Dizziness is an imaginary sensation of rotational movements of the body in space or surrounding objects. There are many causes of vestibulopathies. The main ones include impaired cerebral blood flow, pathologies of the vestibular apparatus, cervical osteochondrosis, and inflammatory diseases of the hearing organ. Dizziness when tilting the head down or up is more common with pathologies of the vestibular apparatus itself. The organ of balance worsens its function due to inflammation, impaired endolymph outflow, decreased blood circulation, and neuritis of the auditory and vestibular nerves.
What is true vertigo?
Dizziness is often considered to be any condition in which a person feels weak, darkened in the eyes, and unsteady in their own body in relation to surrounding objects. The listed factors do not necessarily cause dizziness, but can be caused by disturbances in the visual organs, which experience insufficient blood supply. True vertigo (dizziness) is a feeling in which a person observes objects spinning around him and the ground slipping from under his feet. If a person does not receive timely support, he may fall and even be injured in a state of dizziness.
Vertigo is usually accompanied by weakness, nausea, paleness, and the appearance of bluish or red spots on the skin.
This is due to the main cause of most cases of dizziness: a sudden ebb or flow of blood to the brain. Most often, dizziness occurs when standing up suddenly, turning the head, sneezing, bending or squatting with a change in head position.
Cases of true vertigo are typical for people who have problems with the condition of the blood vessels of the brain, cardiac ventricles and the circulatory system as a whole.
When the constant pressure inside the vascular system is disrupted, there is excessive or insufficient load on the walls of blood vessels, and disruptions occur in their normal contraction. The result is a jump in blood pressure levels (from hypotension to hypertension) and a feeling of dizziness.
Regular dizziness when getting up and when lying down is most typical for hypotensive patients, whose blood vessels do not maintain the required level of pressure.
Dizziness when changing body position is a fairly common problem that, according to statistics, affects about 70% of people who do not have serious diseases of the nervous system. Malaise can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and other factors requiring medical attention. Let us consider in detail some of them, as well as options for solving the problem.
The phenomenon of dizziness, or as it is commonly called in medicine, “vertigo,” is a loss of body balance with symptoms of rotation of objects around a person, or of himself. It rarely visits a person on its own. Associated symptoms are often present: headache, nausea, vomiting, noise and ringing in the ears, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat, general weakness.
The head may feel dizzy immediately upon awakening, but more often, with sudden rises or turns of the head, in stuffy rooms, or in transport.
If dizziness occurs due to motion sickness, a hangover, or is the result of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), symptomatic treatment is used and a visit to the attending physician is usually not required. When experiencing motion sickness in transport or on attractions, to prevent unpleasant symptoms, you can take the drug Dramina, and directly for nausea and vomiting, you can take the drug Cerucal (Metoclopramide).
The hangover syndrome is relieved with a soluble Aspirin tablet, and blood sugar rises with fast carbohydrates: a carbonated sweet drink, regular sugar, raisins, Glucose tablets.
Not all causes of dizziness are so harmless. Loss of balance is often observed in the morning when getting out of bed incorrectly and abruptly. Dizziness when changing body position may indicate damage to the vestibular apparatus, and a certain loss of its ability to coordinate the position of the body in space.
Usually such attacks are accompanied by nausea. For vertebrobasilar dizziness, the drug most often prescribed is Betaserc. In addition to a neurologist, in this case a consultation with an otolaryngologist is required. The causes of vestibular vertigo are the following:
- Meniere's disease (disease of the inner ear, there is hearing loss).
- Vestibular neuronitis (the auditory nerve is affected).
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Migraine, epilepsy (usually dizziness serves as a harbinger of an onset attack).
- Intoxication with various chemicals (some types of antibiotics, diuretics).
- Benign positional vertigo.
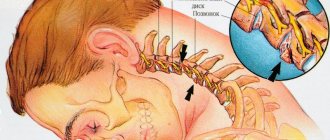
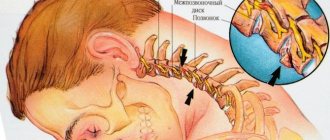
The cause of dizziness is often degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine, when the vertebral artery is pinched and the oxygen supply to the brain deteriorates.
Vascular changes in people over 50 years of age also provoke headaches and limited physical activity. In this case, Betaserc (betahistine hydrochloride) is successfully used for dizziness and spasms due to impaired cerebral circulation.
For dizziness and tinnitus, the drug Cinnarizine has proven itself for many years.
Some patients report loss of balance, vertigo and headache as side effects when using certain medications, for example, when taking Eutirox. The uncomfortable condition is corrected by reducing the prescribed dosage.
Repeated dizziness is a reason to contact a neurologist so that he can conduct an examination and decide which pills are most suitable in this particular case.
Men tend to remain silent and brush aside the problems that bother them, especially at a young age, but if you do not pay attention to dizziness at this age, a number of serious diseases and problems can be diagnosed later, which will be twice as difficult to deal with.
Human nature is structured in such a way that men work with their hands, and women work with their minds, and this is not surprising, because males have greater strength and endurance, and women, as a rule, are more intelligent and intellectually developed.
Therefore, impulses travel to parts of the body in different ways, receptors work at different speeds, and the causes of dizziness in men and women may differ.
Causes
There are several conditions in which there is pressure on the head when tilting the head down. The most serious of them are the following.
Cancer
During cancer treatment, a person may feel sick; Often one or more types of headache are present.
Cephalgia may be caused by the following cancer treatments:
- chemotherapy;
- hormonal treatment;
- biological therapy.
Painkillers taken during cancer treatment may also cause pain, especially when used in large quantities. Long-term use of analgesics can cause mild but persistent headaches.
Bisphosphonates, medications used to protect bones during cancer treatment, can also cause discomfort and tightness that can get worse when you lower your head.
Cervicocranial syndrome
Headaches from the cervical spine are caused by a violation of the structures of the neck (osteochondrosis), intervertebral discs, joints, and ligaments. The cause of pain is considered to be a functional disorder of the musculoskeletal system, but not degenerative changes in the spine (in particular, bone growths, changes in the intervertebral discs that form with age), because they occur in almost all people over 40 years of age. At the same time, cephalalgia when turning or tilting the head is not a mandatory sign.
Pain from the cervical spine manifests itself in episodes. It is usually localized on the right or left, simulating a migraine. Discomfort begins in the neck or back of the head, extends to the forehead, eyes, and ears. The pain is mostly moderate, most intensely felt in the frontal region.
Attacks of cephalgia with cervicocranial syndrome can last up to several days and occur at different periods of time.
Headache is accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- pain in the neck area;
- movement disorders of the cervical spine;
- worsening discomfort during movement;
- increased tension in the neck, trapezius muscles (shoulder blade area).

The following symptoms may also be present:
- mild nausea;
- blurred vision;
- increased lacrimation on the painful side;
- dizziness, instability.
Provocative factors include:
- sudden head movements;
- incorrect sleeping position;
- drafts (very often due to air conditioning);
- overload of the spine due to improper movement;
- forced uncomfortable head position (for example, when working at a computer for a long time);
- stress.
Treatment of cervicocranial syndrome
In case of prolonged or acute (especially post-traumatic) pain in the cervical spine, it is advisable to contact a neurologist or rehabilitation specialist. There are warning symptoms for back and head pain; Rarely, the cause of pain in the cervical spine can be conditions such as:
- infection;
- rheumatic disease;
- tumor;
- vertebral fracture.
Repeated disc herniation in the cervical spine (less often than in the lumbar region) also causes recurrent cutting pain. It can radiate to the upper extremities, does not respond to painkillers, and can lead to weakening of the arm and sensitivity disorders.
In case of acute blockade of the cervical spine, especially after sudden movement, a cold, or overload, muscle relaxants and painkillers (analgesics) are used for a short time. It is advisable to rest and apply dry heat to the area behind the head.
If a more serious cause is refuted and a muscle imbalance is identified, rehabilitation is carried out related to the study of the triggering factor for the occurrence of headaches and its prevention. This is especially true in case of long-term problems. Rehabilitation is aimed at:
- elimination of muscle spasms;
- mobilization of functionally limited joint mobility;
- correction of defective body posture, movement patterns, breathing.
The cause of pain in the cervical spine can also be a functional blockage of the lower parts of the spine, for example, the lumbar region.
If there are no serious problems with the cervical spine, alternative treatments can be used.
Migraine
Migraine has no psychological causes and is not caused by stress. We are talking about a purely biological disorder. Men also suffer from migraines, but in women it is 2-3 times more common. Its characteristic signs are vomiting, sensitivity to light, sounds... It is difficult for a person to move and move.

Approximately 1/5 of patients have an aura lasting 30-60 minutes. It manifests itself in flashes and temporary loss of vision. Patients often experience speech impairment, weakness in the arms and legs, confusion, facial stiffness, and other manifestations.
With a classic migraine, the pain is severe, stabbing, pulsating on the forehead, back of the head, around the ears, jaws, and eyes. Migraine without aura may cause diarrhea, frequent urination, nausea, and vomiting. The painful attack lasts up to 4 days.
Both types of migraines can occur either several times a week or once every few years. Some women experience attacks regularly, for example during menstruation or every Saturday after a tiring week. During pregnancy they often subside.
Migraine treatment
There are two types of treatment - preventive and acute.
Infrequent attacks are usually treated with analgesics. Mild migraines may respond to Aspirin or Aminophenazone taken at the onset of the attack. Small amounts of caffeine have a preventative effect. But most migraine sufferers need stronger medications.
The most commonly used drugs are triptans. They bind to serotonergic receptors, preventing the action of serotonin. These medications work best when used at the beginning of an attack. Taking the drug can be repeated.
Triptans are not suitable for patients suffering from angina, basilar migraine, hypertension, vascular disease, or liver disease.
Ergotamine affects the dilatation stage of headache.
Prophylactic therapy is recommended for frequent attacks (>3 per month). The most commonly used drugs include:
- Propranolol;
- Methipranol;
- Amitritptyline;
- MAOI – antidepressants;
- valproic acid is an antiepileptic drug;
- Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker.
Diseases accompanied by similar manifestations
If the question arises why you feel dizzy when bending down, you should think about the presence of pathological processes. Let's look at what diseases the signs in question indicate:
- Ear diseases. Especially the middle ear. It is a component of the organ of balance. His diseases lead to poor coordination, especially with sudden movements. Therefore, for example, with otitis media, when you lean forward, you feel dizzy. The causes of pathologies often lie in the development of infectious or viral processes.
- Spinal diseases. Especially cervical osteochondrosis. This leads to the fact that the blood vessels that provide nutrition and oxygen supply to brain cells are pinched or compressed. That's why my head is spinning. This can be especially pronounced when the torso is tilted.
- Pathologies of the nervous system. Unstable functioning of the cerebral cortex causes malfunction of all organs. This leads to them working harder and wearing out. After some time, when the strength is exhausted, weakness and dizziness occur. It’s not just the person who is bent over who experiences painful sensations. They also occur when throwing the head back.
- Heart attacks. Lead to deterioration of the heart muscle. This, in turn, provokes low vascular tone and poor blood supply to the central nervous system. When changing posture, the vessels do not have time to adapt to changing circumstances. That's why my head gets dizzy when I bend over.
- Neoplasms in the brain. Malignant cells, growing, compress the arteries and prevent them from fully performing their functions of supplying the brain with blood. This leads to unpleasant sensations both when lowering the head and when raising it up.
- Neuroses. They arise under the influence of psychological and emotional stress. The reasons may be family problems, conflicts at work. Pleasant events can also unsettle the nervous system. For example, a wedding. When experiencing stress, the cerebral cortex works too actively and gets tired quickly. Therefore, it happens that when you bend over, you feel dizzy.
Diagnostics
As noted, the sensation of feeling dizzy when bending down is entirely subjective. Therefore, a person can describe his condition in different ways:
- feeling of objects spinning around;
- a sense of movement or rotation of the person himself in space;
- feeling of falling;
- weakness;
- feeling as if you are about to lose consciousness;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- instability.
Based on how the patient describes his condition, the doctor can determine the type of dizziness: vestibular (true, systemic) or non-vestibular (non-systemic). In the first case, the patient says that he feels the movement of objects around him or the movement of his body in space. It occurs when the vestibular system is damaged. In the second case, all the other complaints listed above are possible.

What diagnostics are used
If a serious illness is suspected, the patient will be asked to undergo several examinations, including:
- Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland
- ECG of the heart
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- X-ray of the cervical spine
- duplex scanning of blood vessels
It is possible that studies will not confirm the presence of serious pathologies. The patient will then be asked to undergo a BPPV test, most often a Dix-Hallpike test. To carry it out, the patient is seated on a couch and asked to turn his head 45 degrees to the side in which discomfort is felt.
Then he is immediately placed on the couch, with his head thrown back, but left in the same position. Such actions should cause an attack of malaise in a couple of seconds. When repeating the test with the head turned to the other side, discomfort does not occur. If the assumptions are confirmed, the patient is diagnosed with BPPV.
Diagnosis of the causes of cervical osteochondrosis
Without fail, on the day of treatment, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests for the patient’s biological components of the body: blood, urine and other materials.
Based on the results obtained, it is not difficult for the doctor to make the correct diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Cervical osteochondrosis causes an inevitable change in the composition of biological materials.
To understand why you feel dizzy and to prescribe correct and effective treatment, a specialist must use a whole system of diagnostic tests:
• firstly, it is necessary to obtain data on the patient's blood pressure in the supine and standing positions;
• secondly, an X-ray examination will help to obtain a detailed picture of the condition of the intervertebral discs, changes in the structure of the vertebrae, the formation or absence of growths on the vertebral discs;
• thirdly, modern magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the cervical spine make it possible to make a reliable picture of the condition of the spine and blood vessels and nerve fibers adjacent to it. Both methods provide accurate evidence of changes in the cervical region.
A detailed examination will allow the specialist to determine whether dizziness is caused by osteochondrosis or a disease of another nature and prescribe the correct treatment.
During pregnancy
Carrying a child leads to very strong stress on the female body. There are two main causes of dizziness when bending down during pregnancy:
- In the initial stages, this is accompanied by intense hormonal changes. Hormones are very active biological substances that can influence the normal functioning of internal organs.
- In later stages of pregnancy, the developing fetus gradually increases in size, squeezing the veins and arteries. This leads to poor circulation and unpleasant symptoms.
Dizziness in an interesting position can act as a norm. However, you should play it safe and tell your doctor about them.
The mechanism of dizziness
Why do you feel dizzy when bending down? This symptom occurs when the balance in the flow of sensory information from the outside is disturbed, as well as when there is a failure in the processing of this information in the brain.
Dizziness is defined as the feeling of the body moving in space. A small formation in the inner ear, the vestibular apparatus, is responsible for these sensations. It performs three main functions:
- body orientation in space;
- ensuring balance;
- image stabilization.
Violation of any of these functions causes corresponding clinical symptoms, not just the feeling of being dizzy.
The main regulator of the function of the vestibular system is histamine. Therefore, another cause of dizziness is the activation of histamine receptors.
Why does it get dark before your eyes when you get up?
People often notice that their vision becomes dark when they suddenly rise from a place. The main reason for this symptom is a lack of oxygen in tissues and organs. This condition is characterized by the term hypoxia. Lack of oxygen causes orthostatic hypotension, which often develops with heart disease. If your eyes darken when getting out of bed, this may indicate that the person has low blood pressure.
Doctors often hear complaints of darkening of the eyes from patients who take medications such as:
- Vasodilators.
- Diuretics.
- Antidepressants.
With a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a person’s vision will always darken. In this case, symptoms such as:
- Weakness in the body.
- Decreased attention.
- Dyspnea.
- Memory impairment.
Darkening in the eyes should not be ignored. First you need to sit down so as not to get injured. Sometimes the darkness in the eyes goes away after the person calms down. When this phenomenon occurs frequently, you need to go to see a doctor.
Symptoms: nausea, dizziness when tilting the head
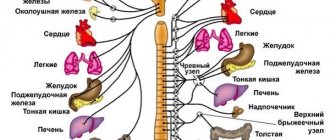
You can count more than 80 diseases accompanied by dizziness and nausea.
Sometimes this symptom is the main one, in other cases it accompanies and aggravates the clinical course of the disease, indicating the degree of involvement of internal organs and systems. The origin of nausea, vomiting, and dizziness involves a reaction from the cardiovascular and nervous system, a specific lesion. Finding out the connection with other manifestations is much easier in an adult who understands what is happening to him, and difficult in a frightened child. We will look at the main causes and diseases in which these symptoms occur.
Dizziness is an unpleasant feeling of lack of stability of surrounding objects; they are perceived as rotating or moving, while a person loses balance, cannot move confidently, or distinguish direction and goals.
It manifests itself in patients when turning the body, bending down (“dizzy”), in the form of attacks of dizziness with nausea and vomiting. A complex system of the vestibular apparatus is responsible for the correct perception and assessment of movements. Its center is located in the cerebellum. But the assessment depends on the state of information coming through special nerve fibers from the sense organs.
Therefore, the “culprits” of dizziness may be:
- central link - in case of damage to the cerebellum caused by diseases of the brain;
- peripheral - if vision is impaired, the vestibular nerve and inner ear are involved in the pathology.
In addition, dizziness is distinguished:
- physiological - there is no pathology of the vestibular apparatus, they arise due to hunger (a drop in blood glucose levels), a stressful situation (a consequence of the release of adrenaline and cerebral vasospasm), motion sickness in transport, overwork;
- systemic (pathological) - always caused by a disease with damage and disruption of the functioning of the cerebellum, the parts that make up the vestibular apparatus, vision, and muscles.
Nausea also has central and peripheral causes. The main vomiting center is located in the medulla oblongata. Receiving signals through internal pathways, at a subthreshold level of irritation it causes not vomiting, but a feeling of its approach.
The brain receives influence on the central zone through the ascending nerves, from the blood, depending on the composition of hormonal levels, glucose and other substances. Toxins and unremoved waste irritate the center and contribute to nausea and vomiting.
Local causes are changes in the acidity of gastric juice, the accumulation of a large volume of undigested food, pain from ulcers and cancer. In this case, the body tries to free itself from overirritation and cleanse the stomach with the help of vomiting.
The causes of nausea and dizziness are associated with the common blood supply to the cerebellum and medulla oblongata. Disturbance in the supply of neurons with oxygen and nutrients during ischemia leads them to a state of hypoxia, the cells are not able to synthesize energy, and the content of electrolytes is disrupted.
As a result, various types of cerebral circulatory insufficiency are clinically manifested with attacks of dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, and transient disturbance of consciousness.
Symptoms of dizziness and nausea are a serious component of many neurological diseases, which are the consequences of circulatory disorders in the brain during hypertensive crises, a drop in blood pressure during states of shock.
Physiological causes of dizziness and nausea include hormonal changes that occur in women during pregnancy and menopause. In girls, signs appear with heavy menstruation. The body's sensitivity to moderate blood loss and lack of nutrition play a role.
Women complain of dizziness, weakness, and staggering when walking. If pain appears in the lower abdomen, you should urgently contact a antenatal clinic and find out the cause.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is considered by some to be a physiological process, while others consider it to be a pathology. There is no doubt that all symptoms appear in adolescents and children. They are associated with hormonal fluctuations during periods of active growth. Schoolchildren often experience dizziness and fatigue. This also applies to young, impressionable women. No organ disorders were detected.
Dizziness and vomiting are a common reaction of the human nervous system to vibration and body vibrations in transport, in flight, at sea. People call it "motion sickness" or "sea sickness." Signs are accompanied by excessive salivation, headache in the temples, and sweating. Associated with low adaptive function of the autonomic nervous system.
Stressful situations - a normal reaction includes the release of catecholamines, which temporarily spasm the blood vessels of the brain. The condition returns to normal after rest and calming procedures. Hypoxia does not reach threshold values and does not cause circulatory disorders in neurons. With frequent repetition, the nature of the changes is disrupted. Vasospasm causes pathology.
Neurological symptoms are very specific. Neurologists check reflexes, the sensitivity of different areas of the body, the nature of movements, stability and balance. Combinations of signs make it possible to judge the damage to certain areas of the brain and peripheral nerves.
Cervical osteochondrosis causes an adult a lot of pain. The disease is caused by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral cartilage. Most often, patients complain of pain in the neck on one side, which intensifies when trying to move.
Severe dizziness and nausea occur when raising the head or turning suddenly. Decreased balance, unsteadiness in gait, and numbness in the fingers are detected. Vestibular neuritis - severe dizziness occurs in the patient when getting out of bed, getting out of a chair, or turning the head. Symptoms appear suddenly and disappear after 2–4 days. Recurrence of attacks is possible.
Meniere's disease is characterized by severe tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness and nausea with bouts of vomiting. Cerebrovascular accidents occur in the form of vascular crises, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. Symptoms depend on the type of disorder and the extent of the process. There are acute and chronic forms.
Neurological symptoms include:
- prolonged vomiting, dizziness and nausea;
- severe weakness in the limbs;
- loss of sensation;
- paralysis;
- feeling of darkening, double vision, flashing of luminous dots;
- loss of visual fields;
- speech difficulties;
- disturbed balance;
- sensation of objects rotating;
- transient disorder of consciousness;
- sleep disorder;
- headaches, feeling of “pulsation” in the head.
Basilar migraine - the aura of the disease is manifested by harbingers, they indicate that signs of the disease will appear after half an hour to an hour. Nausea and dizziness are often the first to indicate the onset of an attack, followed by sharp headaches on one side of the head. Migraine is accompanied by vomiting, darkening of the eyes and flashing spots, and tinnitus.
Brain tumors often cause severe headaches, deterioration of the patient’s condition in a certain position, loss of vision, deafness, vestibular disorders.
source
When you bend down, you feel dizzy: causes, symptoms, what is the danger, doctor’s recommendations, possible problems and treatment of dizziness
There is hardly a person who has not felt dizzy at least once in his life when bending down. Often these dizziness do not mean anything. They are a manifestation of ordinary fatigue and weakness.
But sometimes it can be a symptom of a serious illness that requires diagnosis and treatment.
Therefore, everyone should know the causes of dizziness when bending down, as well as how to get rid of this unpleasant symptom.
Why do you feel dizzy when bending down? This symptom occurs when the balance in the flow of sensory information from the outside is disturbed, as well as when there is a failure in the processing of this information in the brain.
Dizziness is defined as the feeling of the body moving in space. A small formation in the inner ear, the vestibular apparatus, is responsible for these sensations. It performs three main functions:
- body orientation in space;
- ensuring balance;
- image stabilization.
Violation of any of these functions causes corresponding clinical symptoms, not just the feeling of being dizzy.
The main regulator of the function of the vestibular system is histamine. Therefore, another cause of dizziness is the activation of histamine receptors.
Often, dizziness and subsequent fainting are caused by severe emotional stress. It leads to activation of the sympathetic nervous system, due to which the lumen of blood vessels narrows and blood flow to the brain decreases. These can be negative emotions (severe fear, anxiety, excitement) and positive ones (joy, delight).
The condition of feeling dizzy after bending down is completely subjective. The degree of manifestation of this symptom cannot be measured using special instruments. Only from the patient’s words can the doctor understand how much this bothers the patient.
In a person without any diseases, dizziness may occur for the following reasons:
- early pregnancy;
- insufficient intake of nutrients into the body, for example, due to diet;
- mental stress, chronic stress;
- insufficient functional activity of the vestibular apparatus;
- exhaustion of the body due to violation of the daily routine, insufficient rest;
- history of traumatic brain injury;
- taking medications whose instructions list dizziness as a side effect;
- high temperature and humidity;
- unpleasant odors for humans.
In most cases, the sensation of everything spinning around is not dangerous. A person experiences it extremely rarely. But if he constantly feels that when he lowers his head down, he gets dizzy, he should consult a specialist. After all, dizziness can be one of the symptoms of serious diseases.
A person may complain of feeling dizzy when bending down for the reasons listed below:
- Acute infectious diseases. With them, this symptom is combined with aching headaches, general weakness and fatigue, chills and fever.
- Migraine. With this disease, dizziness then develops into severe unilateral pain in the head.
- Osteochondrosis or injury to the cervical spine. Dizziness occurs due to the irradiation of pain from nerves compressed between the vertebrae.
- Neoplasm in the brain.
- Acute circulatory disorder in the cerebral vessels (stroke). Severe weakness, nausea and vomiting also appear. Motor and speech disturbances are possible.
- Hypertension or, conversely, low blood pressure.
- Diabetes. With this disease, dizziness is possible with sudden changes in blood sugar concentration.
- Inflammation of the inner ear - otitis media. Accompanied by severe pain in the ear.
- Damage to the membrane between the inner and middle ear is a perilymphatic fistula. In addition to dizziness, the patient is worried about hearing loss, ear pain, and cough.
- A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood is anemia. Pallor of the skin and mucous membranes occurs, the patient experiences constant weakness and fatigue.
A separate condition is distinguished as vegetative-vascular dystonia. It represents a violation of the tone of the vascular wall. This leads to poor blood circulation in the brain and, consequently, dizziness.
Often, if a person complains of looking down and feeling dizzy, this is not the only complaint. The patient may not present other complaints at first, but the doctor should question him in detail and conduct a series of objective examinations.
Dizziness may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- changes in blood pressure: hypertension (increase) and hypotension (decrease);
- increased heart rate (tachycardia);
- muscle weakness and body aches;
- nausea and vomiting;
- headache;
- heat;
- heavy sweating;
- pale skin;
- ear pain;
- fainting;
- convulsions;
- high blood sugar.
If you feel dizzy when bending down, this is accompanied by any of the symptoms listed above, you should definitely consult your doctor. After all, only a qualified specialist can comprehensively examine the patient and make the correct diagnosis.
In most cases, this symptom is not dangerous. But if an attack begins suddenly, in a place that is inconvenient for a person, it can lead to unpleasant consequences.
If you suddenly feel dizzy when bending down, you may lose your balance. This is especially dangerous if he is alone and there is nowhere to expect help. The patient may faint, which will cause injuries to the limbs and soft tissues, bone fractures, and bruises of internal organs. A concussion is also possible.
The most terrible consequence of dizziness when bending down is hemorrhage under the membranes of the brain. It is dangerous because it may not manifest itself in any way in the first hours after the injury.
During this time, blood accumulates under the lining of the brain. When enough of it has accumulated, the hematoma compresses the brain tissue. As a result, the patient loses consciousness and may fall into a coma.
Therefore, anyone who experiences frequent dizziness should definitely seek medical help to prescribe appropriate therapy.
As noted, the sensation of feeling dizzy when bending down is entirely subjective. Therefore, a person can describe his condition in different ways:
- feeling of objects spinning around;
- a sense of movement or rotation of the person himself in space;
- feeling of falling;
- weakness;
- feeling as if you are about to lose consciousness;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- instability.
Based on how the patient describes his condition, the doctor can determine the type of dizziness: vestibular (true, systemic) or non-vestibular (non-systemic).
In the first case, the patient says that he feels the movement of objects around him or the movement of his body in space. It occurs when the vestibular system is damaged.
In the second case, all the other complaints listed above are possible.
Source: https://nstone51.ru/golovokruzhenie/simptomy-toshnota-golovokruzhenie-pri-naklone-golovy/
What causes dizziness in the absence of illnesses?
It happens that when bending over, a completely healthy person gets dizzy. This may be caused by the following factors:
- Sudden change in body position. In this situation, the circulatory system simply did not have time to adapt to the rapidly changing circumstances. As a result, short-term changes in blood pressure occur, the load on the body increases and dizziness occurs.
- Malnutrition. For example, during fasting or dieting. It happens simply because due to workload there is not enough time to eat. Because of this, brain cells are deficient in nutritional compounds. When bending over, the load increases, causing dizziness and nausea.
- High psycho-emotional stress and frequent stress lead to severe tension in the nervous system, which, as is known, is responsible for the normal functioning of the body. When its resources are depleted, severe dizziness can occur.
Complications of dizziness
In most cases, this symptom is not dangerous. But if an attack begins suddenly, in a place that is inconvenient for a person, it can lead to unpleasant consequences.
If you suddenly feel dizzy when bending down, you may lose your balance. This is especially dangerous if he is alone and there is nowhere to expect help. The patient may faint, which will cause injuries to the limbs and soft tissues, bone fractures, and bruises of internal organs. A concussion is also possible.
The most terrible consequence of dizziness when bending down is hemorrhage under the membranes of the brain. It is dangerous because it may not manifest itself in any way in the first hours after the injury. During this time, blood accumulates under the lining of the brain. When enough of it has accumulated, the hematoma compresses the brain tissue. As a result, the patient loses consciousness and may fall into a coma.
Therefore, anyone who experiences frequent dizziness should definitely seek medical help to prescribe appropriate therapy.
Treatment
Therapy is focused on the underlying disease that triggered the symptom. Treatment of patients who experience attacks of dizziness of vascular origin when bending the neck or torso is carried out with drugs that stimulate cerebral circulation. Treatment of acute attacks is carried out with the help of antiemetics (Prochlorperazine, Promethazine) and vestibular suppressants.
Vestibular suppressants include antihistamines (Dimenhydrinate, Diphenhydramine), anticholinergics (Scopolamine, Platyphylline) and benzodiazepines (Lorazepam, Diazepam). The course of therapy with drugs used to relieve an attack does not exceed 2-3 days due to their effect on vestibular reactions (they slow down and inhibit the natural compensation of static imbalances).
The role of the histamine mediator in the regulation of the functions of the vestibular apparatus has been proven. The therapy uses a specific drug, Betahistine dihydrochloride, which is structurally similar to the mediator. The medicine does not cause sedation or addiction.
Treatment with Betahistine dihydrochloride helps eliminate dizziness and accompanying symptoms - pain in the head area, dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, and imbalance. After a 2-month course of therapy, the following therapeutic effects are observed:
- Improving cerebral circulation.
- Reducing the frequency and severity of dizziness in 97% of cases.
- Stopping attacks – in 13% of cases.
- Hearing improvement – in 73% of cases.
- Reduction of noise in the head and ears area - in 91% of cases.
Electrophysiological examination shows improvement in the functions of the vestibular analyzer. After treatment, the conductivity of the acoustic signal in the area of the auditory nerves and brain stem improves, which is confirmed by electrical evoked potentials.
What causes dizziness, nausea when bending over?
Dizziness is a feeling known to every person. Everyone describes their state of dizziness and loss of orientation differently: their knees buckle, their legs become weak and the ground disappears from under them, before their eyes all objects rotate, float and dark dots – “pixels” – appear. When you feel dizzy, the first thing that affects your sense of balance is your sense of balance.
Why do you feel dizzy?
It is balance and a correct, even feeling of oneself in space that forms our normal state of well-being, and all deviations from this norm cause anxiety. Read more about the causes of loss of balance when walking in another article.
A person perceives the world around him through the senses (the action of nerves and nerve endings), which transmit incoming information to the brain - there the category “what is normal” is determined and consolidated. Everything that is not normal is perceived by us as violations and failures, which is a reason to consult a doctor for advice.
Therefore, dizziness can be both a normal reaction of the body and an alarming symptom. It's worth looking into.
Causes of dizziness
Dizziness as a completely understandable norm: dizziness of the head can be considered a normal reaction of the body under some circumstances. Here the causes of dizziness are quite harmless and lie on the surface.
For example, during strong experiences and uncontrollable emotions, adrenaline is sharply released into the blood. As a result, vascular spasm slows down blood flow to the brain. This in turn leads to loss of balance and dizziness . What emotions contribute to this?
Typically damaging:
- sudden fear;
- increased anxiety;
- “tingling” and “shaking” excitement;
- amazing joy;
- stormy delight, etc.
Dizziness can occur when using any type of transport; so-called motion sickness . The explanation here is also simple: the eyes clearly see the horizon line, however, the vestibular apparatus transmits return signals to the brain, it perceives the motion and, as a result, the head is dizzy.
Something similar happens when riding on swings and carousels, but here the explanation is as follows: the brain does not have time to comprehend everything instantly; it needs time to process the incoming information. The advice on training the vestibular apparatus is also relevant in this case.
The head may feel dizzy due to height - the reason is the work of the eye muscles. When looking down or into the distance, they are in one position, and if the gaze is transferred to nearby objects or objects, the eye muscles occupy a different position. Focus is lost.
It is also possible to have a completely natural, ordinary loss of balance , which occurs due to the fact that the exercise “tilting the head to the sides or forwards and backwards” is performed too sharply and quickly. In this case, you just need to train your vestibular apparatus . However, during physical activity, there are disturbances in the blood supply caused by the same speed and sharpness of movements.
Your head may start to feel dizzy if you don’t eat on time . In this case, the reason is insufficient glucose levels in the body. The same thing happens when you are on a diet for a long time.
When taking certain medications, dizziness is considered a side effect, which already has its own explanation.
Dizziness as a sign of disease or dysfunction of vital functions/organs of a person .
If you feel dizzy and also experience some of the painful symptoms listed below, it could be:
- or a clear indicator of the characteristics of an individual organism and mental activity;
- or the presence of a certain disease, so it is very important to make an appointment with a doctor with existing alarming symptoms. In combination with dizziness, the following symptoms may be observed:
- increase/decrease in blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- unreasonable muscle weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- excessive sweating;
- pallor;
- high temperature, fever, etc.
If there are several of the listed signs, this is a reason to consult a doctor, since there are many diseases and illnesses that are accompanied by dizziness and others like it.
So, here are a few common dysfunctions of a vital organ or disease :
- Diseases of the vestibular apparatus.
- Ear disease Accompanied by severe pain in the ears.
- Ear membrane disease . Hearing is getting worse.
- increases in the cavity of the inner ear. Meniere's disease. Accompanied by constant tinnitus.
- Intoxication, poisoning. Added migraine.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Stroke.
- brain tumor .
- Neurosis.
- Arterial hypotension .
Why does one feel dizzy and nauseous when tilting and turning the head?
As a rule, the first thing that explains dizziness when turning the head and nausea is a disturbance in the activity of the cervical spine. In the cervical vertebrae, the vertebral paired artery passes from the subclavian artery; it supplies brain tissue with blood and substances, including the cerebellum and the back of the brain, where the centers of coordination and balance are located.
Therefore, my head is spinning due to:
- hypoxia;
- lack of oxygen in the balance centers of the brain.
When bending and turning, the vertebral artery is bent or pinched. In such cases, hypoxia develops.
Causes of dizziness and nausea when bending and turning:
- osteochondrosis, spondylosis, intervertebral hernia, spondylolisthesis;
- tumor of the cervical spine;
- disorders not related to the pathology of the spinal column, narrowing of the lumen of the vessel due to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques.
What to do if your head is dizzy to the point of fainting and your vision becomes dark
- If you feel dizzy and nauseous, it is better not to try to hold back the urge to vomit. The body will restore its strength faster if it cleanses itself.
- If you suddenly feel dizzy, you should immediately lie down and try to relax. Position yourself so that your head and shoulders are at the same level - this improves blood supply to the brain. Lie like this for a while. Dim the light so that unnecessary information does not come through your eyes with light - this will strain and damage.
- A cold wrung-out towel or ice will revive the taps
- can also help .
- As a tip for prevention: it’s good to start consuming foods such as eggs, cheese, fish, and nuts every day.
Causes of dizziness to fainting and darkening of the eyes
- Dizziness and darkening of the eyes , fainting, general weakness of the body, nausea and vomiting sometimes accompany normal hunger, acute poisoning, overheating in the sun, symptoms in adults you will find here or overwork, so all of the above symptoms can be experienced by completely healthy people under the above circumstances. As soon as these circumstances cease to affect the body, the symptoms go away on their own, and the general condition normalizes and stabilizes.
- In addition, these signs appear in women during pregnancy or menopause.
- If dizziness and fainting recur, nausea and vomiting do not stop, constant weakness does not go away and lasts for a certain long period, then in this case the cause lies inside the body. Here we should again remind you of the need to be fully examined by specialists, since there are plenty of reasons for the manifestation of such symptoms. Here are just a few of the main ones:
- pathology of the nervous system;
- seizures;
- epilepsy;
- intracerebral hemorrhages;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury; brain tumor;
- thrombosis, atherosclerosis;
- blood pressure surges
- pathologies of metabolic processes;
- intoxication;
- use of certain medications;
- alcoholism, drug addiction;
- infections;
- ischemia, heart failure;
- anemia , etc.
Source: https://novosibmemorial.ru/golovokruzhenie-toshnota-pri-naklonah-ot-chego/
Options for consequences
With adequate and timely treatment, dizziness is usually not dangerous. However, ignoring symptoms can lead to unpleasant consequences for a person. For example, failure to receive qualified medical care and progression of the disease.
Complications
The main complications that can be caused by dizziness are:
- transition of existing ailments to a chronic form;
- traumatic brain injuries, concussions;
- bruises, fractures;
- strokes;
- apathy, depression.
Why do you feel dizzy and nauseous when bending over: reasons and what to do?
Dizziness is a feeling known to every person. Everyone describes their state of dizziness and loss of orientation differently: their knees buckle, their legs become weak and the ground disappears from under them, before their eyes all objects rotate, float and dark dots – “pixels” – appear. When you feel dizzy, the first thing that affects your sense of balance is your sense of balance.
Causes of dizziness while lying down
When the body is at rest horizontally, the head may feel dizzy due to:
- sensations of falling walls and ceilings with closed eyes;
- sensations that objects around are in motion;
- strong feelings of anxiety before bedtime;
- feeling of being stupefied.
When a person changes position, all such sensations can be aggravated. Why is this happening? As a rule, for the same reason - common dysfunction of an important organ or disease, however, the list is slightly different.
This information is discussed in more detail in our similar article on dizziness in a standing and lying position.
Causes of dizziness in a horizontal position
- diseases of the inner ear;
- Meniere's syndrome;
- traumatic brain injury;
- a brain tumor;
- blood pressure surges;
- taking medications with side effects;
- diabetes;
- following strict diets.
Causes of dizziness when walking
When walking, dizziness is due to the following problems:
- poisoning, intoxication;
- Parkinson's disease;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- sclerosis;
- neuroses, psychoses.
Treatment
With complaints of dizziness, you can contact such specialists as neurologists, cardiologists, endocrinologists , but it is better to first visit a therapist. For dizziness (including, but not primarily, since this is a secondary symptom), a certain course of medication is prescribed.
To relax and at the same time gently raise your tone, you can train your vestibular apparatus by performing light exercises:
- Sit with your back straight, turn your head to one side and lie down without changing your position. Movements are smooth.
- Sit down again, turn your head in the other direction.
- Do the exercises for a few minutes, 5 – 7 times a day.
Medicines for dizziness
To treat persistent dizziness, medications are prescribed, their use depends on the symptoms:
- antihistamines : Meclozin, Promethazine, Pipolfen, Diphenhydramine;
- tranquilizers for sedation: “Diazepam”, “Lorazepam”;
- sedatives: “Andaksin”, “Seduxen”;
- against nausea and painful vomiting: Cerucal, Metoclopramide.
Complications
It is important not to ignore dizziness and accompanying symptoms, because if you let it go, you can bring your body to a breakdown, since the causes of systematic dizziness are not very harmless.
Therefore, the first thing you need to do is to consult a doctor.
In order not to deal with complications later, it is important to know what measures to take in case of sudden dizziness and other symptoms.
First aid for dizziness
- Don't panic, just need peace.
- If you feel very dizzy , it is better to sit down and not close your eyes, but look at some object.
- Call an ambulance if there is numbness in the limbs, chest pain and speech impairment.
- Immediately take a lying position and do not make unnecessary movements, do not turn your head.
- You need to take off your tight clothes (it will be good if someone helps) and open the window to let fresh air into the room.
- will help you relax .
- Take ten drops of Atropine or another remedy for dizziness.
12.09.2016
Source: https://mozgvtonuse.com/bolezni/golovokrujenie-pri-naklone-golovi.html
Vertigo therapy
If attacks of lightheadedness occur due to the disease, their cause should be eliminated. The main directions of therapy for dizziness:
- Cupping. Creating conditions for maximum silence and comfort. With BPPV, medication is not required. It is enough to take a course of medications that improve blood circulation or sedate.
- Etiological impact on the cause. The need is to use drugs to combat somatic, infectious, neurological, neurosurgical or ENT diseases.
- Pathogenetic therapy. Systemic malaise is symptomatic. To improve the patient's health, vestibulotic drugs, antihistamines and tranquilizers are prescribed. Medicines including betahistine dihydrochloride have received positive reviews. They are most effective for Meniere's disease - by reducing attacks of systemic lightheadedness, the medications act to improve balance. With a long course of treatment, it is possible to block the progression of the disease.
- Vestibular compensation and rehabilitation: active communication, movement and visual stimulators.
Expert help needed:
- otolaryngologist and neurologist;
- therapist, ENT specialist;
- infectious disease specialist, phlebologist;
- endocrinologist.
How to implement suitable treatment for pathology
Basically, the treatment of dizziness consists of relieving the symptoms of the disease. The etiological form of treatment is organized only with the development of a narrow range of pathological conditions, such as basilar migraine, temporal lobe epilepsy, bacterial labyrinthitis, brainstem stroke, etc.
To prevent the occurrence of dizziness, vestibulolytic medications are prescribed, which affect the receptors of the vestibular apparatus and the central structures of the vestibular apparatus. In addition, antihistamines and tranquilizers are used. Prolonged dizziness is treated with dehydration and intravenous diazepam.
Rate this article: Loading…
Related posts:
Source: VashNevrolog.ru
First aid
If alarming symptoms appear, when you suddenly feel dizzy, you should do the following:
- Lay the victim on his back.
- Loosen tight clothing, if any. For example, take off your tie, unfasten the buttons.
- The victim will need to focus his gaze on one selected point, this will help mentally fix the position of the body.
- It is strictly forbidden to make sudden movements, especially with the head.
- Open all windows in the room to provide oxygen access.
- Apply something cool to the patient's forehead.
- A cotton swab soaked in ammonia will bring you back to your senses.
- Give the victim a glass of water or herbal tea.
If all else fails, you should urgently call an ambulance, and do not take any pills until it arrives.
Therapeutic recommendations
If you get a headache when you bend over, regardless of the cause, try the following tips:
- Place an ice pack on the painful area. Applying cold may help relieve pain.
- Calm down, try relaxing in a hot bath or shower. Sleep or take a walk (if your condition allows).
- Relax in a quiet, dark room. Sit or lie down with your eyes closed. This will help reduce body tension. Quiet, relaxing music is also good for this purpose.
Consequences of osteochondrosis in the cervical region
The head may feel dizzy if the patient has cervical osteochondrosis; its treatment is not particularly difficult if you consult a neurologist in a timely manner. Other problems that arise against this background are dangerous, since in this area lie the vessels that supply blood to the spinal cord and brain. Oxygen starvation of these vital objects causes dizziness, weakness, headaches and nausea. In addition, there is a real threat of stroke, since the vessels are in a compressed state.
If the examination data establishes a diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, then it is necessary to consult doctors with narrower specialties: a vertebroneurologist, whose competence includes osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, herniated intervertebral discs.