Chronic osteochondrosis is characterized by the fact that in its development, acute stages constantly alternate with stages of remission. The period of exacerbation is characterized by pronounced pain manifestations, often of such intensity that people cannot not only move, perform usual actions, but also simply stand or sit. As a result, the main goal of treatment during attacks becomes the need to quickly and effectively relieve pain and stop the suffering of the sick person. It is equally important to relieve spasms in the back muscles and release nerve endings pinched by damaged vertebrae. The use of medications in the form of tablets or topical agents does not always achieve the desired result, because they begin to act some time after administration. Therefore, pain-relieving injections for osteochondrosis are often prescribed to patients. They allow the active substance of the medicine to very quickly get to the right place and begin to act, thereby relieving pain. Also, for osteochondrosis, medications are prescribed in the form of injection solutions, which help restore damaged cartilage and eliminate muscle spasms.
When are injections prescribed?
Injections for the treatment of osteochondrosis are used during an attack of pain during the first days of the acute period. The doctor may recommend injections if signs of osteochondrosis of the lumbar, cervical or thoracic spine appear. The patient should understand that this treatment method aims to relieve the severe symptoms of the disease, but does not affect or eliminate the cause of its occurrence. Therefore, after several procedures, the doctor usually prescribes medications to the patient in the form of tablets and external use to continue treatment.
Types of procedures
In the process of treating osteochondrosis, the following types of manipulations are practiced:
- Intramuscular injections.
- Intravenous injections.
- Subcutaneous injections.
- Drug blockades.
Intramuscular injections
Through intramuscular injections, medications are injected into any of the large muscles of the body: buttock, thigh, shoulder. This type of procedure is in demand for administering a substance in small quantities. In addition to the muscle fibers themselves, muscles also contain elements of the circulatory and lymphatic systems of the human body. Therefore, the active substance administered intramuscularly enters the bloodstream in a short time, beginning to act. The duration of exposure is ensured by the gradual entry of the drug into the blood. For the best result of the manipulation, the patient should relax tense muscles.
Rehabilitation doctor Sergei Nikolaevich Agapkin will teach you how to give injections to yourself:
Intravenous injections
Intravenous injections, which are given for osteochondrosis, are characterized by the fact that the drug is injected into the blood vessel itself - the vein, i.e. it immediately enters the bloodstream and is quickly delivered to the affected area. When carrying out this manipulation, special attention is required to comply with hygienic measures for treating the hands of medical staff, as well as the place where the medicine is administered. Typically, injections for osteochondrosis are placed in a vein located in the cubital fossa, i.e. the middle vein, formed at the junction of the ulnar saphenous and radial vessels.
Subcutaneous injections
Directly under the skin of a person there is a layer of fat, which is penetrated by a large number of small blood vessels. When the drug enters them, it almost immediately enters the bloodstream and begins to act. Subcutaneous manipulation in the treatment of osteochondrosis can be performed in the following areas.
- Upper shoulder region.
- Axillary part.
- Subscapular region.
- Side of the abdomen.
- The anterior surface of the femoral region of the leg.
The preparatory stage for a subcutaneous injection does not differ from the preparation when other injections are given for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, as well as the thoracic and cervical spine. However, the injection itself should be fundamentally different. In any of the places indicated above, a small amount of skin is grabbed in the form of a fold and the drug is injected. At the same time, the nurse is faced with the task of minimizing the possibility of damaging blood vessels and nerve roots. Manipulations cannot be carried out in a place where there is swelling of the subcutaneous fatty tissue or a compacted area of tissue that is formed due to incompletely absorbed medication from a previously performed procedure.
Drug blockades
With the help of medicinal blockades used to treat osteochondrosis, excessive muscle strain is relieved, spasms of blood vessels are eliminated, swelling is reduced, inflammatory processes are stopped, and pain is relieved. Two types of blockades are practiced:
- Paravertebral blockade means that with the help of several injections, active substances are introduced into the area where the nerve roots of the spinal column exit. As a result of the manipulations, the receipt of nerve signals that arrive due to compression of the roots is prevented. In this way, a sick person is relieved of pain.
- An epidural block is characterized by the fact that an injection is placed in the epidural space, which surrounds the spinal cord. Whether the procedure will be effective depends on what kind of substance is administered.
Neurologist Konstantin Sergeevich Susorov shows how paravertebral blockade is done:
Blocking injections are given using combinations with NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone), antispasmodics, or one anesthetic drug (Novocaine, Lidocaine).
In the following cases, treatment with blockades cannot be carried out:
- The presence of pustules on the human body.
- The patient has a significant change in the anatomical structure of the spine, which makes the blockade impossible from a technical point of view.
- The patient has an individual intolerance to anesthetic drugs.
Spine pathologies
What is intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia (another name is thoracalgia) is pinching, irritation or compression of the spinal nerve. Due to the nature of the pain (on the left, in the heart area or under the heart), during the first attacks, many patients confuse the disease with cardiovascular pathologies, for example, a heart attack.
Pain with intercostal neuralgia can occur in different parts of the patient’s body near the spine: throughout the chest, on the right or left side of the back, under the shoulder blades. Often the painful sensations are girdling in nature. As a rule, intercostal neuralgia develops due to the course of other diseases of the spine: osteochondrosis, scoliosis, tumors and abnormal position of the vertebrae. In addition, the disease can be caused by the following factors:
- Long-term exposure to low temperatures.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Injuries to the ribs, chest, spine.
- Tumors localized in the spinal cord.
- Poisoning of the body.
- Nerve damage.
- Spondylitis, kyphosis, other diseases of the spine.
- Diabetes.
- Age-related changes.
- Severe strain in the back muscles.
- Fatigue, stress.
- Herpes.
- Pleurisy.
- Pathological changes in the chest.
- Rib diseases.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Hormonal changes.
- Rapid growth (in children).
- Climacteric, post-menopausal period (in women).
- Bad breath is caused by parasites! Find out how to get rid of {amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
- Nail fungus will no longer bother you! Elena Malysheva tells how to defeat fungus.
— Losing weight quickly is now available to every girl, Polina Gagarina talks about this {amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4xYIS1mU_vY
— Elena Malysheva: Tells you how to lose weight without doing anything! Find out how {amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
- Ultrasound. Not the main method of examination for intercostal neuralgia (due to high bone density).
- X-ray. Helps to see abnormalities in the structure of a person’s bones.
- CT scan. The tomogram will show bone and soft tissue.
- Myelography. During the examination, a contrast agent is injected into the spinal canal, with which you can see changes in soft tissues due to the disease.
- Contrasting discography. A contrast agent is injected into the area of the intervertebral disc.
- MRI. Allows you to fully examine the structure of damaged tissue or bone structures.
- Electrospondylography. Helps to identify pathology at the initial stage of occurrence.
What is used to treat osteochondrosis?
Several groups of medications help to cope with back and neck pain due to osteochondrosis.
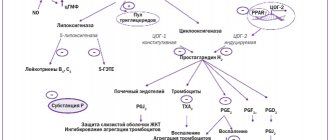
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NSAIDs contain active substances that reduce fever, pain, and inflammation. With their help, the sensitivity of the nerve roots is reduced, thereby blocking pain impulses. In addition, the pain decreases as a result of the removal of inflammation: the swelling that has formed in the inflamed area decreases.
When injections are prescribed for osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine, the following non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often chosen:
- "Diclofenac" - the drug is considered more effective in the process of suppressing inflammation than in the process of reducing pain and lowering the body's temperature response. It has a negative effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, which is why it must be used in combination with drugs that reduce acidity in the stomach. The effect of a Diclofenac injection is observed for about 10-12 hours. The price of the medicine is about 40 rubles.
- "Ketorol" is a drug that has a pronounced analgesic effect. In the process of suppressing inflammation and reducing fever, it is less effective. It has an undesirable effect on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and can cause bleeding. The result of the injection lasts approximately 5-6 hours. Cost from 190 rubles.
- Movalis is a medicine that is more effective in suppressing inflammatory reactions than in relieving pain and reducing fever. It does not have a negative effect on the rate of blood clotting, as well as on the occurrence of disorders of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum. The effect of movalis lasts for one day. The drug costs from 110 rubles.
Pharmacist Maria Luneva talks about the drug Ketorol:
Almost all drugs in the NSAID group have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract and liver. They often cause internal bleeding and provoke the progression of existing pathological changes. Parenteral intake of these drugs into the body to some extent reduces the likelihood of negative reactions.
Painkillers
To alleviate a person’s condition and reduce the pain reaction, injections are prescribed that relieve pain for osteochondrosis of the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spine.
- "Analgin" - effectively relieves pain, is not used against inflammation. It is administered intramuscularly or intravenously after 8-12 hours.
- "Voltaren" - helps cope with fever and inflammation.
- Tramadol is a medicine that belongs to the group of analgesics. By acting on brain receptors, it effectively suppresses pain. The effect of the drug occurs approximately 20-30 minutes after manipulation and lasts for 5-6 hours. Long-term use of the medicine is not recommended due to rapid addiction to it.
- Analgesics are combined with antispasmodics to achieve better results. Manipulation relaxes the back muscles, reducing pain. Medicines in this group cost from 120 rubles (Tizalud, Tizanidine) to 400 rubles (Mydocalm). Injections are repeated 2 times a day.
Chondroprotective agents
Chondroprotectors stop destructive processes in cartilage and stimulate their regeneration. They also relieve pain and inflammation. The following chondroprotective drugs are prescribed as injections for lumbar, thoracic, and cervical osteochondrosis:
- "Alflutop" - relieves pain well and also helps reduce inflammation. Stimulates metabolic processes in tissues, regulates their nutrition.
- “Mukosat” is a drug that prevents the destruction of cartilage tissue, has a pronounced analgesic effect, and reduces the inflammatory response. The effect after the injection lasts up to 48 hours.
- Chondrogard, Rumalon, Donu and other similar medications are also prescribed to restore damaged cartilage tissue.
Instructions for use of the drug "Dona":
When prescribing chondroprotectors, injections are given intramuscularly every day or 2-4 times a week. In any case, treatment with chondroprotectors is long-lasting; noticeable results, according to patient reviews, occur approximately six months from the start of treatment.
Vitamin complexes
"Milgamma" is a complex medicine that contains B vitamins and an anesthetic element (lidocaine). Costs about 200 rubles. It has a positive effect on the body in case of osteochondrosis: improves blood flow, blocks pain, relieves inflammation. The result develops quickly, but does not last long. Milgamma injections help restore pinched nerve endings of the spinal cord and eliminate discomfort in the affected area. The medicine is administered intramuscularly (using 1 ampoule per day) for 7 to 10 days.
Similarly, Combilipen injections are given as a combination remedy.
In the form of injections for osteochondrosis, the doctor often recommends injecting vitamins. They promote regeneration, stop the inflammatory reaction, and increase blood supply to tissues. Vitamin complexes are used in the remission stage.
- Vitamins A and E are available as oil-based solutions. These vitamins are given exclusively intramuscularly. The usual course of treatment lasts several weeks.
- Vitamin D (ergocalciferol) is necessary to restore the balance of calcium and phosphorus. It is given intravenously and subcutaneously.
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is produced as a solution in water. Ascorbic acid is given both intramuscularly and intravenously. The required number of procedures for treatment will be determined by the doctor.
- Nicotinic acid (vitamin PP) has a beneficial effect on blood vessels. Injections for cervical osteochondrosis restore tissue nutrition, improving blood flow. Nicotinic acid is administered intramuscularly for two weeks.
Neuralgia of the back: causes in adults, symptoms, treatment
Intercostal neuralgia causes a lot of inconvenience, pain and the inability to lead a full life for a large number of people.
To get rid of its symptoms, the doctor develops a treatment program, and injections for intercostal neuralgia become the main point in complex therapy. The cause of the disease is compression of the nerve roots that pass between the ribs, or their severe irritation. Intercostal neuralgia manifests itself as severe pain, which becomes more intense with a deep sigh, coughing, sudden movements - bending and turning the body.
The disease is a number of serious ones that have a lot of unpleasant consequences, so timely diagnosis and treatment should be carried out by an experienced doctor. This is explained by the fact that in terms of external signs and manifestations, intercostal neuralgia is similar to diseases such as renal colic or pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
In order for the patient to quickly get rid of the symptoms of the disease and return to a normal, full-fledged lifestyle, the doctor will select the most appropriate drug treatment based on the general picture of the disease, the results of an X-ray examination, laboratory tests and the overall picture of the disease.
There is no need to say once again that self-medication is unacceptable, because under the mask of intercostal neuralgia the symptoms of other, more dangerous diseases can be hidden, and self-administered medications can give various side effects (if the dosage is incorrectly calculated or if there is a tendency to exhibit allergic reactions to the components of the drugs ).
In the first days of the disease, the patient, in addition to urgently consulting a doctor, can be advised to rest completely, refrain from work, and sleep on a hard and level surface, with the exception of high pillows.
First of all, a patient suffering from manifestations of intercostal neuralgia needs to be relieved of the excruciating pain syndrome that interferes with sleeping peacefully, eating, breathing deeply and simply moving normally. For this purpose, a number of different groups of medications are used.
Neuralgia of the back is always accompanied by severe pain resulting from compression of the nerve endings by inflamed or damaged tissues located around them. This is not a specific diagnosis, but a set of symptoms caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from ordinary hypothermia to malignant tumors of the spine.
The first and most noticeable sign of back neuralgia is severe acute pain, which can occur after excessive physical exertion, prolonged work or rest in an uncomfortable position, and even after any sudden movement. As a result of overstrain and muscle spasm, the nerve endings are irritated, provoking attacks of pain.
In people suffering from neuralgia of the back, the pain, as a rule, intensifies when inhaling, as well as during coughing and sneezing, and many patients compare their sensations at this moment with an electric shock. By carefully palpating your back, you can quite accurately determine where exactly the pain is localized, but often it radiates to other areas.
For example, when the cervical spine is affected, the pain spreads to the head and even the eyes, which is why neuralgia can be confused with a migraine attack or otitis media. Patients cannot turn their heads without experiencing severe pain, and often complain of numbness in their fingers.
Thoracic neuralgia is characterized by more pronounced symptoms - it is characterized by pain in the back, arms and abdominal area, which is accompanied by a decrease in pressure, increased sweating, heart rhythm disturbances and pallor of the skin. This condition feels similar to a heart attack or pneumonia.
If the problem is hidden in the lumbar spine, the patient may suffer from severe muscle spasms, trembling limbs, weakness in the legs, swelling and increased sweating, which makes it difficult for the person not only to bend and turn, but even just to stand.
The causes of neuralgia are varied, ranging from diseases of the musculoskeletal system, most often osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernias, and ending with allergic reactions, injuries, heart disease and even long-term stress. But no matter what causes this pathological condition, we must not forget that in adults the back is one of the most vulnerable places, which means that any discomfort in this area is a reason to consult a doctor and, if necessary, further complex treatment.
The treatment of spinal neuralgia is primarily based on taking medications. Medicines successfully cope with pain that prevents patients from leading their usual lifestyle, relieve inflammation in tissues and restore normal blood circulation. For this purpose the following are appointed:
- Painkillers. Their task is to alleviate the patient’s condition by inhibiting certain areas of the brain responsible for receiving and processing signals about the occurrence of pain. As a rule, for this purpose, ordinary analgesics that are freely available in pharmacies (Baralgin, Paracetamol, Acetaminophen) are sufficient, but if the attacks become too intense, more effective means may be needed - narcotic-based drugs that are available only by prescription (Tramadol, Codeine, Fentatine). In addition, patients with neuralgia may be prescribed blockades, which involve the injection of medication into deep tissues directly at the site of the lesion. Most often these are injections of novocaine or lidocaine, but in some cases hormonal substances that reduce inflammation - prednisole or hydrocortisone - are also injected in parallel.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. This is the main component of drug treatment for neuralgia of the back. NSAIDs help to cope with the inflammatory process, pain and swelling, restoring normal blood flow to the damaged tissue area. Most often, patients are prescribed Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Movalis, etc.
- Anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants. Eliminate the main cause of pain in back neuralgia - muscle cramps and spasms. The most effective drugs of this kind are considered to be “Gabapentin”, “Finlepsin”, “Mydocalm” and “Sirdalud”.
- B vitamins. Strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight inflammation due to neuralgia, and partially relieve discomfort and back pain. For this purpose, patients are prescribed Neurorubin, Neurovitan or Kokarnit.
- Antidepressants. The need for them arises due to prolonged acute pain, which affects not only the physical well-being, but also the emotional state of a person, consumes his strength and further undermines his health. In this case, patients are prescribed Amitriptyline or Duloxetine.
In addition to tablets and injection solutions, treatment of back neuralgia involves the use of topical drugs with a similar analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. These can be various ointments, gels or patches that act locally on the lesion, for example, “Finalgon”, “Fastum Gel”, “Voltaren Gel”, pepper patch, etc.
As soon as the attacks of acute pain subside, physiotherapy comes to the fore in the treatment of neuralgia of the back. These procedures have virtually no contraindications and effectively cope with the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, bringing long-awaited relief to patients. And for those for whom drug therapy is not recommended at all (elderly people, children and pregnant women), physiotherapy is truly irreplaceable.
Patients with neuralgia of the back are prescribed:
- UHF therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- ultrasound treatment;
- Magnetic and laser therapy;
- fluctuarization;
- paraffin applications;
- mud baths;
- acupuncture.
The duration of therapy depends on the degree of neglect of the problem and the individual characteristics of the patient, but in the vast majority of cases, the course of treatment includes no less than 5 and no more than 12 procedures. As a result, blood circulation and lymph flow improve, muscle tension is relieved and pain is significantly reduced.
Massage also plays an important role in the treatment of back neuralgia. Its main purpose is to relieve muscle spasms, so the procedure is carried out in a gentle manner, especially if the pain still partially persists. To increase the effectiveness of the massage, it is recommended to do it after a bath and in combination with warming creams.
It is impossible to cope with back neuralgia without regular exercise. Exercise therapy helps reduce the intensity of pain, relieve muscle spasms, eliminate congestion in the back and, of course, increase the tone of the body as a whole. But to achieve the desired result, the issue of physical activity must be approached with caution - a set of exercises must be developed by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s condition, his capabilities and the presence of other diseases.
Physical therapy should not be performed during an exacerbation of the disease. In this case, first of all, you should relieve pain and reduce inflammation with the help of medications, and only then proceed to reasonable physical activity. The first classes are best done in a gentle manner, gradually increasing the number and complexity of exercises.
Folk remedies
Various traditional medicine recipes are also an integral part of the treatment of back neuralgia. They serve as a good addition to drug therapy, allowing you to improve blood circulation, relieve muscle tension, swelling and inflammation in the pathological area. Folk remedies with a sedative effect, which alleviate both the physical and emotional state of the patient, are also indispensable for neuralgic pain.
- speed of the effect. After all, the tablet is finally absorbed in the intestines, where it should go. In addition, everything that is absorbed necessarily passes through the portal vein, and for the most part, is metabolized and transformed in the microsomal system of the liver. Medicine delivered intramuscularly or intravenously acts faster;
- the ability to deliver medicine directly to the right place. It is this possibility that underlies blockades. In neurology, a blockade is an injection of one or more drugs administered intramuscularly for therapeutic purposes to the site of maximum pain in order to induce conduction anesthesia or break the “vicious circle” of myofascial syndrome.
Contraindications
Each group of drugs has contraindications for use. In any case, injections for osteochondrosis are not given if a person has an individual intolerance to the drug, hemophilia, or purulent inflammation in the injection area. Injections are often prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Injections in the treatment of osteochondrosis of any part of the spine effectively relieve pain and help relieve inflammation and spasms. However, they should not be used without a doctor’s permission, so as not to aggravate the situation.
When severe pain appears in the back, lower back, joints, of course, first of all it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. If it is a lumbago from hypothermia, lumbago, or pinched sciatic nerve, intervertebral hernia, etc., you should definitely undergo examination by a neurologist, osteopath, and possibly a gynecologist, urologist, gastroenterologist, since back pain can be not only from spasm of muscles and ligaments , but also for some diseases of internal organs. After a thorough diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe NSAIDs and B vitamins in injections for back pain as part of complex therapy.
What injection medications exist to relieve back pain?
Today, in the treatment of acute pain in the lumbar region and back, medicine finds new principles and algorithms than 50 years ago. The main emphasis in the fight against pain is on eliminating pain with the help of NSAIDs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that suppress inflammation and reduce pain, as well as muscle blockades.
And after the removal of severe spasms, it is recommended to refuse to immobilize the patient, that is, to conduct physical therapy exercises and perform massage. Most doctors insist that a person during back pain syndromes should not limit his activity as much as possible.
It has also become popular and effective to prescribe combined vitamin complexes that can have a moderate analgesic effect, these are vitamins B12, B6, and B1. It is believed that vitamin B12 has a more significant analgesic property. Why these particular vitamins?
Recently, these drugs have begun to be considered in medicine as moderate analgesics, since they are neurotropic - they normalize the innervation of muscles, participate in the transmission of excitation, in the metabolism of mediators, influence metabolism, processes in the nervous system, and promote the restoration of damaged nerves.
Over 90 different studies have proven that the use of B vitamins in clinical practice led to a significant reduction in pain in the acute phases of inflammation in complex treatment. Therefore, they can be used either individually or in the form of complex preparations of B vitamins.
Most complex drugs in this group contain the anesthetic lidocaine, which enhances the local analgesic effect. However, it should be remembered that the use of this group of vitamins makes sense only for acute pain in the back, joints, alcoholic polyneuropathy, myasthenia gravis B12 for 10-14 days, and for chronic recurrent diseases they become ineffective.
In cases where painkillers do not help, specialists can offer the patient a method of injections and stretching. It is as follows: after the patient lies on his stomach, the most painful seals or points where the pain is most intense are found in the muscles, and an injection with a novocaine solution is made exactly perpendicularly.
Immediately after the injection, passive stretching of the muscle is performed, after which a hot compress is placed on this place. Then, when the compress is removed, the patient should make active movements, exposing the painful muscle to maximum movement.
The purpose of the novocaine blockade is to “turn off” the nerve. Therefore, the injection points should be as close as possible to the exit points of the nerves, for example, sciatic - at the greater trochanter of the femur, for intercostal neuralgia - in the corresponding intercostal space, for osteochondrosis - at the outer edge of the extensor of the back, etc. It is also advisable to carry out epidural blockades for chronic pain syndrome, for example, for herniated intervertebral discs.
Below is a list of medications prescribed by your doctor according to indications. Only a doctor determines the advisability of using B vitamins, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and chondoprotectors. The information below is for informational purposes only; the course of treatment and dosage is determined by a specialist.
List of injections used for neuralgia
Neuralgia develops quite quickly and causes many complications. Since the course of the disease is very painful, therapy is often carried out by injections of neuralgia, which can quickly eliminate painful sensations.
The main advantages of injections
Neuralgic injections have many advantages over other types of drugs. In particular, there are the following advantages
- high speed of action;
- the ability to deliver medicine to the right place;
- the ability to quickly relieve pain.
During the injection, the drug penetrates directly into the bloodstream and acts much faster, so that even the most severe pain can be eliminated in just a few minutes.
Anesthesia block is based on the ability to place drugs in the right place. Blocking is an injection of one or more drugs that is administered locally intramuscularly to the area of maximum pain for therapeutic purposes.
Injectable drugs used
When neuralgia occurs, it is usually accompanied by very severe pain, so it is important to know what injections can be used to eliminate pain and normalize health. Among the most popular drugs, the following should be noted:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- multivitamins;
- muscle relaxants.
Anti-inflammatory drugs have a fairly pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. When given as injections, they relieve attacks of pain very quickly and for a long time.
Important! To achieve maximum results in therapy, it is advisable to combine all groups of drugs in combination with local products such as creams, gels and ointments.
When treating neuralgia in the first days, injections are mainly used, and after the intensity of the pain syndrome decreases, a gradual transition to drug treatment in tablet form occurs.
Anesthetics
Injections for neuralgia are considered the most effective method of eliminating acute pain. In this case, the active substance penetrates directly into the area of nerve endings, so the treatment result is almost instantaneous. Within a few minutes, the intense pain syndrome is eliminated and does not recur for several hours.
The main disadvantage of injection therapy is the short duration of action and the lack of a pronounced therapeutic effect. With injections of analgesics, you can only eliminate an acute pain attack, but you cannot cure the disease or influence the cause of its occurrence. The best analgesics used in therapy are, for example:
- Ketonal;
- Analgesics;
- Keteral;
Denebol;
- Dexalgin;
- Movalis;
- Milgamma.
These drugs are used in short intervals of 5-10 injections. It is not recommended to increase the number of injections, as these are quite strong drugs that can cause various types of side effects.
Painkillers should be combined with vitamin B injections, which are also administered intramuscularly. This enhances the effect of analgesics and eliminates all existing signs of pathology.
Blockades
Anesthetics may be used for acute and persistent pain caused by neuralgia. For this purpose, drugs such as lidocaine, novocaine, and xylocaine are mainly used. The affected nerve endings are filled with analgesics, which leads to very rapid pain relief. Flocesterone or hydrocortisone, which are considered analogues of glucosteroid hormones, are often prescribed for blocking purposes. These medications have an additional anti-inflammatory effect. However, such drugs have certain contraindications, so they should be prescribed only under the supervision of a doctor.
When your back or joints hurt, injections of B vitamins should help
B vitamins can also be taken in tablet form, but naturally, intramuscular administration of drugs is considered more effective. Let's consider what drugs of this group exist on the modern pharmaceutical market, their general indications, contraindications, side effects, methods of use and comparative prices in pharmacies:
MilgammaMilgamma 5 amp. price in pharmacies 220 rubles, 10 amp. 400 rub. 25 amp. 900 rub. The composition of all these drugs is the same: Lidocaine, Thiamine, Pyridoxine Cyanocobalamin. Indications: Used for neurological diseases and nervous system disorder syndromes in complex therapy:
|
Combilipen5 amp. 100 -120 RUR, 10 amp. 170-210 rub. Contraindications: Treatment cannot be carried out if:
|
Neurobion3 amp. 220 RUR - Neurobion does not contain Lidocaine in its composition Side effects: Tachycardia, increased sweating, rarely - allergic reactions - rash, itching, urticaria, skin reactions, difficulty breathing, anaphylactic shock. In case of overdose - nausea, vomiting, dizziness, tachycardia. |
Trigamma5 amp. about 100 rub. Application: All of the listed injections for back pain are administered deeply intramuscularly, 2 ml 1 time per day for 5-10 days, then you should switch to 2-3 times per week for 14-21 days. or taking vitamins orally. |
Sedatives
These drugs are available in tablets, injection solutions, ointments and gels. They are taken in tablets. To quickly relieve pain, injections are given and IVs are placed.
The course of treatment with anesthetics is short, it does not exceed 4-5 days. They disrupt the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Painful sensations worsen the well-being of patients, plunge them into a state of prolonged stress, create a feeling of discomfort, and reduce the quality of life. Taking sedatives for intercostal neuralgia helps relieve nervous tension, relax skeletal muscles, and normalize the condition of the sick person.
Herbs with a sedative effect are used separately or preparations are made from them. It is worth drinking infusions and decoctions from them. Pharmaceutical preparations have an effective effect: syrups, tinctures.
They drink a sedative at night. It promotes good sleep, proper rest, and relieves nervous and muscle tension. Essential oils: lavender and peppermint have an excellent relaxing effect.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7RBBsvL3PBU
The composition of the drug includes the following elements:
- the active element contained in one tablet in the amount of fifty or one hundred and fifty milligrams is tolperisone hydrochloride;
- Excipients include: citric acid monohydrate, oxygen silicon dioxide, stearin acid, talc, microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, lactose monohydrate.
- Also, in addition to the tablet itself, it is placed in a shell for better passage through the digestive system, which includes: oxygen silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, lactose monohydrate, macrolog, hypromellose.
Efficacy, contraindications and side effects of NSAIDs
Painkillers, of course, are used only as symptomatic therapy; they help eliminate pain in the joints and back, but do not eliminate the cause of its occurrence; in addition, 50% of patients may experience various side effects.
In more than 50 studies aimed at identifying the best pain reliever, researchers found that not a single NSAID drug was more effective than other pain relievers, and some of them are very expensive drugs. The only thing to pay attention to when choosing is that some generics (Russian diclofenac, for example) are significantly inferior in effectiveness to original drugs (European Diclofenac).
Also, these studies were aimed at identifying a drug with the least side effects. As a result, it was found that Ibuprofen is the least toxic of all NSAIDs.
The manufacturers of the new Cox-2 inhibitor, Celebrex, claimed that it had the least side effects, but studies did not find convincing evidence of this fact.
Therefore, when choosing a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, you should remember that they have almost the same anesthetic properties, the same side effects, but different frequency, intensity, severity of side effects, harmful effects, and, not least important, different prices. For example, Meloxicam has less effect on the stomach and intestines than aceclofenac (Aertal). Indomethacin gives a pronounced analgesic effect, but destroys cartilage with prolonged use and is now used less and less.
Moreover, doubling the dose does not reduce the intensity of pain, and in the case when one non-steroidal drug does not help (if it is not a fake), replacing it with another does not make sense. Moreover, based on research, we can also conclude that they are not much more effective than regular paracetamol. You can learn more about all ointments for back pain from our article.
Choice of pain medications
For chronic pain, before prescribing an anesthetic, the doctor determines the causes and nature of chronic pain - referred, neuropathic or central, and prescribes appropriate treatment.
If the pain is acute, then the doctor determines the risk of side effects on the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular complications, if the risks are not great, and:
- no dyspepsia - then any NSAID
- If you have dyspepsia, it is better to use ibuprofen (or diclofenac, naproxen), nimesulide (or miloxicam)
If the risk of cardiovascular complications is high, then NSAIDs should be avoided and Paracetamol and opioids should be used. With a moderate risk, it is possible to prescribe nimesulide, subject to adequate correction of blood pressure (amlodipine, see drugs for lowering blood pressure).
If the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding is high, NSAIDs + definitely proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole). It is understood that taking NSAIDs in itself is a sufficient risk even with a single dose, so the standard is that all NSAIDs are taken in combination with proton pump blockers, regardless of the risks of gastroduodenal bleeding.
When the risks of gastrointestinal side effects and cardiovascular complications are combined - Nimesulide + acetylsalicylic acid + omeprazole.
If the pain subsides within 5-7 days, then continue treatment until it is completely relieved. If acute pain does not subside within a week, then muscle relaxants and local anesthetics are prescribed. Local administration of corticosteroids is possible if the diagnosis of tuberculosis of the joints or spine is excluded. If the pain is very severe and there is no effect from painkillers, the infectious nature of the pain should be excluded (tuberculosis pathology - consultation and examination at an anti-tuberculosis dispensary), joint pain due to gonorrhea, syphilis or other infection.
Review of painkillers in injections
All known NSAIDs for injection, with their general contraindications and side effects, and average prices in pharmacies are presented in the table:
MeloxicamMovalis (3 amps. 530 RUR) Amelotex (3 amps. 280 RUR) Arthrozan (3 amps. 190 RUR) Indications for the use of NSAIDs: Symptomatic treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, elimination of pain - musculoskeletal, back pain of any etiology, postoperative and other pain. |
KetoprofenArtrosilene (6 amps, 170 rubles) Ketonal (10 amps, 200 rubles) Flamax (5 amps, 110 rubles). Flexen (6 amp. 280 rub.) Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any component of the drug, heart failure, pregnancy and lactation, severe liver or kidney failure, aspirin-induced bronchial asthma, children under 16-18 years of age, inflammatory bowel diseases, exacerbations of gastric ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding. Cerebrovascular diseases, coronary heart disease, any severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, concomitant use of antiplatelet agents (clopidogrel, acetylsalicylic acid) prednisolone, liver dysfunction, severe somatic diseases. With caution: gastrointestinal diseases, Helicobacter pylori infection, edema, fluid retention, diabetes mellitus, long-term use of NSAIDs. |
KetorolacKetorol (10 amp. 130-150 rub.), Ketanov (10 amp. 100 rub.) Ketorolac (10 amp. 70-90 rub.) Application: The solution for injections for back pain should be administered deeply intramuscularly in a dosage selected by the doctor depending on the age of the patient and the intensity of the pain. Up to 65 years of age, a single dose of 10-30 mg is prescribed. IM every 4-6 hours. For persons with impaired renal function or over 65 years of age, a dose of 10-15 mg IM once or every 4-6 hours. The maximum daily dose should not be more than 60-90 mg. and the duration of therapy is no more than 5 days. |
DiclofenacDiclofenac (5 amp. 40 rub.) Voltaren (5 amp. 270 rub.) Naklofen (5 amp. 50 rub.), Ortofen (10 amp. 40 rub.) Side effects: Digestive system: often - diarrhea, gastralgia, constipation, vomiting, nausea, heartburn, hepatitis, acute pancreatitis. Urinary system: frequent urination, nephritis, edema, acute renal failure. Respiratory system: shortness of breath, laryngeal edema, allergic rhinitis, difficulty breathing. Central nervous system: dizziness, headache, drowsiness, hyperactivity, psychosis, hearing loss, depression, blurred vision. CVS: fainting, increased blood pressure, pulmonary edema. Hematopoietic organs: eosinophilia, anemia, leukopenia. Blood clotting: rectal, nasal, gastric bleeding, from a postoperative wound. Dermatological manifestations: urticaria, skin rash, skin peeling, Lyell's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Allergic reactions: swelling of the eyelids, wheezing, shortness of breath, change in facial skin color, itching of the skin, rash, heaviness in the chest. Other: often - weight gain, swelling of the ankles, face, fingers, legs, increased sweating. |
Lornoxicam
Overdose: vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, peptic ulcers, metabolic acidosis, renal dysfunction. Interaction: Simultaneous use of NSAIDs with acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal painkillers, as well as corticosteroids, calcium supplements, ethanol, can lead to gastrointestinal bleeding and the formation of gastrointestinal ulcers. Concomitant use with paracetamol increases the risk of nephrotoxicity. |
Indications for use
The drug is used for all conditions in which hypertonicity of muscle tissue is observed. In addition, the medicine helps reduce pain. This medicine is used in the following cases:
The choice of the required dosage (150 mg or 50 mg) of tablet forms depends on the stage of the pathological process, the general somatic condition of the patient and the severity of muscle spasm.
Mydocalm injections are preferable in the presence of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, with frequent vomiting and inability to swallow (dysphagia). In addition, injections have the ability to quickly enter the systemic bloodstream, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract (a high percentage of drug bioavailability).
Despite the impressive list of indications for the drug, Mydocalm is not recommended for use in several cases. Namely:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Myasthenia gravis (literally – muscle weakness).
- Children's age up to 3 months. From 3 months to a year, exclusively tablet forms are used (50 mg or 150 mg). The injection form is contraindicated in children under 18 years of age.
- Solution for injection in ampoules is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
As we can see, tablets of 50 mg and 150 mg have slightly fewer contraindications than injections. However, the instructions state that Mydocalm tablets should be used in exceptional cases when the benefit to the mother significantly outweighs the risk to the health of the fetus.
Episodes of overdose with tablet forms of the drug have not been described in medical practice. An overdose of Mydocalm in injections can be manifested by the appearance of ataxia (the appearance of problems with coordination of movements), tonic and clonic convulsions, as well as the development of dyspnea (shortness of breath) and respiratory arrest.
The required dosages and the required frequency of administration can only be prescribed by the attending physician. The approach to therapy with Mydocalm is strictly individual.
For intramuscular administration, use 100 mg 2 times a day, and for intravenous administration - 100 mg 1 time a day.
- the drug can be used together with sleeping pills and sedatives, since it itself does not have a sedative effect;
- drinking alcohol during treatment with Mydocalm is not prohibited;
- the drug enhances the effect of medications based on niflumic acid;
- anesthetic drugs, as well as various psychotropic substances enhance the effect of Mydocalm.
Painkillers in tablets
When your back hurts badly, your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory, painkillers in tablets; previously it was believed that oral administration slows down the onset of action, reduces effectiveness and leads to more severe side effects from the gastrointestinal tract. Today it is believed that intramuscular administration and oral administration provide the same bioavailability of the drug. Side effects from the gastrointestinal tract are realized through the suppression of the arachidonic acid system, that is, not through direct contact with the mucous membrane, but after absorption into the blood. Therefore, the side effects are almost the same when taken orally and when injected.
Basic NSAIDs in tablets
- Celebrex (active ingredient celecoxib 10 pcs. 400-420 rubles)
- Arcoxia (active ingredient etoricoxib 7 pcs. 520 -600 RUR)
- Texamen (active ingredient tenoxicam 10 pcs. 200-250 rubles)
- Nise, Nimulid, Nimika (active ingredient nimesulide price 20 pcs. 80-140 rubles)
- Nalgesin (active ingredient naprxen 10 pcs. 110-130 rubles)
- Movalis, Arthrozan, Meloxicam (substance Meloxicam price 20 tablets 40 rubles, Movalis 20 tablets 250 rubles)
- Ketanov, Ketarol, Ketorolac (substance Ketorolac price 20 tablets 40-60 rub.)
- Naproxen, Nalgesin (substance Naproxen, 120-260 rubles)
- Artrosilene, Bystrumkaps, Ketonal, Flexen (substance ketoprofen 20 pcs. 150 rub., Bysrumkaps 10 pcs. 250-270 rub., Flexen 30 pcs. 170 rub.)
- Burana, Nurofen, Faspik, Ibuprofen (substance Ibuprofen price 20 pcs. 15 rubles, Nurofen 12 pcs. 110 rubles, Faspik 6 pcs. 100 rubles, Burana 10 pcs. 80 rubles)
- Voltaren, Diclak, Naklofen, Ortofen, (substance Diclofenac price 20 pcs. 40 rub., Voltaren 20 pcs. 200 rub., Ortofen 30 pcs. 20 rub., Diclofen 10 pcs. 70-100 rub.)
- Aertal 20 tab. 400 rub. — active substance Aceclofenac.
- Xefocam 10 pcs. 130-200 rub. - Lornoxicam.
Combined painkillers
- Dolaren, Panoxen (20 pcs. 120 rubles) - diclofenac + paracetamol.
- Neurodiclovit (30 pcs. 300 rubles) - diclofenac + B vitamins.
- Next (RUB 120-170) - paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Muscle relaxants
Most of the pain is based on muscle spasm, which itself tightens the nerve root and causes secondary radicular syndrome, so in many cases muscle relaxants are prescribed as an anesthetic:
- Tolperisone - peripheral action, Mydocalm (instructions for use, tablets, injections 30 tablets of 50 and 150 mg 300-400 rubles), Tolperisone 30 pcs. 150-200 rub.
- Hydroxyzine - central with inhibition of the central nervous system, suitable for severe pain, Atarax 25 pcs. 300 RUR, Hydroxyzine 25 pcs. 200 rub.
- Baclofen is also centrally acting, Baklosan.
- Tizanidine - central action, Sirdalud (2 mg. 30 pcs. 230 rub., 4 mg. 30 pcs. 330 rub.), Tizanil (2 mg. 30 pcs. 170 rub., 4 mg. 30 pcs. 250 rub.), Tizalud (2 mg. 30 pcs. 140 rubles), Tizanidine 4 mg. 30 pcs. 150-200 rub.
Intercostal neuralgia: treatment at home. Ointments, injections and tablets for intercostal neuralgia
Remedies for neuralgia in the form of ointments and gels quickly relieve pain. They instantly penetrate through the skin pores into the deep tissues, to the lesion, reduce the severity of the pain syndrome and eliminate swelling.
External agents stimulate blood circulation, distract from pain, and relieve nervous tension. Thanks to them, blood supply to the sore spot improves, nutrition of damaged tissues, and pain goes away.
Preference is given to ointments. Their rate of penetration into tissue is higher than that of gels. In the early stages and for severe pain, ointments are used that can relieve muscle spasms and relax muscles.
For patients suffering from severe pain, try not to prescribe ointments with a burning effect. By increasing stimulation at the site of the lesion, it is possible to provoke the development of an ischemic crisis or heart attack due to excessive outflow of blood from the coronary vessels.
Chondoprotectors
Chondroitin sulfateMukosat (5 amp. 250-500 rub.), Chondrogard (10 amp. 600 rub.), Chondrolon (10 amp. 800-1100 rub.), Artradol (10 amp. 700 rub.) Chondroitin sulfate - this drug is an anti-inflammatory drug, which is prescribed for the treatment of diseases of the joints and spine. It slows down bone tissue resorption, improves calcium-phosphorus metabolism in cartilage tissue, stops the destruction of connective and cartilaginous tissue, and accelerates recovery processes. Reduces pain and increases mobility of the spine and joints. It is structurally similar to heparin, and therefore prevents the formation of blood clots in the subchondral and synovial beds. |