusions are observed, the diagnosis is made based on the following methods:
- X-ray – the presence of skull fractures is determined;
- spinal puncture;
- computed tomography - the localization of damage, the presence of hematoma, and edema are revealed.
After receiving accurate results, adequate therapy is prescribed.
Treatment
Some people self-medicate for a head injury, which is not recommended, especially if there is even the slightest suspicion of a concussion or hemorrhage. How to treat a head injury is determined by the doctor; the methods depend on the nature of the injury and its location.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed to reduce symptoms:
- analgesics – to reduce pain;
- medications to regulate the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- sleeping pills to normalize sleep;
- nootropic drugs are prescribed to prevent complications, as well as to restore brain function;
- diuretics;
- anticonvulsants - prescribed in more severe cases in the presence of seizures.
For topical use, ointments are used that have a strengthening effect on blood vessels, relieve swelling and help eliminate hematomas. During the rehabilitation period after injury, doctors prescribe physiotherapeutic measures.
A specialist will tell you how to treat a bruise at home. For this, compresses made from tincture of ginseng, lemongrass, and eleutherococcus are recommended.
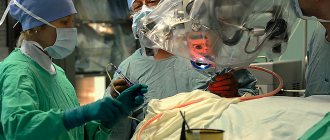
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, surgical treatment is indicated, for example, for a head injury from a fall, if it is accompanied by damage to the integrity of the brain structures.
Most often, operations are prescribed for damage to the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain. Craniotomy is performed by drilling a hole through which dead tissue is removed. During the postoperative period, the patient should be under the supervision of doctors.
In case of a head injury due to a fall, treatment is prescribed based on the diagnosis. If the injury is not dangerous, then the following recommendations must be followed:
- bed rest for several days;
- adhere to the instructions of the treating specialist and ensure that you take prescribed medications;
- during the rehabilitation period, exclude physical activity;
- if the left side of the brain is injured, then it is better to lie on the right side, and vice versa;
- during the recovery period, it is better to avoid using gadgets and TV or limit such leisure activities to a minimum;
- Long walks in the fresh air are necessary.
If the back of the head is bruised, bruises and bumps also cannot be ignored, especially if unpleasant symptoms appear. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid unpleasant complications.
Consequences of a bruise
Complications can be different, it depends on the location and severity of the injury. Minor injuries resolve on their own in a short period of time. In case of serious injuries, the development of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- waking coma (apallic syndrome) - patients are conscious, but they are not able to react to what is happening, and are absolutely indifferent to the people and objects around them. There is a reaction only to pain;
- paresis – partial loss of motor function.
- brain cyst;
- brain abscess - the formation of a cavity with pus during the development of the inflammatory process;
- ICH, or intracranial hypertension syndrome, is increased intracranial pressure;
- constant headache - does not go away for six months or more;
- meningitis is an inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain;
- development of secondary epilepsy;
- death or disability cannot be excluded in case of severe injuries;
Consequences of a bruise on the back of the head:
- decreased performance and concentration;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- depression;
- regular dizziness;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- weather dependence.
If you hit the back of your head during a fall, the consequences of the impact can be serious, so it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination.
The success of therapeutic measures depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment and the severity of the injury.
Source: //golovnie-boli.com/bolezni-golovy/ushib-golovy.html
Causes
If you have a headache after a fight, it is better to immediately seek medical help. Contusion of the brain and bone structures of the skull occurs due to a direct blow to the skull area, mechanical impact with acceleration, and compression of the cranial structures. Common situations associated with injury:
- Road accidents.
- Falling from height.
- Industrial injuries.
- Traumatic injuries as a result of a fight or attack.
- Sports activities.
Depending on the strength of the traumatic impact, damage of varying degrees of severity occurs - reversible disorders (concussions of the brain) and irreversible (foci of crushed brain structures). The crush site is a variable area of the cerebral hemispheres, in the area of which the meninges are ruptured and particles of alternative brain matter are present.
The crush site is characterized by a functional and structural change in the nervous tissue (neurons, gliocytes, nerve fibers, synapses) and elements of the vascular system, in the area of which multiple hematomas appear. Bruises of the skull are usually accompanied by the formation of foci of hemorrhage.
The crush site in the acute period of TBI manifests itself clinically as an intracranial space-occupying process (hematoma, tumor) and contributes to the progression of hypertensive-dislocation syndrome. As a result, life-threatening conditions associated with pinching and compression of the brain stem may develop.
Which doctor should I contact if I have a concussion?
Let's figure out which doctor to go to if you have a concussion. After a concussion, even a mild one, you must see a doctor whose activities are in one way or another related to head injuries.
Surgeon
Sometimes a traumatic brain injury can be accompanied by additional bodily injuries: fractures, dislocations, cracks in the bones of the skull, bleeding. In this case, especially if emergency surgery is required, the traumatologist will send the patient to the general surgery department. In all other cases, consultation with a surgeon is usually not required.
ENT
an otolaryngologist if there is bloody discharge from the ear or tinnitus continues for more than a day .
If you have nosebleeds or suspect a septal injury after a blow or fall, you should also seek advice from an ENT specialist.
Oculist
With a traumatic brain injury, contusion of the eyeball can occur. If, after a diagnosed injury, you experience pain in the eyes, severe nausea, dizziness, redness of the eye, obvious decreased vision, fog before the eyes, or floaters, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
You should not rely on the fact that everything will go away on its own, since with a concussion and contusion of the eyeballs, swelling of the cornea , hemorrhage, and detachment of the iris can occur. All this requires immediate treatment from a specialist.
Traumatologist
The first doctor you should contact after receiving a traumatic brain injury. A traumatologist will examine the victim, provide first aid, give an initial opinion and send him for further treatment to a neurologist, surgeon or other specialized specialists. The traumatologist can also decide on further hospitalization of the victim.
Neurologist
Primary physician in the treatment of concussion. After discharge from the hospital, the injured person must be observed by a neurologist for a year. If the injury is minor and you have not contacted a traumatologist, you should definitely visit a neurologist. He will prescribe the necessary additional studies to exclude post-traumatic effects on the brain and prescribe treatment.
Symptoms
Injuries in the skull area are differentiated based on severity. In accordance with this classification, they are divided into mild, moderate and severe forms. Symptoms depend on the severity of the damage. A mild form, known as a concussion, is accompanied by symptoms:
- Darkness, loss of consciousness (lasts several seconds, minutes).
- Disorientation in space and time, confusion of thoughts.
- Amnesia (memory loss) of retrograde or anterograde type.
- Pain in the head area (intense, bursting, acute), dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Noise, buzzing in the ears.
- Pain in the eye orbits.
Symptoms
After hitting or falling your head on a hard surface, the brain is shaken inside the skull. This contributes to the temporary separation of the cerebral cortex from the brain stem sections.
A sharp vascular spasm occurs, which goes away after a short time, but cerebral blood flow is temporarily disrupted. What are the main symptoms of a concussion?
- Depression of consciousness immediately after a blow or fall. Loss of consciousness is not always present - it may be a state of stupor or disorientation.
- Vomiting immediately after an injury, one-time, is usually one of the main symptoms for diagnosing a concussion.
- Increased or slowed heart rate, a sharp jump in blood pressure for a short time.
- The victim turns pale, then turns noticeably red.
- Darkening of the eyes, tinnitus, dilated pupils.
Diagnostics
Timely, correct diagnosis significantly improves the prognosis for severe head injuries; the doctor identifies the nature and extent of the damage and determines what to do. Priority methods of instrumental diagnostics are CT and MRI. During neuroimaging, the exact localization of the pathological focus, the presence of intracranial hematomas, and the extent of the pathological process are detected.
To assess the state of consciousness, the criteria of the Glasgow scale are used. In a hospital setting, a blood test is done to determine the concentration of glucose and electrolytes, blood clotting indicators. In some cases, lumbar puncture is indicated (confirmation of the presence of intracranial bleeding, exclusion of infectious lesions of the central nervous system).
First aid
In case of a head injury, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness and severe neurological deficit, it is necessary to immediately call emergency doctors. First aid for a mild blow to the head that provoked a concussion is to do the following:
- Place the victim in a horizontal position.
- Perform sanitation (cleaning) of the oral cavity (without raising the head and flexing the spinal column in the cervical region).
- Turn your head to the side to avoid vomit entering your respiratory tract.
- If there is an open wound, treat it with antiseptic treatment and apply a bandage to stop the bleeding.
- Until the doctors arrive, do not let the victim sleep, constantly talking to him.
If there are no visible injuries affecting the soft tissues and bone of the skull, a cooling compress (ice wrapped in a towel, cloth soaked in cold water) can be applied to the site of the injury. Exposure to cold reduces pain, prevents the formation of hematomas and the development of perifocal edema.
First aid for a severe head injury, which is accompanied by a disorder of respiratory function and cardiac activity, involves artificial heart massage and ventilation of the lungs (mouth-to-mouth breathing).
Feeling dizzy after hitting your head
This is a small but rather complex organ, which is located approximately in the center of the head, one of the sections of the auditory system - in the inner ear.
The basis of the vestibular apparatus is made up of spherical and elliptical sacs; they contain domes, the tops of which are represented by an accumulation of crystals of calcium salts. From the apex, ciliated cells diverge in a dome-shaped manner, connected to the endings of nerve fibers.
When a person tilts their head or changes their body position, the hair cells to which the nerve endings are attached also change their position. The nerve fibers receive the corresponding signal, which is transmitted to the visual structures, spinal and cervical regions.
And the entire nervous system coordinates the changed position of the head or neck. With rapid changes in the direction of the body, hair cells begin to rush, signals from nerve endings are confused.
As a result, the balance of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted, and the person feels dizzy.
Signs of a concussion in children
Although the symptoms of a concussion disappear quickly, recovery can take a long time for teenagers and children. The pathological condition in patients in this category can worsen even due to fluent reading.
Doctors say that severe TBI can affect a child's brain activity and development. The patient's condition and symptoms of the disease may become more complicated with subsequent skull injuries several years after the concussion. Changes in the neurophysiology of the brain center are observed most often after the third episode.
Consequences of trauma in adults
Early symptoms of a concussion most often disappear within 2-3 days or weeks, but can persist for a long period of time, accompanied by various complications. In 10-20% of cases, signs of TBI may be present for 2-3 months. Patients over 55 years of age take longer to recover than younger victims.
Factors that can complicate the course of the pathology:
- psychological disorders;
- abuse of smoking, alcohol-containing drinks;
- prolonged depression;
- state of stress;
- associated diseases.
In the future, a concussion can cause decreased mental and physical activity, including loss of temporary memory. This condition, if left untreated, can persist for up to 3 years or more after TBI.
Signs of a traumatic brain injury
To provide first aid to a victim of a fall or blow, it is necessary to know the symptoms of a concussion. Immediately after injury, only some of the signs of the pathological condition may be present, depending on the severity of the injury.
The most common symptoms:
- Vomiting, feeling of nausea.
- Migraine attacks after a concussion.
- Hyperactivity or depression.
- Fainting, loss of orientation.
- Convulsions, dilated pupils (of different sizes).
- Confusion of phrases.
- Discomfort from bright light or harsh noise.
Following a blow to the head (which may also involve an unnaturally severe neck movement), such as in a car accident, followed by short-term or long-term impairment of consciousness, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- The head or neck feels dizzy and hurts (often in the back of the head).
- Be sick.
It should be taken into account that the sooner the impact is followed by unconsciousness and nausea, the worse the prognosis for a concussion.
X-rays and CT scans are important to rule out bleeding or skull fractures.
The actual symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of a concussion arise from its very definition. The short-term loss of consciousness that occurs after an impact for 30 minutes is divided into 3 stages:
- From a few seconds to 5 minutes.
- Up to 15 minutes.
- Up to 30 minutes.
If after the blow unconsciousness lasts longer than 30 minutes, we are not talking about a concussion, but about a more severe form of brain contusion or cerebral hematoma.
First symptoms
People almost always get injured when they fall, and it doesn’t matter in what setting it happened: at home, at work, during sports activities.
Often, after a blow, the head hurts, which may already indicate a concussion.
In most cases, the injured person loses consciousness for a while and does not remember under what circumstances he was injured.
In an adult
- headache, and not necessarily only at the site of impact;
- you want to sleep too much or, conversely, feel an unusual surge of energy;
- you feel sick and vomit at least once;
- you feel dizzy, coordination of movements is impaired;
- noise in the ears;
- seeing double;
- the pupils have enlarged and taken on a different shape or diameter;
- convulsions appeared;
- you are irritated by bright lights and loud sounds.
The child has
In children, such injuries are even more common than in adults.
- nausea, vomiting;
- the baby spits up too often when feeding;
- a small child has a swollen fontanel;
- the skin is too pale, especially the face;
- the baby cries and is capricious, eats and sleeps poorly;
- there is a slow pulse;
- increased body sweating;
- The child complains that he has a headache.
it is necessary to determine the severity of the injury in order to prescribe effective therapy. There are different types of traumatic brain injuries: mild concussion, moderate, severe. To determine the nature of the damage, special diagnostics are used:
- X-ray;
- ultrasonography;
- neurosonography;
- echo-encephalography;
- CT scan.
slight concussion
- the head throbs and hurts, dizzy;
- standing hard;
- the skin becomes very pale;
- with a microconcussion there is double vision;
- be sick;
- there is a feeling of weakness;
- the body sweats a lot.
moderate brain contusion
This type of injury is much less common than the previous one. The following are signs of a moderate concussion:
- fainting, the duration of which is at least a quarter of an hour;
- headache and dizziness;
- nausea accompanied by frequent vomiting attacks;
- severe weakness;
- high blood pressure;
- tachycardia or bradycardia.
severe traumatic brain injury
This is a very serious injury that requires long-term hospital treatment. Such skull injuries can lead to very dangerous complications. A severe brain injury, the symptoms of which are listed below, can even provoke a long-term coma. Often it disrupts the functioning of all body systems. Signs of a severe concussion:
- prolonged loss of consciousness;
- Visual acuity is impaired, hearing decreases, speech becomes unclear and incoherent;
- memory loss;
- pupils dilate;
- the pulse quickens, the heart rhythm goes astray;
- blood pressure rises;
- possible states of coma, stupor, stupor;
- probable ear bleeding;
- swallowing function is impaired;
- body temperature rises significantly;
- breathing becomes weak and rare.
signs, symptoms and diagnosis of concussion
If you experience frequent dizziness, you should start by visiting a neurologist, and then contact an otolaryngologist. At the same time, you will be asked to undergo vestibular tests (caloric test, rotational tests), as well as posturography - a study of the interaction of the visual, vestibular and muscular systems in ensuring balance.
To diagnose a possible disease of the hearing aid, pure tone threshold audiometry and acoustic impedance measurements may be needed; to find out the condition of the blood vessels - ultrasound scanning or computed tomography.
Stress prevention
If you notice that stress causes dizziness, tachycardia, and pressure surges, the only way out of this situation is to eliminate the cause of the tense state.
Avoid, if possible, communicating with people who make you worry and drive you to a nervous breakdown. Or, as a last resort, keep such communication to a minimum.
Walk outdoors more often. Walking has a strengthening effect on the heart and blood vessels; fresh air will improve the nervous system. The sun's rays will promote the production of the hormone of joy - serotonin. Learn to enjoy life, try to see the positive even where there seems to be none.
Source: https://golowabolit.ru/skolko-kruzhitsya-golova-posle/
Treatment methods
In case of a mild concussion, the patient is advised to rest in bed. If you hit the back of your head or any other part of your head, the first thing to do is call an ambulance. The doctor will assess the severity of the condition and, if necessary, carry out rehabilitation measures, which include:
- Tracheal intubation.
- Air duct insertion.
- Connection to a ventilator.
- Administration of plasma replacement solutions (Polyglukin, Rotsdex, Reogluman).
- Dehydration therapy (Lasix, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone).
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed, during which intracerebral and meningeal hematomas are removed and impaired blood flow is restored.
What to do after hitting your head
Statistics show that in everyday life and in sports, a head blow is one of the most common types of injuries.
You can get it in different ways: during a fight, slipping on ice or accidentally hitting the corner of furniture. The injury that occurs after hitting the head can be very dangerous.
Damage to the temple area often causes fainting, and damage to the parietal part usually leads to a concussion and disruption of the integrity of the skull bones.
Types of damage
Neurologists and other specialists identify several types of traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) diagnosed after blows to the head.
Concussion (CHM)
To obtain SGM, it is enough to accidentally hit a hard object. As a result of the collision, a double displacement of the brain occurs: first it moves in the direction of the impact trajectory, and then returns to its original location. Thus, the negative impact caused by the collision is doubled.
SHM accounts for 70% of all reported head injuries. It is equally common in children and adults. The consequences of a head blow during a concussion manifest themselves in the form of:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- short-term (up to a quarter of an hour) fainting;
- inability to remember events that preceded the injury;
- feelings of weakness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- noise and ringing in the ears;
- breathing problems;
- attacks of vomiting;
- pain in the eye area;
- visual impairment.
These signs can be observed even after a blow to the jaw (and not just to the head). At the same time, it becomes difficult for the victim to chew.
Blood pressure returns to normal quickly after a concussion, and body temperature changes slightly. However, feelings of nausea, dizziness and sleep disturbances (including insomnia) persist for a long time.
If BMS is suspected, the person must be taken to the hospital for examination. If there are no complications, the patient can continue treatment at home, using not only the doctor’s recommendations, but also some folk recipes. A head massage and a linen cloth patch help especially well in this case.
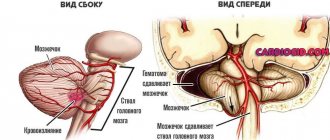
Brain compression
The danger of this condition is associated with possible damage to the stem formations in the cerebellum area, which regulate the blood circulation process and allow a person to breathe.
As soon as possible after the injury occurs, the victim is examined for the presence of hematomas. If detected, they are urgently removed, since hemorrhages can increase compression of the brain and worsen the patient’s condition.
Brain contusion
With this diagnosis, the result of blows to the head is damage to the cranial vault and brain tissue, which is often accompanied by the development of necrotic (dead) areas. A brain contusion can even be caused by a strong punch (therefore, this type of TBI is a common occurrence in boxing). Associated symptoms of injury include:
- neurological disorders;
- loss of consciousness;
- pain in the back of the head (the head will throb painfully for several weeks).
Victims sometimes feel dizzy and experience a feeling of pressure in the temporal areas. The injury may be complicated by a fracture of the skull. Sometimes it looks like a dent on the surface of the head, but if fragments of the cranial bones damage the cortical tissue and enter the medulla, this will lead to disruption of the vital functions of the body.
Minor bruises usually occur in childhood (about 1/5 of all cases of TBI) due to the increased activity of children, who often fall and hit their heads.
More severe injuries occur at older ages and are usually accompanied by impaired visual acuity, dilated pupils and increased body temperature.
Due to the most severe injuries of this type, all body functions deteriorate.
To normalize the condition after a brain contusion, the patient is prescribed drugs that have antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. Products that strengthen the vascular system and promote its restoration are also used.
Axonal damage
This type of injury leads to severe disturbances of consciousness (concussions), which soon cause stoppage of brain activity and falling into a coma. The main treatment for axonal damage is life support. It is impossible to determine the recovery time, since it will depend on the individual characteristics of the body.
By severity
In accordance with another classification, 3 types of TBI are distinguished depending on their severity.
| Severity | Number of points on the Glasgow scale |
| Light | 14-16 |
| Average | 9-13 |
| Heavy | 8 |
However, no matter how severe the blow to the head was, its consequences can be minimized if the necessary assistance is provided to the victim in a timely manner.
Features of the development of TBI in children
In infants and one-year-old children, after hitting their head, the body temperature can rise to 38 ° C or higher. In the presence of open wounds, this is a consequence of infection, and in other cases - the result of stress, the development of inflammation or the use of inappropriate medications.
Blows to the head received by children are especially dangerous because the child cannot clearly describe his sensations. This makes diagnosis and subsequent treatment difficult. However, it is precisely at the moment of receiving the grass that you can notice that the baby:
- turned pale;
- became drowsy and lethargic;
- has a rapid heartbeat and uneven pulse.
Subsequently, the baby experiences frequent vomiting. He constantly spits up when feeding and becomes restless. Problems with sleep appear. With a concussion, these symptoms completely disappear after 3-4 days.
In newborns and infants, as well as in older people, a concussion develops with preservation of consciousness. This is due to their physiological characteristics.
First aid
If a person falls and hits his head, then signs of a TBI will begin to appear almost immediately; you just need to pay attention to it. He will begin to feel nauseous or may faint. You need to help in such a situation quickly and confidently. To do this you need to do the following:
- Call an ambulance;
- Apply ice or a cold compress to the victim’s forehead (this will constrict the blood vessels, reducing the likelihood of bleeding, bumps and bruises, and will also reduce swelling);
- Carry out a careful examination of the patient: if he has pain in the neck, then perhaps we are talking about an injury to one or more vertebrae (in this case, you should try not to change the person’s position unless absolutely necessary);
- If the victim has lost consciousness, give him a sniff of ammonia (you should not hit the cheeks in this situation, as this may aggravate the patient’s condition);
- Treat all damaged areas of the skin (with wounds and abrasions) with hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin solution;
- In case of gushing bleeding in the temple area, you need to press the vessel tightly with your fingers, then apply a furatsilin bandage, secure it with a plaster and wrap it with a bandage (if the necessary remedy is not at hand, it can be replaced with miramistin ointment);
- If the victim begins to feel sick or vomit, then you need to lay him on his side and try to make the vomit come out as freely as possible (use homemade gauze swabs or a piece of any clean cloth to wipe the patient’s mouth).
Now all that remains is to wait for the ambulance to arrive. However, this sequence of actions is not always necessary. If a person simply has a headache after a blow, then there is no need to call a team of doctors. But it is worth taking the victim to the hospital, since not a single TBI goes away without leaving a trace, which means he needs the help of specialists.