Average rating of clinics - 1330 patient reviews
Determination of abnormal processes occurring in the internal region of the cranium is possible in several ways.
The most well-studied and long-used method is traditional radiography. However, even she is not always able to recognize the causes of the disease.
The nuclear resonance scanning method has been used for more than thirty years, but it is constantly being improved over time.
Modern devices are capable of not only determining the localization of pathology with high accuracy, but also identifying the causes of its occurrence. One of the most popular types of MRI of the brain is MR angiography of the brain.
Initially, in order for the doctor to see the affected area of the vessel in the internal zone of the organ, it was necessary to introduce a coloring substance into this particular channel, as well as the presence of an X-ray machine. The method was quite painful and had complications. With the introduction of devices operating on the principle of generating magnetic fields, the traumatic method faded into the background.
Operating principle of MPA
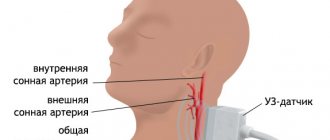
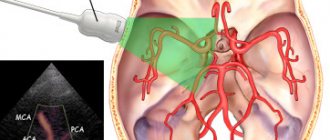
In the circulatory system of the brain, the main role is played by arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood enriched with oxygen to the brain, and veins carry out the outflow of blood that is practically without oxygen. During the examination, the entire circulatory system of the brain is scanned.
The method of examining the blood supply system using a tomograph is particularly effective when studying the carotid, vertebral and intracerebral arteries. This method is particularly sensitive to flows of moving blood. MR angiography, unlike other diagnostic methods, is capable of identifying stenotic (narrowing the lumen) and occlusive (impairing patency) processes in the arteries. The earlier these problems are detected, the more effective the prescribed treatment can be.
MRI is based on the use of a high-frequency magnetic field. Under its influence, hydrogen atoms become active. Aqueous solutions, one of the components of which is hydrogen, are the basis of the human body. That is why, during magnetic resonance imaging, all structures in which hydrogen is present are clearly visible. The effect of a magnetic field is harmless to humans, so the study can be done as many times as necessary.
In the circulatory system of the brain, the main role is played by arteries and veins.
A tomograph scans tissue at the cellular level and transmits information to a computer. The raw data is converted into 3D images using a maximum intensity projection (MPI) algorithm. Blood vessels (or rather, the blood flow in them) have an increased intensity of the reflected signal, and the tissues surrounding them have a weaker one.
VARIETIES OF DIAGNOSIS METHOD
MR angiography examination of the brain differs according to the method of drug administration:
- catheterization - the drug enters the vessels through an artery in the femoral part of the body. It allows contrast to be transported through the circulatory system to the area being examined;
- puncture - the solution enters the body through a puncture of a certain vessel.
Diagnostics differs in the extent of the area:
- general - viewing all vascular systems of the brain;
- selective - visually inspect one vessel;
- superselective - a reduced capillary in one of the general system is examined.
Magnetic resonance superselective angiography is used in medical practice as a method of endovascular treatment. After diagnosis is made, microsurgery is performed. The methods used are thrombosis or embolization.
When diagnosing, doctors use computer and magnetic resonance imaging and MRI angiography. Diagnosis is carried out using special tomographs. They are used due to the absence of injuries, and are considered one of the safest examination methods.
Indications for MRA examination of the brain
Magnetic resonance angiography of the brain is prescribed in situations where it is suspected that the “culprit” of the problem is vascular pathology or a blood supply disorder caused by some other reason. These are the following symptoms and conditions:
- frequently recurring headaches;
- dizziness;
- loss of hearing or vision (complete or partial);
- noise in ears;
- pain in the neck;
- periodically occurring (for no apparent reason) nausea and vomiting;
- vascular disorders in diabetes mellitus;
- strokes and pre-stroke conditions;
- suspicion of a tumor of any etiology;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- head injuries;
- adjusting the effectiveness of treatment.
Angiography using a tomograph is performed according to indications at any age.
ESSENCE OF THE METHOD
You need to know what magnetic resonance angiography is. This technique involves injecting a special contrast agent based on iodine into the artery of the cerebral system. Often used drugs are Ultravistit, Omnipaque, Triiodtrast, Urografin. They allow you to visually see the internal capillaries on the x-ray image. They are introduced into the body by puncture, but if this option is not possible, the patient is given a catheter. After the contrast agent enters the vessels, several images are taken, which have two projections.
Important. From the side and in a straight line, they are assessed by a radiologist. Based on them, the doctor makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of the disease being studied.
Contraindications for diagnostics
Angiography using a tomograph is performed according to indications at any age.
Unfortunately, some diseases may be contraindications for MRA diagnostic procedures. This type of diagnosis cannot be performed :
- in the presence of infectious or inflammatory diseases;
- in acute periods of mental illness;
- with existing heart failure;
- in case of allergy to iodine and iodine-containing drugs (when conducting a study using a contrast agent);
- with decompensated liver or kidney failure;
- if the patient’s body contains implants made of metal alloys, spoke-shaped structures for osteosynthesis, metal dentures;
- with an implanted pacemaker or insulin pump;
- in case of blood clotting disorders;
- in patients weighing more than 150 kg;
- during pregnancy and lactation.
It should be noted that structures made of titanium, copper, and ceramics located on the body (or inside it) are not contraindications to the procedure. All other metals (or alloys of them) under the influence of a magnetic field can move and cause damage to tissues and organs. If the patient has a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia), the examination is performed under general anesthesia.
Possible complications from the procedure
The examination procedure is absolutely painless and does not cause any inconvenience to the patient, except for being forced to lie motionless in the dark for a long time.
There are no side effects or complications; Even when using substances containing gadolinium, the risk of developing an allergic reaction is minimal. Therefore, magnetic resonance angiography is the only method that can be prescribed to patients with an allergy to iodine contrast agents.
Due to the lack of X-ray exposure, diagnostics can be repeated without harm to health.
Before contrast material is injected, a saline solution is sometimes injected into the vein, which can cause a reaction in patients on dialysis or with kidney failure. Therefore, those sent for examination first fill out a special questionnaire or questionnaire, which includes all associated diseases.
During the MRA procedure:
- exposure to a magnetic field and radio frequencies can cause various sensations in the patient - warmth, tingling, which quickly and completely disappear;
- excitable or nervous patients may experience discomfort from the sounds of the device, so before starting the study the doctor suggests using earplugs;
- In patients with severe claustrophobia or other mental disorders, confined spaces and darkness can cause uncontrollable panic attacks. In this case, sedatives and light general anesthesia are used;
- patients weighing more than 100 kilograms may simply not fit into the device, since it is designed for certain loads.
After the procedure, you may experience slight discomfort caused by prolonged lying in a motionless position. A recovery period is required only for those patients who underwent magnetic resonance angiography under general anesthesia.
What can be revealed during an MRA examination?
During this diagnostic procedure, the following diseases and pathologies of cerebral vessels can be visualized:
- aneurysm defects (pathological protrusion of the vascular wall in a separate area);
- dissection of the walls of blood vessels;
- deformation of blood vessels (pathological expansion or narrowing);
- abnormalities in the development of blood vessels (asymmetry of their branching, excessive looping of the vascular network, etc.);
- identify the condition of the ring of vascular hemispheres;
- determine the condition of the arteries in the cerebral cortex;
- see the functioning of the cranial veins.
What will angiography show?
Magnetic resonance angiography is indispensable for diagnosing functional changes in the vascular bed:
- congenital heart defects;
- stenosis (narrowing of the lumen) and thrombosis of blood vessels;
- aneurysm (stretching of the walls) of the aorta and aneurysm dissection;
- atherosclerotic formations;
- vasculitis (inflammation of the walls of blood vessels).
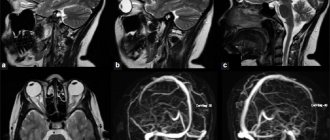
During the examination, the specialist receives an absolutely reliable and detailed image of the vessels: normal arteries and veins have a smooth and clear contour, without loops and sharp bends, thickenings as the lumen decreases (vascular “branches”).
Thus, when dealing with pathology, a specialist can accurately determine any, even the smallest, anomaly and the cause of a violation of the blood supply to the organ. For example, based on the results of MRA, foci of ischemia as a result of traumatic brain injury or stroke, multiple sclerotic changes in cerebral vessels, various hematomas, cysts, tumors, etc. are diagnosed.
Preparatory actions
The examination lasts about 30 minutes.
No special preparation is required for a diagnostic procedure using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. If during this diagnostic procedure it is necessary to administer contrast, then the following actions must be performed:
- testing for allergies to iodine-containing drugs;
- performing urine and blood tests;
- taking an ECG;
- consultation with a therapist.
It is advisable to have on hand the results of other diagnostic methods performed previously to examine the brain (if any were performed). Including the results of previous MRA procedures. If for any indication the examination must be carried out under general anesthesia, then you need to notify the anesthesiologist about any allergies to medications. In addition, before anesthesia, a 6-8 hour fast is required.
To ensure that the examination results are as accurate as possible, it is not recommended to consume alcoholic beverages or blood thinning medications a week before the diagnostic procedure.
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF DIAGNOSIS
Vascular angiography is performed using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. The fundamental element of this diagnostic method is nuclear magnetic resonance. The research option completely excludes ionized radiation. Diagnosis is carried out both with and without the use of drugs. The iodinated substance improves the visibility of the artery structure. In case of individual intolerance, the patient is examined without the use of medications. The photographs are processed using a computer system and are obtained in three dimensions. This allows you to study arteries, veins and the entire bloodstream in detail.
The subject remains in the tomograph tube for quite a long time. Therefore, the procedure is not prescribed for people suffering from claustrophobia. If a person has metal, electronic or artificial implants, MR angiography is not performed.
This diagnostic option is modern, which allows the doctor to obtain all the information on the vessels of the brain, which is impossible with a conventional x-ray image. When magnetic resonance imaging is prohibited, conventional angiography is performed.
Brain research technique using MRA method
Before the procedure, the patient must remove all metal jewelry. Clothes should not have metal buttons or other decorative elements. The patient is placed on the couch, a contrast agent is injected intravenously, and the couch is pushed horizontally into the machine. During diagnostic manipulation, the doctor can maintain two-way communication with the subject.
The examination lasts about 30 minutes. During this time, the patient must lie still. After completion of the procedure, the patient comes out of anesthesia under the supervision of a doctor (if anesthesia was used). The specialist who conducted the study analyzes the received images and issues a conclusion (along with the images and the disk). The examination procedure is completely painless and does not affect the patient’s further well-being.
MRA is an innovative non-surgical method for diagnosing cerebral vessels. Completing this examination guarantees an accurate diagnosis and timely prescription of adequate treatment.
DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES
Before the study, the patient signs consent. An intravenous catheter is placed in the treatment room 20-30 minutes before the start of the diagnosis. It allows the doctor to have access to the blood vessels. Afterwards, the patient is given premedication, medications are taken that reduce the risk of side effects and discomfort when performing diagnostics. The patient is given painkillers, tranquilizers, and antihistamines.
The subject is placed on a special table and connected to a heart monitor and heart rate monitor. The skin is treated with a painkiller and anesthetic, and then the desired vessel is punctured. Often it is not possible to get in the first time, for this reason a small area of skin is cut or the femoral artery is punctured, where the catheter is inserted.
The patient does not feel pain when it moves through the arteries, since the internal tissues do not have receptors that are responsible for pain. X-ray allows you to monitor the movement of the catheter in the bloodstream. When it reaches a certain vessel, a contrast agent in a volume of 8-10 ml is introduced into the body through it. It is preheated to the level of human body temperature. After it enters the body, unpleasant sensations arise - a metallic taste, blood flows to the face, and it becomes hot. Symptoms go away on their own within a few minutes and do not require medical intervention.
After receiving the medication, X-ray images are taken in frontal and lateral projections. The gap between each is about a second. This allows you to examine veins, arteries, and capillaries in detail. The images are developed immediately after the procedure and sent to the doctor for evaluation. If there is the slightest doubt, the patient is given an additional substance and an x-ray is taken.
Upon completion of the examination, the catheter is removed and a sterile bandage is applied to the puncture site. The duration of the procedure is about an hour. But after it the patient remains under medical supervision for about 7 hours.