In medicine, a vegetative crisis (panic attack) is usually called a spontaneously arising state of anxiety, flowing into horror, and accompanied by a variety of somatic (vegetative) manifestations. The causes of attacks of fear and panic lie not in medical pathologies, but in human psychology. how panic attacks and psychosomatics further.
Classification
Somatic diseases are divided into 2 categories. The list of acute diseases is more often typical for children and adults under 30 years of age. Pathologies appear more often in girls and women. Some may be inherited.
The second category is chronic pathologies. They enter this stage from the acute phase. In young children, somatic diseases are rarely diagnosed, more often starting from adolescence.
Classification:
| Types of pathologies | Characteristic |
| Conversion | Occurs after a neurotic conflict. For example, deafness, paralysis, blindness. These somatic diseases are temporary. |
| Organic | Their development is provoked by stress, strong feelings, and fear. Such somatic diseases are often accompanied by severe pain. Localization may vary. |
| Pathological disorders | Their occurrence depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. For example, increased hyperactivity of a child can cause increased injuries, and addiction to fatty foods can lead to obesity and diabetes. |
In childhood, somatic diseases usually appear as a result of defective development, birth injuries, or under the influence of external causes. Some pathologies develop in the mother’s womb and become more severe after birth. The main symptoms of somatic diseases are pain, loss of appetite, insomnia, manifestations of dysfunction of internal organs.
Which way to choose to heal psychosomatic infertility? According to Louise Hay or “Spiritual Integration”?
Is there an alternative to affirmations in healing psychosomatic infertility?
Yes, I have.
The relatively recently developed proprietary technology of psychologist Konstantin Dovlatov - “Spiritual Integration” - can significantly reduce the time for diagnosis and subsequent treatment of this and other abnormalities in the functioning of the human body.
When using it, in contrast to the treatment of psychosomatic infertility in women according to Louise Hay, a student of the course who has mastered the skills of the technique is able to individually, without the help of a curator, find out the cause of her pathology.
And the effective use of the resources of your mind, direct dialogue with your soul contribute to the physical healing of the disease.
You can learn a little about the author’s exclusive technique – reintegration – by watching this video.
For students who do not have the opportunity to undergo live training, there is a chance to learn technology online.
You can view reviews of this technique here.
Just recently, the author’s technology “Spiritual Integrationics” by psychologist Konstantin Dovlatov has made a revolutionary breakthrough in solving the entire range of problems of modern man: from diseases to financial and personal issues.
For the first time in the world, this system allows the course participant to independently, without the help of specialists, determine the hidden causes of diseases and problems both in himself and in people close to him.
And the main thing is to eliminate them, initiating the process of physical healing.
Such exceptional skills arise in the course participant when entering the state of “500” (high vibrations) and dialogue with his own soul.
You can unveil the veil of secrecy and become familiar with the exclusive reintegration technique by watching this video.
It is worth mentioning an important point for many: the training is possible both in a live format and without leaving home, online.
Therefore, only you can decide how to get rid of allergies.
Enuresis
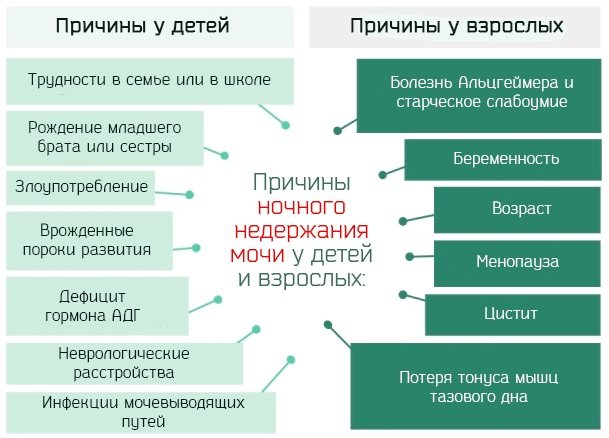
Somatic diseases (the list of diseases can begin with enuresis) often manifest themselves in childhood. For example, involuntary urination during sleep. Pathology can appear at any age, most often in children 5-6 years old.
Kinds
Monosymptomatic (nocturnal) enuresis is mainly diagnosed. It has two forms. Primary – when the child did not have dry nights. If children have not peed in their sleep for at least 6 months, this is a secondary form of enuresis.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptom is involuntary urination. There are no other external manifestations except anxiety and drops of urine. Episodes of involuntary urination usually occur within 4 hours of each other. Patients develop neurotic disorders of varying severity.
Causes
Enuresis can be inherited or occur as a result of certain diseases:
- bladder dysfunction;
- excess urine production;
- deep sleep;
- constipation;
- diabetes;
- cystitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- bladder injuries;
- kidney diseases;
- infections in the urinary tract;
- small bladder capacity.
The causes may be birth injuries, acquired or congenital diseases of the spinal cord or brain.
Prevention
Creating a calm, supportive environment. Stress and worries are eliminated. It is necessary to promptly treat concomitant diseases.
Treatment methods
Drug treatment:
- "Minirin" is instilled into the nose before bedtime. The dosage is selected depending on the age of the child.
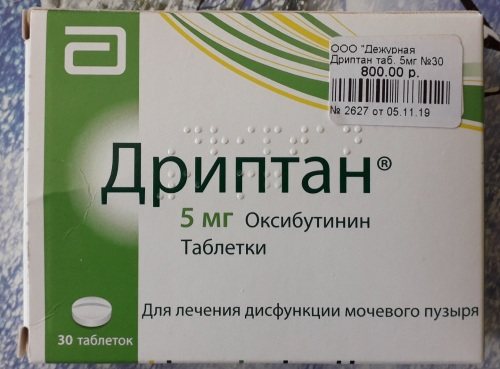
- "Driptan" is given for high bladder tone.
- "Indomethacin" in suppositories. They are placed at night for children from 6 years old.
Bladder training is used as a treatment. It is necessary to delay the urge, gradually increasing the time. It is necessary to control fluid intake. The most effective method is “urinary alarm”, using a special device. As a result, a conditioned reflex is developed.
Who is susceptible to psychosomatics
All people are susceptible to stress and illnesses due to it, but a special risk group are those who live for the sake of others, against their desires, their nature, their needs. The risk group also includes vulnerable people with hyper-responsibility, a weak type of nervous system, the desire to please others, to earn attention and recognition.
What other features are endowed with those who are susceptible to psychosomatics:
- isolation;
- inability to express emotions or prohibition on their expression;
- irritability;
- inability to accept and express warm feelings;
- touchiness;
- rancor;
- pessimism;
- dependence on other people's opinions;
- anxiety;
- fixation on the past;
- inadequate self-esteem;
- irresponsibility;
- indecision;
- complexes;
- fears.
Illness is a reflection of personality disharmony, fears, complexes, self-dislike, and contradictions. Illness is a reflection of a person’s thoughts and actions. If you are sick, then you need to ask not “Why?” and “Why?”, but you need to ask “For what?”. Illness indicates mistakes. It gives a signal that something needs to be changed in life, worldview, behavior, thinking. Psychosomatic diseases are lessons.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a serious deformity of the spine. In this case, it becomes distorted and the posture is disturbed.
Kinds
Up to 3 years of age, scoliosis is infantile (infantile), from 3 to 10 years old – juvenile (children’s), from 10 to 18 years old – juvenile.
Depending on the apex of the arc, the pathology is divided into:
- upper thoracic;
- chest;
- thoracolumbar;
- lumbosacral;
- combined.
Based on the curvature of the spinal arches, they distinguish between C-shaped (with one), S-shaped (with two), Z-shaped (with three) scoliosis.
Stages and degrees
The stage of the disease is determined by the severity of the deformation and curvature in degrees:
- I – insignificant, less than 10;
- II – moderately expressed, from 10 to 25;
- III – clearly expressed curvature with the appearance of a rib hump, from 25 to 50;
- IV – sharply expressed in the spine, chest, with compression and displacement of internal organs, more than 50.
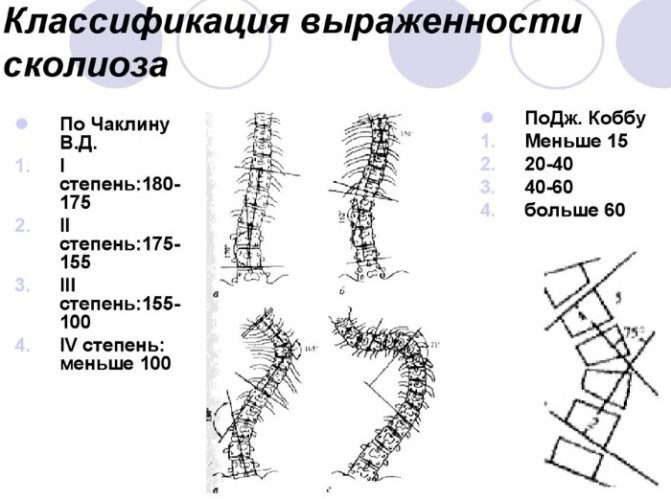
Scoliosis of the spine. Degrees by degrees according to Cobb, Chaklin
Scoliosis can be congenital or acquired.
Symptoms and signs
At the onset of the disease, asymmetry of the shoulders, drooping head, and sloping pelvis are observed. Curvature is observed when the torso is tilted. Then there is a displacement of the vertebrae, a protrusion of the muscle roll in the lumbar region. The curvature is visible even without tilting.
Gradually, a distinct hump appears, muscle contractures, and bulging ribs. At the last stage, signs of deformation become clearer and stronger. The main symptoms of scoliosis include pain in the back and head, difficulty breathing and coordination, and increased fatigue.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of scoliosis include:
- underdevelopment or weakness of the muscular system during the period of active growth of the child;
- incorrect posture while sitting;
- excess weight;
- asymmetry of the pelvis, legs;
- birth injuries;
- abnormal development of the spine;
- tumors;
- congenital hip dislocation;
- cerebral palsy;
- polio.
Scoliosis can be caused by diseases of the spine, joints, legs, and metabolic disorders.
Prevention
Maintaining correct posture, morning exercises. You need to choose exercises to strengthen the spine, muscle corset, and pump up your abs. If the reason is different leg lengths, then it is recommended to wear orthopedic shoes. For prevention, you need to play sports and swim.
Treatment methods
If the spinal deformity is less than 40 percent, treatment is conservative. In other cases, surgery is required.
Conservative treatment includes:
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- kinesio taping;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- wearing an orthopedic corset.
At stages 1 and 2 of scoliosis, manual therapy, massage and exercise therapy are sufficient. Other methods are used to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Get to the truth
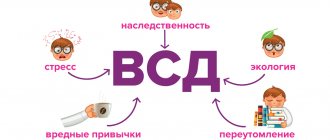
Despite the fact that psychotherapeutic techniques are actively combined with traditional treatment, it is psychotherapists who help to get to the bottom of the true cause of the disease. In fact, it is worth noting that the psychosomatics of VSD can be corrected without any difficulties; this ailment is an excellent example of how the final successes of treatment depend on the patient’s desire.
But the main condition is that you need to contact specialists directly for help as early as possible. You cannot limit yourself only to folk remedies or any medications. The maximum that can be achieved in this case is to stop the attacks, but the problem may not only remain with the person, but will also develop further.
Flat feet
Flat feet is a change in the skeleton of the foot, a decrease in the height of its arch with loss of spring functions. This makes walking difficult and changes your gait. The disease is detected from birth or it develops gradually, with increasing load on the lower limbs.
Kinds
Flat feet can be congenital or acquired. The disease is divided into several types - rachitic, paralytic and traumatic. Statistical flatfoot is diagnosed most often. In orthopedics, the disease is divided into longitudinal, transverse and combined. Pathology can be elastic or rigid.
Stages and degrees
The disease has three stages of development. The first is characterized by an almost imperceptible deformation of the foot. Fatigue appears in the legs after physical activity or long walking. Pressure on the feet causes pain.
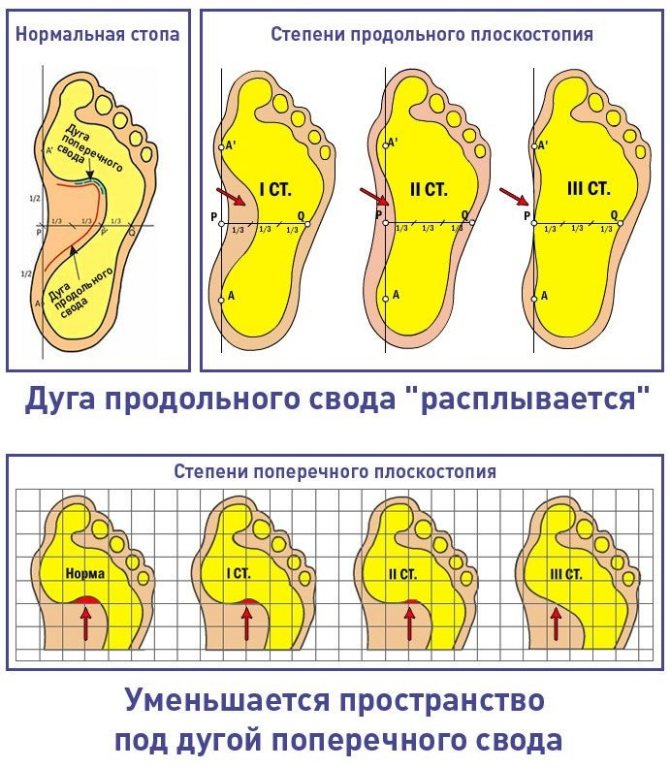
The second stage of development - the arches disappear, the foot becomes spread out. Swelling appears in the lower legs, and the pain intensifies. The sensations are highly intense and long lasting. Walking is difficult.
Third degree - severe deformation of the foot, gait changes. The pain becomes constant and radiates to the spine. The child begins to have a headache, it is difficult for him to walk in ordinary shoes, and any physical activity is painful. By evening, your legs swell.
Symptoms and signs
Affected feet have a swing-like appearance, a convex sole, and a flattened, concave dorsum. Installation - heel, with sharp pronation and abduction of the toes. When walking, children quickly get tired, the shoes wear down on one edge of the heel and sole. Clinical symptoms are pain in the foot, swelling, decreased arch height. Calluses, curvature of the spine, herniated discs, and inflammation of the menisci may appear.
Causes
Congenital flatfoot occurs due to abnormal intrauterine development.
The acquired develops due to:
- lack of connective tissue;
- myopia;
- inflection of the gallbladder;
- hereditary factor;
- weaknesses of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus;
- rickets;
- bone lesions;
- paralysis

Flat feet are caused by improperly selected shoes (tight or worn out), obesity, long walking, and planovalgus foot deformity.
Prevention
It is necessary to select the correct shoes (by size) for your child. You need to play sports (especially swimming, football and basketball). Flat feet are prevented by walking barefoot on the ground, pebbles, and sand. It is necessary to control calcium-phosphorus metabolism, control body weight, preventing obesity.
Treatment methods
Treatment cannot be delayed; for congenital flat feet, therapy begins from the first days of the child’s life. The main methods are massage of the feet and legs, exercise therapy, fixing them with bandages, plaster casts and night orthoses.
If the disease worsens, surgery for subtalar arthroeresis is necessary. Children should not wear soft shoes, only hard ones with insoles that raise the arch.
Magnetic therapy, ozokerite and paraffin applications, mud compresses, and hydromassage are used as additional treatment. The optimal period for performing surgical operations is 8-12 years.
On the relationship between the physical and mental
Our ancestors believed in the two-way nature of the relationship between body and psyche. They believed that healing the body begins with healing the soul. The cause of physical illness was seen as a discrepancy with the spiritual nature. Eliminating unnatural behavior and distorted thoughts returns the patient's body to a healthy state.
Today they talk about the dual influence of soma and psyche on each other. Stress, worries, worries leave traces on the bodily level. Blood pressure increases, turning into hypertension, and constipation appears. Even a broken leg does not occur on its own.
In a stressful situation, the body protects the psyche and takes the blow. Against the background of negative changes in the body, depressing mental reactions are formed. This negatively affects the functioning of the human body:
- anxiety levels increase;
- feeling unwell;
- vitality decreases;
- there is a loss of strength.
If the body’s reactions to a physical illness are repeated, this is the beginning of a psychosomatic illness.
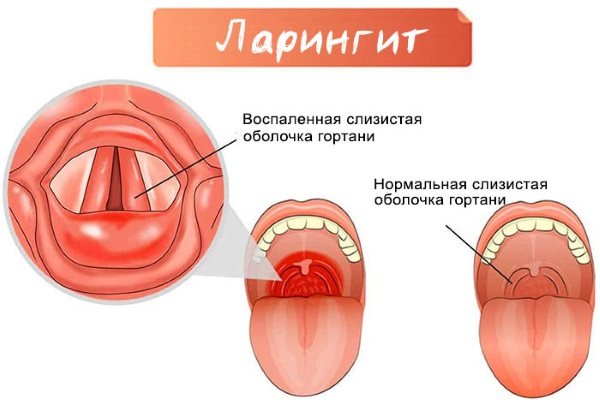
Laryngitis
This is an inflammatory pathology of the larynx, accompanied by difficulty breathing and hoarseness. It can be either an independent disease or a complication after influenza, ARVI, or respiratory system infections. Viral laryngitis can be transmitted to other people.
Kinds
According to intensity, the disease is divided into acute and chronic.
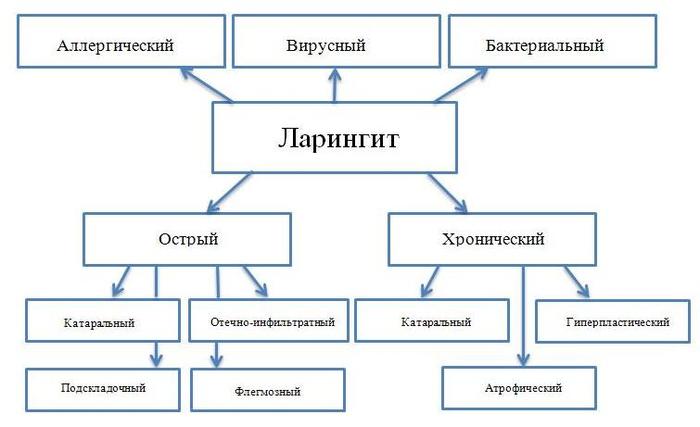
Classification by shape:
- catarrhal;
- stenosing;
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- hemorrhagic;
- diphtheria;
- phlegmonous.
The chronic form of the disease can transform into a malignant tumor.
Stages and degrees
There are 4 stages of the disease. The first lasts 2-3 days, the symptoms are blurred, the child feels only slight discomfort. The second stage lasts 3-5 days. Tachycardia, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing appear. The third is accompanied by a protracted barking cough. The fourth stage of laryngitis is very dangerous for a child. Convulsions, toxicosis due to false croup, and bradycardia may occur.
Symptoms and signs
The first signs of laryngitis are hoarseness, heavy breathing, and a barking cough. When breathing, you can hear hissing and wheezing. They are felt in the upper part of the respiratory tract. The temperature rises sharply to 38-39 degrees. The child becomes nervous and has trouble falling asleep (especially at night). Blueness appears around the mouth.
Causes
The main causes of laryngitis include bacteria and viruses, and diseases of the larynx of a viral nature.
Other reasons:
- Food;
- allergic reactions to dust, household chemicals, and other external factors;
- tendency to swelling of the throat;
- loose texture of the nasopharynx;
- reaction to medications;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- overloaded vocal cords;
- poor oral hygiene;
- avitaminosis.
Chronic pathologies of internal organs or warm, dry air in the room can provoke laryngitis.
Prevention
It is necessary to prevent the child from screaming and singing. Avoid giving children very hot or cold drinks and ensure they drink plenty of fluids. You can drip essential oil onto the pillow - fir, eucalyptus, menthol. You need to add sage and chamomile to your child’s tea. It is necessary to promptly treat pathologies of the respiratory system and throat.
Treatment methods
Medicines are prescribed depending on the type of disease and its intensity.
Can be used:
- antihistamines (Zodak, Fenistil), which reduce swelling and neutralize toxins;
- mucolytics, antitussives (“Lazolvan”, “Gerbion”, “Ambrobene”);
- antiseptics (“Faryngosept”, “Strepsils”, “Lizobakt”) eliminate a sore throat and are taken after meals;
- antipyretics (“Nurofen”, “Ibuprofen”, “Paracetamol”);
- antiviral drugs (“Anaferon”, “Acyclovir”);
- nasal (Naphthyzin, Knox-spray) restore nasal breathing;
- hormonal drugs (“Dexamethasone”) in the form of inhalations;
- antibiotics (Sumamed, Azithromycin, Cefazolin) for bacterial laryngitis.

Inhalations with herbal decoctions and infusions, and foot baths with natural extracts also help. The method of breathing over hot boiled potatoes helps a lot. You can rub warming ointments into the chest and neck, rinse your mouth with herbal infusions. Among the auxiliary methods, magnetic therapy and UHF are used.
Formation of a panic attack
When explaining the occurrence of a panic attack, patients try to indicate “real” reasons, for example, a pre-stroke condition. In fact, they may have no idea about this condition, but point to it as a trigger for fear.
However, in such explanations the cause-and-effect relationship is broken: it was not tachycardia that caused fear, but fear that caused tachycardia.
In the real picture of events, the chain of causes and consequences looks like this:
- The emergence of fear of death. This phobia is basic, underlying all other fears. It can appear in connection with some real events in a person’s life (the death of a loved one, a serious illness) or vivid impressions made by a book or film.
- Under the influence of the fear of death, processes are launched in the subconscious that develop their own symbolism, signifying the approach of death. This is precisely what is associated with the individual propensity to initiate attacks in a certain situation (in the subway, on an airplane, etc.).
- Receiving signals from the subconscious, the body reproduces the scenario of death on the physical level - fainting, breathing problems, arrhythmia.
- Assessing the situation, a person sees vegetative manifestations and concludes that death is close, and therefore falls into a state of panic.
This relationship also explains the short-lived nature of panic attacks: the body cannot constantly sweat and choke without objective reasons.
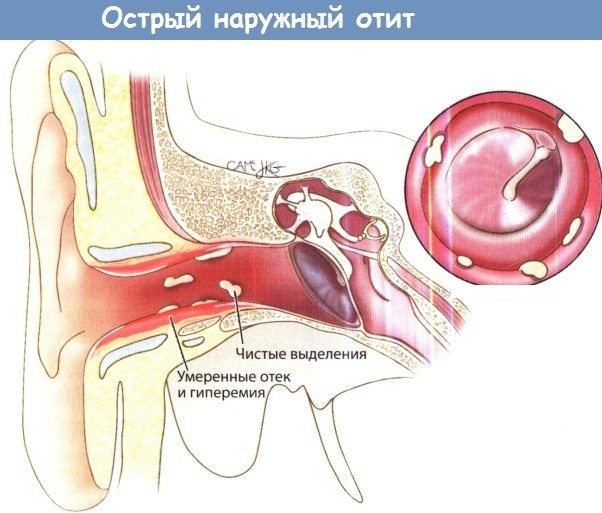
Otitis
Somatic diseases (the list of diseases necessarily includes otitis media) are often associated with inflammatory processes. For example, inflammation of the inner, middle and outer ear. The disease is accompanied by pain and purulent discharge. For young children, the disease can be life-threatening.
Kinds
Otitis can be external, middle or internal. By distribution - one-sided or two-sided.
Otitis media is also divided into several types:
- purulent;
- serous;
- catarrhal;
- bullous
The latter form is rare in children.
Stages and degrees
Otitis begins with an acute form. At the initial stage (pre-perforation), the symptoms are pronounced. It can last from hours to several days. Pus accumulates, but does not break through the membrane. It thickens and becomes covered with a white coating.
In the second stage (perforated), the membrane breaks through. Pus and mucus come out. The temperature drops and the symptoms subside. This period of illness lasts up to a week. The third stage is reparative (final). The perforation is scarred, no pus is released, and hearing is restored. If the acute form of the pathology is not cured in time, it becomes chronic.
Symptoms and signs
Common symptoms for all types of otitis media include pain and noise in the ears, high fever, and deterioration or loss of hearing. Diarrhea, nausea and vomiting often occur.
The child's appetite is impaired and purulent discharge appears from the ears. Kids become lethargic and irritable.
Causes
Otitis media can be caused by injuries, open wounds and cuts. Through them, the infection enters the blood. Children can injure themselves if they try to clean their ears themselves.
Other reasons:
- water getting into the ears;
- excessive hygiene, when protective sulfur is completely removed;
- E. coli, fungi, staphylococci;
- chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx (for example, sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis);
- colds, hypothermia;
- ARVI;
- overheat;
- allergic rhinitis.
The reason may be a decrease in immunity, incorrect position for feeding infants.
Prevention
In windy weather, the child needs a hat. Avoid swimming in cold or cool water; it is important to prevent head and ear injuries. You need to teach your child to blow his nose with his mouth open. If your baby is often sick, you can get the Prevenar vaccine.
Treatment methods
To treat otitis, anti-inflammatory drugs in drops and ointments are used. They are instilled or applied as a compress. If there is a boil, it is allowed to ripen. And then they open it. Levomekol or Bepanten is applied to the wounds.
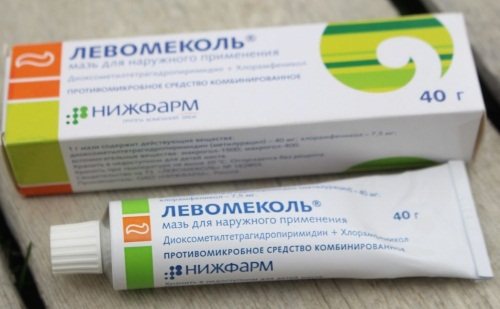
To eliminate pain, the child is given Ibuklin and Nurofen. If otitis is of a bacterial nature, antibiotics are prescribed (Sumamed, Amoxicillin). When the disease is caused by fungi, oral ointments and Candibiotic ear drops are used.
Additionally, inhalations with medications or herbs are prescribed. Electrophoresis and halotherapy are used. Among the traditional methods, instillation of boric alcohol into the ears, compresses with salt or camphor oil, and insertion of turundas with propolis or calendula help. For external inflammation, furacilin alcohol is used.
Help yourself
To find out how panic attacks and psychosomatics are connected in a particular case, you can think about some topics:
- the presence of moments of sexual or physical violence in the family;
- the presence of traumas closely related to sudden tragedies in one’s life or among loved ones;
- situations when, upon requesting help and support, a person received rejection from loved ones;
- what was the state before the panic attack: stress, fear, conflict situation;
- ease of communication with parents: how they communicated in childhood, what feelings they experienced, what made them sad or happy.
Sometimes the cause of attacks can be found quite simply, after which you can begin to work on it using available means: meditation, art therapy, etc. A famous psychologist recorded a video on these topics
What is a panic attack? What are the causes and symptoms of this disorder? How to treat panic attacks? In this article you will find out the answers to all these questions.
“After several debilitating years with panic attacks, suddenly there was a lull.
Not for several weeks now. Is it possible that the PAs have healed themselves, or will they come back?” There can be no clear answer in this case. Let's analyze the mechanism of PA (panic attack).
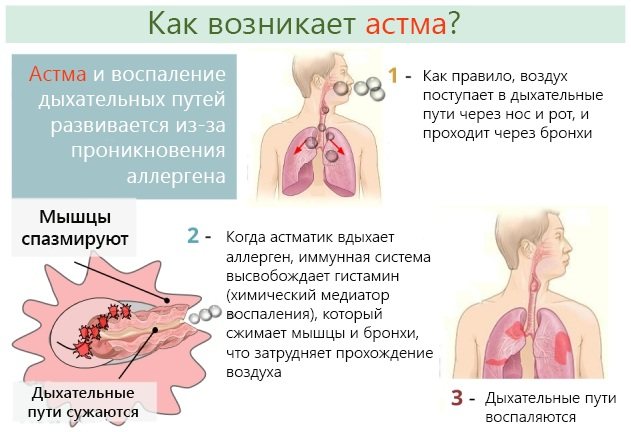
Bronchial asthma
Somatic diseases (the list of diseases includes asthma) often affect the respiratory tract. This is chronic inflammation. Asthma is a common childhood pathology. The course of the disease may be atypical. Preschool children are more likely to suffer from asthma.
Kinds
The disease is divided into several forms - allergenic, non-atopic, physical activity and resulting from obesity. The last two types are rarely diagnosed.
Stages and degrees
The nature of asthma can be mild, moderate, or severe. The disease occurs in two stages. With exacerbation, the symptoms become more distinct and stronger. During remission – absent. This period can be of three types - complete, partial and pharmacological.
With complete remission, the child can lead a normal life. When partial, he experiences discomfort, shortness of breath and wheezing, and quickly gets tired.
Symptoms and signs
With asthma, the temperature does not rise. Generally, severe excitability, sleep disturbance, and irritability are observed. During attacks, coughing, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing begin. You can hear wheezing in the lungs, you can see a strong retraction of the chest and supraclavicular fossa. The main sign of an approaching attack is that the nasolabial triangle turns blue.
Causes
The main causes of asthma are external irritants and allergens. This could be medicines, pollen, household chemicals, dust. Often the disease is caused by mold and animal hair.
Other reasons:
- viral infections;
- poor environmental conditions;
- tobacco smoke;
- hereditary factor;
- predisposition to atopy.
Asthma is often caused by heavy physical activity and frequent stress.
Prevention
It is recommended to breastfeed your baby for up to one year. If there is no milk, buy only high-quality formula. Complementary foods are given in strict order and only with the permission of a doctor. Allergenic foods are excluded from the diet. It is recommended to remove from the room all objects that accumulate dust.
You need to do wet cleaning daily. You cannot have pets (especially cats and dogs). Bed linen should only be made from hypoallergenic materials. The room needs to be ventilated daily. Boost your immunity with exercise and food.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen is developed individually. It includes therapeutic exercises, diet, and physiotherapy. To relieve attacks, aerosols such as Ventolin, Berotek, and Salbutamol are used.
If additional severe symptoms are present, hormonal medications are prescribed. Spacers are used to inject medication into young children. They deliver powder into the body, which relieves the attack.
Compressor and ultrasonic nebulizers are also used to treat asthma. For basic therapy, antihistamines are prescribed - Suprastin, Tavegil, Loratadine.
Drugs that stabilize the membrane include Ketotifen and Intal. Antibiotics (for example, Sumamed) can be used in the treatment of chronic asthma. Children over 5 years of age are prescribed the ASIT method (introducing a small amount of allergen into the body).
Bronchitis
Somatic diseases (the list of diseases includes pathologies of the respiratory system) often affect the bronchi. This is an inflammatory process affecting the mucous membrane. Usually develops from 3 years of age, in infants it occurs in a severe form.
Kinds
There are several classifications of the disease. Depending on the duration, acute and chronic forms are distinguished.
By:
- pathogen - viral, bacterial and allergic (the first two forms are contagious);
- severity of the course - simple, obstructive and protracted;
- localization – tracheobronchitis, bronchiolitis.
Damage to the bronchi can be one- or two-sided.
Stages and degrees
Bronchitis begins with an acute stage that lasts 3-14 days.
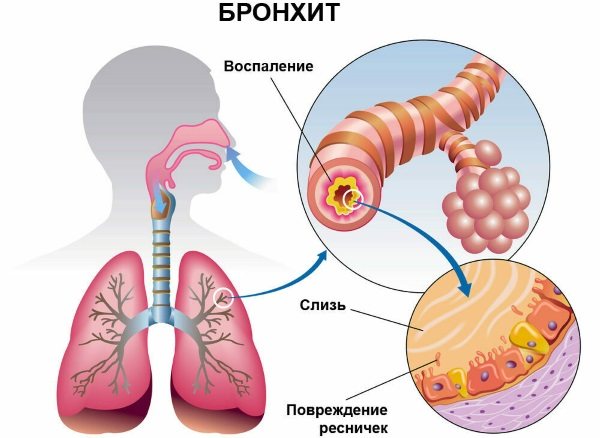
Then the disease can become chronic. At the first stage, primary symptoms appear, at the second - the type of cough changes, and sputum discharge increases. On the third, recovery begins.
Symptoms and signs
The incubation period is 3-5 days. During this period, the child experiences loss of appetite, headaches, and sore throat. Shortness of breath, asphyxia, and itching in the nose often occur.
Then a cough appears (maybe to the point of vomiting), wheezing and whistling in the chest, a runny nose with green or white discharge. Children develop a febrile state, the temperature rises, and conjunctivitis is diagnosed. Without treatment, the pathology develops into pneumonia.
Causes
The main causes of bronchitis are abnormal development of the respiratory system and a weakened immune system. In infants, the disease quickly progresses to pneumonia.
Other reasons:
- allergies to household chemicals, smoke, dust, pollen;
- prematurity;
- birth injuries;
- contracting an infection from another person;
- atypical structure of the nasal septum.
Bronchitis can appear as a complication due to sinusitis, tonsillitis and pharyngitis.
Prevention
You should not allow a child to become hypothermic, and treat incipient runny nose and cough and respiratory tract diseases in a timely manner. It is necessary to provide the body with a full complex of vitamins.
Treatment methods
It is necessary to provide the child with peace, periodically ventilate the room, and increase fluid intake. Eliminate fatty, sweet and fried foods from your diet.
Drug treatment:
- antipyretics (“Cefekon”, “Nurofen”);

Tsefekon D - painkillers (“Papaverine”, “No-Shpa”);
- antiviral drugs (“Arbidol”, “Interferon”);
- antitussive syrups (“Stoptussin”, “Libexin”);
- for a dry cough, give “Prospan”, “Gerbion”;
- expectorants (“Mukaltin”, “Bromhexine”);
- for allergic bronchitis they give Zyrtec, Fenistil.
Antibiotics (Sumamed, Amoxiclav) are given to a child only after a bacterial infection. To liquefy sputum, give herbal infusions and decoctions, and do inhalations with them. Additionally, physiotherapy methods are prescribed - UHF, UV irradiation, electrophoresis.
In addition to the listed somatic diseases (the list of common diseases includes tonsillitis, chickenpox, rubella), secondary pathologies may develop - gastrointestinal tract, diabetes mellitus, obesity.
Rare, difficult or incurable diseases include cancer, hepatitis, and heart failure. Many somatic pathologies, including severe ones, are rare in children; mild ones are quickly treated.
Features of treatment
In order to get rid of psychosomatic diseases, there is no point in using medications or any other conservative methods. If you do not get rid of the problem of an emotional nature, then dealing with physical health will be pointless. In the treatment of psychosomatic diseases, it is very important to find an individual approach. In order to do this, it is very important to contact a highly qualified psychotherapist. However, even the patient himself, by looking inside himself and conducting self-analysis, will be able to determine for what reasons this or that disease arose.
Currently reading: Bulimia as a delayed suicide
If doctors discover psychosomatic illnesses in a child, this means that all family members should undergo treatment. And in this case we are not talking about traditional healing methods. It is very important to visit a psychologist who can understand the psychological state of the child’s parents. In order to eliminate psychosomatics, it is very important to determine the cause of its origin, and most often it lies in the wrong environment at home. According to psychologists, even in order to cure adult patients, it is necessary to involve his relatives and friends. For maximum results, the therapist needs to work with the entire family. In order for psychological changes to occur, it is very important to change the environment. To do this, you need to somehow defuse the flow of family life or even move to another home.
However, in many cases, psychosomatics is hidden so deeply that it takes a lot of time and effort to identify it. For this, it is recommended to undergo a special psychotherapeutic course. Of course, for maximum results, doctors will also prescribe you the use of special medications.