First signs and symptoms, which doctor to contact
The trigeminal nerve, inflammation (symptoms of pathology can be confused with dental diseases) which can significantly worsen a person’s quality of life, is the largest node in the cranial cavity.
The main symptom of the disease is severe acute pain in the face. Most often, sensations appear in the area of the upper and lower jaw. A sign of illness can be confused with the appearance of dental problems.
Therefore, the first thing patients do is turn to dentists for help. If, after consultation with a dentist, it turns out that the discomfort has other causes, the patient is referred for treatment to a neurologist or neurologist. Pain increases during eating, talking or hypothermia.
Pain varies in nature:
- typical;
- atypical.
The typical form has the property of cyclicity: with periodic increase and decrease. Its characteristic features are considered to be shooting pains, starting from touching the face, localized near the eyes or nose in the lower part of the face. The syndrome can bother a person once a day or every hour.
The atypical form of the disease is rare. The syndrome is characterized by a constant nature of pain that envelops most of the face, which may not subside. This form is more difficult to treat.
Additional signs of the disease include:
- tearfulness;
- increased salivation;
- paresthesia or numbness in the area of the lips, nose, eyelids;
- change in facial skin color (redness);
- involuntary contractile movements of the facial muscles.
Diagnostics
Human anatomy is such that it is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis based on symptoms. That is why it is sometimes quite difficult to diagnose by eye whether the trigeminal nerve hurts or whether it is due to another disease.
Any doctor, in order to find the cause and source of the disease, must conduct a correct diagnosis. When treating the trigeminal nerve, it consists of a conversation with the patient, examination and palpation of his face, and review of the hospital card.
Very often, an MRI or CT scan must be done to accurately determine the diagnosis. In Moscow, you can contact some treatment centers for electroneurography, electroneuromyography or electroencephalography procedures. Such instrumental research methods allow us to have a more accurate picture of the disease.
With severe symptoms, making a diagnosis is not difficult. The main task of the doctor is to find the source of neuralgia. Differential diagnosis should be aimed at excluding oncology or another cause of compression. In this case, they talk about a true condition, not a symptomatic one.
Examination methods:
- High-resolution MRI (magnetic field strength greater than 1.5 Tesla);
- computed angiography with contrast.
The nature of pain in neuralgia of the intercostal nerves
In order to distinguish a symptom and find out which part of the body is experiencing pain, it is enough to conduct several tests. Since intercostal neuralgia affects the nerve roots coming from the spine, one should remember their main function.
The spine performs the main function of movement in this area, therefore, with the next attack, the pain will intensify with movements in the chest. Usually there is unbearable pain, severely limiting movements in the body. When you try to straighten up, the pain intensifies, forcing you to remain in a half-bent position.
Since the ribs are attached to the spine, any movement of them also causes pain. This is especially noticeable when taking a deep breath. Additionally, some patients notice that they had back pain in the shoulder blade area the day before the attack.
The pain most often occurs on one side, left or right, above/below the chest lasts for a short time, but residual symptoms remain for a long time. In the case of this disease, this does not matter much, since pinching of the nerve root can occur on any side and height of the ribs. It is extremely rare that symptoms occur in the upper chest, more often at the level of the heart, which causes additional concern in patients. Pain in the heart or abdomen quite often accompanies neuralgia; this localization only indicates the affected nerve.
Photo of the area where intercostal neuralgia hurts
It should be understood that if there is pain in the chest area, it is necessary to exclude diseases of the organs that are located in this region, namely the lungs and heart.
If the pain comes from the heart, it will not increase with movement, but rather with some kind of physical activity. Let's say that while walking, when the pulse and blood pressure increase, more blood comes to the heart, its work increases and signs of problems with the cardiovascular system will appear.
If the problem is in the lungs, the pain will not change in any way when changing position, and much more often it occurs when exhaling.
Intercostal neuralgia is also not characterized by skin rashes, itching, etc. If, a couple of days after an attack of pain, characteristic pimples appear on one side of the body, this may indicate shingles.
Pain in the mammary gland in women may also indicate a disease, but to rule out other problems, a consultation with a mammologist may be recommended.
Classic picture. What kind of pain occurs with intercostal neuralgia:
- Acute attack, sudden pain in the chest area;
- The patient leans forward and freezes in one position;
- Breathing is held so as not to intensify the pain;
- Shooting pain piercing the whole body;
- The attacks are repeated, but in the intervals between them there is nothing particularly disturbing;
- Often, there is acute pain and discomfort in the spine;
- The duration of the attack is from several seconds to several hours.
How to relieve an attack of pain
It should be understood that during an attack the patient will not be able to take any fast-acting medicine. Pills or even injections will not have time to act on the nervous system so quickly. Various ointments are not able to eliminate such intense symptoms, even if used regularly. There is a factor that causes nerve pinching and it needs to be addressed immediately.
To alleviate the condition, it is better to lie down on a flat surface, it could be a bed, a bench or the floor. The patient should be reassured and given some time to rest. After lying flat without moving, the symptoms usually begin to go away, but this does not last long.
In emergency situations, pain can be controlled with strong analgesics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
To get rid of intercostal neuralgia, you should consult a vertebrologist, who will send you for examinations and find out the cause of the infringement.
Further, a course of spinal correction may be recommended to completely eliminate the problem. Special exercises to relieve pain should not be performed until the cause is clear, as you can harm yourself. To eliminate severe pain in the ribs, you need to eliminate various displacements in the costovertebral joints, and then monitor the optimal loads on the back.
Similar:
What are the symptoms and signs of intercostal neuralgia?! What treatment for intercostal neuralgia is effective?! Intercostal neuralgia on the right or left side - what to do? Ignatiev G.V. provides back treatment in Kyiv 2019
- Upper neck pain
- VSD of mixed type
- Back pain while sleeping
- Kyphosis
- Manual therapy training
Deviation classification
In neurology, there are two forms of trigeminal neuralgia:
- The primary form is called idiopathic, it occurs due to damage to the nerve itself. The disease is a consequence of compression of nerve fibers.
- The secondary form (symptomatic) is a complication of the underlying disease (multiple sclerosis, autoimmune and inflammatory processes, infections, injuries).
The disease is classified by specialists according to other criteria. These include the localization and etiology of the disease. Determining the nature of the pathological process (infectious, traumatic, compression, etc.) allows you to quickly select effective therapy.
Prevention
The main ways to prevent the disease include hardening (to increase immunity), maintaining a healthy lifestyle (to normalize metabolism and prevent diseases such as diabetes), timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs, and prevention of hypothermia and injuries.
Acute neuritis of the facial nerve. Treatment of neuritis. Advice from neurologist M.M. Shperlinga (Novosibirsk).
Taking into account early diagnosis, detection of the causes of the disease, their elimination, and competently prescribed treatment, one can count on a complete recovery of the patient or on the onset of a significant improvement in his condition and elimination of symptoms. It is difficult to say how long the treatment will take - each case is individual.
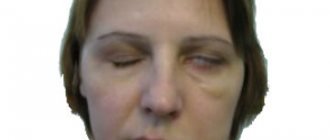
If treatment is incorrectly prescribed, incorrect or late diagnosis is made, or the patient ignores the doctor’s basic recommendations, there is a possibility of developing atrophy of the facial muscles, tightening of skin areas (which is an almost irreversible process), damage to the nervous system, chronic spasms and twitching, chronic forms of rhinitis and conjunctivitis.
Many factors in the development of this disease can be prevented:
- Avoiding hypothermia of the face and exposure to drafts.
- Timely treatment of diseases that cause trigeminal neuralgia (caries, sinusitis, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, herpetic infection). Identification and adequate treatment of these diseases reduces the risk of neuralgia.
- Prevention of facial injuries.
- Maintaining immunity at a high level.
- Minimizing contact with infectious patients and infectious infections.
- Elimination of psycho-emotional stress.
Methods of secondary prevention include complete and timely treatment.
Trigeminal neuralgia is not life-threatening, but attacks are painful. The prognosis for trigeminal neuralgia depends on the cause that caused the development of this disease, the premorbid background, the age of the patient, and the duration of the disease. In young patients, trigeminal neuralgia, with proper treatment, has a favorable prognosis and does not recur in the future. In old age, against the background of concomitant pathology and metabolic disorders, the prognosis for complete recovery is unfavorable.
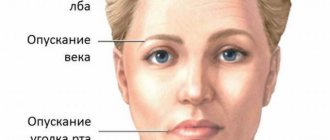
Prognosis for restoration of function in case of facial nerve paresis:
- Recovery occurs in 40-60%.
- After 1-1.5 months, in 21-32% of cases, contracture of the facial muscles develops, characterized by contraction of the muscles of the affected half, so it seems that the healthy side is paralyzed.
Causes, etiology and pathogenesis

The exact mechanism of trigeminal neuralgia is not fully understood. It is believed that it is based on a pathological change in the myelin sheath of the fibers caused by compression of the root. Compression at the site where the nerve exits the pons of Valori is created by altered blood vessels or a tumor. In the case of multiple sclerosis, the problem is provoked by the formation of a plaque in the region of the trigeminal nerve nucleus.
Medicine knows more than 50 factors that cause the pathological condition. The most common are:
- Arterial aneurysm - the wall of the vessel grows and becomes deformed, creating pressure on the nerve fibers. The situation is typical for elderly patients.
- Chronic inflammation in adjacent areas: caries, sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media.
- Benign and malignant tumors at the base of the brain.
- Facial and skull injuries, surgical interventions that caused deviation of cerebral structures.
- Herpetic infections are a common cause of NTN. In this case, the course of the disease resembles neuropathy. A person experiences itching in the area of the first branch of the nerve, moderate pain.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the skull, in which the passages are initially too narrow.
- Multiple sclerosis, which provokes a deterioration in the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus.
Unfavorable factors that increase the risk of developing the disease include old age (over 50 years), exposure to stress and depression, and a tendency to allergies. When hypothermia occurs, signs of neuritis are observed - pain is accompanied by numbness of the gums, skin of the chin, and lips.
Massage technique for different areas
Depending on the area where the massage is performed, the massage technique may vary and include a certain set of actions. A general requirement in this case is careful hand hygiene of the person performing the procedure. It is best to lie down on a straight surface, but if there is no one to help and you have to do the massage yourself, then a sitting position is allowed.
Forehead area
The forehead is the largest area of the face. It is quite convenient to perform manipulations on it.
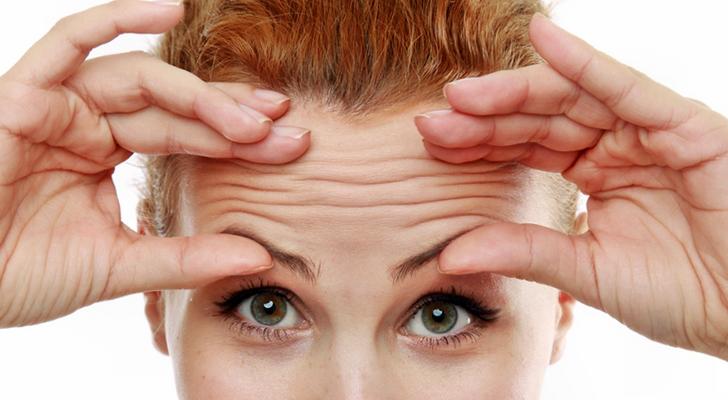

Forehead massage is easy to perform, as it is a fairly large area of the face.
Recommended movements:
- Stroking with the palm. They are carried out in the direction from the center of the forehead to the temples;
- Rubbing with fingertips. Draw along a horizontal line from the center of the forehead to the temples and back;
- Stroking with the palm in a vertical direction: from the eyebrow growth line to the hairline;
- Rubbing with fingertips: from the eyebrow line to the hairline;
- Pinching the skin. A small amount of skin is pinched between the thumb and index finger. First in the vertical direction, and then in the horizontal;
- Tapping the frontal area with your fingertips.
Cheek area
All manipulations in this area are carried out in the following directions: from the temples to the wings of the nose and then to the earlobes. In this case, the massage trajectory should not be straight, but in a semicircle.
Recommended movements:
- Stroking with the palm;
- Rubbing with the edge of the brush;
- Point massage with fingertips in a circular motion;
- Tickling with fingers;
- Point pressure with fingertips;
- Finger tapping;
- Pinching the skin.
Additionally, stroking of the nasolabial folds can be carried out using the thumb, stroking the entire facial oval with the palms, as well as the upper part of the head from the forehead to the occipital lobe.
Nasolabial area
The massage is carried out in the following directions: from the chin in a semicircle to the wings of the nose, and then from them to the bridge of the nose, and finally to the tip of the nose.

Massage of the nasolabial area is carried out using the index and middle fingers.
Recommended movements:
• Rubbing; • Point pressure with fingertips; • Point movements with slight shifting of the skin; • Stroking with the whole palm; • Pinching the skin.
Eye area
This is a fairly small but sensitive area. Manipulations must be performed with the eyes closed in order to minimize the risk of injury.
Recommended movements:
- Move your fingers around the eyes from the outer corner to the inner: along the lower edge with one middle finger, along the upper edge with two middle and index fingers;
- Rubbing. Performed with the index finger around the eye. The movements should be pointwise circular;
- Pinching the skin along the eyebrow growth;
- Stroking the eye sockets.
Shiatsu technique
This method involves acupressure, namely acupressure for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. The mechanism of application is to apply moderate pressure on certain points of the face using the fingertips.
Key points:
- Above the eyebrow growth line;
- Above the eyes (on the crease of the eyelid);
- On the temporal fossae;
- On the sides of the wings of the nose;
- Under the cheekbones;
- Between the lower lip and chin;
- On the back of the neck.
The duration of one pressure should be 10-15 seconds, after which the next one is carried out. Pressing the points is carried out from top to bottom, namely from the eyebrow arches to the back of the neck. If necessary, several approaches can be carried out.
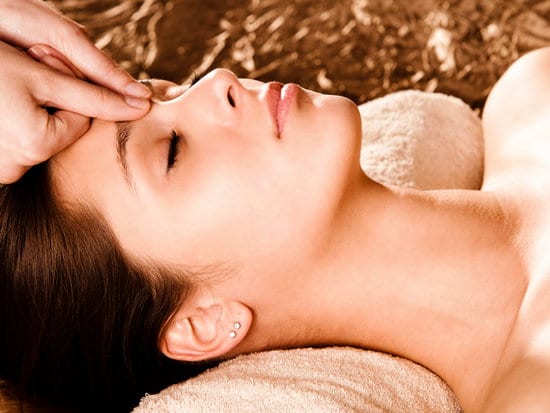

For inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, Shiatsu massage is recommended by pressing on certain points
The effect of this type of massage can be enhanced by using a piece of ice. In this case, the movement pattern is as follows: ice is applied to the selected point for 10-15 seconds, after which pressure is applied with a warm fingertip for a similar time, and ice is applied again. And only after all three consecutive movements can you move on to the next point. Ice not only relieves pain, but also stimulates blood circulation in the face.
How to treat neuralgia in the initial stage
Painful changes in nerve fibers can appear for various reasons:
- injuries;
- past infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
- tumors;
- diabetes;
- osteochondrosis;
- atherosclerosis.
Burning, paroxysmal or chronic pain can occur in nerve fibers located throughout the body. Depending on the area of the lesion, neurites are distinguished:
- intercostal (gives in the area of the heart, chest, under the scapula);
- shoulder joint;
- post-herpes;
- lumbar;
- inflammation of the trigeminal (sensitive nerve of the face or trigeminal neuritis), sciatic, ulnar, occipital nerve;
- femoral;
- pterygopalatine node (pain affects the temples, neck, and sometimes spreads to the hands);
- neuroma of the foot (Morton's disease).
How to cure neuralgia as soon as its symptoms appear? The first is the correct diagnosis, because
Under the guise of this disease, problems with the heart or blood vessels may be hidden, so it is important to be examined by a doctor for the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms. The main problem of the disease is severe pain that can make you unable to work, and the goal of getting rid of a disease such as neuralgia is to treat the pain syndrome with anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics
At the initial stage, the following may help:
- anti-inflammatory ointments with fir oil;
- acupuncture for local pain relief;
- warming compresses.
Folk remedies
To relieve painful symptoms, there are proven self-medication methods:
- Black radish juice is mixed with lavender oil.
Proportions: per spoon of juice, two drops of oil. Rub the mixture over the location of the nerve. To enhance the heating, apply a woolen bandage. Use the product up to 6 times a day, for 3 days. - A boiled hot egg is peeled, cut in half and each half is applied to the affected area on the face.
- Hot salt is poured into a bag and the inflamed area is warmed up. The method relieves pain well.
- Fresh geranium leaves are applied and fixed with a bandage on the painful area. Carry out the procedure for 3-4 hours, up to two times a day.
- Aloe is good at treating inflammation. Juice, immediately after squeezing, take a teaspoon, before meals, 3-4 days.
- A compress made from marshmallow roots is considered an effective method of relieving pain. Place the crushed roots in 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew for a day. Soak a clean cloth in warm infusion and apply to the sore spot. Cover the compress with a towel and leave for an hour. After removing the lotion, wrap your face again.
- An infusion of chamomile flowers will help with neuralgia in the jaw area. Pour a teaspoon of chamomile into a glass of boiling water and let cool to room temperature. Rinse your mouth up to five times a day.

All of these remedies are suitable for home treatment, but provide only temporary relief. To eliminate the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a doctor, only he will give recommendations for effective therapy.
NTN is a fairly common disease . When treating it, you need to eliminate the cause, this is the only way to get rid of painful attacks. It is important not to delay your visit to the doctor, and then there is every chance of defeating the insidious disease.
Treatment
Treatment of occipital neuralgia can be conservative or surgical. First of all, they try to cope without surgery.
Conservative treatment methods include:
- use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Naproxen and others). The drugs have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect;
- the use of muscle relaxants, that is, drugs that reduce muscle tone. This is justified in cases where the development of occipital neuralgia is caused by muscle spasm along the path of the nerve. The most effective among this group of drugs are Tizanidine (Sirdalud) and Mydocalm;
- use of anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Gabapentin, Pregabalin) and antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Duloxetine). Similar actions are taken in cases of persistently unrelieved pain;
- occipital nerve block. This manipulation involves the introduction of a mixture of medicinal substances into the points at which the nerve exits the skin. These can be hormones (Hydrocortisone, Diprospan, Dexamethasone), or anesthetics (Lidocaine, Novocaine), or a mixture of them. If the blockade is performed correctly, the pain syndrome is eliminated. Sometimes the blockade needs to be repeated after some time;
- methods of physiotherapy (ultrasound, laser therapy, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy);
- massage, physical therapy complexes;
- acupuncture;
- manual therapy and spinal traction (suitable for degenerative processes in the cervical spine).
If conservative treatment methods fail to get rid of occipital neuralgia, then surgical treatment is resorted to. Surgical intervention can be of two types:
- microvascular decompression. This type of surgical treatment is used in cases where the occipital nerve is compressed by nearby structures (in particular, pathologically altered vessels);
- neurostimulation. A special device that generates electrical impulses is implanted under the skin in the neck area. The impulses suppress painful stimuli. The patient himself can regulate the activity of the neurostimulator.
And yet, in most cases, it is possible to cope with neuralgia of the occipital nerve without the participation of surgeons.
Thus, to summarize the above, it should be said that occipital neuralgia is a pathology of the peripheral nervous system, the main manifestation of which is a headache in the back of the head. The disease does not pose a threat to humans, but significant pain syndrome becomes a fly in the ointment against the background of a normal state of health. Occipital neuralgia is easily diagnosed, but always requires a search for the true cause of its occurrence. You can get rid of the disease using conservative or surgical methods. The main thing is not to delay your visit to the doctor.
Neuropathologist at the Siena-Med clinic Bukhtoyarov S.N. talks about what occipital neuralgia is, what its symptoms are, principles of diagnosis and treatment:
Clinical guidelines
There is no single method for getting rid of the disease, but there are general directions along which doctors prescribe a therapeutic course. It includes taking painkillers and anticonvulsants.
Physiotherapy and vitamin therapy are carried out in combination with medications. If the course is insufficiently effective, the patient may be offered surgical intervention.
“Clinical protocol for the diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia”, approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 12, 2014, can be found here
Prescribing additional drugs
When the facial nerve is cold, treatment is selected on an individual basis. Centrally acting muscle relaxants are often prescribed, including:
- "Sirdalud".
- "Baklosan."
- "Baclofen."
The above drugs help eliminate muscle spasms. Patients are recommended to take antidepressants before going to bed. Trazodone and Amitriptyline are often prescribed. B vitamins are also administered intramuscularly. If the facial nerve is cold, then special creams and ointments can be applied topically. They must contain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components. These medications will help relieve pain. The most commonly used drugs are:
- "Diclofenac".
- "Bystrum-gel".
- "Diklak."
Drug therapy
At the initial stage of the disease, with timely diagnosis confirming the absence of complications, conservative methods of therapy are used. But in about half of the cases, only temporary improvement occurs.
Medicines gradually become addictive and practically do not stop painful attacks. Another disadvantage is the side effects.
For drug treatment, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of injections, ointments and tablets.
To quickly relieve pain from trigeminal neuralgia, injections and droppers are good, but they cannot be used for a long time, they act on the gastrointestinal tract. Usually the injection course takes 5-7 days.
Tablets are also harmful, so their use is limited to 10 days and a strictly prescribed dosage. Ointments for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia can be used longer because they are applied only to the affected area, and their substances almost do not enter the bloodstream.
Taking vitamins
The intake of vitamins, mainly group B, is important in the complex treatment of NTN. The following compounds are necessary for the normal functioning of the central and peripheral nervous systems:
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) - prevents cellular aging, participates in intracellular metabolism and helps normalize nerve impulses.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) - regulates protein metabolism processes in nerve cells. Participates in the elimination of “waste” protein breakdown. An important reagent in a number of processes in the formation of neurotransmitters.
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is an essential participant in many processes of the central nervous system. Responsible for the synthesis of nucleic acids and methionine.
The most effective way to “deliver” vitamins to the body is intramuscular administration. They help enhance the therapeutic effect of other drugs and accelerate it. This allows you to reduce the dosage of drugs with side effects, and also reduces the overall duration of therapy.
Painkillers
For neurological pain, adjuvant (non-narcotic) analgesics and opiate (narcotic) drugs are prescribed.
Recently, adjuvant agents have been preferred in treatment because they provide a positive effect with a minimum of side effects.
Adjuvant analgesics are divided into two groups:
- Anticonvulsants (anticonvulsants). The most commonly prescribed drug is carbamazepine. The doctor prescribes the dosage to each patient individually. Pain relief occurs already on the 2-3rd day of taking the drug. Side effects include (rarely): nausea, blurred vision, loss of appetite, drowsiness.
- Antidepressants. Amitriptyline is especially in demand due to its reliability and availability. Doses and use are prescribed by the attending physician. It has a pronounced sedative (calming) and anti-anxiety effect. Possible side effects: dry mouth, blurred vision, diarrhea, constipation, tachycardia, weakness.
Typically, antidepressants are prescribed in conjunction with anticonvulsants to enhance the analgesic effect.
Blockade
In these cases, to relieve acute pain, a simpler method is widely used - alcohol-novocaine blockade. The method consists of interrupting the conduction of the nerve with its anesthesia. An injection of an alcohol solution with novocaine is made at the points of innervation of the branches.
The disadvantage of this method is its short duration of action. After about two months the pain returns. With repeated blockades, the pain relief effect decreases, and the remission time becomes shorter each time.
Anti-inflammatory tablets and antibiotics
The doctor may include the following medications in the therapeutic complex:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to suppress the synthesis in the body of biologically active substances responsible for the occurrence of an inflammatory reaction. Nimesulide, Meloxicam, and Ibuprofen are often prescribed. Medicines relieve the symptoms of inflammation, but do not eliminate the cause.
- Antibiotics - prescribed in case of an infectious bacterial cause of the disease, such as Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physical effects on skin receptors help their rapid recovery. They improve blood flow to the affected area, and the irritating effect helps to restore lost sensitivity.
Physiotherapy is prescribed during a period when there is no acute pain, for atypical neuralgia or during a period of typical remission.
Main methods of influence:
- Applications with paraffin , heated paraffin is applied to the affected area of the face. The procedure improves metabolism and nutrition in tissues.
- Bernard currents , the effect of diadynamic currents on the painful area. This method is also used in the acute period, due to its effect on the pain threshold. Prescribed only in complex treatment.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture) , a method of influencing pain points. Improvement often occurs from the first procedures.