As a rule, doctors are not consulted about this. The problem is solved with the help of analgesics or sedatives. This way the true cause of the discomfort is erased. But an associated type of headache often appears - medicinal (abusive).
In severe cases, the symptoms of cephalgia can reach an intensity that the victim is simply unable to fight - up to visual hallucinations, loss of spatial orientation, amnesia, and numbness of body parts. In these situations, we are talking about urgently preventing disability and saving lives.
Which doctor should I contact if symptoms appear?
From the point of view of pathophysiology, there is injury to axons - processes coming from the spinal roots.
Nerve endings send ectopic signals during recovery. Nerve growth can become a pain generator, especially if scar tissue and neuroma form. Another mechanism for the development of neuralgia is compression or damage to the nervinervorum, the nerve that provides communication between the central nervous system and innervated organs. Afferent impulses arise in the nerve sheath, which lead to peripheral neuropathic pain. Painful manifestations are most severe with surgical trauma to the nerve, the infectious nature of inflammation, for example with herpes. More often, doctors do not determine the exact cause of the pathology and consider it idiopathic.
Conditions with different etiologies can lead to intercostal neuralgia:
- infectious lesions;
- muscle damage;
- subluxation of costochondral joints (at the level of attachment of ribs and cartilages);
- rupture of the costovertebral ligament;
- postherpetic inflammation;
- trauma after surgery.
During acute pain, ion channels of receptors attached to the intercostal nerves along their entire length are activated by molecules that are released during damage and inflammation. From the nerve in the periphery, a signal begins to arrive from the chest area to the thoracic region of the central nervous system.
The cause of intercostal neuralgia can be:
- increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- adhesions after surgery;
- bruises and old fractures in the ribs and chest;
- excessive stress on the abdominal muscles and respiratory muscles;
- scoliosis and uneven tension in the back muscles;
- radicular syndromes;
- infectious lesions and inflammation of soft tissues.
Other factors of neuralgic syndrome:
- pregnancy;
- pressure from the tumor;
- sternum fractures, vertebral compression fractures.
The mechanism of development of chronic intercostal neuralgia is much more complex, since it involves the central nervous system, peripheral damage and psychological influences. The triggering factor is structural injury or inflammation, which forms a focus in the cerebral cortex - a “memory of pain.” It is he who reminds of a once injured nerve in certain situations - severe psycho-emotional stress.
The cause of idiopathic pathology remains unknown. In the absence of trauma, herpes infection, surgery, or a history of thoracic disc herniation, it is assumed that the underlying cause is myositis or excessive muscle tension. Spasm of muscle fibers occurs with prolonged coughing, physical activity, and inflammation. Edema tissue compresses the nerve, causing symptoms of neuralgia.
With intercostal neuralgia, differential diagnosis is important. First, you need to consult a therapist to rule out pathologies of the heart, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. If neuralgia is suspected, the patient is referred to a neurologist who collects anamnesis about injuries, stressful situations, and pain in the thoracic region.
If soft tissue damage is suspected, they are sent to a surgeon, and sometimes to an orthopedist, to exclude the influence of osteochondrosis and hernias in the thoracic region on the appearance of symptoms.
Idiopathic intercostal neuralgia is associated with insufficient opening of the chest on one side - due to postural characteristics. The diaphragm, the main respiratory muscle, is in spasm on one side, which provokes overstrain of the muscles of inhalation or exhalation. An osteopath or chiropractor who studies the characteristics of posture and muscle tone can deal with such a problem.
How to relieve pain with pharmaceuticals
Treatment of neuralgia is carried out conservatively, with the help of vitamins, antibiotics, painkillers, anticonvulsants, sedatives and restorative drugs. To relieve pain from neuralgia, doctors prescribe drugs such as Nise, Analgin, Baralgin, Movalis. To relieve muscle spasms, I prescribe Mydocalm. Painkillers are usually used up to 3 times a day.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are used in injections, ointments, suppositories and tablets. Analgin, Ketorol, Ketonal are used in injections. Non-steroidal drugs against inflammation include Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomecin, Piropsicam, Naproxen.
Ointments such as Menovazine are often used. It warms by increasing blood circulation. It contains natural oils that have a vasodilating effect, such as essential oils, turpentine, as well as pepper tincture and bee and snake venoms. It also contains Nonivamide, Demethylsulfoxide, Niboxyl, and benzyl nicotinate.
It is known to use pepper patches, which heat up, thereby providing an analgesic effect.
Massage
It is strictly forbidden to use massage to relieve attacks of pain in the first three days of illness. It is connected after the acute period of the disease has passed, and it is designed to eliminate residual symptoms, prevent repeated muscle spasms and the development of relapses.
Massage for neuralgia should be carried out only in the absence of even mild pain in the patient.
The main technique for performing massage for neuralgia:
- Stroking - the patient’s skin is stroked with light movements, the person relaxes and becomes receptive to the main massage.
- Rubbing - increases blood circulation in the skin and upper layers of muscles. You should rub actively, but so that there is no pain.
- Kneading. It is effective after preparing the muscles for this process in the two previous stages. The spasm is relieved, blood circulation is improved and the conduction of nerve impulses is improved.
After the massage, be sure to wrap yourself in something warm and avoid drafts and hypothermia.
Symptoms of neuralgia on the right and left
Chest pain is the main symptom of intercostal neuralgia. When a peripheral nerve is damaged, neuropathic pain occurs, depending on external influences. The pain is described as shooting, burning and deep. Patients complain of changes in sensitivity, attacks and soreness of the skin without affecting it. Patients say that there is pain in the chest, pressure, and fever.
The peculiarities of neuralgic pain are that it is diverse. It can be sharp and piercing, burning or, on the contrary, dull, it occurs constantly or in attacks. Sensory and motor nerves are simultaneously affected, so manifestations include:
- tingling;
- paleness or redness of the skin;
- muscle twitching;
- sweating
Unlike heart pain, symptoms occur on the right side, and not only under the shoulder blade, but also in the area of the collarbone and lumbar region, where the abdominal muscles are located.
Pain with intercostal neuralgia is often one-sided - on the right or left. Nerve damage occurs in 80% of cases after thoracotomy during thoracic artery bypass grafting or tumor excision. The nerve may be damaged during resection of a rib compressed by a retractor, or after it is cut. In old age, when the rib joints are damaged, neuralgia develops without significant injury.
Diagnosis of nerve problems
Diagnosis of neuralgia requires the use of different methods, since neither general tests nor visual examination can answer the question - which nerve is causing the problem, or whether it is associated with other diseases. To determine the headache factor, you must:
- undergo a computed tomography scan - the results will show with high accuracy changes in the structure of the neck and other parts of the head;
- X-ray - will show the structure of the bones of different areas;
- MRI will provide information about the condition of soft and bone tissues.
Intercostal neuralgia: how to relieve pain at home?
There are situations in which taking medications is not recommended, or the person himself is not a supporter of taking pills. This is why traditional medicine exists. Homemade recipes are usually used in the form of ointments and rubbing solutions.
For neuralgia, a compress with beeswax is often recommended.
Below are some of them:
- You can prepare a tincture from fir cones, dandelions and pine needles. The preparation is simple, you just need to take all the necessary ingredients and pour vodka over them. This makes a good warming alcohol solution, which is used for rubbing before bed.
- They also make a compress with beeswax. The wax is heated by steam and applied to the sore spot and bandaged; it is recommended to do the procedure before bed.
- Dry lilac buds and pork fat are used to make an ointment. The mixture is made in a ratio of 1:4, after crushing the lilac buds.
Turpentine ointment is one of the most effective remedies.
Very often, patients resort to self-medication; this is justified in cases where a doctor has been consulted and the main treatment has been prescribed. Therapy at home and treatment with folk remedies can only be perceived as auxiliary, emergency measures. The following can be applied in this case:
- Boil the chicken egg, then peel it and let it cool completely. When the egg has completely cooled, we begin to roll it over the chest area, where the pain is localized.
- Intercostal neuralgia: how to relieve pain? Using flax seeds. Pour boiling water over them, let them steam for about five minutes, then put them in a gauze bag. We apply this bag to the skin where the pain is most noticeable.
- Those who suffer from pain due to intercostal neuralgia should at least once try the folk remedy made from aspen buds. Fresh buds are taken, crushed, then take one tablespoon and add liquid Vaseline to it (the volume should be at least four tablespoons), mix well to obtain a homogeneous mass. The consistency will be like an ointment; rub it into the skin of the chest, where the pain is localized.
- Tincture of iodine can also relieve pain quite well. One tablespoon is mixed with glycerin in a ratio of 1 to 2, then everything is mixed well until smooth. With this mixture, meshes are regularly drawn on the patient’s chest.
- Turpentine ointment is one of the most effective remedies. Take two tablespoons of turpentine, mix with four tablespoons of Vaseline, thoroughly mix the ingredients until smooth. The ointment should be elastic. If pain occurs, it is necessary to lubricate the affected area.
The main thing to remember is that it is important not only to relieve pain, but also to treat the cause directly. Therefore, all treatment at home should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
How to treat intercostal neuralgia with physiotherapy?
What methods of physiotherapy exist we will consider below.
- Transcranial electroanalgesia (treatment is carried out using a low-frequency current pulse, has an analgesic effect of approximately 20-40 minutes for a course of 5 to 10 days).
- Diadynamic therapy (impact of pulsed current only in the form of a half-sine wave to relieve pain, procedure for 20 minutes, from 5 to 7 days).
- Fluctuarization (current relieves pain and tissue regeneration improves, approximately 6 procedures from 5 to 15 minutes).
- UHF therapy (treatment is carried out by an ultra-high frequency electric field, reduces pain, participates in tissue nutrition and restores the body's defenses, from 6 to 12 sessions of 5-20 minutes are carried out).
- Ultrasound therapy (improves blood circulation, relieves pain, session 12-15 minutes for 6-12 procedures).
- Darsonvalization (uses low current, promotes nutrition and blood supply to tissues, course 10-15 days for 10-15 minutes).
- Magnetotherapy (works using a high-quality magnetic field, relieves pain, session lasts 15-30 minutes, up to 20 procedures).
- Laser therapy (relieves pain, provides general strengthening of tissues, is treated in 10 sessions of 10-15 minutes).
- Electropheresis with anesthetic and analgesic medication.
- Applications of paraffin, ozokerite (improves blood flow, metabolic processes, promotes regeneration, course 10 days for 20 minutes).
- Treatment with mud (relieves pain, improves regeneration and promotes tissue nutrition, relieves inflammation)
- Acupuncture (improvement occurs due to the effect on biologically active zones, improves blood circulation and relieves pain, up to 20 procedures are calculated).
Surgical intervention
Surgeries are indicated only in rare cases when physiotherapy and medications do not produce any results in eliminating scalp neuralgia. Any surgical intervention in the functioning of nerve endings can lead to irreversible consequences and complications. The most commonly prescribed methods are:
- nerve dissection or destruction using an inflatable container - the procedure is necessary to eliminate severe pain. If the operation is performed correctly, no complications arise;
- removal or modification of a vessel that irritates the nerve - relieves pain well, but can reduce the sensitivity of the facial muscles;
- alcohol blockades - freezing the damaged fiber, which relieves pain for a short period of time;
- glycerin injections – a course of treatment eliminates pain for 3-5 years.
Treatment methods for intercostal neuralgia
Depending on the cause of the pain, a treatment plan is selected. Initially, Ibuprofen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, but not longer than 5-7 days. It is better to apply topical lidocaine patches to block the nerve.
For recurrent attacks, various levels of intervention are carried out to help cope with pain:
- Selective radiofrequency ablation is used to reduce pathological impulses from nervous tissue.
- If the nerve is affected by the adhesive process after surgery, the suture is excised for a complete cure.
- Injecting pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs directly into the nerve sheath helps relieve chronic pain.
- Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) therapy is used to activate nerve function and improve conduction.
The course of treatment for intercostal neuralgia includes not only painkillers. Several groups of drugs are needed:
- Anticonvulsants (Pregabalin, Gabapentin) dampen excess excitation signals, inhibiting the conduction of pain impulses.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline) and serotonin reuptake inhibitors (Duloxetine) relieve tension in chronic pain syndromes.
- Relieving swelling is provided by venotonics, drugs from the group of diuretics. Sometimes antihistamines are prescribed.
- In case of severe inflammation, corticosteroids are used. They are necessary for postherpetic neuralgia.
- Antiviral drugs for herpetic rashes reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
Helpful information
At home, painkillers and local distraction medications are prescribed - menovazin, ointment with ichthyol, cooling or warming gels with a combined composition (diclofenac with menthol) are suitable.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia is supplemented with B vitamins, namely B1, B6, B12, which accelerate the restoration of the nerve sheath, reduce inflammation and pain. Neurologists practice prescribing the drug Neurorubin in tablet form.
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy
Intercostal neuralgia is often caused by poor posture. Exercises that strengthen the postural muscles alleviate the symptoms of the pathology. The goal of the workout is to relieve the back muscles and open the chest. Performed while standing with your back against the wall:
- move the head back, giving the cervical lordosis a normal shape;
- imagine that your shoulders do not lean back, but move apart to the sides;
- smooth out excessive lumbar lordosis - remove the habit of hyperextending the lower back when trying to straighten up: near the wall, try to lay the lower part of the ribs on the surface as you exhale.
Place your hands on the front of your ribs and inhale, opening your chest to the sides. Perform the exercise for five minutes 3-4 times a day, trying not to increase the deflection in the lower back while inhaling.
Among the methods of physical therapy for intercostal neuralgia are:
- acupuncture;
- manual therapy (to restore the thoracic and cervical spine, ligaments and muscles, relax the fascia of the nerves);
- therapeutic massage with warming creams and ointments (aimed at relaxing the muscles in the chest and back, relieving pain);
- Shiatsu (pressure on biologically active points of the body that are associated with the affected organ);
- osteopathy (a method that allows you to restore the position of the anatomical parts of the chest).
Physiotherapists use gentle Graston therapy techniques, ultrasound to soften the muscles surrounding the nerve, and kinesiological taping. Home exercises with a foam roller will help relax the fascia of the chest and back. Heat helps to temporarily relax muscles, and ice blocks inflammation and swelling and relieves acute pain.
At home, you need to do stretches by raising your arm above your head and leaning to the side to open the chest, stretch the intercostal muscles, blood vessels and nerves between the ribs.
Stretching in the doorway will help with spasm of the pectoral fascia. Place your arms bent at an angle of 90 degrees to your body on the doorposts and lean forward slightly, stretching the front of your chest.
To stretch the back muscles, use a table or a high stand for support. Place your palms on the surface, step back and bend, leaning forward with straight legs.
Repeat stretching exercises 3-4 times a day for 30-60 seconds. Self-massage of the lower and inner side of the chest just below the collarbone will help relieve pain from intercostal neuralgia.
Massage
Osteopathic massage is performed to release the nerves. The specialist will relax the muscles and fascia of the neck to improve blood circulation and function of the thoracic region. Then the mobility of each rib will be worked on, releasing the nerves.
Acupressure massage affects reflex zones, improving blood supply to organs and relaxing their ligaments. Restrictions in the mobility of the pleura after inflammation or pancreatitis can provoke neuralgia.
Muscle pain due to active physical exercise, respiratory diseases accompanied by thoracalgia and neuralgia. Chinese acupressure works against spasms:
- A point on the midline of the sternum at the height of the fourth intercostal space between the nipples. Massage for 1-3 minutes.
- A point at the level of the fourth intercostal space on the sides of the anterior midline. Press with your thumb, index and middle fingers for 1-2 minutes.
- In the middle of the supraclavicular fossa (above the collarbone) in the center - press with the index and middle fingers for 1-3 minutes.
- Points on the lateral part of the chest at the outer acromial edge of the clavicle. Press with your thumbs for a minute.
- A point on the back 1.5 cm away from the spinous process of the fifth thoracic vertebra. Press and massage with your thumbs for 2 minutes.
- A point on the inside of the forearm above the transverse crease of the wrist, the width of your own palm. Massage for a minute until discomfort disappears.
Vacuum massage with cups improves blood supply to the muscles, cleanses them of waste products and relieves swelling.
You can use the vacuum method at home. Ordinary glass jars are installed along the paravertebral area along the entire back. Using a soft jar, a massage is performed - rubbing along the ribs to stimulate blood supply. Vacuum massage relaxes muscles and provides blood flow to restore the nerve.
Heat helps relieve spasms and release nerve endings. When using woolen belts and wearing warm sweaters, patients feel better – the intensity of pain decreases. You can use a regular heating pad, an electric heated blanket, sew a bag and fill it with salt, which is heated in a saucepan. Pepper plaster and regular mustard plaster are suitable.
At home, applying glycerin with iodine to the skin will help reduce pain. The solutions are mixed in equal parts in a bottle. Using cotton wool, the product is applied to the ribs, excluding the spine. The procedure is performed before bed, after which you put on a cotton T-shirt and go to bed under a blanket.
How to relieve pain during pregnancy?
Before taking any measures, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Any medications for neuralgia during pregnancy should be used only as directed by a doctor.
Doctors usually prescribe the following treatment:
- Acupressure helps relax muscles. It is the spot, regular one that is contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Medicines that relieve pain.
- Using bee venom ointment.
- Light exercises that improve blood circulation.
- Bed rest.
- If the pain is unbearable, the blockade is removed with novocaine.
- Pain-relieving ointments and rubbing solutions are allowed for pregnant women.
- Complex of vitamins, including B and C.
- Reflexology and physical therapy.
The doctor always selects individual treatment based on the development of the disease, its stage and, of course, the duration of pregnancy.
It is impossible to completely prevent the development of neuralgia in pregnant women. But to prevent it from occurring, you need to adhere to several rules: do not allow excessive physical activity, do not overcool, avoid large crowds of people during epidemics, wear a bandage, strengthen your immune system, eat right, do not be nervous, take care of yourself in all respects.
Self-medication for neuralgia is unacceptable; you should definitely consult a doctor. Timely measures taken will help avoid many complications.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia
People think about preventing attacks in case of a recurrent form of neuralgia, which is associated with postural characteristics. The goal of prevention is to increase thoracic mobility:
- Wrap the chest with a towel, inhale with resistance and open the ribs to the side for 5-10 minutes a day.
- Use gymnastics with arm swings and torso turns, simulating walking, to improve the mobility of the rotational vertebrae of the thoracic region.
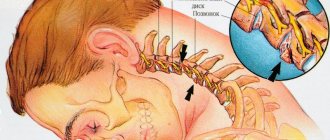
- Avoid moving your head forward or propping your cheek with your fist - all this causes an imbalance in the tone of the cervical muscles.
You can prevent the occurrence of intercostal neuralgia and neuritis, as its manifestations, by:
- avoiding hypothermia and colds;
- promptly treat inflammatory diseases of adjacent organs and tissues.
Smoking promotes inflammation and injures the capillaries with each breath, causing tension in the lining of the lung. The result is a spasm of the respiratory muscles. You should not use compression wraps or corsets if there is spasm of the intercostal muscles, as this makes it difficult for the chest to move.
The main symptom that is characteristic of this disease is severe pain.
The main symptom that is characteristic of this disease is severe pain. In this case, the pain has the character of an intense burning sensation, lumbago, and can be aching, sharp, piercing and sharp. Due to the fact that the pain is very pronounced, this can affect changes in the functioning of the heart - provoke tachycardia; breathing can also be impaired; at the time of shooting, a person is simply not able to breathe.
If you press on the ribs and the area adjacent to them, pain and discomfort will also inevitably occur. Physical activity, overexertion, overwork, coughing, sneezing, careless, sudden movements - all this aggravates the pain symptom. Therefore, the first thing that needs to be done is to relieve the symptoms, which simply limit a person’s physical activity and prevent them from living fully, and only then treat the cause of the disease, that is, the pinching or inflammation itself.
Causes
Why does intercostal neuralgia occur, and what is it? The main cause of neuralgia is compression and irritation of the intercostal nerves due to inflammatory and degenerative changes in the spine. Most often, the pathology does not occur independently, but develops against the background of another disease.
In this regard, there are certain causes that lead to the occurrence of intercostal neuralgia:
- back and chest injuries;
- hypothermia;
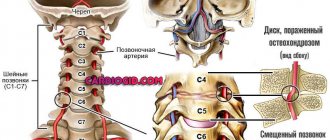
- spinal pathologies – scoliosis, deforming spondylosis, osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs;
- internal (diseases of internal organs) and external (taking medications, exposure to heavy metals) intoxication;
- past infectious diseases (tuberculosis, herpes zoster, brucellosis);
- malignant tumors of the lungs and pleura;
- diseases of the nervous system (multiple sclerosis, polyradiculoneuritis);
- decreased immunity;
- allergy.
In the vast majority of cases, the “culprit” is osteochondrosis, which leads to the destruction of cartilage tissue, as a result of which the nerve roots are compressed and sharp pain occurs. Pathological changes in the spinal column cause muscular-tonic syndrome (impaired muscle tone), which greatly complicates the situation.