“My daughter was born two weeks premature. I can’t say that the pregnancy was easy and without complications. While I was carrying the baby, I managed to suffer from an acute respiratory viral infection and even ended up in the hospital with renal colic. But at the antenatal clinic they reassured me: “Everything is fine, there is no reason to worry.” I wasn't worried. And when there was less than a month left before the planned meeting with my baby, my legs began to swell and my blood pressure began to rise. The gynecologist looked at my tests and said: “We can’t wait, we’ll give birth,” and straight from the consultation I went to the maternity hospital. An examination at the maternity hospital showed that the child had severe hypoxia. The doctors spoke to each other in some incomprehensible medical terms, and I sat on a chair, roared, stroked my stomach and asked: “Be patient, dear, be patient a little. Everything will be fine with you."
I was given an emergency caesarean. I remember how much I worried that they wouldn’t bring me a baby for a long time. “Rest, mommy, while you can. Then you won’t sleep for a long time,” the elderly midwife told me. I didn’t think then that her words would become prophetic.
Our problems started almost immediately: he doesn’t want to take the breast, but he will take two sips and sleep, after 15-20 minutes he wakes up and screams. And so on in a circle. I followed doctors like a stray dog. I held my daughter with one hand and the aching stitch with the other. “Doctor, look at my child. I think we have a problem." In the department they already looked at me like I was having a seizure. And a week later we were discharged.
And then real hell began. My daughter screamed and cried around the clock. She slept fitfully and only in her arms. And the local pediatrician said: “She’s just hungry, feed her better,” “There’s not enough milk, feed her,” etc. We went to the doctors. They changed one neurologist to another, but no one saw any serious health problems in my daughter.
It got to the point that even my husband told me: “You need to be calmed down. The child just feels your condition, so he doesn’t sleep.” He took the pillow and moved to another room. This is what broke me. I thought that he was probably right. I just put up with the constant crying of my baby and slowly went crazy from fatigue.
We continued to go to the clinic, received vaccinations as scheduled, and none of the doctors even doubted that perhaps these vaccinations were contraindicated for us.
Doctors started talking about the fact that there was “something wrong” with the child when my daughter was 11 months old. It seems like we need to start walking, but we just learned to sit normally. And then everything began to grow like a snowball. And more and more often the consequences of intrauterine hypoxia began to slip into the words of doctors. Well, why only now?
Now my daughter is already 3.5 years old. She still doesn't talk. At all. We haven’t heard either “mom” or “dad” from her yet. Her neurological status is described in a way that is more reminiscent of a medical encyclopedia. Mountains of medications, endless consultations with doctors and complete uncertainty about the future... But most importantly, it’s so disappointing that I was right. If the doctors had paid attention earlier... why talk about it now.”
This letter came to our editors from the city of Aktobe. Who is right in this situation and who is wrong is not for us to judge. But this is only one story, one of tens and even hundreds of thousands of similar stories. This phenomenon is too common - fetal hypoxia. But does it always lead to severe and sometimes irreversible consequences? And is it possible to prevent the development of complications? We tried to collect brief and objective information for future parents.
Hypoxia, oxygen starvation of the fetus - expectant mothers hear these terms very often. They scare some people, while others, on the contrary, do not pay much attention to them.
Characteristics of the pathology
Brain hypoxia is a lack of oxygen supply to the brain; pathology in a newborn often leads to serious impairments in physical and mental development. Perinatal (occurring from the 22nd week of gestation to the 7th day of the baby’s life) encephalopathy of hypoxic etiology is diagnosed in 5% of newborn infants.
Damage to brain structures makes up 60% of the total number of diseases that affect the nervous system and are identified in childhood; they often arise as a result of disruption of the birth process. The consequences of oxygen starvation of the brain in newborns are expressed in the development of diseases - cerebral palsy, MMD (minimal brain dysfunction), epilepsy.
Under hypoxic conditions, metabolic processes are disrupted, in particular the peroxidation of lipid fractions (LPO), which leads to the accumulation of free radicals and the development of hydroperoxide (conversion of lipids into primary LPO products with subsequent damage to the lipid layer of the cell membrane). As a result, the permeability of neuronal membranes increases, and a disorder of cerebral hemodynamics occurs, occurring according to the ischemic-hemorrhagic type.
Types of hypoxia
Impaired oxygenation (oxygen saturation) of the blood correlates with peripheral and central hypoxia. In the first case, the pathogenesis involves pathological processes affecting the respiratory tract and alveolar blood flow. Dysfunction of the respiratory center underlies the pathogenesis of central hypoxia. Etiological factors provoking the occurrence of peripheral hypoxia:
- Respiratory distress syndrome (severe respiratory distress, detected mainly in premature newborns, which is associated with underdevelopment and immaturity of the lungs).
- Aspiration (entry into the fetal respiratory tract) of amniotic fluid.
- Pneumothorax (presence of air in the pleural cavity of the lung).
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (a disease of morphologically immature lungs, detected mainly in premature infants).
- Congenital anomalies of the respiratory system.
Central hypoxia of the brain in children develops as a result of arterial hypotension, arterial hypertension, and maternal anemia. Hypoxic encephalopathy can be provoked by malformations of the fetal brain and placental insufficiency (impaired placental function).
There are chronic (perinatal) and acute (labour) forms. The first correlates with disruption of the course of pregnancy, the second is associated with injuries and pathologies resulting from labor.
Why is this happening
In newborns, oxygen starvation can be antenatal (prenatal) or postnatal in nature. The following phenomena can cause hypoxia in the fetus:
- infectious diseases suffered by a pregnant woman in the 1st trimester;
- intrauterine infections (toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, syphilis, etc.);
- threatened miscarriage;
- carrying multiple fetuses (multiple pregnancy);
- pathologies of placenta formation, disruption of blood flow between the maternal body and the fetus (for example, with compression of the umbilical cord loop);
- complicated pregnancy history (maturity, gestosis, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, etc.);
- blockage of the fetal respiratory tract with amniotic fluid or mucous masses;
- malformations of the child (immaturity or pathologies of lung tissue, metabolic disorders, etc.);
- diseases of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus), kidneys, bronchi and lungs (asthma, chronic bronchitis) and cardiovascular system (arterial hypertension, heart defects) in the expectant mother;
- Rhesus conflict (blood group conflict is also a risk factor);
- smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs, treatment with sedatives during pregnancy.
Most often, hypoxia in a newborn develops during childbirth. Common causes of its occurrence include:
- premature, rapid or prolonged labor;
- a long anhydrous period after premature rupture of fetal fluid (amniotic fluid);
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- natural childbirth with multiple fetuses;
- weak labor activity;
- eclampsia.
An additional risk factor for hypoxia in children is low fetal weight.
Postpartum oxygen deficiency (asphyxia) can develop as a result of improper care of the newborn, incomplete expansion of the lungs and subsequent pneumopathy, as well as congenital defects and infections that lead to impaired cerebral circulation, depression of the function of the respiratory center and other respiratory disorders.
Causes
Hypoxia, which causes brain damage in newborns, has a polymorphic etiology. The occurrence of pathology correlates with many influencing factors:
- Mother's age is under 20 years or over 40 years.
- Separation of the placenta before the due date.
- Placenta previa (incorrect location).
- Preeclampsia (a complication of pregnancy in the third trimester associated with changes in the mother’s blood pressure, which increases sharply or slowly and evenly).
- Violation of the due date (premature, late).
- Meconium (the baby's first feces) enters the amniotic fluid.
- Pathologies of the fetal heart (bradycardia, tachycardia, muffled tones).
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Diseases suffered by the mother during gestation.
- Mother has a history of diabetes mellitus.
- Uncontrolled use of pharmaceutical drugs by the mother during pregnancy.
Placental insufficiency is considered the main cause of hypoxia in the antenatal (prenatal) period. The pathology occurs against the background of deterioration in the absorption of nutrients necessary for the development of the fetus, substances entering through the placenta, and due to a disruption in the process of their absorption. Accompanied by impaired gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide).
Labor hypoxia (acute)
Hypoxia can also occur during childbirth, then it is called intrapartum. This type (acute hypoxia) most often no longer depends on the mother, but is a consequence of delayed or unqualified obstetric care. Therefore, every woman in labor, going to the maternity hospital, should imagine what qualified obstetric care during childbirth and the normal birth process should look like, and not allow experiments to be carried out on herself or put up with frankly incorrect medical care.
In the early 60s, aggressive obstetric care began to be widely practiced in the Soviet Union, even during normal births, with the use of birth stimulants. These methods include: drug stimulation of contractions and puncture of the amniotic sac. Such assistance poses a serious threat to the health of both the newborn and the mother. A quick birth is not natural, because the organisms of the child and the woman in labor must adapt, while harsh intervention during childbirth is fraught with birth injuries and acute fetal hypoxia is often the result of unjustified actions of medical staff.
Read also:
What foods can cause colic while breastfeeding?
The main causes of hypoxia during childbirth
- Placental abruption prematurely.
- Weakness of labor.
- Umbilical cord entanglement.
- Polyhydramnios.
- Multiple births.
Diagnostics
Instrumental methods include neurosonography, electroencephalography, lung radiography (if congenital pneumonia and other inflammatory processes in the respiratory organs are suspected). Infants with low body weight, identified hypoglycemia (low glucose levels) and insufficient glycogen stores are especially susceptible to damage to brain tissue due to oxygen deprivation. The condition of the newborn is assessed using the Apgar score. Criteria used:
- Appearance and condition of the skin (color).
- Heart rate (pulse).
- Facial expression (contraction of facial muscles), which occurs as a response to an irritating factor.
- Motor activity, muscle tone.
- Breathing parameters.
For each criterion, the condition is assessed on a scale from 0 to 2 points, then all points are summed up. Testing is carried out at 1 and 5 minutes after the baby is born. A score of 8-10 points indicates a satisfactory condition of the baby. A score of 6-7 points (1 minute) indicates mild hypoxic damage, 4-5 points (1 minute) is a sign of centralization of blood circulation, which is accompanied by a disruption in the functioning of organs, primarily the central nervous system.
A score of 0-3 points indicates a severe degree of oxygen starvation, which occurs with severe disruptions in the functioning of organs and systems. A comatose or shock state may develop. The baby begins to hear from the first minutes of life; testing in accordance with the criteria of the Apgar scale reveals its sensitivity to external stimuli: when the doctor inserts a catheter into the baby’s nasal passages, a healthy baby begins to sneeze.
Diagnosis of chronic hypoxia during pregnancy
It is quite difficult to diagnose oxygen starvation in the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy without functional diagnostic equipment, so the expectant mother needs to take care of her health as best as possible - spend more time in the fresh air, eat well and rationally, avoid contact with toxic chemicals, which, by the way, , include household chemicals and some types of products for salon procedures. You should also give up all bad habits and avoid stressful situations if possible.
Symptoms
There are 3 periods of development of perinatal encephalopathy, which occurs as a result of oxygen starvation - acute (from the moment of birth to 30 days of life), restorative (from 30 days to 1-2 years of age), outcome. The clinical picture varies according to the period of its course. The acute period is accompanied by the following syndromes:
- Increased neuro-reflex excitability. The symptom complex is typical for a condition of 6-7 points (Apgar). Typical signs: increased spontaneous motor activity, sleep disorder (restless, interrupted), difficulty falling asleep, prolongation of the waking phase in the structure of the day, unmotivated crying. In parallel, dystonia (pathological contraction) of muscles, increased unconditioned reflexes, tremor (shaking) of the limbs and chin area are observed.
- Convulsive. Typical signs: tonic-clonic or tonic seizures. In parallel, clonic convulsions of local localization and hemiconvulsions (convulsions in one half of the body) occur.
- Hypertensive-hydrocephalic. The syndrome is typical for a state of 4-6 points (Apgar). It manifests itself as an increase in the diameter of the skull, divergence of the seams of the bone structures of the skull, and bulging of the fontanel. Typical signs: horizontal nystagmus, descending strabismus, muscular dystonia, flinching, involuntary Moro reflex (extending arms to the sides). Signs often observed: sleep disturbance, cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin).
- Oppression. The syndrome is typical for a state of 4-6 points (Apgar). Typical signs: lethargy, physical inactivity (weakened muscle activity), weakened motor activity, hyporeflexia (weak innate reflexes).
- Comatose. The syndrome is typical for a state of 1-4 points (Apgar). Typical signs: lethargy and adynamia (lack of motor activity), hypotonia and atony (lack of tone) of muscles. Reflexes do not appear, the pupils do not react to a light stimulus, and there is no reaction to pain. Signs observed: disturbance of the respiratory rhythm, the appearance of apnea (stopping breathing), muffled heart sounds, decreased blood pressure values.
More often, several syndromes appear in a complex. The acute period is characterized by a predominance of general cerebral disorders without clearly demarcated focal symptoms. In premature babies, increased neuro-reflex excitability may indicate reduced levels of convulsive readiness, which is associated with the activation of convulsive, epileptiform processes.
Treatment methods
If symptoms characteristic of an acute period of oxygen starvation of the brain are detected in children, treatment includes organizing ventilation and correcting disorders caused by respiratory distress syndrome. Surfactant analogues are prescribed, which promotes regression of neurological symptoms. Main directions of therapy:
- Antioxidant (reducing the effects of oxidative stress).
- Metabolic (regulation of metabolic processes).
- Vascular (strengthening and regulating the tone of the vascular wall).
- Dehydration (increased osmotic pressure of blood plasma).
- Anticonvulsant, antiepileptic.
Therapy is aimed at normalizing homeostasis (self-regulation) and metabolism, improving tissue metabolism, reducing the permeability of the walls of the elements of the circulatory system. Massage, therapeutic exercises and other health procedures are indicated during the recovery period. In parallel, symptomatic treatment is carried out aimed at eliminating the neurological deficit.
Massage and exercise therapy for children with hemisyndrome
Massage for a child with hemisyndrome is done in a differentiated manner. The tense side is massaged deeply, slowly, alternating with passive stretching of the tense muscles. The healthy side can be massaged in a general strengthening mode.
Let's consider an example of massage for left-sided hemiparesis in a child under 1 year old. You can do it according to the following scheme: massage the back, then the front surface of the body, stomach and chest, then massage the legs, first the healthy one (right), then the tense one (left), then massage the arms, also first the healthy one, then the tense one. The neck can be done at the end of the session. When massaging the back, a relaxing massage is done on the left, and a slightly tonic massage on the right of the spine. When massaging the pectoral muscles on the left, you can move your left hand away from the body and massage the pectoral muscle in a stretched state. After the massage, you need to do exercise therapy, its active part. When conducting gymnastics, we try to do regular exercises appropriate to the child’s age, which teach the child the necessary skills. Of particular interest will be those exercises in which the ontogonists of tense muscles are tensed, because the tension in them becomes less. The goal is to achieve symmetry of movement and equal strength between the right and left parts of the child’s body in all exercises.
Massage, exercise therapy, physical therapy, these are the most important ways to eliminate hemisyndrome in children.
If your child has hemisyndrome, try to carry out treatment with the help of a professional pediatric massage therapist or exercise therapy instructor. Don’t waste time, you basically have it for about 1 year, everything that was not removed from the child before walking will then become more and more difficult to eliminate every month. After 2 years, it is generally difficult to achieve even small results in the treatment of hemisyndrome.
If it so happens that you don’t have children’s massage therapists nearby, you can then try to treat yourself, it’s better than nothing. If you find yourself in such a situation, you have difficulties in self-treatment, you can write to us by mail [email protected] or WhatsApp +79266057470, we will try to advise you. If you have any questions on this topic, also write to us, we will definitely answer.
The author of the article is massage therapist Alexey Vladimirovich Matrosov.
Possible consequences
The consequences for the brain during hypoxia in a newborn depend on the duration of the pathological process. In infants, the amount of oxygen used by the brain is about 50% (in adults - about 20%). A large amount of incoming oxygen causes accelerated metabolism of oxidation processes.
Depending on the period of oxygen starvation, changes in the medulla can be expressed in the form of local edema (mild form) or necrotic tissue damage (severe form), accompanied by hemorrhagic impregnation (hemorrhage). If hypoxia is combined with ischemia, damage occurs to areas sensitive to oxygen deficiency (cortical structures, thalamus opticus, cerebellum) with the formation of foci of necrosis. There are different degrees of the pathological process:
- 1st degree. Edema-hemorrhagic.
- 2nd degree. Gliosis of encephalic origin.
- 3rd degree. Leukomalacia (necrotic changes in the white matter).
- 4th degree. Leukomalacia accompanied by hemorrhage.
Cerebral hypoxia of 1st and 2nd degree in a newborn is curable. Hypoxic damage to brain structures of the 3rd and 4th degrees occurs against the background of irreversible death of neurons with the ensuing consequences - brain dysfunction, the appearance of severe neurological symptoms, and the risk of death. Hypoxia in newborns is in 2nd place after prematurity in the overall structure of causes of perinatal mortality.
Hypoxic encephalopathy, which develops during the perinatal period, is a pathology that can have serious consequences. Regular visits to the doctor during pregnancy and compliance with medical recommendations reduce the risk of developing pathological processes. Correct treatment of the newborn will help reduce the negative impact of oxygen deficiency on the brain.
The brain is the most complex and important organ in the human body. For it to function well, many factors are necessary. One of the most important conditions for normal brain function is sufficient access to oxygen. The brain of a newborn is especially sensitive to oxygen starvation. The damage that results from cerebral ischemia can leave an impact for the rest of your life. How modern medicine copes with this condition and whether there are reliable methods of prevention, you will learn by reading our article.
Brain hypoxia in newborns - consequences of the disease
Hypoxia in children can occur during fetal development or at birth. Lack of oxygen can lead to health problems for the child. If cerebral hypoxia is diagnosed in newborns, the consequences are of interest to all parents.
Much will depend on how long the baby lacked oxygen, as well as on the timeliness and correctness of the decision. The pathology is quite common, and it is found in 6% of newborns. Parents need to understand what they are dealing with so that the right measures can be taken.
Characteristic
Brain hypoxia in newborns is a pathology in which the child experiences a lack of oxygen supplied from the mother to the fetus. Often this problem occurs during pregnancy, so a woman needs to closely monitor her health and the condition of the baby.
Hypoxia occurs acute and chronic. The first type often occurs due to a difficult birth, which significantly affected the health of the child. In the chronic form, the child experiences oxygen starvation for a long time.
It is important to know the features of this condition in order not to aggravate the situation and prevent a significant deterioration in the baby’s health.
Lack of oxygen cannot be called a safe pathology, because it has many complications.
The disorder affects the internal organs, especially the lungs, heart and liver. In some cases, the baby may even receive disabled status. Only timely treatment will prevent the occurrence of dangerous complications.
Varieties
Brain hypoxia in children can develop due to both external and internal factors. There are several types of pathology that are important to identify for further treatment.
Types of hypoxia:
- Respiratory hypoxia . It appears due to the fact that a person’s respiratory system is impaired. Often the disease appears as a side effect of asthma, brain damage and muscle paralysis.
- The disease is hypoxic in nature a. It is determined when the head does not receive enough oxygen from the outside world. A similar situation arises, for example, when climbing to a height.
- Circulatory pathology . It is isolated if a person has diseases of the cardiovascular system. Against this background, there may be a disturbance in blood flow, due to which oxygen does not reach the central nervous system in sufficient quantities. As a result, the person is in a state of shock. Ischemic stroke often occurs due to this condition.
- Tissue pathology . It appears when there are problems with the absorption of oxygen by cells. Fasting occurs due to enzyme blockade. Often, pathology can appear if a person is constantly in contact with poisons or drugs hazardous to health.
- Hemic hypoxia . This disease occurs when there is a problem with oxygen transportation. The vessels lack this element, as well as hemoglobin. The problem occurs when poisoning is caused by poisonous elements, as well as gases.
Regardless of the type of disease, it is important to start treatment in a timely manner to prevent serious complications. First, you will have to undergo diagnostics so that you can be sure of the presence of a specific disease.
Signs
When cerebral hypoxia occurs in a newborn, various manifestations occur that can be noticed by both parents and doctors. It is impossible to diagnose the pathology on your own, so it is important to immediately consult a doctor . After the examination, it will be possible to clearly say what problem we encountered.
Main symptoms:
- Malfunctions of the heart. Murmurs, increased pulse, arrhythmia, and bradycardia may be present.
- The child has a small blood volume.
- A newborn baby does not cry at the moment of birth.
- There are vascular thrombi.
These deviations in most cases are detected in the maternity hospital. Finding them is the task of doctors, not parents. At the same time, the mother can independently notice disturbances in the child, which may indicate hypoxia. You should definitely pay attention to them in order to diagnose hypoxia in a timely manner.
Signs:
- Presence of seizures.
- Restless sleep in a newborn.
- Constant crying for no reason.
- The child shudders when touched.
- Trembling of arms, legs and chin while crying.
- Impaired muscle tone.
- The baby is constantly freezing.
In this case, you should definitely consult with your doctors in order to take timely measures. At the same time , it is important to determine the degree of hypoxia in order to understand how serious the violations are. If oxygen starvation is severe, then the most unfavorable consequences are possible.
Apgar grades
A child is given a grade at birth based on how well all systems in the body function. For this purpose, the Apgar scale is used, which is used by doctors. First, the condition is assessed in the first minute of life, and then after 5 minutes.
What are the possible points:
- From 0 to 3 – severe form of hypoxia.
- From 4 to 5 – average severity of oxygen starvation.
- From 6 to 7 - mild violation.
- From 8 to 10 – everything is fine with the child.
The frequency of breathing, the presence of reflex activity, skin color, and muscle tone will be assessed . Attention is also paid to the heart rate. Depending on whether the child has impairments, a specific score will be assigned. Mild hypoxia goes away on its own within 5 minutes, but other degrees require treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
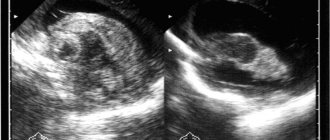
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to undergo an examination. Even during pregnancy, a woman will need to perform an ultrasound of the fetus, a movement test, and also listen to the heartbeat. Based on the results of the research, it will be possible to understand whether there is a threat to the baby.
After birth, the baby undergoes an ultrasound of the brain and a neurological examination. If deviations are noticed, then the presence of hypoxia can be suspected.
During treatment, breathing is first restored using aspiration, then artificial ventilation can be used. A solution of glucose and cocorboxylase is injected into the umbilical cord. For bardycardia, a heart massage is performed, and adrenaline and other medications are injected into a vein. After this, the child will need to be given vitamins, undergo infusion treatment, and also undergo oxygen therapy.
Consequences - video
The most dangerous is the acute form of cerebral hypoxia. It is this type that can lead to various deviations that affect a person’s quality of life. It is imperative to undergo a course of treatment in a timely manner if you want to maintain your child’s health.
Various consequences arise when the baby is not given the right help. In such a situation, pathology can negatively affect the quality of life. Complications can be both mild and serious.
Possible consequences:
- Accelerated heart contraction. In this case, increased blood pressure is observed. During hypoxia, blood flow is redistributed, which can lead to trophic disorders. The danger is that internal organs may stop functioning normally.
- The breathing frequency becomes different. The person experiences shortness of breath.
- The brain produces a large number of red blood cells. This creates a risk of blood clots.
- Seizures often appear in childhood.
- Visual function deteriorates.
Cerebral hypoxia or another type of pathology should not be left to chance. Therapy must be completed, and the child must be observed by a doctor to monitor changes. If treatment is not started promptly, developmental delays can often occur. Children gain weight worse, do not speak for a long time, and also have neurological disorders. To prevent this, it is enough to visit a doctor in time and undergo a course of treatment.
Source: https://nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/patologii-golovnogo-mozga/posledstviya-gipoksii-u-novorozhdennyh.html
What is cerebral ischemia?
Cerebral ischemia is a condition that develops as a result of its oxygen starvation (hypoxia). This disorder can occur in the prenatal period, during childbirth and in the first hours of life. Immediately after birth, the rapid maturation of the central nervous system (CNS) begins; every moment new neural connections are formed that will be responsible for the functions of the body throughout life.
During this period, the brain experiences an increased need for oxygen, so any disruption of oxygen supply and hypoxia has a damaging effect on it. Nerve cells that die as a result of cerebral hypoxic disorders are not restored, and their death affects brain function.
What kind of disease is this?
Throughout the entire period of gestation, the fetus remains in the uterus. During this period of time, his lungs are not breathing at all. They are completely filled with special water. The lungs can produce so-called breathing movements, but through them the flow of oxygen will not enter the baby’s body.
Therefore, the only source of vital oxygen during this period is the placenta, which can release it from the mother’s blood. If the oxygen supply is disrupted, the fetus experiences the development of hypoxia or so-called oxygen starvation.
Degrees of disease and symptoms in newborns
As a rule, the disease makes itself felt from the first minutes of the baby’s life. A very important indicator is the first breath and cry of a newborn. Their delay serves as a sign to doctors that the brain does not have enough oxygen.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the extent of ischemia and the damage to brain cells caused by it. Pediatricians distinguish three degrees of clinical manifestations of ischemia:
- The first, or mild, degree is characterized by lethargy or increased agitation in the first week after birth. During this period, the child is under the supervision of a neurologist in the maternity ward. After being discharged home, he also needs patronage.
- Second, or middle, degree. The general lethargy of the child is accompanied by neurological symptoms, which manifest themselves as trembling of the chin when crying, squint, and convulsions. Children with moderate ischemia require hospital treatment.
- The third, or severe, degree is characterized by depression of respiratory and other reflexes, there are signs of ischemic hypertension and hydrocephalus. Immediately after birth, such babies are placed in intensive care, where they receive intensive therapy. After discharge, the child is registered with a pediatric neurologist, who conducts further outpatient treatment and monitors the baby.
Diagnosis of the disease
As already mentioned, the very first method of diagnosing a baby’s condition is monitoring motor activity. At the first suspicion, the expectant mother should immediately contact her doctor, who, in turn, uses the following diagnostic methods:
- Auscultation. This method involves listening to the fetal heartbeat using a special tube that is applied to the pregnant woman's stomach. Auscultation is performed immediately during the expectant mother’s visit to the doctor. Unfortunately, this method is not as informative as possible, since the degree of error is quite large.
- Cardiotocography. This method is used most often. In this case, ultrasound sensors are attached to the pregnant woman’s belly, having previously determined the best place to listen to the heartbeat depending on the position of the fetus. Heartbeats during CTG are recorded on paper over a certain period of time.
- Doppler. This diagnostic method allows you to examine blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord and fetus.
- Biochemical and hormonal studies of mother's blood.
- After birth, the Apgar score to determine the condition of the baby.
Now let's figure out how to treat hypoxia in a newborn.
Causes of development of ischemia in children
- poor conditions during pregnancy (malnutrition, stress, overload);
- acute and chronic diseases of the mother during pregnancy (anemia, cardiovascular pathology, diabetes mellitus);
- early and late toxicosis;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs);
- pathologies of the placenta (previa, abruption, calcification);
- umbilical cord disorders (clamping, entanglement around the fetal neck).
In addition to the period of pregnancy, cerebral ischemia develops during or after childbirth. The disease can occur due to the following factors:
- difficult, traumatic childbirth;
- premature delivery and birth of a premature baby;
- use of delivery aids (vacuum, forceps);
- consequences of drug stimulation of contractions;
- ingestion of amniotic fluid or meconium into the respiratory tract of a newborn;
- birth bleeding.
Chronic intrauterine hypoxia
Everyone knows that while in the womb, a child cannot breathe on his own. Despite the fact that his lungs are already formed, they are filled with fluid. Even when the child tries to make breathing movements in utero, they do not work. Before birth, a child breathes only through the placenta, the so-called baby's place. This means that the intrauterine well-being of the child depends on how the expectant mother feels and how the blood vessels of the placenta work.
Risk factors for the development of chronic intrauterine hypoxia:
- various types of anemia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- kidney diseases;
- bronchial asthma;
- diabetes;
- post-term pregnancy;
- threat of miscarriage;
- bleeding;
- smoking, alcoholism and drug addiction;
- exposure to toxic substances, including certain medications;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus, especially in the first half of pregnancy;
- toxicosis in early pregnancy.
Consequences and complications
Grades 1 and 2 ischemia have a favorable prognosis. With timely treatment, it is possible to compensate for the violations that have occurred and prevent their impact on the child’s development. Severe ischemia causes widespread damage to the central nervous system.
Children who have suffered the third degree of ischemia need special attention from both parents and doctors. They often experience impairments in vision, hearing, and coordination of movements. Such children may have neurological abnormalities (strabismus, convulsions) and inappropriate behavior (overexcitability, lethargy). They find it more difficult to learn new skills and learn in school. Particularly advanced cases of ischemia result in the child's disability.