Almost every modern person is familiar with a headache. Many are so accustomed to this that when it occurs, they automatically drink a painkiller and continue to calmly go about their business.
This algorithm of behavior is fundamentally wrong, since pain is a very characteristic symptom indicating serious problems. Constantly “ignoring” such body signals can lead to the subsequent need for expensive and lengthy treatment.
A man complains of headaches after a concussion
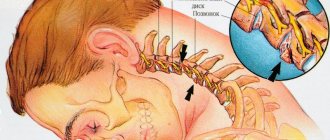
Pain in the head, regardless of its location, can indicate both banal fatigue and serious problems in which medical intervention becomes necessary. Pain syndrome that develops after an injury, does not have clear boundaries, and often spreads to the eyes requires special attention. Unlike pain, for example, which develops as a result of psycho-emotional overload, post-traumatic pain syndrome cannot be ignored. Pain syndrome after traumatic brain injury (TBI) can be of two types - acute and chronic.
Start
Signs of a concussion can vary. They, as practice shows, differ depending on the age of the victim. Therefore, it is worth understanding: a child, an adult and an old person have different signs.
The first step is to understand how grass manifests itself in an ordinary middle-aged person. The first time after the impact plays a huge role. Typically, during this period, one-time vomiting, clouding of mind (with short-term amnesia), and rapid breathing are possible. Also, after a blow to the head, the victim has a headache with any movement, the pulse quickens or slows down. These manifestations disappear very quickly; they can accompany a person for half an hour. It all depends on the degree of injury.
Types of headaches and the mechanism of their development after a concussion
Post-traumatic headache
In the development of cephalalgia after traumatic brain injury, several leading mechanisms can be identified:
- Vascular.
- Neuromuscular.
- Liquor.
- Neurotic.
- Shell.
In practice, a combination of several mechanisms is often encountered, which somewhat complicates the diagnosis and selection of effective treatment for cephalalgia after a concussion.
Cephalgia with TBI appears after injury and gradually increases, which is associated with various reasons:
- Increased intracranial pressure - occurs as a result of a violation of the cerebrospinal fluid dynamics after a blow to the head, in this case the patient will experience pressing pain in the occipital region, in some cases spreading to the area of the crown and forehead.
- Irritation of nerve endings localized on the membranes of the brain - as a rule, a similar effect is observed if there is swelling of the brain tissue.
- Impaired blood circulation in the cerebral arteries - a sharp blow provokes a violation of vascular tone, resulting in a spasm of the arteries, which entails the development of pain.
- Overstrain of the muscles of the neck and head leads to the development of tension headaches, manifested by pressing unpleasant sensations over the entire surface of the head.
Depending on the severity of the injury, cephalgia can occur in acute and chronic forms, varying in duration and intensity of pain attacks.
4.1. Epidemiology
Migraine is one of the most common forms of primary headache, which has been known to mankind since ancient times. The disease is caused by hereditarily determined dysfunction of vasomotor regulation.
Migraine is manifested by paroxysmal attacks of pulsating headaches, often in one half of the head, accompanied in most cases by nausea, sometimes vomiting, photophobia (poor tolerance of bright light) and phonophobia (poor tolerance of loud sounds).
Chronic cephalgia
Sometimes after a traumatic brain injury, pain does not appear immediately, but increases gradually over several weeks after the injury and persists for a long time. In such cases, they speak of chronic post-traumatic headache, the distinctive feature of which is a prolonged pain syndrome (more than 8 weeks).
Patients suffering from a chronic form of cephalgia complain of headaches of various localizations, and the nature of the pain can be throbbing or pressing. Most often, patients are tormented by diffuse cephalgia; an attack can last several hours or not stop for several days, completely exhausting the patient. As a rule, patients become irritable, quickly get tired and are unable to do their usual work.
Chronic post-traumatic headache may occur after TBI
All chronic headaches can be divided into groups according to symptoms and mechanisms of development:
- Migraine-like cephalalgia.
- Tension headache.
- Cluster headache.
- Cervicogenic cephalgia.
- Liquor-hypertensive cephalgia.
In adults
The first signs of a concussion are clear. But, as practice shows, defining injury in this way is very problematic. Typically, diagnosis is based on a description of a citizen’s complaints. What can be observed some time after receiving a concussion?
There are many options for the development of events. In any case, with serious injuries, you will experience nausea and even vomiting. We are talking about repeated incidents. General weakness of the body, sleep disturbances (usually in the form of insomnia), pressure surges - all this also indicates a concussion.
Does your head hurt for a long time after hitting your head? Something like migraines has started? Is the temperature fluctuating? Does your face turn red for no reason? Then it's time to go to the doctor. You most likely have a concussion. It is noted that in adults, trauma is often manifested by memory loss (amnesia), sweating and tinnitus. It is possible that you will simply feel uncomfortable. Pay special attention to these signs.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the severity of the injury.
In adults
In older patients, the system of manifestations differs. Among the possible signs of a pathological condition.
- Impaired consciousness. In domestic medical practice, it is believed that with a concussion, the maximum duration of loss of consciousness is an hour. In foreign countries the period is several times longer.
Usually, with damage to cerebral structures, if they are purely functional in nature, fainting lasts several minutes, more often - even less. In approximately half of the cases, the patient does not lose consciousness at all, but remains in a stunned state.
After TBI, tomography is performed. To exclude morphological, structural changes in cerebral fibers.
- Nausea is the first sign of a concussion, associated with disturbances in the nutrition of cerebral structures and nerve tissues. It is not dangerous, but it is extremely difficult for patients to tolerate and causes a lot of discomfort to people.
- Vomit. As a rule, one-time and only in the initial period, immediately after a concussion.
- Amnesia of various forms as symptoms of a concussion does not always occur. There are two classic cases. Retrograde memory loss concerns events that preceded the damage. Congradnaya - during the acute period.
Anterograde loss of memories is much less common. That is, from the moment of injury until recovery to a relatively normal state.
This symptom of a concussion is associated with disruption of the temporal lobe of cerebral structures and functional failure of the cortex. As a rule, it disappears completely, leaving no negative consequences.
- Headache. It may develop some time after the injury. After a few hours and even a day.
This is a non-specific phenomenon. The intensity of discomfort is significant, especially with severe shaking. The correction is symptomatic; analgesic drugs are used.
- Dizziness. Signs of a concussion in adults also affect the vestibular system: coordination of movements, orientation in space are impaired, and one’s own body feels weightless.
This symptom accompanies a person throughout the entire acute period, up to several weeks. It fades gradually as brain function recovers.
- Weakness. A feeling of softness in the limbs, the inability to move normally.
- Noise in ears. Squeaks, rustles, hum. Patients describe this uncomfortable sensation in different ways. Healthy people also have sound. It is associated with uniform blood flow through the vessels located in the skull.
Changes in the tone of noises and their intensification are associated with disturbances in the trophism of cerebral structures and uneven movement of liquid connective tissue through the vessels. The condition may interfere with sleep, rest, and work.
- Heart activity disorders. Acceleration, deceleration, irregular rhythm. An alarming pathological sign indicates that the functions of the brain stem are impaired.
The help of specialists and constant monitoring in a hospital are required. These forms of concussion, which affect fundamental areas of nerve tissue, are life-threatening. Cardiac arrest and death from complications are possible.
- Insomnia. A mild concussion is manifested by vegetative symptoms, including disruption of night rest: a person quickly “falls through” and wakes up after 10-15 minutes. So all night.
Or he can’t sleep at all. In such a situation, special drugs are used. Usually light, so as not to overload the already damaged brain.
- Blood pressure surges. Again, this is not always the case. The nature of the manifestation is also vegetative, associated with a violation of the central regulation of the work and tone of blood vessels and cerebral structures.
- Increased sweating. Hyperhidrosis.
The clinical picture becomes the factor that acts as a criterion for classifying the severity of the deviation.
A concussion can be recognized by basic symptoms: nausea, spatial orientation problems, and disturbances of consciousness. In mild cases, a more in-depth diagnosis is needed.
In children
In younger patients, the list of manifestations is almost always the same. This is due to the structural features of cerebral structures and their incomplete formation.
Manifestations of injury include:
- Dizziness. Intensive throughout the acute period. Causes complete loss of activity. It is impossible to study or play.
- Weakness, lethargy, drowsiness.
- Nausea and vomiting. Children are characterized by repeated episodes of reflex evacuation of the contents of the digestive tract. This is a feature of the clinic only for younger patients.
Fainting and amnesia are uncommon. Although there are exceptions.
First aid
The steps are simple. If the victim is unconscious, you need to call an ambulance. Then the algorithm is like this:
- Place the patient on his back with his head turned or on his side. To prevent a person from choking on vomit.
- Check pulse, breathing.
- Clear the oral cavity of mucus and stomach contents if a reflex act has occurred.
- Provide fresh air flow.
Resuscitation measures are carried out as needed. But, as a rule, they are not needed. The condition does not pose such a danger.
Upon arrival of the ambulance, the patient should be escorted to the car.
Attention:
If a person is initially conscious, this does not mean anything. You still need to see a doctor.
It makes sense to help the patient get to the nearest hospital and get a consultation. Because such a TBI, although not so dangerous, is an insidious condition.
If there are signs of a concussion after a blow or fall, the help of a neurologist is required: primary diagnostic measures are prescribed, then treatment is carried out.
Emergency action will help shorten the recovery period and improve the overall prognosis.
What's happening
The brain is a vital organ, so it is located in the cranium and is surrounded by bones that perform a protective function. When there is excessive impact from a blunt object or a person falls, a sharp shock to the head occurs. In this case, the brain, which is 70% fluid and a soft structure, hits the walls of the skull, which leads to trauma. In this case, the vessels of the microvasculature are damaged with small pinpoint hemorrhages in the tissues, swelling of the intercellular substance, which is a consequence of the release of blood plasma from the vessels, and an inflammatory reaction. Against the background of such traumatic changes, the nutrition of neurocytes (cells of the nervous system) may deteriorate, with subsequent irreversible changes in them.
To imagine the mechanism of development of a head injury and damage to the structures of the central nervous system, you can shake half a bottle of mineral water. In this case, the liquid hits the walls of the vessel with the formation of a sufficiently large number of bubbles.
In children
Hitting your head doesn't have the best consequences. People often experience concussions after such an injury. A fairly common occurrence, with minor head trauma it does not cause much harm. Only serious damage can negatively affect the development of the body. Especially for children.
It has already been said that a concussion will manifest itself differently at different ages. You will have to closely monitor your child if he hits his head. Newborns usually turn pale and their heart rate increases. But after this, lethargy, fatigue, drowsiness suddenly sets in, and sleep is disturbed. During feeding, numerous regurgitations are possible, the child behaves restlessly, and may cry for no reason for a long time. This injury is difficult to detect in newborns.
But older children can already tell something about their condition. Does your head hurt after hitting your head? In principle, the manifestations of injury are similar to those observed in infants. But only sometimes a child can get short-term amnesia. This is normal and indicates a concussion.
Possible consequences and dangers
The condition goes away relatively easily. But no one guarantees that months and even years later the damage suffered will not affect your health.
The later treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of a negative scenario.
Possible complications of a concussion include:
- Mental disorders. A diverse layer of violations. As a consequence of a concussion, depression, neuroses, especially the anxiety spectrum, and phobias, including newly acquired ones, develop.
Attention:
Psychoses with hallucinations, delusions and other disorders of thinking and perception are especially dangerous.
This is also possible. In the first year, you need to carefully monitor your well-being.
- Headaches of unknown origin. It is impossible to determine the cause even with a thorough diagnosis. The condition remains idiopathic. A symptomatic course of treatment is prescribed. Relief of discomfort.
- Migraine. Headaches of vascular origin. They occur in fits and starts.
- Encephalopathy. Chronic disturbance of cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Without treatment, there is a high risk of dementia, loss or weakening of cognitive functions.
- Post-concussion syndrome. A complex condition that is almost impossible to treat. Accompanied by excruciating pain and disorders similar to those that occur with encephalopathy.
- Convulsive attacks. Similar to epileptic symptoms, only without obvious signs of increased electrical activity of nerve tissue.
Illnesses due to concussion occur in 10-15% of clinical cases, mainly represented by relatively harmless episodes of headaches and coordination problems.
Old men
What else should you pay attention to? In older people, hitting the head has quite serious consequences. Basically, like at any other age. Only older people are more vulnerable. And their concussion manifests itself somewhat differently than in children or young people.
Most often, old people will have a headache after a blow, and they will also experience disorientation for some time. Short-term amnesia in old age is also common. Pressure surges, pale skin, loss of consciousness - all these are signs of a concussion. True, as practice shows, primary loss of consciousness in old age occurs less frequently than in young people. Take this into account.
The most common causes of concussion
- Road traffic accident. This cause accounts for about half of all fatal cases of traumatic brain injury. Many of those who survive become disabled.
- In production. This is one of the most common causes of TBI (traumatic brain injury). It can be caused by just hitting your head on a hard surface. There can be, as in an accident, different types of these injuries: closed and open. They can also vary in severity, forms, and other indicators.
- Sports. Absolutely any strong blow to the head on a hard surface can cause a concussion. Can there be a concussion from being hit by a ball? The answer is unequivocal - yes.
- Criminal case. For this reason, a person must be hit on the head in order for him to receive a TBI.
Can you have a TBI without hitting your head? Maybe. As is the case with a shock wave, which can cause a TBI if a person simply slips and falls on ice.
Attention! Parents of teenage children need to be especially careful. Especially boys. They are more likely than girls to get hit on the head with books or even briefcases, in particular from their classmates. Also, boys more often take part in fights, ride on railings, and demonstrate their dexterity and courage in various other ways.
The problem is that this rarely happens without landing hard and hitting your head. You should be especially attentive to a teenager’s complaints of headache and/or dizziness.
Headaches due to traumatic brain injuries of varying severity and duration
It is not a rare occurrence that moderate traumatic brain injuries suffered by a patient are characterized by the fact that after a short period of time, people who have suffered the injury begin to be bothered by a sharp headache of tension. Such pain may be characterized by pronounced vegetative-vascular manifestations, which include post-traumatic vegetative-vascular dystonia, cephalalgia in its various forms and manifestations, and others. Basically, the observation of similar symptoms can occur if there are head injuries. At the same time, only the extremely acute period of injury is taken into account here, and especially the last acute period. These may be bruises of the poles of the lobes of the temple, as well as the lobes of the forehead, which involve the structure of the limbic region or the hypothalamus region in the process.
If a person who has suffered a TBI complains of the appearance of unpleasant headaches of a periodic nature in the acute period of TBI (which lasts about three weeks) or the chronic period of TBI (occurs after three weeks from injury), then in this case it is urgent to take measures to exclude chronic intracranial hematoma, where headache is delayed in nature.
It is also not uncommon for patients to be treated for headaches immediately before a traumatic brain injury. However, compensation for tension headaches became unnoticed after such a trauma, that is, headaches with active manifestations were observed again, only after moving into the post-traumatic period. This process occurs if there is decompensation of pathogenetic mechanisms.
Localization of pain
Often, it is the location of the “accumulation” of pain after hitting the head that can indicate a particular injury. True, it is not recommended to diagnose yourself. It is advisable to consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Does your head hurt when you bend over after an impact? Quite normal. But try to concentrate and understand exactly where and what type of pain bothers you. A concussion is usually indicated by a pulsating sound localized in the back of the head.
Additionally, the victim, regardless of age, will experience dizziness. All signs of injury disappear after approximately 2-3 weeks, but sometimes they persist for a longer period of time. What to do if you just hit your head hard? What measures need to be taken immediately? It doesn't matter whether you have a concussion or a simple bruise, you need to understand exactly what to do.
How long does a headache hurt after a concussion?
Complete recovery of the brain of a patient with a similar diagnosis takes up to 6-12 months. Normally, pain after a mild or moderate concussion goes away within 2-4 weeks. In severe forms of injury, recovery can take up to 2 months, during which time cephalalgia will continue to haunt you. Such indicators are relevant for cases of timely identification of a problem and implementation of specialized therapy.
If the symptom does not resolve within a few weeks after the standard period, further examination should be carried out.
Summary of the article
Consequences of a bruise
For a head injury, first aid consists of the following:
- put cold on the site of the impact, this will make it possible to reduce pain and swelling, keep it for several hours, but avoid hypothermia.
- the victim must be laid on a horizontal surface, which will make it possible to avoid another fall due to weakness and dizziness;
- regardless of the severity of the condition, take the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance; exclude intake of water, food and medications;
- in case of hematoma, apply a compressive bandage;
- Warming compresses with alcohol can only be used after a few days.
First aid for a head injury can be provided by anyone, but qualified medical assistance will still be required.
If a child suffers a head injury, first aid must be provided; it must also be taken into account that the symptoms in children may not appear as pronounced as in adults.
Complications can be different, it depends on the location and severity of the injury. Minor injuries resolve on their own in a short period of time. In case of serious injuries, the development of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- waking coma (apallic syndrome) - patients are conscious, but they are not able to react to what is happening, and are absolutely indifferent to the people and objects around them. There is a reaction only to pain;
- paresis – partial loss of motor function.
- brain cyst;
- brain abscess - the formation of a cavity with pus during the development of the inflammatory process;
- ICH, or intracranial hypertension syndrome, is increased intracranial pressure;
- constant headache - does not go away for six months or more;
- meningitis is an inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain;
- development of secondary epilepsy;
- death or disability cannot be excluded in case of severe injuries;
Consequences of a bruise on the back of the head:
- decreased performance and concentration;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- depression;
- regular dizziness;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- weather dependence.
If you hit the back of your head during a fall, the consequences of the impact can be serious, so it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination.
The success of therapeutic measures depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment and the severity of the injury.
What are the risks of brain injuries and what help can be provided to the victim?
Any strong blow to the head area can injure the brain, including those cases where the skull remains intact. Despite the fact that the brain is enclosed in soft shells and “floats” in the cerebrospinal fluid, it is not 100% protected from inertial impacts on the inner surface of the skull. If the skull is fractured, the brain can be damaged by bone fragments.
Any general practitioner, when meeting for the first time and taking a medical history, will definitely ask whether his new patient has a history of traumatic brain injuries. Brain damage can affect a person’s emotional and mental state, the functioning of his internal organs and vital systems for years.
Types of brain injuries and their signs
According to the Research Institute named after. N.V. Sklifosovsky, in Russia the main causes of brain injuries are falling from a height (usually while drunk) and injuries received during criminal actions.
In total, these two factors alone account for about 65% of cases. Another 20% are road traffic accidents and falls from heights. This statistic differs from the global one, in which road traffic accidents account for half of brain injuries.
Globally, 200 out of every 10,000 people suffer a brain injury every year, and these numbers are trending upward.
Health restoration programs... Cost of rehabilitation...
Brain concussion . It occurs after a minor traumatic impact on the head and represents reversible functional changes in the brain. Occurs in almost 70% of victims with traumatic brain injuries. A concussion is characterized (but not required) by a short-term loss of consciousness - from 1 to 15 minutes.
Having returned to consciousness, the patient often does not remember the circumstances of what happened. In this case, he may be bothered by headache, nausea, less often vomiting, dizziness, weakness, pain when moving the eyeballs. These symptoms subside spontaneously after 5–8 days.
Although a concussion is considered a mild traumatic brain injury, about half of victims have various residual effects that can reduce the ability to work. In case of a concussion, an examination by a neurosurgeon or neurologist is required, who will determine the need for a CT or MRI of the brain, or electroencephalography.
As a rule, hospitalization is not required for a concussion; outpatient treatment under the supervision of a neurologist is sufficient.
Compression of the brain . Occurs due to hematomas in the cranial cavity and a decrease in intracranial space. It is dangerous because due to the inevitable infringement of the brain stem, the vital functions of breathing and circulation are disrupted. Hematomas that cause compression must be removed urgently.
Brain contusion . Damage to the brain substance due to a blow to the head, often with hemorrhage. May be mild, moderate or severe. With mild bruises, neurological symptoms last 2–3 weeks and go away on their own.
Moderate severity is characterized by mental disturbances and transient disorders of vital functions. With severe bruises, the patient may remain unconscious for several weeks. Brain contusions, their degree and condition during treatment are diagnosed using computed tomography.
Treatment is medicinal: neuroprotectors, antioxidants, vascular and sedative drugs, B vitamins, and antibiotics are prescribed. Bed rest is indicated.
Axonal damage . Axons are long, cylindrical extensions of nerve cells that can be damaged by a blow to the head.
Axonal injuries are multiple axonal breaks accompanied by microscopic hemorrhages in the brain.
This type of brain injury leads to the cessation of cortical activity and the patient falling into a coma, which can last for years until the brain starts working again. Treatment consists of maintaining vital functions and preventing infectious diseases.
Intracranial hemorrhage . A blow to the head can cause destruction of the wall of one of the blood vessels, which leads to local hemorrhage into the cranial cavity. Intracranial pressure instantly increases, causing damage to brain tissue.
Symptoms of intracranial hemorrhage are severe headache, depression of consciousness, seizures, vomiting.
There is no single treatment tactic for such cases; depending on the individual picture, medical and surgical methods are combined to remove and resolve the hematoma.
Consequences of head injuries
Various consequences of a brain injury can manifest themselves during its treatment, during the rehabilitation period (up to six months) and the long-term period (usually up to two years, but possibly longer).
First of all, these are mental and autonomic dysfunctions that can complicate the patient’s entire future life: changes in sensitivity, speech, vision, hearing, mobility, memory and sleep disorders, confusion.
The development of post-traumatic forms of epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and brain atrophy is possible. The more severe the injury, the more negative consequences it brings with it.
Much depends not only on proper treatment, but also on the rehabilitation period, when the patient gradually returns to normal life and it is possible to track the onset of post-traumatic diseases in time in order to begin their treatment.
History knows cases where brain injuries led to the emergence of new talents in the victim - for example, increased ability to study foreign languages or exact sciences, fine arts or music.
This is called acquired savant syndrome (acquired savantism).
Often these abilities are based on old memories - for example, the patient may have studied Chinese for some time at school, forgotten it completely, but spoke it again after an injury and continued learning with better success.
First aid for head injuries
Anyone can find themselves in a situation where there is a person nearby with a head injury. Knowing the rules for providing first aid, you can alleviate his condition and even save his life.
- Signs of a serious traumatic brain injury include blood or clear fluid (CSF) leaking from the nose or ear and bruising around the eyes. Symptoms may not appear immediately, but several hours after the injury, so if there is a strong blow to the head, you must call an ambulance immediately.
- If the victim has lost consciousness, breathing and pulse should be checked. If they are absent, you will need to perform artificial respiration and cardiac massage. If there is a pulse and breathing, the person is placed on his side before the ambulance arrives, so that possible vomiting or a sunken tongue will prevent him from suffocating. You cannot sit him down or lift him to his feet.
- In case of a closed injury, ice or a cold wet towel should be applied to the site of impact to stop tissue swelling and reduce pain. If there is a bleeding wound, you should lubricate the skin around it with iodine or brilliant green, cover the wound with gauze and carefully bandage your head.
- It is strictly forbidden to touch or remove fragments of bones, metal or other foreign bodies protruding from the wound, so as not to increase bleeding, damage the tissue even more, or cause infection. In this case, a gauze roll is first placed around the wound, and then a bandage is made.
- The victim can only be transported to the hospital in a supine position.
The hospital conducts an examination, determines the severity of the patient’s condition, and prescribes diagnostic procedures. For open wounds with bone fragments or other foreign bodies, the patient requires urgent surgery.
Rehabilitation therapy
The rehabilitation period is necessary in order to maximally return to the patient the functions lost due to injury and prepare him for future life. International standards suggest the following measures for rehabilitation after brain injury:
- Neuropsychological correction - to restore memory, attention and control over emotions.
- Drug therapy to restore blood circulation to the brain.
- Speech therapy classes.
- Different types of psychotherapy - to relieve depression.
- Aquatherapy, stabilometry, PNF therapy - to compensate for movement disorders.
- Physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, transcranial therapy) - to stimulate brain activity.
- Dietary nutrition - to supply brain cells with all necessary amino acids.
- Providing physical comfort and attentive nursing care.
- Family counseling - to create an environment of mutual understanding in the family.
The optimal time to begin rehabilitation treatment is 3–4 weeks from the moment of receiving a head injury. The greatest success in recovery can be achieved in the next 1.5-2 years after discharge from the hospital, then progress will slow down.
Source: https://www.pravda.ru/navigator/travma-golovnogo-mozga.html
Cool
To avoid the formation of a lump on the head after a blow (including hematomas), immediately after the injury it is necessary to apply ice to the site of the injury. A damp, cold towel also works.
In general, cool the injury site by any means. This approach will not only prevent the appearance of bumps and bruises, it will also help to cheer up and improve the general condition of the victim. Especially when it comes to minor injuries. If you suspect something serious, call a doctor or an ambulance immediately!
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out by neurologists. There is no time to hesitate. Manifestations of a concussion are nonspecific: with equal success, the signs may correspond to more severe injuries.
What measures does the doctor take:
- Oral interview and history taking if the patient is conscious. Very briefly, just to understand the situation. There is no time for lengthy conversations.
- Examination of a person.
- Routine neurological examination: reflexes, pupil reactions, condition of the fundus.
- MRI allows you to recognize a concussion with the highest accuracy. Unfortunately, in many places there are still no devices, so you can only rely on the intuition and experience of the doctor.
Once the diagnosis of FBS has been established, more severe brain damage has been ruled out, and first aid is administered.
Then, if the doctor considers it necessary, additional, more in-depth diagnostic methods are prescribed. For example, encephalography.
The next task is to catch complications in time, eradicate them at the outset, or, ideally, prevent them altogether.
Video
A seemingly insignificant blow to the back of the head can actually turn out to be a serious injury and lead to unexpected consequences for the victim. In the brain structures of the occipital part, bundles of nerve fibers responsible for the functioning of the visual system are concentrated. Even a slight bruise to the back of the head, not to mention more significant and serious injuries to this part of the head, can lead to the development of visual disturbances or complete blindness, as well as the appearance over time of consequences associated with damage to the nervous system.
If you hit the back of your head, then in order to reduce the likelihood of complications, the person suffering from a head injury should definitely undergo diagnostics from specialized doctors and, if violations are detected, follow their further recommendations.
Bed rest
Does a person feel sick after hitting their head? Most likely he has a concussion. The next point of action is compliance with bed rest. That is, immediately after the blow it is necessary to transfer the “victim” to a horizontal position. But in such a way that after regaining consciousness the person feels comfortable and comfortable.
By the way, for concussions, the absence of brain tension, as well as bed rest, are the main methods of treatment. Therefore, try to provide the person with peace for a while. Just don’t leave the victim alone - maybe he will need your help!
IT'S TIME TO REST
This was Matt Mastrantano's first concussion diagnosis, but he and his doctor suspect he may have had a couple more undocumented injuries during his childhood. This was indicated by the fact that Matt's illness was severe. Mastrantano received pills from the doctor and recommendations to “lie down at home” (Matt refused hospitalization). But after a couple of weeks the situation worsened: nausea from the slightest movement, dizziness and severe headaches. “There were days when I had to lean on the walls on the way to or from work to avoid falling,”
- says the amateur athlete.
Later, he finally went to the hospital, where he was surprised to learn that no special pill “for concussions” still existed. This happened because, until recently, little attention was paid to mild TBI. Academician Alexander Potapov explains: “We need drugs that would protect brain tissue during injuries and speed up their recovery afterwards. Over the past 20-30 years, many experimental neuroprotectors have been tested, but they have not been proven to work.”
Now all hope lies in the female hormone progesterone, which has already shown some effectiveness in the treatment of TBI and is absolutely safe. But even if it turns out to be a panacea, progesterone will enter clinical practice in 10-15 years.
And if you get hit on the head, still go to the doctor and go to the hospital on his orders. “With a concussion, there is a period during which less activity, both mental and physical, is indicated for better recovery,”
says Steven Leffler, chair of the department of emergency medicine at the University of Vermont School of Medicine. While you lie in complete peace, doctors will stuff you with nootropics (substances that improve the transmission of nerve signals in brain tissue and protect areas with impaired blood circulation from oxygen starvation), drugs that improve blood circulation and reduce blood viscosity, and vitamins. Well, monitor your condition, no matter how it worsens.
All this helped Mastrantano. Despite the delay in starting treatment, almost all symptoms have now disappeared. However, Matt still suffers from headaches. “I’ll have to live with this somehow now,”
- he says. Matt is playing Frisbee again, but now he's wearing a helmet. The other players laugh, Mastrantano just grits his teeth.
However, the doctors are unhappy with Matt's behavior. "People ask me, 'If I played football and got a concussion, when can I get back to playing?' I can answer - in 50 years, because it is unknown,
says Douglas Smith. “ We don’t know if it will be possible at all.” To be honest, we still don’t know much about the brain.”
And Matt’s helmet won’t save him if something happens. A helmet doesn’t really save you from everything.
Treatment of headaches after injury
Articles and videos
Traumatic brain injuries are a common cause of cephalalgia and other neurological disorders. Pain often indicates the development of life-threatening complications that require emergency care (including surgery). If chronicity occurs, then symptomatic treatment of headache after injury is carried out using the same techniques and drugs as for primary cephalgia.
Types of post-traumatic headaches (PTTH)
All PTTH are divided into chronic and acute. Acute pain includes pain that develops during the first two weeks after a head injury and persists for no more than two months.
The chronic type of cephalalgia also appears in the first 2 weeks, but bothers the victim for a longer period.
Acute PTTH is usually symptomatic. Their severity and localization are directly dependent on the nature and severity of the damage.
The appearance of pain is possible in the “light interval”, i.e. with a general improvement in the first hours or days. If acute headaches occur after a head injury, treatment should begin after identifying their specific cause. A thorough examination is mandatory (incl.
fluoroscopy, CT and MRI) to exclude brain contusion, the presence of intracranial hematomas and hemorrhages under the arachnoid membrane.
Characteristic features of PTHA against the background of subarachnoid hemorrhage are:
- high degree of severity;
- rapid development of meningeal syndrome;
- increasing pain when straining, turning or tilting the head;
- hyperthermia;
- associated nausea and vomiting.
With brain contusions, cephalalgia is more intense on the side of the injury. It tends to intensify with percussion (tapping). Important: In some cases, acute PTTH is caused by damage to the muscles of the cervical region.
Chronic post-traumatic cephalgia acquires an independent character; often they develop as a result of a relatively mild traumatic brain injury against the background of a reversible neurological defect and the absence of significant changes in the structures of the central nervous system.
Such pain can haunt the victim for many months and even years, and in the long term they sometimes progress. Painful sensations can be boring, pressing or pulsating, and there is usually no clear localization.
The duration of attacks ranges from several hours to 2-3 days. In particularly severe situations, pain torments the patient every day.
How to deal with post-traumatic headaches?
Treatment of acute PTTH involves taking emergency measures to eliminate the cause that caused them (elimination of hematoma, etc.). For concussions, the following medications are prescribed:
- Cerebrolysin (peptide complex to improve metabolism in nerve cells, administered intravenously);
- Mildranate or Actovegin (antioxidants for intravenous administration);
- Cavinton (a drug for improving cerebral blood flow);
- Diacarb (dehydrant to prevent cerebral edema).
If chronic post-traumatic pain develops, treatment is carried out using the same methods as for most primary headaches. One of the most important components of therapy is the psychological rehabilitation of the patient. They very often have concomitant mental disorders - anxiety and depression.
To cope with such conditions, the help of a qualified psychotherapist is required. During the recovery period, hypnotherapy and neuroprotective therapy, as well as acupuncture, are widely used. For pain that spreads from the neck to the back of the head, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises, as well as exercises in the swimming pool.
Drug treatment is carried out in two directions - stopping attacks and preventing them. Analgesics and β-blockers are indicated to relieve pain. In many cases, vascular agents are useful in the treatment of post-traumatic headaches. With their help, microcirculation in the brain pool improves.
Thanks to this, regulatory processes in the central nervous system are restored. Memory impairment and other cognitive disorders are indications for the use of nootropics in the treatment of headaches after injury. The fight against reversible mental disorders often requires the prescription of tricyclic antidepressants.
They stabilize the psycho-emotional state and normalize sleep. For the treatment of acute and chronic post-traumatic pain, patients are prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, including folic acid, B vitamins and phosphorus.
Intense cephalgia, accompanied by insomnia, is an indication for taking sedatives - Dormiplant or Adaptol.
Combination therapy may include manual therapy sessions. Patients suffering from chronic PTTH need to be observed by a neurologist.
Authorship and editing of the text:
Head of the Department of Psychiatry and Narcology of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist Popov A.G., psychiatrist-narcologist Serova L.A.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7
Call! We work around the clock!
Peace and quiet
The next point is suitable for all cases in which a headache occurs after hitting your head. A person needs to be provided not only with bed rest, but also with silence. Make sure that there are no additional sources of noise around the victim. In this case, the headaches will not be as severe and will pass faster.
It would be good to provide a person with sleep. You can use sleeping pills. Just don't overdo it. In general, doctors do not welcome such a decision. A person must fall asleep on their own.
The last thing to note is that sometimes the pain can be dulled with painkillers. A very good approach, especially if you just hit your head hard, and now you can’t rest, sleep, or just get to the doctor. It is recommended to take tablets available without a doctor's prescription. A few No-Shpy tablets should help. It is prohibited to take potent drugs without a doctor’s prescription, even in case of an unbearable headache.
Basically, that's all. If you have headaches for a long time after hitting your head, consult a doctor. Usually, drug treatment is not required for concussions or bruises. Only in extreme cases. Performance is also not disrupted too often. So don't panic if you hit yourself!