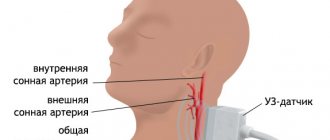
SCT (spiral computed tomography) angiography is rightfully considered the best technique for examining both the vessels of the brain and organs, systems and tissues of the whole body. Despite this, there are certain contraindications to cerebral angiography. Some of them are related to the principle of obtaining information during the study (X-ray radiation), others are related to the need to introduce a contrast agent into the blood, since this research method requires the introduction of contrast for better visualization of the walls of blood vessels.
The difference between spiral CT and standard tissue angiography is only that the X-ray tube and the procedure table are in continuous motion. Otherwise, the principle of the study is similar to computed tomography.
Spiral computed tomography of the abdomen
The procedure creates a multi-layered image of organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, etc.). The indication for it is pain in the abdomen, pelvis, as well as a number of diseases of the small and large intestines, internal organs.
It is used in diagnostics:
- Appendicitis, pyelonephritis, kidney and bladder stones, diverticulitis, abscesses
- Pancreatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, inflammatory processes and polyps in the intestines, internal bleeding
- Cancer of organs located in the abdominal cavity
- Diseases of blood vessels and lymph nodes
Before the procedure, the patient must be prepared and a contrast agent is used.
Spiral computed tomography is a relatively new (invented in 1972) and highly informative method of medical diagnostics, which is based on X-ray radiation. The device is designed in such a way that the X-ray tube and many rows of sensors rotate around the area under study and take many “frames” at once, which are then transferred to a computer, which processes all the resulting images and builds them into sections of the human body on the monitor...
Research must be carried out on an empty stomach. A few days before SCT, exclude from the diet foods that cause gas formation in the intestines (legumes, whole grains, cabbage, radishes, soda, grapes and others). Take activated charcoal a few hours before.
The night before, cleanse your colon with an enema. Do not eat before the procedure.
Before SCT, the patient will need to remove all metal objects and lie in the appropriate position. With contrast spiral computed tomography, if we are talking about the study of the brain, blood vessels, kidneys and liver, the patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent. For CSCT of the intestine, the drug is taken orally.
Types of SCT
Preparing for the examination
The study does not require special preparation. It is often used to diagnose emergency conditions. For routine examination, it is recommended to abstain from food 3 hours before SCT. Before the procedure, the patient is explained that he must lie still. Spiral tomography is a quick examination method, which is especially important for acute diseases, injuries, and examination of children. A venous catheter may be necessary for bolus contrast.
SCT is a technique that allows you to quickly provide maximum information about most diseases of the brain and its membranes, as well as vascular pathologies. Installing such equipment in emergency departments will significantly speed up the diagnostic process and increase the effectiveness of the medical care provided.
The essence of diagnosis
The first spiral tomograph appeared in 1988 and became an indispensable assistant for doctors.
This method is based on scanning the body with X-rays, which are converted into electrical signals and further processed by a computer. It allows you to quickly obtain an accurate result with an unprecedented error of only 1 mm.
During a session in the clinic, the table with the patient moves, but around the patient, as if in a spiral, the X-ray tube with the surface on which the detectors are located additionally rotates. The device recognizes tumors up to 1 mm in size. This is extremely important in oncological diseases for the timely detection and elimination of the source of the disease. One anatomical area is scanned on an outpatient basis within 3-5 minutes. The laser camera takes wide-format photographs.
Amazing results can be obtained on modern 64-slice (multi-slice or multi-slice) high-speed tomographs - quickly obtaining two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of excellent quality with a low level of radiation.
Such an examination is indispensable for injuries, bone fractures and damage to internal organs, malignant tumors and strokes, when it is necessary to obtain information about the diseased organ in the shortest period of time. This technology replaces many modern research methods, for example, ultrasound diagnostics.
Procedure
4 hours before the examination procedure, food and water intake is stopped.
Before examining some organs, the patient must undergo preparation - drink a contrast agent (urografin). Detailed instructions for preparing for the procedure will be given by the specialist who will conduct the examination.
The dinner before the procedure is light; for breakfast it is better not to eat solid food, preferably liquid porridge and juice.
The patient lies down on a movable table that slides into a special tunnel - a scanning device. For the patient’s comfort, the table is equipped with special pillows and belts; they help limit his movements during the procedure so that the photographs are clear and not blurry.
Patients who cannot lie still for a long time and hold their breath for a short time (children or nervously excited patients), or are susceptible to claustrophobia, are given a sedative.
In another office there is a computer station with a doctor-technologist working on it, controlling the scanner using the screen. During the procedure, he talks to the patient and gives the necessary instructions.
The spiral computed tomography procedure is completely safe. Although the patient receives a small dose of X-ray radiation, it is so insignificant that it does not cause any harm to the body. There is a risk when administering a contrast agent or sedatives. The patient must inform the doctor about any allergic reaction he has to medications or iodine, which is part of the dye.
If the person being examined has diabetes, asthma, kidney failure, heart disease or thyroid disease, you should also tell the doctor about this. The examination is contraindicated for pregnant women. If there is an urgent need, it is still performed, but the uterus is covered with a lead screen.
In the case of examination of internal organs, you must stop eating and drinking 4 hours before the SCT examination. In some cases, for certain examinations, the patient will need to undergo minimal preparation - take a contrast agent orally. Detailed recommendations on the method of preparation should be given by the radiologist who will directly perform the study. The evening meal before the study should be fairly light, and for breakfast it is better to avoid solid food.
At the time of the examination, the patient will be placed on a movable table, which moves into the tomograph scanner tunnel. To limit movement during the diagnostic period, the patient is, if necessary, fastened with special belts and pillows, which are necessarily equipped with the tomograph table. This is done to ensure that the pictures are of the highest quality.
In the case of children, disabled people, patients with claustrophobia who cannot remain still and calm, sedatives or light anesthesia can be used. In the adjacent SCT room there is a room with computers, where the radiologist is located and directly from which the tomograph is controlled and instructions are given to the patient during the examination.
Contraindications for SCT angiography
This method of diagnosing pathologies, although painless and non-traumatic, has an impact on the human body as a whole due to the effects of X-rays (albeit minimal) and the administered contrast. After the examination, there may be unpleasant consequences of varying intensity:
- Reaction to X-rays.
- Allergic reaction to contrast.
- Malfunction of the kidneys.
There are strict contraindications to CT scans of cerebral vessels. This research method is not used:
- For examination of pregnant women.
- For those suffering from kidney diseases.
- In the presence of pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- For patients with high obesity and/or severe diabetes.
- If the patient has a tendency to cardiac arrhythmia and hypotension.
- In case of serious condition of the patient.
Spiral computed tomography should be prescribed by a doctor only after a complete examination and standard types of diagnostics.
What can SKT do?
Computed tomography is simply irreplaceable in diagnosing the conditions of any bone structures, the condition of the lungs, and mediastinum in humans. SCT is also widely used in the study of abdominal organs (liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas), adrenal glands, kidneys, and pelvic organs.
Spiral computed tomography is leading in the diagnosis of complex bone injuries, multiple injuries (for example, road accidents) of bones and internal organs, in the diagnosis of complex or multiple injuries of the skull and acute injuries and hemorrhages of the brain.
SCT is also widely used by ENT doctors for a detailed assessment of the condition of the paranasal sinuses, auditory canals and temporal bones, since no other diagnostic method can compare with the accuracy and “depth” of computed tomography.
In studies of the spine using SCT, it is possible to determine the smallest damage in the bone structure, pathological calcifications in the ligamentous apparatus; to diagnose the condition of the intervertebral discs, it is best to use MRI.
The advisability of prescribing SCT in each individual case should be determined by the attending physician, who will subsequently interpret the results obtained from CT taking into account the entire picture and characteristics of the patient.
Features of SCT scanning
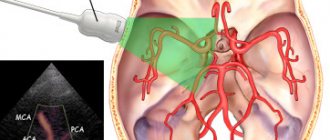
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels allows doctors to identify blood flow problems, and the depth and degree of pathologies of the vessels supplying blood to the brain. When performing angiography of cerebral vessels, the use of a contrast agent is mandatory. It is administered to the patient immediately before the start of the procedure, and the contrast is removed from the body over the next two days.
CT angiography is prescribed mainly for those patients who are suspected of oncology, stenosis, thrombosis of cerebral vessels, or hemorrhage. The procedure is not ordinary, it requires preparation and has its contraindications.
Principle of the diagnostic method
When examining the abdominal organs, the patient will be asked to drink 500–1000 ml. drinking water with a contrast agent dissolved in it in order to “separate” the stomach and intestines from nearby organs and tissues, as well as to ensure that intestinal loops do not create additional “interference” for the radiologist during the study. This is the so-called oral contrast.
The same technique of intravenous administration of a contrast agent is very often used in order to “highlight” areas with pathological changes, to study the blood flow of tumor formations, or specifically to study blood vessels.
For the first time, an SCT device became available and indispensable for doctors in 1988. The operating principle of this diagnostic is based on scanning the body using X-rays, which, after going through the stage of conversion into electrical impulses, are transmitted to a computer for further processing.
During the examination, the tomograph table with the patient moves, and at the same time, an X-ray tube with many sensors-detectors rotates around the human body in a spiral manner. With this SCT scanner it is possible to visualize neoplasms of various types up to 1 millimeter in size. And this is in our time one of the most important indicators for oncological diseases for taking the necessary measures for the timely elimination of the source of the disease.
One area of interest in the body is diagnosed on such a scanner in just 3-5 minutes, and then images of the highest quality are printed using a computer. Amazing results can be obtained on modern 64-slice (multi-slice or multi-slice) high-speed tomographs - quickly obtaining two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of high quality.
SCT has a number of differences and advantages over conventional computed tomography:
- the scanning speed and quality of the resulting images are much higher
- obtaining more accurate images in 3D projection. Such images are more informative in identifying the nature and location of pathologies
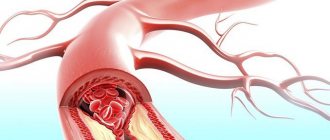
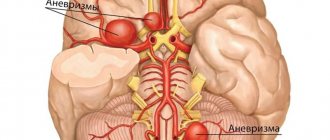
- the use of spiral diagnostic techniques has made it possible to use it in angiography, namely for visualizing arteries, determining vascular aneurysms, their narrowing and extent
- non-invasiveness in comparison with ventriculography, myelography
- absence of blood flow artifacts in the image
- a significant reduction in the dose of X-ray radiation on the human body, in comparison with conventional tomography (when studying several areas simultaneously, radiation doses are not summed up).
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS AND VOTE
- High speed of information collection (scanning). In a short period of time (up to 20 seconds), an image of one anatomical area (abdomen, lungs) is formed. The quality of the pictures is very high.
- Obtaining more accurate spatial 3D images. Three-dimensional models more accurately show the nature and location of the pathology. The use of spiral scanning techniques made it possible to use angiography, i.e. examination of the arteries, to identify vascular aneurysms, narrowing, and their extent.
- Non-invasiveness in comparison with ventriculography, myelography.
- There are no blood flow artifacts in the image.
- Reduced X-ray exposure to the patient compared to conventional tomography. Even when studying several anatomical zones simultaneously, radiation doses are not summed up.
With the spiral version of CT, the X-ray tube rotates around the table where the patient being examined lies. The table itself moves translationally along the longitudinal axis at one speed or another depending on the research objectives. As a result, the trajectory of the emitter relative to the patient has a spiral shape. The advantages of this method compared to conventional CT are:
- Faster scanning, which reduces the impact of artifacts on image quality due to patient movements, breathing, and swallowing.
- Coverage of a large area by examination in a short period of time, including the ability to simultaneously scan several anatomical areas.
- Less radiation exposure. Compared to traditional tomography, the absorbed dose is approximately 30% lower.
- High level of accessibility for studying almost any area of the body.
- Highest image quality and clarity. Multi-slice computed tomography models provide the highest resolution, and the three-dimensional modeling function allows you to visualize the extent of the pathological process and its nature.
- Providing CT angiography with the ability to assess the blood supply to parts of the brain in three-dimensional images.
Advantages of spiral tomography
With the spiral version of CT, the X-ray tube rotates around the table where the patient being examined lies. The table itself moves translationally along the longitudinal axis at one speed or another depending on the research objectives. As a result, the trajectory of the emitter relative to the patient has a spiral shape. The advantages of this method compared to conventional CT are:
- Faster scanning, which reduces the impact of artifacts on image quality due to patient movements, breathing, and swallowing.
- Coverage of a large area by examination in a short period of time, including the ability to simultaneously scan several anatomical areas.
- Less radiation exposure. Compared to traditional tomography, the absorbed dose is approximately 30% lower.
- High level of accessibility for studying almost any area of the body.
- Highest image quality and clarity. Multi-slice computed tomography models provide the highest resolution, and the three-dimensional modeling function allows you to visualize the extent of the pathological process and its nature.
- Providing CT angiography with the ability to assess the blood supply to parts of the brain in three-dimensional images.
What does SKT “dislike”?
First of all, these are movements. Any movements during scanning of the study area distort the resulting images, of course, reducing their information content for the doctor. If in a series of images obtained, even just 1-2 scans are distorted by motion artifacts, then subsequent 3D reconstructions will already have defects and their information content for the doctor, of course, will be reduced.
Secondly, metal. Metal is to X-rays what a mountain is to the sun—it leaves a “shadow.” A large amount of metal in the examination area can significantly distort the resulting images. But if the metal is located in any place other than the area being examined, it cannot in any way affect the quality of the scans.
Tomography of the lungs
Such an examination is simply irreplaceable for detecting lung cancer or metastases. It is prescribed if there are signs of cancer and the x-ray did not show accurate information about the location and size of the tumor. They also do tomography for lung abscess, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, parasitic lung cysts, hernias, pleurisy, diseases of the heart and leading vessels, and some types of pneumonia.
Before the procedure, the patient is injected into a vein with an iodine-based contrast agent. Therefore, if he has an allergy to iodine, it is necessary to inform the doctor. There is no preliminary preparation of the patient.
Brain tomography
It is widely used in diagnosing head injuries in patients in severe and super-severe condition, symptoms of changes in blood circulation in the brain, high intracranial pressure, and various neurological disorders. We see changes in tissue density already in the early stages. The device detects pathology (abscesses, neoplasms, cavities) that may not be visible with a conventional tomograph. The procedure helps prevent and detect diseases such as stroke and heart attack.
The survey is used for:
- Determining the cause of headaches, systematic confusion, sudden onset of paralysis, impaired sensitivity of individual parts of the body, various visual disturbances. And also if there is a suspicion of a brain tumor, intracranial bleeding, or rupture of an aortic aneurysm.
- Diagnosis of inner ear dysfunction in hearing impairment.
- Developing a plan for an upcoming operation or assessing the success of an already performed brain operation.
- Determining damage to areas of the brain and providing assistance for stroke.
- Ensuring safe access and eliminating the possibility of brain injury during biopsy.
In some cases, the procedure is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent intravenously, which facilitates the detection of tumors, cysts, metastases, atherosclerotic plaques, and blood clots.
SCT of the brain does not require preliminary preparation of the patient.
This technique has a wide range of indications, which, depending on the purpose of the study, can be divided into groups:
- Screening for symptoms and syndromes of unknown origin: headaches, dizziness, history of loss of consciousness, suspected brain tumor.
- Emergency examination.
- It is carried out in the case of a convulsive syndrome that has arisen for the first time, or when its character changes, in combination with symptoms of organic brain damage, mental disorders, recent trauma, high body temperature and some other pathological manifestations.
- Traumatic brain injury, if it is accompanied by loss of consciousness, polytrauma, focal neurological symptoms, and a violation of the blood clotting process. A penetrating head injury requires an emergency scan.
- Headache with a sudden onset or a significant change in its characteristics, in the presence of focal symptoms, mental and cognitive disorders.
- A mental disorder accompanied by headaches, high blood pressure, meningismus, focal symptoms, and also in HIV-infected people.
- Planned SCT is prescribed for the final diagnosis.
- Treatment control.
- For therapeutic and diagnostic procedures and surgical interventions, in particular, punctures or hybrid operations performed under tomographic control.
Types of examination
SCT of the brain allows you to obtain detailed images of the vascular network, anatomical and pathological formations of any of its parts. Studying the obtained data not only ensures accurate diagnosis, but also provides the opportunity for neurosurgeons to plan in detail the course of an operation or any invasive procedures on brain structures.
Since the advent of the first tomograph, four generations of devices have replaced each other one after another. Spiral CT scanners belong to the third generation of equipment. In them, the emitter and detectors go through a full circle of rotation per step of table movement, which significantly reduces the examination time. Currently, the most advanced tomography method is scanning using a multilayer or multispiral tomography apparatus with a large number of detectors. In 2005, the first device was released with two radiation sources, which allows obtaining clear images of the heart at an accelerated heart rate and improves the differentiation of vessels, organs, and formations located close to each other.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor may choose one or another type of tomography:
- Native CT scan of the brain is a screening method in which no radiocontrast agent is administered. Allows you to assess the severity of damage due to traumatic brain injury, the nature of changes in arachnoiditis, prescribed in the acute period of a stroke, to diagnose meningioma, tumor or pituitary cyst, to clarify the type of hydrocephalus.
- CT with intravenous enhancement is prescribed to diagnose a brain tumor, vascular aneurysm, and malformation. In most cases, the technique allows you to visualize the localization of the pathological process. Contrast is injected immediately before scanning manually or with bolus enhancement using a syringe-injector, providing visualization of vessels in different phases of contrast.
- CT angiography is performed with a bolus injection of radiopaque contrast agent. The goal is to obtain a three-dimensional image of the cerebral vasculature. The study allows you to detect stenosis or occlusion of arteries and vein thrombosis, malformations and aneurysms.
- Perfusion CT. During the study, cerebral blood flow is measured by changes in the X-ray density of tissue during the passage of intravenous contrast through the vessels.
SCT results
The resulting SCT images must be examined by a radiologist (a doctor who specializes in CT, MRI, X-ray studies and has the appropriate certificate). It is necessary to “read” all the scans, study the provided medical information. documentation, compare it with the obtained CT image, describe the study, draw a diagnostic conclusion, shoot film with scans. On average it takes about 1-3 hours. At ACMD, we undertake to prepare the results for delivery by the end of the Clinic’s working day.
After the examination, you receive films with scans and a diagnostic report, which will be signed by a radiologist. Also, the diagnostic report may contain recommendations regarding your further actions (which doctor to contact with these results, what types of further examination are recommended, and so on).
Renal tomography
This method of kidney examination is used:
During the procedure, a contrast agent is used to improve the clarity of the image. The day before the examination, the patient is prepared according to the generally accepted scheme.
Tomography of other organs
SCT of the eyes, facial fragments and sinuses is widely practiced. The device detects disturbances in the structure of these organs and foreign bodies that have penetrated them.
SCT of the spine shows cracks, fractures of the spine, infected areas in the spinal canal, abscesses, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias, arthritis, osteoporosis, neoplasms and metastases in the spine and other organs, congenital anomalies of the skeletal system.
For limb injuries and joint damage, tomography is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
SCT of the chest reveals diseases of the heart, lungs, coronary arteries, esophagus, larynx, and large blood vessels. With its help, tuberculosis, aortic aneurysm, and tumors are detected. It is not recommended to eat food 4 hours before the procedure. This is what a picture of the heart obtained during the examination looks like.
For more information about how and for what purpose the study of human internal organs is carried out using a multispiral tomograph, see the video.
Multislice computed tomography (MSCT)
Many people have to undergo tomography during their lives. Which one is better - regular, spiral, magnetic resonance, share your opinion on this topic in the comments, let's discuss this issue together.
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Is MSCT harmful to a child and is MSCT dangerous during pregnancy?
Contraindications for CT:
- pregnancy at any stage of gestation;
- not recommended for children under 14 years of age;
- not recommended for existing multiple myeloma and recent ionization examinations;
- excessive weight of the patient;
- inability to take a supine position.
Contraindications for contrast enhancement:
- uncompensated thyrotoxicosis;
- history of severe reactions to an iodine-containing drug;
- renal failure with a significant decrease in clearance;
- with caution in severe bronchial asthma.
Contraindications for cardiac CT:
- an irregular rhythm that cannot be made regular with medication (for example, a permanent form of atrial fibrillation);
- inability to hold your breath for 15 seconds.
Children are especially susceptible to radiation exposure (and with MSCT, the radiation dose can reach up to 12 mSv versus 0.5 mSv with conventional radiography), they have a greater risk of developing cancer. This happens because the tissues of a child’s (and even more so the unborn) body are in a phase of continuous growth, and, therefore, are more susceptible to DNA changes.
Also, the chance of developing a tumor after MSCT is much higher in a child than in an adult, because there is actually more time for a tumor to develop in children than in adults and the elderly. To reduce the risk of consequences, it is highly not recommended to perform MSCT on children until the process of active tissue growth has completed (up to 14 years).
When choosing a center where to undergo MSCT in Moscow and St. Petersburg, focus on the one that uses at least a 16-slice, and preferably a 32 or 64-slice device. When planning MSCT or SCT with bolus contrast, ensure that an anesthesiologist is available at the selected center to possibly assist in the event of a contrast reaction.
The examination is not carried out for pregnant women due to the teratogenic effects of radiation. Despite the lower radiation dose of SCT compared to conventional tomography, it is still higher than with a single x-ray.
Other contraindications are associated with possible complications from the administration of contrast:
- allergy to contrast agent or iodine;
- general severity of the condition;
- severe renal failure;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- multiple myeloma;
- decompensation of diabetes mellitus.
An obstacle to the examination may be the patient’s heavy weight, since the equipment used for examination has some restrictions on body weight.
The SCT examination is absolutely painless; the scanner itself does not directly touch your body.
The method is based on X-ray radiation. Naturally, during an SCT study, the patient is exposed to x-rays, therefore, when prescribing this study, the doctor must have fairly compelling reasons and take into account the negative impact of x-rays on the body.
An absolute contraindication for SCT is pregnancy and breastfeeding. Also, SCT is strongly not recommended for children without significant reasons. In other cases, you should consult your doctor.
You can do a computed tomography (CT) scan in Kyiv at the ACMD clinic, a 64-slice tomograph (the radiation level is reduced significantly!)
Contraindications
The examination is not carried out for pregnant women due to the teratogenic effects of radiation. Despite the lower radiation dose of SCT compared to conventional tomography, it is still higher than with a single x-ray.
Other contraindications are associated with possible complications from the administration of contrast:
An obstacle to the examination may be the patient’s heavy weight, since the equipment used for examination has some restrictions on body weight.