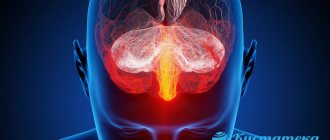
Head injuries are considered the most dangerous because they can be accompanied by serious consequences and complications. If the blow is light, then slight pain may be noted, but with strong impacts, a concussion, skull fracture, brain damage and other serious disorders often develop.
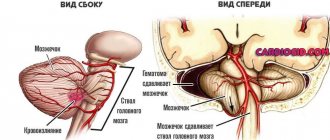
A bruise on the back of the head caused by a fall is considered especially dangerous. It may be accompanied by tissue swelling, intracranial hemorrhage, brain displacement and other unpleasant consequences. If you receive this injury, you should take the first rehabilitation measures and call an ambulance.
Characteristic signs of injury
A neck bruise can manifest itself in two main types: open (a rupture of the surface tissue occurs) or closed (the soft or bone tissues of the neck, as well as the cartilaginous formations of the throat, suffer). Sometimes the spinal cord or its nerve and vascular endings are damaged.
In order to very quickly decide what to do in this dangerous case, you need to have a good understanding of the full set of basic signs of a bruise with various types of damage. They are directly related to the cervical spine, and its injuries are fraught with serious consequences. The clearance in the vertebrae is very small, so muscles, ligaments, nerves or blood vessels may be damaged.
The main symptoms that most often manifest such a bruise are:
- Severe pain in soft tissues.
- Significant difficulty moving.
- Unbearable migraine.
- Severe swelling of the affected area.
- Local increase in temperature.
- Constriction of the pupils.
- Noticeable tremor of the hands or head.
- Pain in the shoulder area.
- Numbness.
A combination of such symptoms may indicate a bruise, dislocation or displacement of a vertebra, damage to a column, sprain of the cervical muscles, rupture of ligaments or disruption of the integrity of the cartilage.
First aid
If you have a neck injury, the injured person needs immediate first aid.
The first step is to call an ambulance, and before its arrival the patient is given any painkillers.
If a person has fallen and is lying down, then you should not move him to another place in order to avoid increasing possible damage. He needs to be provided with maximum peace.
It is necessary to ensure that the patient receives the maximum amount of fresh air if breathing is difficult.
If he has completely lost consciousness, he needs to be turned on his side so that if vomiting occurs, it does not flow into the esophagus.
Ice or a cold compress should be applied to the area of the neck bruise, localized on the right or left. But keeping it on the damaged area for more than a quarter of an hour is not recommended, since such a measure can cause hypothermia or infection.
Treatment of chronic post-traumatic headache
The doctor selects a comprehensive treatment for attacks. Abuse of painkillers and early cessation of therapy is dangerous for the patient with severe mental, neurological and psychological disorders. The prescription of maintenance drug therapy depends on the characteristics of the treatment of pathology in the acute period.
There is no single scheme for stopping attacks. Adaptation to the outside world and return to social life is carried out gradually. A victim with minor head injuries is prescribed anxiolytics and vascular nootropic drugs.
For vegetative and emotional disorders, psychotropic drugs combining antidepressant, vegetotropic, anxiolytic and sedative effects are appropriate. Such drugs do not impair the functioning of the heart and liver and are suitable as monotherapy.
Additionally, massage of the neck and head area, physiotherapy, magnetic therapy, acupuncture, and laser reflexotherapy are prescribed. For anxiety and depression, you will need the help of a psychologist or neuropsychiatrist.
To relieve post-traumatic complications, the doctor selects vasoconstrictors, non-steroidal, vasoactive drugs, as well as anticonvulsants and antidepressants.
↑
https://gidpain.ru/bolit/hronicheskaya-posttravmaticheskaya-golovnaya.html
Therapeutic measures
In case of a neck injury, the patient must first be taken to the hospital for diagnostic measures.
They necessarily include clarification by the doctor of all the circumstances of the injury, careful palpation of the damaged area, and examination of the degree of mobility of the spinal column or limbs.
It is required that the patient, in addition to the traumatologist, be carefully examined by a neurologist to determine:
- preservation of reflexes:
- degree of muscle conduction;
- no damage to the brain or spinal cord;
- clarification of the level of nerve response to touch.
If hemorrhage is suspected, it is advisable to perform a puncture. It is usually prescribed for severe injuries to the neck or spine, severe swelling of soft tissues or large bruises.
In order to make a final differential diagnosis for a bruise, it is necessary to conduct a survey radiography in three projections.
After the treatment plan has been outlined, the doctor injects an analgesic (Diclofenac, Analgin). In the case when a painful shock occurs, a blockade is carried out with local anesthetic drugs (Novocaine, Lidocaine). It is possible to use electrophoresis with pharmacological agents.
To reduce severe swelling and eliminate local inflammation, hydrocortisone or Prednisolone is used intravenously.
If diagnostic measures have demonstrated that there is no concussion, damage to muscles and ligaments, as well as signs of a fracture, then the patient is given a course of therapy. At the same time, his condition is monitored and if there are no signs of deterioration, he is discharged from the hospital.
When there is a suspicion of damage to the spinal cord due to a bruise, the spine is fixed, and preventive ventilation is carried out.
In addition, the patient is prescribed:
- vitamins;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- sedatives;
- tranquilizers;
- muscle relaxants;
- nicotinic acid;
- calcium, etc.
In cases where the injury threatens the life or health of the patient, surgical intervention is performed. Surgery may be necessary if the spinal cord is pinched, severe neurological symptoms occur, there is a threat of paralysis, there is deformation of the vertebrae, the structure of bone formations is disrupted, the functions of the brain are changed, or there is an intractable pain syndrome.
What to do if your head and neck hurt after a blow
Does your head always hurt after a blow? Is it dangerous? Typical questions interest many. This pain may indicate a concussion, vascular ruptures, or internal hematoma. It is possible to help a patient at home, but qualified help is still more acceptable.
When should you seek help?
Immediately after hitting your head, you need to pay special attention to the type of pain syndrome and its characteristics. The following features in the patient’s condition may be alarming:
- for a long period after the blow, the pain does not subside and continues for some time;
- Even strong analgesic drugs are not able to relieve pain;
- the blood pulsates so strongly that temporal pain and tinnitus appear;
- neck movements are constrained, making it difficult to turn.
The following factors will help determine the state of the brain:
- unconscious state;
- often feel dizzy;
- darkens in the eyes;
- vision deteriorates, the image becomes blurry;
- speech disorders appear;
- frequent urge to vomit;
- the entire body is weakened;
- puffiness and bruising appear under the eyes.
If a concussion occurs, then not only does the head hurt after the blow, but also hallucinations, convulsive attacks, and loss of orientation in space appear. Associated symptoms include disturbances in motor coordination, irritability, and inadequate response to loud sounds or bright lights.
If you lose consciousness but feel well, you should still be examined by a doctor. Trauma can cause hematomas, vascular ruptures, and inflammatory processes.
Hospitalization is mandatory if the head blow occurs in the temporal region. A patient who avoids treatment exposes himself to irreversible and serious consequences.
Cases with neck and back injuries are dangerous. After all, damage or displacement of the vertebrae can lead to damage to blood vessels, disruption of blood supply to the brain and the appearance of pain.
[]a2mOnvQjVUY[/]
If a person hits his head hard, the following complications may occur:
- a split personality appears;
- speech becomes incoherent;
- Nervous disorders are observed;
- memory weakens, the cognitive system fails;
- hearing and vision deteriorate, taste and smell are impaired;
- convulsions and paralysis can ultimately lead to a coma.
There are certain cases when a visit to the doctor is vital:
- injuries with bleeding lasting more than 15 minutes;
- pain in the head and neck intensifies and is accompanied by nausea;
- body temperature exceeds 38 ºС;
- convulsions are observed;
- the ability to move independently is lost;
- changes in the size of the pupils with subsequent loss of vision;
- breathing becomes difficult, loss of consciousness occurs.
Drug treatment
After a person hits his head so much that a number of symptoms appear, it is advisable to use the following drugs:
- piracetam - its action is aimed at improving metabolism at the level of brain cells and relieving pain;
- etamsylate stops bleeding and improves blood circulation in the brain;
- ascorutin strengthens the walls of blood vessels;
- aminophylline helps relieve swelling and normalize blood pressure;
- Diacarb (diuretic) helps lower blood pressure, reduce swelling and stress on the heart;
- Antibacterial drugs are recommended for ruptured eardrums.
What to do if a person received a head blow and the necessary drugs were not nearby? In this case, medications from the first aid kit are suitable: nurofen, analgin, spasmalgon, paracetamol, unispasm.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SzaZ7_5vwoE
It is also important to balance the electrolytes (calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium) in the body after a head impact. They affect muscle function. When hit, convulsions may occur. To prevent them, you need to consume an adequate amount of electrolytes. Therefore, the main thing is to avoid dehydration and drink more fluids to replenish electrolytes in the body.
A child who hits something and experiences severe pain needs to be examined and hospitalized. Often hidden damage is very difficult to identify, especially at home.
[]B9WIfq9HP[/]
A hit to the head can provoke very serious complications, so a qualified specialist can not only prescribe medications, but also contribute to positive changes in the body:
- improve metabolism;
- strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- relieve swelling;
- restore blood circulation.
It is important to remember that if a girlfriend or boyfriend, respectively, hits her or hits her head, you need to immediately go to the hospital. Thus, there is a greater chance of preventing various injuries. Bed rest, minimal physical activity, and avoiding computers and TV will help preserve your health and speed up your recovery.
Useful tips and recipes of traditional medicine
If a person hits his head, what should he do? For a speedy recovery, you just need to follow the doctor’s recommendations and follow some rehabilitation rules.
- Rest and only rest. After injuries, it is better to lie down, rest or sleep. Good sleep will help relieve pain after impacts. Meditation and complete silence will also be beneficial. A cold compress with water or cabbage leaves can alleviate the general condition of the body. You can relieve spasms and relax with mint tea.
- Medicinal herbal tinctures. They can soothe and relieve pain. Most often, teas or drinks made from vegetables are recommended. Ideal would be: potato decoction, tomato juice, carrot-beet juice, motherwort tincture or St. John's wort.
- Acupressure is quite effective in relieving painful sensations. The impact on the temple area in the form of rubbing stimulates the body's production of natural painkillers.
- It is better to get rid of bruises in the early stages of their occurrence. If a person hits his head so badly that hematomas and abrasions appear, he urgently needs to use a flax plaster, viper fat or other pharmaceutical products.
- Aromatherapy has an auxiliary effect. You can relax before bed after taking a bath based on essential oils with lavender, lemon, grapefruit, sage, mint, chamomile, and eucalyptus. Massaging the temples, forehead and other painful areas will bring a relaxing effect and help you forget the ominous blow.
This type of therapy can be different. Essential oils are added dropwise to a container with warm water and placed in a resting or sleeping area. After such procedures, it is better to sleep, rest, and relax.
[]-vd7VzUPAwg[/]
To avoid unpleasant and dangerous situations that threaten your health, you must adhere to basic safety rules.
Timely consultation with doctors can maintain health and prevent possible consequences.
Source: https://upraznenia.ru/bolit-golova-sheya-posle-udara.html
Recovery
In order for a patient to be able to return to a normal lifestyle and gain full working capacity after a neck injury, a long rehabilitation period is required.
At this time the following is carried out:
- use of leeches;
- wearing a corset;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy;
- oriental medicine;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- paraffin;
- mud therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- reflexology.
It is very important to determine the timing and position of the patient while observing bed rest.
How he will eat should also be carefully considered. How much fluid he needs and how it will be supplied to him, it is advisable for the victim’s closest relatives or himself to take care of such measures if there is no one to help.
If you have a neck injury, you need good sleep, no unnecessary physical activity, and complete peace of mind.
However, staying in bed all the time is also not recommended. Moderate physical activity, daily gentle exercises with constant complication of exercises, as well as water procedures are required.
Possible consequences
In the absence of immediate medical attention, severe complications can occur if you have a neck injury.
Among them may be:
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- paresis or paralysis;
- dysfunction of internal organs;
- coma;
- swelling of the spinal cord;
- compression of the nerve roots;
- hernia;
- internal hematoma;
- oxygen starvation of tissues;
- collapse;
- pinching of blood vessels.
Similar article - Itching and burning of the scalp, causes, treatment
The most terrible can be the long-term consequences of a neck injury, especially when the patient did not seek help in time or serious damage remained undetected.
If the spinal cord is affected during the injury, then persistent dysfunction of the internal organs may subsequently occur. There may be a disturbance in the sensitivity of certain areas of the body, as well as changes in the activity of various systems.
Sometimes there is a gradual decrease in the range of movements in the neck or limbs, up to the complete inability to perform active actions. In such a case, long-term serious treatment is necessary, and it does not guarantee a complete return to normal condition.
The neck muscles are very vulnerable and when struck they cannot protect the underlying structures.
The vertebrae perform a colossal function both in supporting the entire body and in innervating all organs and systems.
Therefore, a neck injury should be taken very seriously. It must be remembered that this part of the spine has seven joints and each of them can be seriously damaged. The vessels responsible for the blood supply to the brain pass through this place, so an injury can have a very serious impact on a person’s entire condition.
One of the most dangerous pathologies is a fracture of the cervical spine. The danger is damage to the upper portion of the spinal cord, causing paralysis or death. Why does my neck hurt after hitting my head
?
Who solves the problem and how?
The Americans really sounded the alarm back in 2010. In one year, high schools across the country reported 50,000 concussions after playing football: more than among basketball, baseball, softball and wrestling players combined. In 2015, the American Federation released a new set of rules: all players under 10 years of age are prohibited from hitting the ball with their heads during training and games, and players from 11 to 13 are prohibited from hitting the ball during matches .
British scientists, in turn, found that head impacts are more dangerous for girls than for boys ; they are more likely to get concussions.
However, the main problem is that it is still not scientifically confirmed whether there is a real connection between heading and brain problems .
“The first study we conducted in the early 2000s did not give clear conclusions,” says Gordon Tyler, chairman of the professional football association. “We are now ready to invest in new research and, with the development of new technologies over the past 15 years, we hope to get answers.” I am disappointed that FIFA or other confederations have not taken up this issue as the governing authorities of football, but we have agreed with the FA that we will carry out a study together.
“We can send all the footballers for examination and find out how many of them have dementia,” the director of the medical department, Dr. Charlotte Cowie, explains the FA’s position. – We will get statistics, but this will not solve the problem. To make decisions like banning head play at the child level, we need serious research, a panel of experts and a scientific process that will provide reliable answers. We want to study retired players and get the main answer: is it true that dementia is more common among footballers than among the general population?
On Thursday, the FA officially announced that serious research into how football affects health and the risk of dementia will begin in January 2018 .
Causes of pain during injury
Pain is the body's natural response to injury. In addition to headaches, the victim may experience weakness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, memory impairment and dizziness.
In severe cases, loss of consciousness and coma develop. These symptoms are a sign of compression of the brain matter and damage to nerve cells.
The nature of the sensations and possible consequences depend on the type of injury. Pain may be caused by:
- falling;
- blow to the head with a sharp or blunt object;
- head injury at work or during an accident.
If a person experiences a headache after a blow, it is important to immediately consult a doctor for an examination and a full diagnostic examination.
According to statistics, up to 70-80% of head injuries result in a concussion. This pathology is characterized by severe neurological problems, and one of its common symptoms is headache. Do you always get a headache after hitting your head? What could this indicate? And how to treat a concussion?
Head injuries have serious health consequences. They can cause concussion, bruise, brain contusion, vascular rupture or interstitial hematoma. Even minor damage can lead to further problems: why you get a headache after hitting your head, what consequences this can lead to, and how to avoid complications: read more in our review.
Read how to help a child after a head injury. In what cases is urgent hospitalization necessary?
Why does throbbing pain appear in the head? What to do if an alarming symptom appears.
If they begin to bother you regularly, prompt action should be taken
Each of us faces headaches more than once throughout our lives. Of course, it is not always a cause for serious concern. A headache can come from both overwork and lack of sleep, changes in atmospheric pressure and - as is familiar to many representatives of the stronger sex - from a large amount of alcohol consumed.
General symptoms
A bruise on the back of the head in a child and an adult is usually accompanied by similar symptoms. But for children, even minor damage can be fatal, this is due to the thin and soft structure of the skull of the head.
Each form of injury may exhibit certain symptoms. Typically, in mild cases, the following symptoms are observed:
- fainting (this condition can occur within a few seconds or minutes);
- the person is poorly oriented in space, he may experience confusion of thoughts;
- Memory loss may be observed, it can be retrograde or anterograde;
- after the blow, a sharp pain in the head may immediately appear, and dizziness may occur;
- nausea, which may be accompanied by vomiting;
- there may be noise and buzzing in the ears;
- pain in the eye area.
Injury to the occipital region of the head, which is mild, is easily tolerated, but it is still important to provide first aid on time. And you shouldn’t delay calling the doctors, because even a small blow can cause complications in the future.
With a moderate injury to the head or back of the head, the following signs and conditions appear:
- prolonged fainting, which can persist for several minutes or hours;
- inhibited state and limited space, a person cannot adequately perceive the environment;
- sometimes there is memory loss;
- headaches with a diffuse nature;
- Meningeal symptoms may be present - rigidity of muscle tissue in the occipital region, blocked ears, short-term hearing loss, paralysis, problems with sensitivity, a feeling of numbness, tingling in the limbs, in the face.
It is worth noting! If the skin is damaged, blood and cerebrospinal fluid may appear from the physiological openings of the head - nasal openings, ear canals, pharynx.
Sometimes there is a hematoma on the back of the head after a fall or a violation of the structure of the skull. In this case, you should be especially careful; it is better not to touch the victim, because even the slightest sudden movement can be fatal.
It is important to call an ambulance immediately. In addition, other serious problems may occur:
- Heartbeat disorder (tachycardia, bradycardia).
- Blood pressure readings may be high.
- Breathing problems, which may be due to obstruction of the airway.
During the acute period, primary brainstem symptoms may appear - horizontal, slow, chaotic eye movements, pupils may dilate or contract, unstable changes in the tone of muscle tissue. In case of severe injury, a neurological deficit is clearly manifested, which is accompanied by severe depression of consciousness and falling into a coma.
Types of injuries caused by blows to the head
A person can hit his head against a wall, put his forehead against the glass on a bus, or get hit with a bat or a stone. A significant number of traumatic brain injuries are recorded among motorists involved in accidents.
A blow with a fist to the eye, to the scalp, to the temple, to the neck also leads to injury. Even an infant can receive a traumatic blow to the head when passing through the birth canal.
Possible consequences of impacts:
- Hematoma on the face, scalp, scalp.
- A lump that looks like a skin bump, without a bruise.
- Bleeding from the nose, ears.
- Damage to the skin, abrasion.
- Significant damage to soft tissues, rupture of skin and muscles.
- Facial bone fracture.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage.
- Brain concussion.
- Fracture of the skull bones.
- Fracture of the base of the skull.
Risk factors for concussion
Most often, a concussion occurs after a fall, impact, during sports, or as a result of a traffic accident. Often found in children who hit their heads while playing. If there is loss of consciousness, nausea, dizziness and/or headache (particularly in the back of the head), the victim must be taken to a doctor immediately.
Principles of treatment
If the victim has a headache after a blow: what to do in this case? Follow the doctors' recommendations:
- Provide emergency assistance to the victim. If he is conscious, place him on a hard, flat surface, raising his head and shoulders slightly higher than his pelvis and legs. If a person is stunned and does not respond to speech addressed to him or other stimuli, place him on his right side, slightly tilting his head back and turning his face down. In this case, the left limbs should be bent at an angle of 90 ° and lie freely on the ground. This position will provide the victim with easier access to fresh air into the respiratory tract, and will not allow him to choke on gastric contents in case of possible vomiting.
- Call an ambulance or take the victim yourself to the emergency room for a primary medical examination.
Learn how traumatic brain injuries are classified by severity. What symptoms are used to determine the severity of TBI?
Read about the consequences of a hematoma on the head after a blow. What to do if a hematoma appears.
After a person hits his head so much that a number of symptoms appear, it is advisable to use the following drugs:
- piracetam - its action is aimed at improving metabolism at the level of brain cells and relieving pain;
- etamsylate stops bleeding and improves blood circulation in the brain;
- ascorutin strengthens the walls of blood vessels;
- aminophylline helps relieve swelling and normalize blood pressure;
- Diacarb (diuretic) helps lower blood pressure, reduce swelling and stress on the heart;
- Antibacterial drugs are recommended for ruptured eardrums.
Similar article - Meningococcal infection incubation
What to do if a person received a head blow and the necessary drugs were not nearby? In this case, medications from the first aid kit are suitable: nurofen, analgin, spasmalgon, paracetamol, unispasm.
- piracetam - its action is aimed at improving metabolism at the level of brain cells and relieving pain;
- etamsylate stops bleeding and improves blood circulation in the brain;
- ascorutin strengthens the walls of blood vessels;
- aminophylline helps relieve swelling and normalize blood pressure;
- Diacarb (diuretic) helps lower blood pressure, reduce swelling and stress on the heart;
- Antibacterial drugs are recommended for ruptured eardrums.
If the pain continues to torment, you need to be examined in a hospital. There may be serious damage that is difficult to diagnose on your own. For example, in order to avoid the onset of inflammatory processes, a specialist will prescribe treatment with antibacterial drugs.
In addition, the doctor will give recommendations for taking medications to alleviate the person’s condition after injury. For example:
- Improving metabolism between brain cells with piracetam. The drug helps cope with severe headaches and dizziness.
- Strengthening the walls of blood vessels with ascorutin.
- Prevention of swelling in the brain with high blood pressure by taking aminophylline.
- Restoring normal blood circulation with ethamsylate.
Treatment of occipital injury is prescribed by a specialized doctor (neurologist, traumatologist or neurosurgeon) after diagnosis and determination of the severity of the injury.
For a mild bruise or concussion, treatment can be done at home. To do this, the doctor may prescribe the following measures and recommendations:
- Bed rest and silence for the first few days after the stroke.
- Painkillers if you have pain in the back of your head.
- Apply a compress to the impact site with magnesium solution twice a day in the first days.
- Treatment of the injury site with ointments (Heparin ointment, Troxevasin, Traumeel-gel).
Severe injuries to the back of the head require mandatory hospitalization and treatment under the supervision of doctors. In such cases, the following may be added to the treatment methods and measures described above:
- Sedatives.
- Antiemetic and antinausea tablets.
- Medicines that normalize blood circulation and nourish the brain.
- Physiotherapy course.
After completing the main treatment course and discharge, the patient is given the following recommendations:
- providing an easier operating mode;
- exclusion of physical and emotional stress in the first month after discharge;
- limiting the time spent at the computer;
- regular exposure to air;
- normalization of sleep;
- restriction in the daily menu of foods that provoke vasospasm and the development of headaches.
After a certain time, even if you feel well, you need to visit a doctor for a preventive examination. This will reduce the likelihood of complications and subsequent unpleasant sensations that interfere with living a full life.
How to relieve discomfort?
If you experience headaches and dizziness a few hours or days after hitting your head, you can try to relieve the discomfort at home. If you notice signs of a concussion, it is best to seek medical help.
At home
A prerequisite for the recovery of a patient with a head injury is compliance with bed rest. For at least three days, the patient should lie down, not watch TV, not play on the computer, tablet, or phone. After a head injury, you cannot listen to music on headphones for several days, get into arguments, or experience significant emotions (get very upset, rejoice, cry).
To eliminate nervous overexcitability, you can brew teas with medicinal herbs: chamomile, nettle, mint, lemon balm, Chinese lemongrass.
If a woman hits her head, her neck or the back of her head hurt, you can make lotions with grated potatoes or pumpkin paste.
Abrasions and scratches can be lubricated with goose fat or the wound healing ointment Bepanten can be used. Alcohol or beetroot-honey lotions are good for bruises.
With the help of a doctor
It is advisable to visit a doctor after each injury and receive recommendations for treatment. Only a doctor can determine during examination whether there is damage to the bone structures and how much damage has been caused to the soft tissues. With the help of an in-depth examination, it is possible to determine how damaged the brain tissue is and whether the vessels of the head and neck are damaged.
Elderly people fall and get hit very often. If your elderly grandmother hit her head, now the back of her head hurts, and she feels very dizzy, the doctor may recommend taking the following set of medications:
- To normalize cerebral circulation and increase cerebral vascular tone - Piracetam, Noofen, Cavinton.
- To relieve tissue swelling - Diacarb, Furazalidone.
- To stop bleeding - Etamzilat, Vikasol.
- With the development of meningitis, the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the tissues of the head and face, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs.
- If the patient suffers from nausea - Cerucal.
- With a significant increase in blood pressure, patients are prescribed Eufillin.
For pain relief, combination drugs are most often recommended: Solpadeine, Aspasmik, No-shpalgin, Codelmixt, Pentalgin. They have an anti-inflammatory effect and relieve pain for a long time.
You can’t just endure it if your head hurts after a blow, and painkillers don’t bring relief. Instead of increasing the dose of pills on your own, you need to see your doctor again and undergo a brain examination with an MRI or CT scan.
First aid for injury
Typically, if the head hits a hard object, the classic signs of a traumatic brain injury will begin to appear. The most common symptoms of TBI after a person falls and hits themselves - loss of consciousness, vomiting - confuse others who do not know what to do with the victim.
If the blow was strong, immediately after the injury, before the ambulance arrives, you can provide the following assistance to the victim:
- Place the person on their side or so that the shoulders and head are slightly elevated. This will prevent a situation in which the victim may choke on vomit.
- Make sure that the person does not move. The neck should be in one position and not rotate.
- If your temple has been damaged, you need to carefully apply something cold, but under no circumstances press on the injured area. The same goes for bumps and spreading bruises.
If there are bleeding abrasions, it is advisable to treat them with a solution of furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide.
If a person hits the back of his head, then the nature of the actions that need to be performed in case of a back injury directly depends on the severity of the blow and the symptoms that appear in the first minutes.
If there is a slight blow to the back of the head, consciousness is present, and there is no nausea or signs of disorientation, the victim should be given the following assistance:
- put it on the sofa or bed;
- ensure silence;
- apply a cold compress in the form of ice wrapped in a towel to the back of the head every 15 minutes with a break of half an hour;
- treat an abrasion or hematoma if the skin is damaged as a result of the blow;
- Show the victim to a doctor to rule out a mild concussion.
Loss of consciousness even for a short period of time, nausea, dizziness and disorientation in space may indicate a more serious traumatic effect: the development of a concussion or the formation of intracranial hematomas. In such cases, people with the injured person should promptly take the following actions:
- Carefully place the victim on a flat, hard surface. If there is a possibility of damage to the vertebrae of the neck or back, then moving it is not recommended. In this case, you should carefully turn the injured person on his side so that he does not choke on the mass in case of vomiting, and raise his head a little.
- Call a medical team immediately and do not let the victim fall asleep until they arrive.
- Measure the injured person’s pulse and ask him how he is feeling, so that he can then provide this information to the doctors.
If the symptoms are severe, the victim should not apply compresses to the injury site or give painkillers. A decrease in symptoms and dulling of sensations as a result of taking them can complicate the diagnosis of injury and lead to the prescription of incorrect treatment.
How serious is the problem?
Doctors record: today in Britain 850 thousand people suffer from dementia. And among them there are many football players.
One of them is Matt Theese . He played football in the 1960s and 70s in England and Scotland and his strong point was always heading. Now 78, Matt is cared for daily by his wife May.
“We have an order that we follow,” she says. – It’s difficult: every day Matt is usually quite quiet, he doesn’t talk much, he doesn’t know that this is his house . This whole thing breaks my heart. We are in the final stages, which could last 2 years or 10 years - no one knows for sure.
– Tell us, who did you play for? Shearer asks Teese.
- “Luton”, then I... What happened after?
“You played in Scotland,” the wife adds. – Then to Grimsby, and then to Charlton Athletic.
- Oh yeah…
– Central midfielder or striker?
- Forward. I scored goals! - Tiz answers happily, and his wife shows a typical photo from the 1970s: Matt jumps out and heads the ball into the goal.
Sometimes Matt goes to Sports Memories support group meetings. The charity helps older people suffering from dementia, depression and loneliness by engaging them in social activities and evoking career highlights. The biggest fear for people with dementia is losing connection with family and community, and sport is a huge part of life for many Britons, giving them the opportunity to socialize over legendary matches and famous players. Sports Memories is now working with the Professional Football Association (PFA) to produce a booklet for former players suffering from memory loss.
– May, do you think football is to blame for your husband’s illness?
- Without a doubt. I have no problem telling you at least 8 other football players who played during that era and suffered from dementia or Alzheimer's disease. My grandchildren play football, but I don’t go to their matches, it makes me feel bad. The senior plays as a defender and he constantly clears the ball with his head. I just can’t look at it - because I know very well what this can lead to.