Removal from coma - this is how we can formulate what we do when working with seriously ill patients after a major stroke, traumatic brain injury, or acute intoxication.
Our expert in this field:
Khartukova Natalya Evgenievna
Anesthesiologist-reanimatologist, deputy chief physician for anesthesiology and resuscitation
Call the doctor
Ultimately, this is precisely the goal of all our efforts, the doctors of the anesthesiology and intensive care department of the Medicine 24/7 clinic.
Our goal is not just to ensure vital processes, combat complications and prevent new complications. Although this requires continuous monitoring of the patient, constant therapeutic measures, and high-tech equipment. It is important not just to save a person’s life and maintain his livelihood. It is important to bring him out of the coma with the most favorable prognosis.
Relatives and loved ones of the person with whom the misfortune happened ask us about this. What will he be like after a coma? What will his life be like after the coma?
This largely depends on factors that we cannot influence. And we talk about this directly. For our part, we do everything to achieve the maximum possible. And sometimes the impossible.
And such cases occur in the practice of our clinic. Therefore, you should never despair or give up. Even in the most severe condition, when a person is in a 3rd or 4th degree coma, hope remains. As long as he breathes and we keep him alive.
Areas of use of the method
This treatment method is necessary to prevent extensive hemorrhages due to traumatic brain injuries. In neurosurgery, the method is often used for complex operations performed simultaneously on one patient. It has been proven in practice that after such an anesthesia-coma, the rehabilitation process goes much faster. For people with rabies, an artificial coma is currently the only chance to be cured. So far, research is being conducted in people with epilepsy, but the results in 90% of cases are positive.
Purpose of using medicated sleep
By introducing a person into an unconscious state, they pursue different goals.
- Medication-induced sleep during childbirth is necessary so that a woman can rest from severe pain during prolonged contractions. The drugs are administered in the first half of labor. The woman and child must be constantly under the supervision of a doctor. Strong sedatives can penetrate the placenta and reduce motor activity in newborns. If the instruments show that the baby feels discomfort, the mother’s sleep is interrupted.
- In dentistry, artificial sleep is used instead of general anesthesia in the treatment of abscess, periostitis, and during jaw surgery. It is recommended for people who are afraid of pain and fear the dentist.
- Pneumonia, caused by a complication of an atypical influenza virus, causes degenerative changes in the lungs, leading to death. To avoid this, the patient is placed in an artificial coma.
- Stroke and cerebral infarction impair blood circulation, promote the death of nerve cells and tissue necrosis. Medicinal sleep helps reduce intracranial pressure and speed up the rehabilitation process.
- Neurosurgery and traumatic brain injury can cause swelling and tissue necrosis. Prolonged sleep slows down blood flow, constricts blood vessels, and stabilizes intracranial pressure. The complex action removes fluid from brain tissue, eliminates venous congestion and normalizes the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
An artificially induced coma is necessary for patients with large-scale burns to reduce suffering from unbearable pain.
Rehabilitation period
Not all cases of impaired consciousness require a long rehabilitation period. According to statistics, recovery from a coma caused by diabetes, high doses of drugs or alcohol does not last long. In such cases, impaired consciousness is present before the toxic substance is eliminated from the body.
Coming out of a 3rd degree coma after a TBI or 1st degree equally requires rehabilitation measures. First of all, measures are taken to restore brain function. Not in every case, amnesia develops, but there is a deterioration in memory and attention.
How do you recover from a coma after a TBI? During this period, the ability to sit and walk without assistance and available means is lost. Confusion of consciousness is observed, the person loses orientation in space. The following specialists help correct such disorders caused by prolonged impairment of consciousness:
- neurologist (helps restore speech);
- psychologist (normalizes the psycho-emotional state);
- occupational therapist (helps improve motor skills);
- neurologist, physiotherapist, etc.
When recovering from a coma after a TBI, there is no need to immediately subject the patient to physical and mental stress on the first day. Rehabilitation should take place gradually. How many months or years it will take to fully restore the activity of the central nervous system, and what the prognosis will be, depends on the severity of the traumatic brain injury.
Rehabilitation after a coma consists of assisting the patient in all everyday activities: eating, going to the toilet and showering. Developmental games are required to help restore motor skills, memory, and speech. It is important to normalize your diet so that it includes all useful vitamins and microelements.
To restore muscle tone, massage procedures are prescribed, which are carried out in a specialist’s office and subsequently at home. During the massage, you can use any essential oil. The procedure also helps improve blood circulation. The main condition is continuity of therapy, even if the first positive changes are visible.
Degrees of coma
For reference. According to statistics, about 8% of patients who survive a stroke go into a coma. Mostly these are elderly people with significant brain damage, changes in its position, edema, weakened by other diseases.
There are several stages in the development of coma during stroke. This gradation will make it possible to make a forecast regarding how recovery will proceed.
The first degree is said to be when the patient exhibits lethargy and does not show any reactions to stimuli, including pain. The patient can swallow, perform some movements, and see. The probability of survival is high. This is a moderate coma or precoma. They usually come out of it after three hours. Upon exiting, the person experiences some inhibition.
In the second degree, depressed consciousness is noted. The person is asleep and does not react to external stimuli. His breathing is uneven, his pupils are constricted. Involuntary muscle contractions occur. These signs characterize severe coma or stupor. It sometimes lasts for several days.
Patients in the third degree are unconscious and have no reflexes. Any impact on the tendons causes cramps. No reaction to light is detected. Muscle tissues are relaxed. Heart rhythm is unstable, temperature is low, blood pressure is low. There is no chance of surviving a stroke with this type of coma. This condition sometimes lasts for several days.
With the fourth degree of severity there are also no reflexes. Body temperature is extremely low. The pupils are dilated. Breathing is unstable, irregular, and there are long delays. Brain function is impaired. There is no chance of survival, the person dies.
For reference. Usually, to correctly assess and determine the type of coma during a stroke, the Glasgow scale is used. It is based on a person's ability to open their eyes, move and speak.
Thus, it is assessed whether a person opens his eyes independently, in response to pain, speech, or remains with his eyes closed. A comatose state during a stroke is stated if the patient scores 8 points or less.
When is an induced coma used?
To understand what an induced coma is, you should consider the main areas of use of the method.
- In case of head injuries, the method is relevant for the prevention of extensive hemorrhages.
- The technique is also used to carry out a whole series of complex operations. More often the method is used for neurosurgical effects. Doctors say that after such a coma, the rehabilitation process requires less time.
- It is advisable to use such treatment in order to bring the patient out of complex status epilepticus.
- Treatment of rabies with coma is at the experimental stage, but ongoing studies have shown positive results.
How to treat?
This is a cycle of targeted actions that ensure that patients are placed in a coma due to medical conditions, such as stroke or pneumonia. The duration of the coma depends on the nature and severity of the disease. This period can range from several days to several months. Conclusion from this condition can be carried out only after the cause and signs of the disease have been eliminated.
Before this, a comprehensive examination of the patient is required to determine his condition.
Symptoms
What this “induced coma” is can also be understood by the signs that arise when a person is immersed in a special state of consciousness. During it it is noted:
- Drop in blood pressure;
- Significant reduction in heart rate;
- Cancellation of reflex states and feelings;
- Muscle shutdown;
- Decrease in body temperature;
- Stopping the gastrointestinal tract.
To avoid oxygen deficiency, patients in vegetative states are connected to mechanical ventilation before drug administration. Thanks to this, a special mixture of oxygen is supplied to the lungs.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, there are several stages of coma:
- Stage 1 – superficial;
- Stage 2 – moderate;
- Stage 3 – deep;
- Stage 4 – beyond.
This condition is resorted to when the patient needs to reduce intracranial pressure. In this case, the swelling subsides and tissue necrosis does not occur. This procedure is carried out in the intensive care unit, under the strict supervision of doctors, with continuous infusion of drugs. Most often, these drugs include barbiturates, thanks to which the central nervous system is depressed. Doses of narcotic analgesics are administered in large quantities.
Signs of an induced coma:
- immobilization and complete muscle relaxation;
- unconsciousness, absence of all reflexes;
- decreased blood pressure and body temperature;
- intestinal tract failure;
- decrease in heart rate.
In this condition, due to a decrease in all vital processes, the brain experiences oxygen starvation. Therefore, a person is connected to artificial ventilation, due to which the blood flow is enriched with oxygen, which tends to the brain. It is worth noting that in this condition, all vital functions of the body are recorded by specialized equipment, which is controlled by a resuscitator and an anesthesiologist.
An induced coma is characterized by specific symptoms. When applying the method, the following is noted:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure, it becomes lower than normal;
- heart rate less than 60 beats per minute;
- no reflexes and reduced or absent sensitivity;
- muscle mass is atrophied;
- a sharp decrease in human body temperature;
- the gastrointestinal tract stops working.
To prevent death in a person in an artificial coma from oxygen deficiency, patients are connected to a ventilator even before being introduced into it. A mixture enriched with oxygen will get there.
Coma due to meningitis
Coma due to meningitis. It develops with inflammation (mostly purulent) of the soft and arachnoid membranes of various etiologies (meningococcus, pneumococcus, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Haemophilus influenzae Afanasyev-Pfeiffer, etc.).
In the pathogenesis of coma, the main role is played by inflammatory changes in the membranes, their swelling, liquorodynamic and hemodynamic disorders, brain edema with dislocation of the brainstem, an increase in body temperature to 39 - 41 ° C, and often DIC syndrome. Characteristic is the acute development of coma against the background of hyperthermia, general malaise, drowsiness, tactile, optical and acoustic hyperesthesia, severe headache and repeated vomiting. The patient's posture is noteworthy: the head is thrown back, the lower limbs are bent at the knee and hip joints. Skin rash, bradycardia, Kernig and Brudzinski symptoms, stiff neck muscles, pathological reflexes, and cranial nerves are often observed. Generalized and partial convulsive seizures develop. Impairment of consciousness increases to the point of coma. Lumbar puncture reveals increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure, high pleocytosis (neutrophilic in purulent meningitis, lymphocytic in serous meningitis), and increased protein content. Changes in glucose and chloride levels are often determined. Changes in the fundus indicate the development of optic neuritis.
Urgent Care. The patient is hospitalized in the intensive care ward or in the intensive care unit of an infectious diseases hospital. For purulent meningitis, after an intradermal test, large doses of benzylpenicillin are administered intramuscularly or intravenously - 3,000,000 - 6,000,000 units every 3 hours (daily dose up to 320,000 units). In case of a very serious condition of the patient, endolumbar administration of benzylpenicillin sodium salt from 5000 IU to 50,000 IU in a sterile isotonic sodium chloride solution is allowed at the rate of 10,000 IU per 1 ml of solvent; An appropriate amount of cerebrospinal fluid is first removed. For endolumbar administration, 1/3 of the volume of a 10-gram syringe is filled with penicillin solution and 1/3 with air. If benzylpenicillin is intolerant, other antibiotics are used (chloramphenicol sodium succinate 75-100 mg/kg body weight per day intravenously or klaforan 1-2 g intravenously every 4 hours for 6-8 days), after which a control study of the cerebrospinal fluid is done. In case of intolerance to antibiotics for purulent meningitis, it is permissible to prescribe long-acting sulfonamide drugs - sulfamonomethoxine and sulfadimethoxine. Pathogenetic therapy includes the appointment of rheopolyglucin - 100 - 400 ml, isotonic sodium chloride solution - 400 - 800 ml per day, 5% glucose solution - 500 ml. The total amount of fluid administered should not exceed 40 - 50 ml/kg per day.
Mechanism of action
The difference between drug-induced sleep and anesthesia lies in the length of stay in the state. In the first case, this period can reach several weeks. Under the influence of barbiturates, metabolic processes in the nervous tissue slow down. 60% of oxygen and glucose entering the brain support its bioelectrical activity. 40% of oxygen and glucose ensure metabolic processes and other activities.
In a patient in a state of drug-induced sleep, the bioelectrical activity of the brain is significantly reduced, which leads to an increase in free oxygen and glucose, which are redirected to maintain cellular metabolism in the nervous tissue. This is why a person is put into an artificial coma, in order to reduce the negative effects of oxygen deficiency and avoid hypoxic damage to the brain matter.
Risk of mortality from bacterial meningitis
If a person falls into a coma with bacterial meningitis, then, according to medical statistics, in 62% of clinical cases this leads to coma.
The only thing that can increase the patient’s chances of recovery is correct diagnosis and treatment. But, even despite therapy, patients still have post-symptoms of the disease such as:
- Speech impairment (complete or partial);
- Mental retardation;
- Brain swelling.
Clinical symptoms of meningitis are expressed in: chills, high fever, profuse vomiting, nausea, stiff neck; In young children with meningitis, the fontanel is strongly bulged.
The state of coma develops in the case of extensive damage to the meninges or when the substance of the brain is damaged by the inflammatory process.
Keep in mind
Meningitis can develop in both an adult and a child - there are no special predispositions to this severe and serious disease.
Traumatic brain injury (coma, acute period)
Poorly differentiated (stem) cells are transplanted into the subarachnoid space through a spinal puncture.
Treatment is carried out in an intensive care unit.
The transplanted cells awaken the patient's consciousness and contribute to his subsequent neurological rehabilitation.
The cell transplant undergoes 3-level testing, which includes two enzyme immunoassays and one PCR testing.
During the acute period of the disease, the risk of possible complications is minimized by appropriate drug therapy. No complications were registered in the separated period.
Stages of induced coma
These include:
- Superficial.
- Moderate stage.
- Deep.
- Transcendent stage.
It is necessary to prepare before inducing a coma. The patient is transferred to the intensive care unit.
The state of induced coma is caused in 2 ways:
- With the help of medications (for example, sodium thiopental).
- Gradual cooling of the body and organism.
The second method is practically not used, only in cases of allergies to drugs. The patient is always given a pre-calculated amount of medication proportional to age and weight. They are called barbiturates. Sodium thiopental belongs here.
They have a depressing effect on the central nervous system – the brain and spinal cord. Depending on the time of the operation, the doses are selected. Immediately after intravenous administration of drugs, complete relaxation of ligaments and muscles occurs, and the body goes limp. An artificial coma ensues. What this is is now clear.
In a vegetative state, the indicators of all the patient’s organs are recorded and are constantly under the control of doctors and nurses. The duration of the coma can be set to any length, depending on the purpose for which the patient was immersed in it. In this case, the main task of the medical staff is to prevent cerebral edema and necrosis.
The real one can last from several hours to tens of years. A medically induced coma has clear time limits.
First signs of coma
Coma with encephalitis begins suddenly. Already on the second day after the development of meningitis, there is a high risk of a sharp deterioration in health. Before a person falls into a coma, he complains of:
- Lethargy throughout the body;
- A sharp increase in body temperature;
- Increased drowsiness;
- Severe headache;
- Dizziness;
- Loss of coordination in space;
- Nausea, vomiting, recurring periodically.
Before a coma, the patient's cardiovascular activity is disrupted - shortness of breath may appear and convulsions may begin.
If a patient's brain is affected by meningitis, then... his upper eyelids begin to droop - the phenomenon of ptosis, paralysis of the eye muscles occurs, and the limbs do not move.
Treatment of coma due to meningitis is possible, the main thing is to contact a medical facility in time and make the correct diagnosis.
There were no signs of trouble
“Now everything is fine with us,” this phrase will be repeated repeatedly by a pretty short blonde. This is Alla, the wife of Mikhail But-Gusaim, one of the most difficult patients of the Moscow Research Center for Surgery, Transplantation and Hematology. She leads us into the room and carefully covers her husband with a blanket, adjusting the catheter in his neck. During the conversation, the woman will look away several times, as if she is reliving a month without sleep or peace. Her crystal blue eyes will fill with tears, which she will shyly brush away, because now everything is fine with the family.
Alla and Mikhail BUT-GUSAIM have gone through a difficult journey together and dream of returning home.
49-year-old Mikhail sits down on the edge of the hospital bed and shares his story in a slightly hoarse voice. More precisely, the small part of him that he remembers; we will try to recreate the rest with the help of his wife and doctors.
— I live in Pinsk, I work as the director of the local enterprise Amkodor-Pinsk. Of course, we all knew about the coronavirus and took measures like wearing a mask and constant disinfection. But it’s one thing to read the news, and another thing to experience all the horrors of the disease. On May 11, Monday, I felt unwell: the temperature rose and noticeable shortness of breath appeared. I didn’t immediately attach any importance to this, I thought: it’s nonsense, I drank cold water from the well, and that’s why I caught a cold. But every hour it got worse.
“The next day we called a therapist, he prescribed medications for ARVI,”
Alla helps to put together the puzzle of history. “Literally nothing worked; on Saturday my husband could no longer breathe freely. I resisted going to the hospital, hoping that my body would cope with the disease on its own. But it didn’t work out: on May 17, Mikhail was taken to the intensive care unit of the Pinsk Central Hospital in extremely serious condition. The man admits: even then he was half-conscious. Doctors did a CT scan, which showed bilateral pneumonia, and received a positive test result for coronavirus. There was only one way out - a medically induced coma and connection to a ventilator. From then on, a dream that lasted several weeks began for Mikhail, for his family - a period of fear for the life of his beloved son, husband and father, and for doctors - a time of struggle. Back then no one knew who would emerge victorious from this struggle.
Diagnosis and consequences of coma
Coma can cause disability and even death
During diagnosis, a neurologist must not only identify the causes of coma, but also determine its degree and type. It is difficult to collect anamnesis in this case, since the patient is unconscious. The doctor conducts a conversation with relatives and family to find out whether the patient had any complaints, what he did before falling into a coma, and whether he had chronic diseases.
Examination of the patient, identifying his reaction to pain and the reaction of the pupils to light is of important diagnostic importance. To make an accurate diagnosis, the following procedures are prescribed:
- CT. Computed tomography is an X-ray examination of internal organs. The picture is displayed on the monitor. This examination is quite informative; it shows the presence of tumors, cysts, and hemorrhages in the brain. If a contrast agent is used, kidney function is first checked.
- MRI. Examination with a magnetic tomograph is safe and informative, but in coma there can be difficulties. It is necessary to determine the presence in the patient’s body of metal shunts and prostheses that can be attracted to the device, causing tissue rupture. X-ray radiation is not used in this case; negative effects on the body are excluded.
- Blood analysis. A complete blood examination is carried out, hormone levels, the presence of infections and chronic diseases are determined. A general and biochemical blood test will help identify not only disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, but also complications of coma. A blood test also helps determine the presence of toxins, alcohol, and drugs in the blood.
The consequences of a coma depend on the degree of brain damage. It happens that the patient comes out of a coma, consciousness and motor functions return to him. In some cases, head injuries cause memory loss. If the injury is extensive, the patient may come out of the coma, but the brain functions will remain impaired, only the basic ones will be preserved. This state is called vegetative.
The patient can fall asleep and wake up, swallow food, blink, but does not respond to speech at all, does not speak, and does not walk independently. The duration of this condition, like the coma itself, is difficult to predict. It can last for years and even a lifetime.
How is a person put into a coma?
Preparation depends on why you are being put into an artificial coma. The patient must be transported to the intensive care unit. The state is called in two ways:
- Medication;
- By cooling the body.
The second method is rarely used. Basically, a pre-calculated amount of special medications is administered. Barbiturates and their analogues have a depressant effect on the central nervous system. For immersion, doses are selected according to the stage of anesthesia. Immediately after the start of medication, complete relaxation of the ligaments and muscle frame occurs.
While the subject is in a vegetative state, the indicators of all biological systems are recorded and are under the control of doctors. The duration of an induced coma varies. It depends on the degree and nature of the primary disease. The task of doctors is to cope with swelling of the brain and prevent irreparable damage to the tissues. A normal coma can last from a couple of hours to several years. Medication rarely lasts for a long time.
Meningeal coma
Register Login. Mail replies. Questions are leaders. Who was given mask anesthesia as a child? Did you resist when the anesthesiologist put on the mask? How did you persuade him to breathe into a mask? Leaders in the category Lena-foam Artificial Intelligence. Vlad Oracle. Meningitis and induced coma Nikolas Student, voting 5 years ago Good day, please help me. A good friend of mine was hospitalized with a brain infection. It all started with her having a very bad headache, then vomiting and losing coordination.
I ask you to help me, since I am now in another city and cannot ask the doctors anything. I would like to know what type of meningitis she has and why she was put in an induced coma and whether insurance will cover meningitis? She is now in the Czech Republic taking language courses.
Vote for best answer. Daria Solovyova Master 5 years ago Meningitis can be caused by bacteria or viruses. In this case, we cannot judge this without analysis. An artificial coma is needed to make it easier for the body to cope with the infection.
Apparently the cat had some indications, maybe there were convulsions, maybe brain swelling was starting, or something else. It is very difficult to answer these questions because I have no information about the tests and medical history. Katya Tsvetkova Expert 5 years ago I really hope that Zlata will recover. Yuri Reshetov Sage 5 years ago Meningitis comes in different forms. If she was put into a coma, it means she will be better off. I myself was sick in the army. The main thing is that the puncture is done correctly. Similar questions. They also ask.
An artificial coma, from the point of view of clinical medicine, is a temporary immersion of the patient in an unconscious state, during which there is a deep inhibition of the activity of the cortex and subcortex of the brain and a complete shutdown of all reflex functions. An induced coma is a last resort.
Diagnosis of a person during an induced coma
The condition is diagnosed to study indicators of a person’s brain activity. This is done using the electroencephalographic method. Next, the flow of blood flow to the brain and its oxygen supply is constantly monitored using laser flowmetry. The general condition of the brain is assessed by measuring intracranial pressure in the ventricles of the brain. Diagnostic methods also include CT and MRI; this is mainly carried out to determine the outcome of a medically induced coma.
Medicine has not yet reached a consensus on when coma is considered a hopeless condition. In many countries, it is generally accepted that the state of coma in which a person remains for more than 6 months is considered hopeless.
Since coma is always accompanied by artificial ventilation, indicators must be taken from all vital organs:
- Using an electroencephalograph, data on the functioning of the cerebral cortex is obtained. The device carries out constant monitoring. Without this device, it is impossible to put a person into deep sleep.
- The degree of blood circulation in the brain is measured using a special device inserted into the tissue. Sometimes a radioisotope method is prescribed.
- A ventricular catheter allows you to study intracranial pressure. Thanks to it, the level of oxygen in tissues and the characteristics of metabolic processes at the cellular level are assessed. The technique allows you to learn about all the biochemical reactions occurring in the body. Using a catheter, blood flowing from the jugular vein is taken for analysis.
- MRI and CT allow you to get an overall picture, measure the level of blood flow, and make predictions.
Coma inhibits all functions of the body, including breathing. Therefore, being in a coma is accompanied by artificial ventilation of the lungs, in order to avoid cardiac arrest, the following indicators are taken:
- An electroencephalograph shows data from the cerebral cortex. This is where they begin to enter deep sleep. The device works continuously throughout the entire time you are in a coma.
- Radioisotope control. During this procedure, a special device is inserted into the tissue. It monitors blood circulation in the brain.
- Intracranial pressure. Measured using a ventricular catheter. It records the level of oxygen in tissues, all metabolic processes in organs and tissues. It is used to take blood from the jugular vein for analysis.
- Level of blood flow, predictions of future status. MRI and CT machines help here.
We know why they are put into an artificial coma. But how to get out of it?
Introduction to an artificial coma after a stroke
Sometimes a stroke requires an induced coma. Why is someone put into a coma during a stroke? Medical suppression of the patient's consciousness is sometimes carried out in order to eliminate life-threatening metamorphoses in the brain structures. In case of compression, swelling of the brain or hemorrhage in an organ, the victim is put into an artificial coma.
It is designed to replace anesthesia in the most critical period and promotes vasoconstriction, a decrease in cerebral flow, and also prevents necrosis of brain tissue. Comatosis is induced by administering a controlled high dose of certain CNS depressant drugs under intensive care conditions. This condition can last a long time and requires systematic monitoring by medical staff.
In case of massive hemorrhage, a patient in a coma after a stroke, as a rule, undergoes surgery to remove the formed hematoma. Surgery significantly increases the chances of a favorable outcome.
Comatosis caused by ischemic stroke is treated in a neurological hospital. Such patients are prescribed therapy with nootropic drugs and anticoagulants.
If a person lacks vital functions, he is connected to life support machines. Since euthanasia is prohibited in the Russian Federation, the patient’s life will be supported as long as necessary.
What is a medically induced coma?
This term refers to the unconscious state of the patient, accompanied by a slowdown in blood circulation and metabolic processes in the brain. Also, under the influence of drugs, reflex activity is completely switched off, respiratory processes slow down, and the heart rate decreases. The patient does not feel pain and does not react to external irritating factors.
Medical coma or sedation requires constant medical supervision. The patient is connected to a machine that provides artificial ventilation. This is necessary to maintain respiratory functions and the circulatory system. The human body is considered the most vulnerable during this period; the slightest mistake can provoke death.
Patient in a coma: disconnect or let him live?
People can remain in this state for a very long time. Modern equipment makes it possible to maintain vital functions. But is this advisable?
To answer this question, it is necessary to take into account not only the state of the brain, but also many factors: is there an opportunity to care for the patient, how high is the quality of medical supervision.
The moral side of this issue is no less important. Sometimes a real war breaks out between medical staff and relatives.
To understand whether it makes sense to save the patient’s life, you need to take into account his age, the reasons that caused the coma and many other factors.
The materials posted on this page are informational in nature and intended for educational purposes. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician.

Artificial or drug-induced coma can be considered a special condition in which brain activity slows down and reflexes are completely turned off. A person can remain unconscious from several minutes to several decades. Of course, cases where a person is in a coma for such a long time are rare, but they are still described by medical specialists.
How to get a person out of this state?
The consequences of an induced coma have not been fully studied to this day. They are believed to depend on many other factors. They remove a person from the condition with the help of medications. Particular attention after the procedure is paid to getting rid of complications.
The consequences of an induced coma have not yet been fully studied. They depend on many factors, including the state of the human body entering deep sleep. The patient is also brought out of a medically induced coma with the help of medications. Particular attention is paid to complications.
Since this condition was necessary for the most complex conditions of the patient, rehabilitation takes quite a long time - at least a year. Only after complete recovery of the body can rehabilitation measures be carried out.
Diagnosis of coma
During the period of stay in a state of artificial coma, it is necessary to diagnose the patient’s condition. The effectiveness of administered medications and the degree of vital activity of the body are controlled using:
- An electroencephalogram, which allows you to monitor the state of the cerebral cortex after head injuries, stroke, etc. For this purpose, a special device (electroencephalograph) designed for round-the-clock operation is connected to the patient’s body.
- Radioisotope control - the introduction into tissue of a special device that monitors blood circulation in parts of the brain.
- Ventricular catheter is a method of changing intracranial pressure, fixing the level of oxygen saturation of tissues and organs, and the flow of metabolism in them.
- CT and MRI, which monitor the state of blood flow, allowing one to make a prognosis regarding the further course of the coma.
Constant monitoring of the patient’s vital functions allows one to avoid cardiac arrhythmias and cardiac arrest, and to ensure timely exit from artificially created sleep.
Medical staff monitors the effectiveness of the drugs used and the depth of the coma created 24 hours a day. To avoid the appearance of bedsores on the patient’s body, he is periodically (several times during the day) turned over in bed.
Coma recovery
The consequences of an induced coma have not yet been fully studied. They depend on many factors, including the state of the human body entering deep sleep. The patient is also brought out of a medically induced coma with the help of medications. Particular attention is paid to complications.
Since this condition was necessary for the most complex conditions of the patient, rehabilitation takes quite a long time - at least a year. Only after complete recovery of the body can rehabilitation measures be carried out.
Talking about how a patient is brought out of an induced coma, doctors point out that this process is not one-step and requires preliminary preparation:
- First, the patient is disconnected from the ventilator, training his own breathing.
- Starting from a few seconds, doctors gradually increase the duration of the period of breathing without the device.
- Depending on how long the coma lasted, the patient has to relearn how to walk and perform light care and self-care procedures. The rehabilitation period may take several months.
Recovery from an induced coma occurs gradually. Patients come out of a medically induced coma in different ways: the duration of recovery can be several hours:
- First, reflexes and functions of the autonomic nervous system are restored.
- Consciousness also returns gradually, episodically. In this case, cases of chaotic movements, delirium, and confused consciousness are possible.
- Some patients experience infrequent seizures.
In most cases, patients do not remember anything about the time spent in a coma. Rehabilitation measures are carried out by several specialists at once:
- physiotherapist;
- neurologist;
- masseur;
- psychologist;
- speech therapist.
Doctors are aware that medically induced coma is a risky therapy. Upon completion of treatment, a person will face a long and complex rehabilitation process. Most patients manage to return to their normal life within a year. Moreover, the shorter the duration of the period of stay in a coma, the greater the chance of rapid recovery.
Exit from a medically induced coma is carried out in stages. In the process of removing a person from a comatose state, the ventilator (artificial lung ventilation) is turned off, and substances that support the artificially created state are removed from the body.
After awakening from artificial sleep, organs and systems are always weakened. Normal activity resumes after some time. Recovery takes a particularly long time in patients who have been in a coma for more than one month. In such cases, restoration of the lost ability to self-care and impaired motor activity will be required.
Medical prognosis
After an artificial coma has taken place, the prognosis is not always favorable. The most severe conditions are observed in persons exposed to strokes and severe head injuries. No more than 10% of patients manage to fully recover after drug-induced sleep. About 50% of patients who have been in this condition for several months are unable to lead a full life and die after some time. Up to 30% of patients who survive a coma are completely unable to work and acquire the official status of disabled people.
Despite the potential for an unfavorable outcome and the development of dangerous complications, induced coma is still used in various branches of modern medicine. Medication-assisted sleep is used in critical situations when other methods of saving human life are ineffective.
Forecast and prospect
The saddest prognosis may be for subarachnoid hemorrhage. It occurs as a result of a head injury or rupture of an arterial aneurysm during a stroke. The shorter the period of time in a coma, the greater the patient’s chances of recovery.
Of course, this treatment method is risky, but a successful outcome is not uncommon. After such anesthesia, a person faces a long period of rehabilitation. It takes time for all body functions to be restored. Some people are able to return to normal life within a year, others take a little longer. During the rehabilitation period, it is imperative to undergo a comprehensive examination and follow all doctor’s prescriptions.
The most common complications after a coma can be the following:
- brain damage of various types;
- breathing problems;
- pulmonary edema;
- blood pressure surges;
- heart failure.
Such complications can cause first clinical and then biological death. Vomiting is no less dangerous - masses can enter the respiratory tract. Urinary retention can lead to bladder rupture and peritonitis.
Definition and indications
An artificial coma is a condition that is similar to being under anesthesia, which determines the use of the procedure for patients who need emergency treatment to prevent severe consequences (the development of epilepsy, paralysis, cognitive impairment). Medically induced coma is indicated in situations:
- Surgical intervention.
- Diagnostic examination (invasive, non-invasive).
- Neurosurgical operations.
- Persistent status epilepticus.
Medication-induced sleep is widely used in pediatric dentistry and pediatrics. In some cases, it is prescribed for dental treatment in adults (treatment of pulpitis, installation of orthopedic structures, implants). A number of scientific studies provide evidence of the effectiveness of the procedure in the treatment of persistent cerebral hypertension, which cannot be corrected by other methods.
Disagreements between doctors arise due to inconsistency of results - intracranial pressure levels decrease, but in some cases it is not possible to prevent brain damage. In addition, the success achieved in lowering intracranial pressure is not always maintained after emerging from a medical coma.
Similar results can be observed after an induced coma performed as part of brain surgery or therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the consequences of an ischemic stroke. In a number of patients, brain damage occurs, which subsequently affects cognitive and other functions. Common indications include:
- Carrying out examinations in CT, MRI format.
- Performing cosmetic procedures (complex, long-term rejuvenation procedures).
- Synchronizing the breathing of patients with the operation of the ventilator if artificial ventilation of the respiratory system is necessary.
- Elimination of withdrawal syndrome and alcoholic delirium (a mental disorder characterized by confusion, impaired perception, sensitivity, emotions, cognitive functions).
- Elimination of the consequences of severe TBI.
- Restoring normal blood circulation after resuscitation measures to increase their effectiveness and maintain the achieved positive result.
- Conducting a colonoscopy (endoscopic examination of the inner surface of the large intestine).
A medically induced coma is a state that is achieved through the intravenous administration of sedative pharmaceutical drugs, which allows the patient to fall into deep sleep. These include Sodium hydroxybutyrate, Sodium thiopental, Phenobarbital and other barbiturates. The listed drugs slow down the speed of cerebral blood flow and metabolic processes in the brain, which provokes a number of effects:
- Narrowing of the lumen of cerebral vessels.
- Reducing the volume of the brain matter and, accordingly, tissue compression.
- Decreased intracranial pressure.
- Elimination of swelling of brain tissue.
- Prevention of necrosis of the brain substance.
There are short-term and extended forms. In the first case, we are talking about anesthesia, which is necessary for surgical intervention or diagnostic examination. Extended drug-induced sleep is often practiced in the intensive care unit - this is a condition that is necessary to protect the patient’s brain tissue, which is associated with a favorable outcome in severe TBI, strokes and other pathologies with a complicated course.
The duration of an extended medically induced coma is several hours or days. The indication for the procedure is staged surgical intervention when it is inappropriate to restore the patient’s normal level of consciousness. The extended form is used as part of rehabilitation measures for extensive burns or pneumonia with a severe, acute course in childhood and adulthood.
Patient care
Since the duration of the coma is impossible to predict, the patient needs special care. First of all, we are talking about nutrition. Since it is provided through a tube, the food must be liquid. Often food for children is used (milk formula, fruit and vegetable purees). Hygiene is equally important.
Read also: Stroke poster
To prevent the formation of bedsores and ulcers on the skin and to keep the patient’s body clean, daily treatment with a soap solution is necessary. The patient’s mouth is also cleaned (with wet wipes), and his hair is also taken care of. Long hair is combed every day and washed at least once a week. In addition, the patient's position is regularly changed to avoid the formation of bedsores.
Features of carrying out in childhood
Psycho-emotional reactions of patients often complicate the treatment process and negatively affect recovery. Drug sedation as an alternative to local anesthesia is indicated for some types of dental treatment. Painful manipulations, stress, and unfamiliar surroundings negatively affect the child’s psycho-emotional status.
Usually in such cases, adequate doses of hypnotics (hypnotics) or anxiolytics (tranquilizers, psychotropic drugs that eliminate anxiety) are administered. The disadvantage of sedation is that children are unable to answer important questions during sleep that the doctor may have during treatment.
Deep medicated sleep is indicated in cases where a child is connected to a ventilator. The procedure of tracheal intubation (insertion of a breathing tube into the tracheal cavity) and the lack of speech contact cause discomfort and fear in pediatric patients, which is accompanied by an increase in the concentration of cortisol, a hormone involved in the development of stress reactions.
In parallel, reactions such as increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and tachypnea (rapid, shallow breathing) occur. In these cases, sodium thiopental or Midazolam is usually used.
Consequences and prognosis
This method is used in the most difficult situations, due to the fact that sometimes there are complications after operations. This is especially true for operations in connection with traumatic brain injury, strokes, and arterial ruptures. The sooner you seek help from doctors in these situations, the less sad the consequences after surgery will be.
More than 20% of patients who have experienced an induced coma complain of side effects:
- heart pain;
- disturbance of peristalsis of the small and large intestines;
- renal colic;
- a sharp decrease in immunity.
Often, while in a coma, a person develops diseases of the lungs and upper respiratory tract due to mechanical ventilation.
The procedure is carried out exclusively in the most difficult situations, since there are many undesirable reactions. The worst prognoses are associated with TBI, strokes, and ruptured arterial aneurysms. The longer a person is in this position, the more critical the consequences are.
According to statistics, 25% of patients arriving in an induced coma experience side effects. Violations affect:
- Heart;
- Gastrointestinal peristalsis;
- Kidneys;
- Immunity.
Sometimes, during a coma, an infectious disease of the lungs and respiratory system develops. They are mainly associated with the use of artificial ventilation. Side effects include inflammation of the lungs, bronchial obstruction, formation of adhesions, stenosis, bedsores of the tracheal mucosa.
Some patients noted that during the immersion they experienced vivid hallucinations and nightmares. Around the world, the consequences include neurological disorders in patients after recovery from this state. There may also be delayed reactions. These include:
- Deterioration of memory and thinking;
- Changes in behavioral reactions;
- Loss of some skills and abilities.
In the UK, clinical studies were conducted on people who had been in this condition for more than a year. The following data was obtained:
- 63% emerged from a coma with irreversible pathological processes;
- 27% received varying degrees of disability;
- 10% recovered a satisfactory condition.
Such studies revealed that there are 4 characteristics that influence the prognosis:
- Sleep depth;
- Features of heart rhythm;
- Indicators of brainstem somatosensory reflexes;
- Biochemical blood data.
With the worst prognosis, brain death occurs. This is the stage at which the organ ceases to perform its functions and it is impossible to restore its functionality.
Therefore, risks are always assessed, goals are determined, and for this purpose they are put into an artificial coma. It is believed that full recovery is impossible if a person has been in a vegetative state for more than 6 months.
The prognosis, unfortunately, may vary. The most disappointing results most often result from a rupture of an aneurysm or a stroke, that is, a hemorrhage in the brain. The longer the victim remains in an induced coma, the less chance there is of saving him. When studying the condition, it was found that patients who remained in a coma for more than a year died in 60% of cases or remained at the level of reflexes, in 30% they received disability, 10% of people were restored to normal levels. But in some cases, a medically induced coma is the only saving chance for a person.
Consequences of meningitis
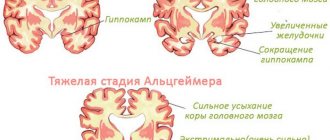
The consequences of meningitis are observed in approximately 10-30% of patients, most of whom are people of retirement age and children under seven years of age.
Early consequences include:

epileptic seizures;- increased intracranial pressure;
- accumulation of fluid under the membrane of the brain;
- changes in the structure of the cranial nerves.
Late consequences of meningitis:
- dementia;
- decreased hearing acuity, hearing loss;
- epilepsy.
The consequences can be not only neurological:
In rare cases:
- memory impairment;
- decreased intelligence;
- stuttering;
- strabismus.
Coma occurs when the soft membranes of the brain become inflamed. The cause of inflammation is bacteria and viruses (meningococci, staphylococci, streptococci, etc.).
The coma state develops against the background of cerebral edema. In this case, the body temperature rises to 41 degrees.
Coma is the final stage of acute inflammation. Before this, the person suffers from a bursting headache, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting.
During a coma due to meningitis, a person's head is thrown back, the lower limbs bend, the skin becomes covered with a rash, and the nerve endings are affected. There may be convulsions and seizures.
A brain tumor
A tumor is the most dangerous possible consequence. It is marked by high fever, headache, rapid heartbeat, seizures and confusion.
In some cases, it can be fatal. The patient requires urgent hospitalization.
Seizures occur in approximately 50% of patients. The first convulsions occur already on the 3rd or 4th day after the onset of the disease.
Paralysis occurs in rare cases. This can only happen if the motor pathways and centers are disrupted.
Hearing impairment
Hearing loss after illness occurs infrequently. It will take about two weeks for your hearing to recover.
However, in some cases, hearing cannot be completely restored.
Possible complications
The effect of a medicated coma is aimed at suppressing brain functions. And since the human brain has not been fully studied, complications may arise. To begin with, it should be noted that there are side effects with long-term use of mechanical ventilation. This effect manifests itself in pneumonia, blockage of the bronchi with adhesions, stenosis, fistulas of the bronchi and esophagus.
After an artificial coma, complications are observed in many patients. The likelihood of their occurrence increases in cases where drug-induced sleep lasted for a long time.
In addition to bedsores, a coma can provoke kidney and heart failure, a sharp change in blood pressure, infectious damage to the body, and neurological disorders. A slowdown in vital functions is fraught with the development of pathologies in the digestive system, problems with urination, rupture of the bladder and the development of peritonitis. With a weak respiratory system, there is an increased risk of pulmonary swelling, pneumonia, and tracheobronchitis.
Diagnostics
The first thing that is most characteristic of meningitis is an acute coma, which can occur even at the initial stage of the disease.
In order to diagnose meningitis in a patient, it is very important to perform a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid. Do not be afraid of this procedure, as it is absolutely safe for humans.
Important!
To determine meningitis and make a diagnosis, it is imperative to perform a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Side effects
Various adverse reactions cannot be excluded:
- pneumonia, adhesions, damage to the tracheal mucosa, bronchitis;
- hallucinations, nightmares during immersion in a state of medical coma, neuralgia after emerging from a coma;
- delayed reactions: a sharp deterioration in memory, changes in behavior, speech, complete forgetting of some abilities, the emergence of new ones, someone cannot start speaking.
Characteristics that influence the state after emerging from a coma:
- sleep duration;
- heartbeat;
- biochemical data during the operation;
- brain death (in this condition it is no longer possible to recover from a coma).
Consequences
Neurosurgeons believe that the consequences that may occur after a medically induced coma depend on the reason that became the basis for putting a person into this state. Ventilation has many side effects. Complications may occur in the respiratory system, which will provoke the development of tracheobronchitis, pneumonia, stenosis, and there is also the possibility of the formation of fistulas in the walls of the esophagus.
As a result of a medically induced coma, consequences such as impaired blood flow, pathological changes in the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, which has not worked for a long time, and renal failure may occur. It is not uncommon for a patient to develop neurological disorders after recovering from this state.