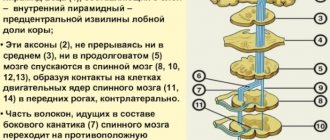
Description of the disease
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome (according to ICD 10 - H82*) is considered a characteristic concomitant disease with cerebral ischemia, which is why it is very rarely considered as an independent entity.
This disease occurs due to circulatory problems both in the brain and throughout the body as a whole. Externally, the syndrome manifests itself as a combination of motor and coordination disorders. Characteristic symptoms also include dizziness, weakness, loss of balance and deterioration in stability when performing various activities.
Causes of development and associated diseases
Vestibular ataxia is associated with damage to any structure of the vestibular analyzer. Most often it is caused by damage to hair cells as a result of an inflammatory process in the inner ear - labyrinthitis. In turn, labyrinthitis can occur as a result of ear injury or when infection passes from the middle ear cavity in acute otitis media, chronic purulent otitis media, complicated aerootitis. The death of hair cells leading to the development of vestibular ataxia can occur as a result of invasive growth of an ear tumor or toxic effects of ear cholesteatoma secretions. Paroxysmal vestibular ataxia accompanies Meniere's disease.
Less commonly, vestibular ataxia is caused by damage to the vestibular nerve, which can be infectious, tumor (with acoustic neuroma) or toxic (with ototoxic drugs) in nature. Often, vestibular neuronitis is associated with a viral infection: ARVI, herpes virus, influenza, etc.
MORE: Cerebellar ataxia pathogenesis. Cerebellar ataxia - features of the development and treatment of the disease
Vestibular ataxia can occur when the vestibular nuclei located in the medulla oblongata are damaged. Thus, vestibular ataxia occurs as a result of compression of the medulla oblongata in individuals with craniovertebral anomalies (Chiari malformation, atlas assimilation, platybasia), brain stem tumors, encephalitis and arachnoiditis of the posterior cranial fossa, demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, acute encephalomyelitis). Vestibular ataxia is a clinical manifestation of chronic ischemia of the brainstem caused by impaired vertebrobasilar circulation due to vertebral artery syndrome, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and cerebral aneurysm. In acute circulatory disorders of this area (TIA, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke), vestibular ataxia is also observed.
Vestibular ataxia is often observed after a traumatic brain injury. Moreover, it can be caused either by the direct impact of a traumatic factor on the nuclei and roots of the vestibular nerve, or by circulatory disorders accompanying the injury (post-traumatic vascular spasm).
Most often, this syndrome indicates cerebral ischemia - a disorder of cerebral circulation (congenital, acquired). It also occurs when there is damage or atrophy to the structures of the brain and the vestibular analyzer.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Osteocondritis of the spine.
- Diabetes.
- Hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
- Malformations of cerebral vessels, aneurysms.
- Heart defects (congenital, acquired).
- Vertebro-basilar insufficiency (weakening of blood flow in the basilar and vertebral arteries).
- Infectious and other diseases that involve vascular damage.
The nature of damage to cerebral vessels can be different: narrowing of the lumen of the vessel or its complete blockage due to prolonged spasm, blood clot, atherosclerotic plaque, fat droplets, embolus, etc.
- Violation of the permeability of the vascular wall with a change in its structure.
The cause may be infectious-allergic, allergic, autoimmune diseases, disorders of the blood coagulation system, blood diseases (anemia), disorders of water-salt and protein metabolism. Hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the brain is aggravated by tissue edema with the formation of a vicious circle: “hypoxia - edema - hypoxia.”
- Neoplasms (tumors, cysts) of the brain and adjacent structures.
- Alcoholism.
- Smoking.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Long-term, unreasonable use of antihypertensives (lowering blood pressure) and other drugs that deplete cerebral circulation.
Factors influencing the development of the syndrome
You need to know that vestibulo-atactic syndrome is a disease that sometimes causes severe changes in the structure and functioning of the brain, which can indirectly affect the coordination of movement, which include cerebral hydrops, cortical atrophy, hypertensive heart disease, etc.
Disorders in coordination and movements appear under the direct influence of the following types of diseases:
- cerebral ischemia (chronic anemia) - it can be congenital or acquired;
- dysfunction and functioning of the cerebellum;
- pathologies localized in the frontal-stem lobes of the brain.
Identifying the cause is a very important step in treating the disease, because in this case it will be possible to remove the root of the problem, and not the side effects of it.
Most often the reason is...
There are many reasons that cause this disorder, but the most common include:
- ischemia, which can be either congenital or acquired;
- disorders affecting the frontal-stem lobes of the brain;
- depletion of the cerebral cortex;
- dropsy of the brain (hydrocephalus);
- high blood pressure;
- atherosclerosis;
- head injuries;
- malignant neoplasms;
- osteochondrosis.
Main symptoms of the disease
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome is an extremely unpleasant disease. Its symptoms interfere with a person’s normal functioning and cause serious impairment of the body’s motor functions. Most often, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- Dizziness and weakness, which manifest themselves in a constant lack of strength.
- Ripple before my eyes.
- Uncertain, shaky gait, poor coordination of movements.
- Nausea.
- Frequent loss of balance causing falls.
- While walking, a person may involuntarily begin to perform strange actions, such as swaying from side to side.
- Distracted attention and changes in brain function.
In addition to the main symptoms, which are expressed mostly in impaired coordination of movement, many patients also complain of tinnitus, insomnia, fatigue and a significant decrease in performance.
Clinical picture
Common symptoms of vestibuloatactic syndrome include:
- dizziness;
- flickering in the eyes;
- gait disturbance;
- headache;
- nausea;
- loss of balance;
- difficulty concentrating;
- feeling of being “thrown” in different directions;
- falls.
You can also identify secondary symptoms:
- sleep pattern disorder;
- feeling of noise and congestion in the ears;
- fast fatiguability;
- lethargy;
- low performance.
Disease severity
Since this syndrome develops very slowly, scientists have identified several stages that can be traced in any affected person. Each of them is characterized by peculiar disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, etc.
- A mild form of vestibulo-atactic syndrome is almost invisible and in most cases all symptoms that appear are attributed to fatigue. During this period, changes in gait and coordination can be observed.
- At the moderate stage, the disease affects the largest area. After which vestibular disorders begin to appear, for example, nausea, an unsteady and shaky gait.
- A severe stage appears in the absence of treatment of previous forms. In this case, falls are possible while walking or standing, which lead to the lack of ability to move independently.
A very small percentage of people suffering from this illness sought qualified help during the first stage. In order for the treatment of the disease to proceed as quickly and successfully as possible, it is necessary to carefully monitor the state of health after suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
What kind of disease is vertigo?
Few people have any idea what the word “vertigo” means. In fact, this word refers to a state of dizziness and loss of balance. What is vertigo and how is it characterized? Anyone who is bothered by this symptom feels the rotation of objects around him, sometimes even his own body spinning in space.
So, what disorders can cause dizziness? The factors that provoke vertigo syndrome can be listed as follows:
- Improper functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
- Pathologies of the central nervous system (tumors, diseases of the cerebral cortex).
- Disorders of the auditory nerve.
- Cardiovascular pathologies.
- Spinal diseases.
Often attacks of vertigo are accompanied by deterioration of vision and hearing, pallor, increased sweating, increased or decreased heart rate, and darkening of the eyes.
Probably, everyone who has learned what vertigo is will be interested in finding out what pathologies the presence of this symptom indicates.
So, dizziness can be caused by the following diseases:
- Meniere's disease.
- Inflammation and mechanical damage to the inner ear.
- Choleastomy.
- Anemia.
- Osteochondrosis.
- PTSD.
- Epilepsy.
- Head injuries.
In order to get rid of dizziness, you need a comprehensive examination by a general practitioner, ENT specialist, or a specialist in VS diseases. After undergoing examinations and necessary tests, it will be possible to determine the exact causes of vertigo and decide on treatment.
In general, this symptom indicates the presence of diseases of the brain and cerebellum, in which nerve signals about a person’s position in space are incorrectly interpreted.
Continuing to talk about what vertigo is, it should be said that there are two types of this pathology:
- Central vertigo. Signs of this type of vertigo are subtle and constantly present. Such dizziness is accompanied by heart rhythm disturbances, hyperhidrosis, and nausea. The causes of this pathology are epileptic seizures, tumors, mechanical damage, cerebrovascular accidents, and hemicrania.
- Peripheral vertigo. It is characterized by severe symptoms lasting more than two days: unsteady gait, poor coordination of movements, cramping abdominal pain, ringing in the ears, fast or slow heartbeat, vomiting, deterioration of hearing and vision. This phenomenon occurs due to pathological processes in the inner ear, side effects of certain drugs, inflammation of the hearing organs, insufficient blood supply to the brain, and diseases of the cerebellum.
Recognizing vestibulo-atactic syndrome is not easy. To determine the diagnosis, the doctor recommends that the patient undergo the following types of examinations:
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the head and spine.
- EEG.
- X-ray of the skull.
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
- Assessment of blood supply to the brain.
- Tests to identify the disease (they are carried out by a neurologist to understand how well the patient maintains balance).
In general, in the absence of unfavorable factors and concomitant pathologies, the syndrome is easily treatable. To treat it, drugs that lower cholesterol levels, drugs that improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in the brain, and drugs with antioxidant effects are used. In some cases, surgery (surgery on the spinal arteries) is performed to eliminate symptoms. It avoids vasoconstriction and improves blood supply to the brain, which leads to a significant improvement in the patient’s condition.
This is a pathology of the inner ear, which is accompanied by attacks of vertigo, hearing loss and tinnitus. The disease was first described by a French physician in the nineteenth century. Today it is diagnosed most often in people aged twenty-five to fifty, mainly in residents of metropolitan areas engaged in mental work.
What is Meniere's syndrome and vertigo and why does this phenomenon occur?
The reasons that cause the development of the disease may be:
- Mechanical head injuries.
- Infectious diseases of the ear.
- Malformations and injuries of the hearing organs.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Disturbances in the outflow of fluid in the inner ear, accumulation of lymph.
- Work in hazardous production.
- Scars in the cavity of the inner ear left after surgical interventions.
Meniere's disease is characterized by paroxysmal progression. As a rule, it is manifested by noise or ringing in the ears, pain inside the ear, decreased hearing, loss of balance, intestinal upset and vomiting, abdominal cramps, increased heart rate, pallor and sweating. Often, coordination of movements during an attack is so impaired that the patient falls.
If there is a suspicion that the patient has this pathology, the doctor conducts the following examinations:
- Assessment of the functioning of the auditory ossicles and muscles inside the ear.
- Examination of the auditory nerve.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- EEG.
- Determination of the amount of fluid in the cavity of the inner ear.
Of course, paroxysmal dizziness can be a sign of more than just Meniere's disease. Vertigo syndrome indicates symptoms of many pathologies, so a thorough examination of the patient is necessary.
What is vertigo? This beautiful word denotes an unusual disease, which is characterized by an unstable, unsteady gait, falling, dizziness of a person, it seems that all surrounding objects are in motion, although this is actually not the case.
The most effective way to determine true vertigo (or simply dizziness) is to discover that dizziness and loss of balance do not appear just like that, but, for example, after riding on rides or swings.
Vertigo disease can be non-systemic and systemic. What does it mean? And the fact that the systemic one can occur due to malfunctions and damage to the vestibular apparatus. You can feel it when moving, both the person himself and objects relative to him. This condition may be accompanied by a feeling of panic, a general deterioration in the quality of hearing, and nystagmus.
Non-systemic vertigo is characterized by darkening of the eyes, fainting, muscle weakness, poor health when pressure changes, and shortness of breath.
Dizziness can be systemic or non-systemic. Systemic vertigo develops when the vestibular apparatus is damaged and is felt as movement of one’s own body and objects. This disorder may be supplemented by autonomic abnormalities, nystagmus, panic, and hearing impairment.
Non-systemic dizziness is characterized by the following symptoms of vertigo - a feeling of “loss of consciousness”, lightheadedness, darkness before the eyes, weakness, fears, discomfort with the development of an increase or decrease in blood pressure, autonomic abnormalities, diseases of the cardiovascular system and breathing.
Despite the fact that vertigo disease has several forms, it is always provoked by the same factors:
- Disturbance in the activity of the vestibular apparatus.
- Dysfunction of the auditory nerve.
- Presence of cardiovascular diseases.
- Pathologies of the central nervous system (formation of tumors of a benign or malignant nature, damage to the cerebral cortex).
- Problems with the spine.
Experts warn patients that if the syndrome occurs quite often (at least 2 times a month), it is dangerous to ignore it, since it may indicate serious problems:
- development of inflammation in the inner ear;
- anemia;
- osteochondrosis;
- epilepsy;
- brain injury;
- Meniere's disease.
It is impossible to determine on your own what causes dizziness; to do this, you will have to visit several specialists at once and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Only after doctors understand the overall clinical picture and figure out what was the primary source of the disease, can they select a competent treatment method that will give a positive result.
In most cases, frequently occurring symptoms of vertigo indicate pathologies of the brain or cerebellum, in which incoming nerve signals about a person’s presence in space are incorrectly deciphered. Today in international medicine there are 2 types of dizziness with vertigo:
- Central. Signs of the disease are very mild, but are present almost all the time. Attacks may be accompanied by arrhythmia, nausea and excessive sweating. Central vertigo most often occurs due to frequent epileptic seizures, mechanical trauma to the skull and the formation of tumors;
- Peripheral. With this type of disease, the symptoms are much stronger and may not subside for 2-4 days. In this case, the person will suffer not only from lack of coordination, but also from discomfort and pain in the abdominal cavity, ringing in the ears, deterioration of hearing and vision, and severe vomiting. This condition is usually a consequence of pathogenic processes in the inner ear, and can also appear after long-term use of certain medications (as a side effect).
Lack of timely treatment, an incorrect diagnosis, or a medical error made during the formation of a therapeutic course can lead to the development of the following complications and negative consequences for the health and life of a patient with vestibulopathic disorder:
- development of ischemic cerebral vascular disease, if it was not yet present at the time of the onset of musculoskeletal dysfunction;
- inability to lead a full and active lifestyle;
- complete or partial loss of ability to work;
- cerebral stroke;
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels supplying brain tissue;
- the development of dementia, which can occur in a person of any age group;
- disability, dependence on the help of loved ones, bedridden or wheelchair-bound;

- physical inability to service one’s own physiological needs;
- the development of a mental disorder that occurs against the background of depletion of the cerebral cortex and degenerative processes in its tissues.
Diagnosis of the disease
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome is a diagnosis that is made to the patient only after he has undergone several types of examinations. First of all, the specialist conducts an external examination and conversation, during which an anamnesis of the disease is collected. Very important data will be information about previous cardiovascular diseases.
Instrumental examination methods are also carried out, with the help of which specific neurological and vestibular disorders are identified:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is prescribed to identify circulatory disorders in the vessels of the brain or other pathologies associated with the central nervous system.
- Ultrasound examination of the cervical spine makes it possible to exclude diseases such as osteochondrosis and the accompanying narrowing of blood vessels, which can cause disturbances in the functioning of the motor system.
- Computed tomography of the brain is prescribed when previous studies have not brought the desired result.
Establishing diagnosis
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. In addition to a general examination and history taking, a neurological and otoneurological examination is prescribed, which makes it possible to determine disorders of the vestibular apparatus in a particular patient.
The following diagnostic procedures will also be prescribed:
- MRI - determines circulatory disorders of the cerebral vascular system, as well as other central nervous system abnormalities;
- Ultrasound - examination of the cervical spine to detect osteochondrosis, in which narrowing of blood vessels occurs.
Article on the topic: Free testosterone index in women - normal indicators, reasons for increase or decrease
Conservative treatment methods
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome - what is it? After answering this question, you should describe possible methods of treating the disease. At the initial stages of the disease, drug therapy is carried out aimed at reducing blood pressure. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels. Also, very often doctors recommend adhering to a special diet, giving up bad habits and normalizing your daily routine.
Further treatment of the syndrome will depend on the severity of symptoms. In order to get rid of the disease, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease, which most often is cerebral ischemia:
- To improve cellular oxygen supply and blood circulation, the drugs Mildronate, Actovegin, and Mexidol are prescribed.
- To stimulate blood circulation in the brain area, the drugs Trental and Cavinton are used.
- If a chronic form of coronary artery disease is detected, antidepressants are additionally prescribed.
- In addition to the use of medications, physical therapy, acupressure of the head, herbal medicine and other procedures help well in this case.
Vertigo - what is it? Symptoms, causes, treatment:
At times I have such severe dizziness that I can’t even lie on my back, everything starts spinning before my eyes, and when I get up, it gets even worse.
They determined that it was due to my osteochondrosis and prescribed Betaserc tablets. I've been drinking them for a week and I seem to feel better. But the drug is not cheap. Thanks for the advice. tell me the amount and dose of betaserc
Wow, I suffered from dizziness for so many years and didn’t know what it was called. By the way, a strict daily routine, taking Eltacin, and regular rest helped me cope with this scourge. These seem to be such simple recommendations, but in my case they turned out to be very effective.
Thank you, useful article, it’s a pity that there is no mention of the side effects of some medications that can cause vertigo, for example, treatment with vimpocetine, and what the patient should do in such cases.
Surgical intervention
Treatment of vestibulo-atactic syndrome most often ends with conservative methods, but in severe cases it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. During the operation, the doctor intersects the vasomotor fibers of the vertebral artery.
It is worth noting that this type of surgical intervention is considered complex, and only a highly qualified specialist in the field of cardiovascular surgery can perform the operation. The qualifications of the doctor are the main factor in the success of the procedure.
With the help of the operation you can achieve the following positive effect:
- the likelihood of spasmodic phenomena of the brain is significantly reduced;
- normalization of cerebral circulation is one of the main reasons for restoring coordination and motor functions.
Forecast
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome responds well to treatment even in advanced stages. The main difficulty may be associated factors, which include age-related changes in the human body or serious illnesses (malignant tumor, cyst and other neoplasms requiring immediate surgical intervention).
With prolonged refusal of treatment, the patient may experience additional problems, which will be expressed in various health problems. The most common symptoms will be chronic headaches, problems with coordination, and changes in the functioning of vital body functions.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of vestibulo-atactic syndrome
A combination of special symptoms—impaired coordination of movements, a visible change in gait, which others describe as “wobbly,” complaints of dizziness, and a tendency to fall “out of the blue”—are grounds to visit a doctor.
After examining the patient and conducting diagnostic studies, it is possible to establish a diagnosis of vestibulo-atactic syndrome. When voicing it, doctors can replace the term with a synonym, using the expression vestibulo-cerebellar syndrome.
This condition is observed in people who have problems with blood circulation (especially with pathology of the vessels through which blood flows to the brain) and the presence of neurological diseases. The progression of the syndrome leads to complete disability of the patient.
Causes and associated diseases
Vestibulo-ataxic syndrome is not a disease, but a condition that is provoked by pathologies already developed in a person.
It accompanies people who have signs of a violation of the blood supply to the brain (they can be congenital or acquired), called ischemia.
These conditions change the functions of the cerebellum and frontal part of the brain, which are responsible for the coordination of movements. Experts include the following to the list of pathologies:
- chronic vascular diseases, resulting in deterioration of blood flow in the vertebrobasilar region;
- atherosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- development of tumor processes in the brain (they can be benign or malignant);
- multiple sclerosis;
- destruction of brain tissue, characteristic of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- dropsy of the brain in children (hydrocephalus);
- cerebral palsy;
- conditions after brain injuries and surgical interventions.
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome can be provoked by several factors. This may be due to unfavorable heredity, trauma (including birth). Aggressive external influences that a person receives throughout his life also contribute to the development of the condition:
- living in areas with hazardous environmental conditions;
- uncontrolled or long-term treatment with certain medications;
- regular excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- radioactive exposure;
- damage by microorganisms that cause infectious diseases and their complications.
Vestibular ataxia can occur against the background of an imbalance or lack of certain microelements and vitamins in the human body.
Classification and main features
Vestibulocerebellar syndrome can manifest itself in a patient to varying degrees. Doctors highlight the following:
- Easy. Its peculiarity is the absence of noticeable disorders in the patient. Those around you and the patient himself may notice minor changes in gait and poor coordination of movements performed.
- Moderate. The gait becomes special - the person staggers to the sides, the coordination of movements is significantly changed. The patient complains of stable headaches, feels dizzy (especially when moving), nausea, temporary darkening, flickering in the eyes, and twitching.
- Expressed. This degree of progression of the syndrome is characterized by the patient's ability to move independently. His gait is characterized by strong, chaotic movements of the body and limbs, which gives reason to others to perceive it as “drunk.” The patient is unable to give his body the desired position. It completely stops listening. The manifestations of additional disorders, which depend on the individual characteristics of the body, are increasing. A pronounced degree of vestibular ataxia presupposes the establishment of disability, since often a person completely loses the ability to work and care for himself independently.
Common symptoms indicating the possible development of vestibulo-atactic syndrome are the following types of coordination and motor disorders:
- inability to intentionally maintain stability of body position (posture) for a certain period of time;
- unsteady gait;
- change in coordination of movements;
- imbalance (both when walking and in a standing position), tendency to fall;
- the appearance of involuntary eye twitching.
Additional signs complement the clinical picture:
- tendency to increased fatigue, tiredness;
- increased headaches;
- frequent dizziness, which may be accompanied by darkening of the eyes, flickering in front of them, and tinnitus;
- it is difficult for a person to concentrate, he becomes distracted;
- thinking is disrupted, mental activity becomes difficult;
- There are difficulties with sleep: it can be short-term, signs of insomnia appear.
The disease can progress and take the form of discirculatory encephalopathy with vestibulo-atactic syndrome. With it, due to oxygen deficiency, irreversible processes occur in brain cells, as a result of which they die, provoking the development of encephalopathy. The process is accompanied by a decrease in intelligence, memory, and dementia.
Conservative treatment
For most patients (especially adults), the first stage of treatment is necessary - normalization (lowering) of blood pressure and restoration of cholesterol levels.
For these purposes, sedatives and statins are used.
Non-drug methods that help achieve such results are switching to a new diet that does not harm the body, as well as an unconditional cessation of smoking and alcohol.
The drugs Trental, Cavinton and others can improve blood supply to the brain. Antioxidants are indicated; the patient may be prescribed Mildronate, Actovegin.
For the treatment of patients with moderate and severe degrees of the syndrome, it is possible to use drugs from the group of antidepressants, benzodiazepine drugs are used.
When the process is aggravated by neuralgia, the patient may be prescribed psychotherapeutic treatment: hypnosis sessions, therapeutic sleep and an element of physiotherapy - massage.
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, surgery is performed. Its goal is to restore blood flow in the vertebrobasilar region. The manipulation is performed by a neurosurgeon. Medical statistics show that significant improvements in condition after it are observed in 7 out of 10 patients.
People's recommendations
Part of the complex of therapeutic measures is the use of traditional medicine. On the recommendation of a doctor, at home the patient can take medications based on natural raw materials:
- garlic;
- lemon balm;
- juniper berries;
- corn silk;
- horseradish root;
- honey;
- herbs (thyme, mint, motherwort).
For each patient, especially a child, the doctor recommends a specific recipe and method of preparing a traditional medicine, taking into account the characteristics of the health condition and the presence of restrictions. The drugs can reduce high blood pressure, improve blood flow, and cleanse the blood of cholesterol.
Exercise therapy
For the treatment of vistibulo-cerebellar syndrome, therapeutic physical education (PT) is prescribed. The gymnastics complex is aimed at restoring lost functions of the vestibular apparatus and stimulating cerebral circulation.
The patient, under the supervision of a physical therapy specialist, begins to perform several turns, bends, head rotations, and repeats the “back and forth” movements. Then the number of exercises of each type increases.
The patient is shown walking in place.
Prevention methods
If there are prerequisites for the occurrence of vestibulo-atactic syndrome and its mild development, doctors recommend the use of preventive measures. These include:
- transition to an active lifestyle, physical activity should be moderate, bring only pleasure, alternate with proper rest;
- restoration of mental balance, avoidance of stress;
- transition to a “healthy” diet, it should be balanced, but at the same time contain only healthy components;
- giving up dangerous hobbies (alcohol and smoking).
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://ProSindrom.ru/neurology/vestibulo-atakticheskij-sindrom.html
Prevention
Prevention of the disease will be a healthy lifestyle and preventing the occurrence of diseases of the cardiovascular system. These actions include:
- Regular medical examination.
- Avoiding stressful situations and nervous tension.
- Quitting bad habits, including drinking coffee.
- Refusal of excessive physical activity.
- Preventing excess weight.
- Reducing the amount of time spent in the sun.
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome is a serious disease, at the first signs of which you should immediately contact a specialist. In addition to the main symptoms, the treatment will eliminate the main cause of the disease, which is associated with poor circulation in the brain. Coordination and movement disorders greatly burden a person’s life, so their treatment should be approached with special responsibility.
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome: development, signs, diagnosis, how to treat
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome is a complex of clinical symptoms caused by chronic vascular dysfunction in the brain and damage to the vestibular apparatus .
This is not an independent nosology, but a secondary manifestation of major serious diseases, mainly neurological. The cause of the syndrome is circulatory disorders in the vertebrobasilar system.
The term “ataxia” refers to a disorder of motor skills—movement, speech, and breathing.
In the modern world, the syndrome is quite common. In patients with impaired cerebral circulation, movement disorders manifest: they lose balance when walking and fall out of the blue, unsteadiness of gait and incoordination of movements occur. Such phenomena are associated with damage to nerve structures. The condition of the muscles does not matter.
Treatment of the pathology is complex and comprehensive, including drug therapy, surgery, physiotherapy, and traditional medicine.
Causes
Vestibulo-atactic syndrome is a manifestation of a number of pathological processes. The most common among them are:
- Traumatic brain injury,
- Cerebrovascular accident,
- Cerebral palsy,
- Hydrocephalus,
- Hypertension,
- Atherosclerotic lesion of large cerebral arteries,
- Malignant or benign neoplasms in the brain,
- Autoimmune diseases - multiple sclerosis,
- Extracerebral tumors
- Brain cell atrophy
- Severe intoxication,
- Brain hemorrhages
- Infections,
- Intrauterine developmental disorder of the skull,
- Hepatitis,
- Avitaminosis,
- Ear diseases,
- Vestibular neuritis,
- Labyrinthitis, labyrinthine infarction,
- Meniere's disease,
- Basilar migraine,
- Cervical osteochondrosis,
- Psychogenic disorders,
- Cardiopsychoneurosis,
- Encephalitis.
Most often, vestibulo-ataxic syndrome occurs in patients with various neurological ailments.
Its development can be provoked by anxiety, stress, nervousness, emotional outburst, psycho-emotional exhaustion, and physical fatigue.
The first clinical signs of the disease remain mild for a long time. As the pathological process progresses, serious problems with coordination of movements arise.
The vertebrobasilar system unites the vertebral and central arteries of the brain, supplying blood to its stem structures. Discirculatory disorders that occur in the human body under the influence of endogenous or exogenous factors lead to hypoxia and ischemia of brain tissue.
The high prevalence of the syndrome and the variety of its clinical forms are due to the high sensitivity of stem formations to oxygen starvation. Oxygen deficiency is the cause of disruption of the energy supply to nerve cells and the interaction of the brain with other parts of the central nervous system. When there is insufficient oxygen supply through the bloodstream to the brain, nerve cells die.
The toxic effects of certain substances enhance this process. Functional disorders occur in various parts of the brain.
Persons most susceptible to developing the syndrome:
- Those who suffered a skull injury during childbirth,
- Having suffered acute infectious diseases,
- Those exposed to radiation
- Having bad habits
- Neglecting proper nutrition with sufficient amounts of vitamins and microelements in the diet,
- With a genetic predisposition,
- Elderly people with age-related disorders in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Vestibulo-ataxic syndrome is a serious illness that requires urgent medical attention. Only timely diagnosis and proper treatment will increase patients’ chances of recovery. Otherwise, the pathology can lead to disability and even death.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the pathology depend on its root cause, the age of the patient and the general condition of the body.
The first clinical manifestations of motor and vestibular disorders in vestibulo-ataxic syndrome:
- Dizziness,
- Cephalgia,
- Flashing "flies" before the eyes,
- Weakness in the legs
- Nausea and vomiting.
These initial signs of the syndrome are nonspecific and often subtle. Most truly sick people simply do not notice them, mistaking them for a banal ailment. If the disease is not identified and treated in time, it will progress.
Symptoms of a later period of the disease:
- Unstable body position
- Unsteadiness of gait,
- Loss of coordination of movements,
- Dark circles before the eyes, decreased visual acuity,
- Loss of balance
- Falls,
- Eyelid twitching
- Sleep disturbance,
- Chronic fatigue, loss of strength,
- Congestion and noise in the ears.
In children, vestibulo-atactic syndrome is manifested by an uncertain gait, imprecise movements, tremor, and speech disorders.
Symptoms of general asthenia often occur, especially in severe cases: shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, pressure fluctuations, pale skin, drowsiness, depression, irregular breathing and pulse rhythms, changes in body temperature, disorientation in time and space, decreased muscle tone, anxiety, restlessness, panic, fear, profuse sweating, impaired concentration.
There are three stages of development of ataxic pathology, each of which is characterized by a specific set of symptoms:
- Mild stage – mild changes in gait and slight incoordination of movements. Due to the lack of specific and pronounced symptoms, the syndrome is extremely rarely diagnosed at this stage.
- Moderate stage - the patient not only staggers, he is thrown from side to side, problems with coordination of movements become pronounced, cephalalgia, nausea, and dizziness occur.
- Severe stage - patients have difficulty moving and cannot hold the body in one position or another, often fall. It is difficult for them to make even the simplest movements. The changes that occur in the brain of patients at this stage are irreversible. All patients are assigned a disability.
A favorable outcome of the pathology depends on how quickly and correctly the doctor determines the stage of the syndrome and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Separately, there is cephalgic vestibulo-atactic syndrome, the main manifestation of which is unbearable headache. It brings discomfort to a person’s life, disrupts appetite and sleep, and reduces performance.
This syndrome is a manifestation of serious diseases of the central nervous system of infectious, inflammatory, oncological or vascular origin. The main goal of doctors is to relieve the patient from painful headaches and eliminate the cause that caused it.
To protect yourself from irreversible neuropsychic processes in the future, you should take the appearance of headaches in the present seriously.
Complications of advanced forms of vestibulo-atactic syndrome:
- fall injuries,
- spasms of cerebral vessels,
- development of cephalgic syndrome with constant headache,
- paralysis,
- stroke,
- death.
Diagnostics
Since vestibulo-ataxic syndrome has many causes, its diagnosis is quite complex. It consists of conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient and is aimed at identifying the main cause of the syndrome and existing concomitant diseases.
Diagnostic measures include:
- Listening to complaints
- Anamnesis collection,
- Determination of neurological status,
- Carrying out functional tests - Romberg, finger-nose, knee-heel,
- General examination of the patient,
- Testing,
- Lab tests,
- Instrumental methods.
Laboratory diagnostics - hemogram, blood biochemistry, urine tests, cerebrospinal fluid examination.
Instrumental methods to confirm the suspected diagnosis include:
- Tomography is a method for identifying tumors in the brain,
- Encephalography - determination of electrical potentials of the brain,
- Rheoencephalography - assessment of cerebral circulation,
- Duplex ultrasound scanning,
- X-ray of the skull and spine.
To carry out differential diagnosis and exclude other pathologies that can provoke dizziness and loss of balance, nuclear magnetic resonance and Doppleroscopy of brain vessels are used. A CT scan of the brain is performed to exclude other damage to the main structures, and vestibulometry is performed to assess the condition of the vestibular analyzer.
Treatment
Treatment of vestibulo-atactic syndrome is complex and multi-stage. It is prescribed by a neurologist or neuropathologist based on the results of a diagnostic examination.
They recommend that all patients lead a healthy lifestyle, following the principles of proper nutrition and completely eliminating bad habits. Mild vestibulo-atactic syndrome in children does not require treatment.
As the child grows older, the disease goes away on its own.
Patients should eat properly, excluding spicy, fatty, spicy, smoked and salty foods, strong tea and coffee, and alcohol from the diet. The daily menu should be enriched with natural juices and foods containing vitamins and microelements. Patients are recommended to eat vegetable soups and salads, fermented milk products, cereals and whole grain bread.
Drug therapy is aimed at normalizing the general well-being of patients and eliminating the main clinical manifestations. Since the causes of the syndrome are not precisely determined, the effectiveness of such treatment is very relative.
Patients are prescribed:
- Statins to combat atherosclerosis - Atoris, Rosuvastatin,
- Hypotonics to lower blood pressure - “Capoten”, “Lisinopril”,
- Antioxidants – “Actovegin”, “Mildronat”, “Mexidol”,
- Vascular drugs - Cavinton, Trental, Vinpocetine,
- Sedatives – “Valerian extract”, “Novopassit”, “Persen”,
- Antidepressants - Prozac, Amitriptyline,
- Sensitizing drugs – “Diphenhydramine”, “Suprastin”,
- Medicines with vasodilating, antiplatelet and neurometabolic effects - “Betaserc”, “Betaver”,
- Steroids – Prednisolone, Dexamethasone,
- Vitamins A, E, B, PP and vitamin-mineral complexes.
Outpatient treatment is indicated for patients with mild to moderate forms of pathology. Patients with an advanced stage of the disease are hospitalized, in the presence of severe complications or their inability to move independently.
If such therapy does not produce positive results, and the patient's condition continues to deteriorate, doctors prescribe intravenous corticosteroids and plasma exchange therapy. In some cases, the only salvation for patients is surgery, the effectiveness of which usually reaches 70%.
Physiotherapy complementary to drug treatment:
- medicinal baths,
- massage,
- exercise therapy,
- oxygen therapy,
- acupuncture,
- hypnosis,
- Ural Federal District,
- reflexology,
- magnetic laser influence.
Special physical exercises increase the resistance of the vestibular apparatus. They normalize coordination of movements, increase the threshold of excitation, and restore the stability of a person’s vertical posture.
Traditional medicine complements, but does not replace, drug therapy. They can only be used after consultation with a specialist. The most common folk recipes intended to treat the syndrome:
- infusion of corn silk or juniper berries,
- remedy of garlic, honey and lemon,
- a decoction of thyme, motherwort, mint and borage,
- spring primrose flower tea,
- remedy of cranberry, honey and horseradish,
- mint infusion.
These general therapeutic measures restore the functioning of the statokinetic analyzer and eliminate dizziness. Patients become more confident in their gait, the functioning of the nervous system improves, and anxiety, restlessness, and panic disappear.
The structures of the vestibular apparatus begin to work fully, the general resistance of the body increases, pain and discomfort disappear, the severity of dizziness and dyspepsia decreases, heart rate and blood pressure levels normalize. The patients' movements become coordinated and their body position becomes stable.
The body's condition noticeably improves, performance is restored, and the quality of life increases.
Prevention
Medical recommendations to prevent the development of the syndrome:
- Balanced and rational nutrition,
- Maintaining a daily routine
- Performing physical exercises that train coordination and the vestibular system,
- Rejection of bad habits,
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle,
- Adequate sleep and rest,
- Prevention of stress,
- Strengthening immunity,
- Fighting obesity
- Limited sun exposure
- Psycho-emotional calm,
- Compliance with medical prescriptions in the presence of concomitant diseases.
Forecast
Any disease, including vestibulo-ataxic syndrome, should be treated in the early stages, when the risk of developing irreversible changes is minimal. If the syndrome is started, the body will not survive.
When the first symptoms of pathology appear, you should consult a specialist for medical help. For the therapy to be effective, it is necessary to determine the cause of the disease.
It is necessary to treat not the symptoms, but to eliminate all etiopathogenetic factors that provoked the disease.
The prognosis of vestibulo-atactic syndrome is favorable if the patient consults a doctor in time and begins treatment. Elderly people and people with an advanced stage of the syndrome have irreversible changes in the body that cannot be treated. The disease progresses steadily and leads to serious consequences.
: “Doctors” program about dizziness
Source: https://sindrom.info/vestibulo-atakticheskij/