Many people suffer from VSD of a mixed type. It includes manifestations of several types of this disease. It is characterized by sudden changes in blood pressure, both downward and upward. Medicine cannot accurately determine the cause of this disease. When all organs function normally, but unpleasant symptoms are present, we can talk about disorders of the nervous system that connects them. VSD with cephalgia (headache) is quite common.
Causes
VSD of mixed type - let's look at what it is. This type of disease is a combination of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive, hypotonic and cardiac type. The first is characterized by high blood pressure, temperature, headache, the second by low blood pressure, weakness, bradycardia, and the third by pain in the heart area. With a mixed type, the listed symptoms may be observed simultaneously, or sequentially replacing each other.
It is still unknown exactly why VSD appears. According to experts, the risk of pathology remains high for the following reasons:
- genetic predisposition,
- emotional instability,
- frequent stressful conditions,
- wrong lifestyle.
Important: Maternal anxiety during pregnancy leads to children subsequently suffering from VSD.
Usually the pathology manifests itself in adolescence. There may be several reasons:
- hormonal changes,
- frequent conflicts,
- mental instability,
- being too busy at school
- lack of physical activity.
VSD of mixed type also manifests itself in adults. The risk group includes people with an unstable nervous system. The disease makes itself felt at this age for the following reasons:
- frequent stressful situations,
- unstable work schedule, excessive workload,
- constant lack of sleep.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is most often diagnosed in people whose work involves mental stress. They usually lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Women are also more likely to suffer from the disease. The reasons for this are as follows:
- Birth of a child. Often this event brings with it postpartum stress, chronic lack of sleep and constant fatigue.
- Average age. Hormonal changes in connection with menopause and a tendency to depression.
Causes of VSD of mixed type
The exact cause of the disease cannot be identified. The causes of this disease can be very diverse. Sometimes the cause can be any other disease (from pathologies of the cardiovascular system to ARVI). But most often, vegetative-vascular dystonia of the mixed type appears due to the following factors:
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
120
on
80
- heredity;
- stress, severe shock, emotional overstrain, impressionability;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hormonal imbalances;
- unfavorable environment;
- poor working conditions.
Diagnosis of VSD
First you need to undergo a full examination. This must be done to rule out other diseases. Afterwards, a consultation with a psychotherapist will be required to determine the cause of the pathology. This is important for the effectiveness of further treatment. To accurately establish a diagnosis, consultation with many doctors is required, such as:
- endocrinologist,
- neurologist,
- ophthalmologist,
- cardiologist,
- gynecologist,
- psychotherapist,
- gastroenterologist
Basic diagnostic methods:
- blood tests,
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, heart and blood vessels,
- radiography,
- monitoring blood pressure indicators,
- electrocardiography,
- rheovasography,
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Doctors should rule out the following conditions:
- somatic diseases – iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, hypertension,
- mental pathologies – depression, increased anxiety.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of mixed type: main symptoms and treatment methods
Vegetovascular (or neurocirculatory) dystonia is a chronic functional disease that includes a complex of syndromes associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). This section of the central nervous system controls the functioning of most internal organs.
In this case, many different symptoms arise from the cardiovascular, digestive, respiratory and other systems. VSD is difficult to diagnose and treat, as it often imitates the picture of organic diseases.
There are two main forms of VSD. The first is described as hypertensive type dysfunction, and it is characterized by excessive activity of the sympathetic division of the ANS.
As a result, one of its most striking signs will be high blood pressure (BP).
The second is called hypotonic, and in this case the tone of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system predominates, which corresponds to low blood pressure.
However, a mixed form is often encountered, in which the activity of both departments is disrupted, without the predominance of each of them. This option is characterized by a combination of symptoms of the two above varieties.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There is still no clear agreement among doctors about the causes of mixed type VSD. Usually they talk about risk factors that lead to autonomic dysfunction:
- genetic predisposition;
- gender (more often develops in women);
- significant physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- other neurological pathologies;
- bad ecology
- endocrine disorders;
- poor nutrition
- bad habits.
Neurocirculatory dystonia often occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance: periods of adolescence, pregnancy, menopause.
As a result of the action of provoking factors, a disruption of the relationship between the brain and subcortical autonomic centers (primarily the hypothalamus) occurs, but the exact mechanism of development of this pathology is unknown.
Clinical picture of mixed type VSD
The symptoms of this disease are very vague and vary greatly among patients. Dystonia often resembles other pathologies, which makes it much more difficult to make a correct diagnosis. There are several main syndromes:
- Cardiovascular – characterized by disorders of the cardiovascular system, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the heart area of various types (stabbing, dull, etc.);
- changes in pressure - both increases and decreases are typical, meteosensitivity very often occurs (i.e., fluctuations in blood pressure associated with the weather);
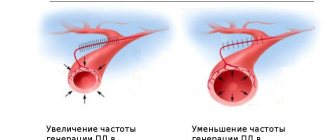
- Sometimes arrhythmias occur - acceleration or deceleration of the pulse, additional contractions (extrasystoles), which is manifested by a feeling of irregular heartbeat.
- Cerebrovascular – occurs as a result of cerebrovascular accident, manifested by the following symptoms:
- cephalalgia (headache)
- decreased productivity;
- dizziness, fainting;
- noise in ears.
- Dyspeptic syndrome – associated with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract:
- pain in the abdominal area of various types, usually not associated with eating;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- flatulence;
- nausea, vomiting, hiccups.
- Bronchopulmonary syndrome usually resembles an asthma attack:
- feeling of difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- feeling of tightness in the chest;
- cough.
- General symptoms:
- constantly elevated (low-grade) or low temperature;
- sometimes there may be hot flashes or, on the contrary, chills;
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- weakness, drowsiness.
- Finally, mental disorders may occur:
- anxiety, fear, panic attacks;
- irritability, tearfulness;
- hypochondria;
- depression
All these symptoms can appear in a patient in various combinations and with varying degrees of severity.
A feature of the course of VSD is vegetative crises, which in the mixed type are both sympathoadrenal and vagotonic.
Hypertensive (sympathoadrenal) crisis Hypotonic (vagotonic) crisis
| Severe cephalgic syndrome | Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing | |
| Paresthesia (crawling sensation) | Dizziness, fainting | |
| High blood pressure (>140 mmHg) | Low pressure (100 beats/min.) | Bradycardia ( |
Source: https://cardiograf.com/bolezni/distoniya/vsd-po-smeshannomu-tipu.html
Prevention
Prevention of VSD consists of the following rules:
- More movement. When working sedentarily, you need to get up every hour and walk around for ten minutes. In the morning, you can jog or exercise. Visit a sports section, swimming pool or gym several days a week.
- It is necessary to be in the fresh air. On weekends, travel outside the city; on weekdays, go for walks in the morning and evening.
- It's important to toughen up. A contrast shower will help strengthen blood vessels.
- Avoid stress. To do this, you can find a calming activity to your liking - playing the guitar or piano, cross-stitching, yoga or meditation.
- Don't work at night. Also, the working day should not exceed eight hours.
- Avoid becoming overweight.
- If your blood pressure drops frequently, you can eat sweets in moderation.
- It is important to get rid of bad habits.
In order for symptoms of the disease to bother you less often, it is important to constantly follow these rules. Vegetative-vascular dystonia requires treatment, otherwise there may be unpleasant consequences.
Vegetative vascular dystonia of mixed type: what is it, symptoms
Vegetative vascular dystonia is usually called a whole group of clinical manifestations indicating the development of functional pathologies of the autonomic nervous system. In medicine, hypotonic and hypertensive forms of the disorder are known, and vegetative vascular dystonia of a mixed type is also often found.
Vegetative vascular dystonia of mixed type: what is it?
The autonomic subsection of the nervous system in the human body functions independently, controlling the work and interaction of all vital systems of the body: cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine. The subsection consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, the disruption of the coordinated work of which causes neurocircular dystonia.
In cases where violations of one of the subsections are clearly manifested, one can easily determine the hypotonic or hypertonic form of vegetative-vascular dystonia. If it is impossible to identify the predominant symptoms or they appear alternately, mixed type vegetative vascular dystonia is diagnosed.
Interesting! Most European specialists do not consider VSD of a mixed type to be a disease, designating functional failures as a transit condition that does not require special treatment. For this reason, the disorder is not listed in the International Classification of Diseases.
In domestic medicine, such a diagnosis is taken more seriously. However, the inability to confirm it using laboratory tests leads to the fact that patients themselves deny the presence of the disease and do not consider it necessary to treat it.
Causes
A larger percentage of mixed-type VSD occurs in women and can occur at any age. The development of the disorder from onset to the onset of symptoms takes about seven years.
Provocateurs of mixed-type vegetative-vascular dystonia include factors such as:
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of birth injuries, disorders of intrauterine development of the body, including maternal stress during pregnancy;
- difficult living conditions, frequent stress, emotional tension;
- increased nervous excitability;
- hormonal disruptions (puberty, menopause);
- chronic pathologies in the spine;
- brain failure;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- decreased immunity;
- presence of allergies;
- presence of bad habits.
Also at risk are women who give birth in the first years of a baby’s life - due to constant fatigue, lack of sleep, nervous tension and increased anxiety of the mother.
Often VSD of a mixed type is preceded by various types of neuralgia, disorders in the endocrine system, and gynecological diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment of mixed type VSD
Due to the fact that various diseases can provoke the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia of a mixed type, examination of a patient with similar symptoms includes the involvement of doctors of narrow specializations - a neurologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist, etc. Also, if necessary, studies such as:
- encephalogram;
- CT scan;
- vascular dopplerography, etc.
If a disease causing a vegetative disorder is found, mandatory therapy is prescribed. In addition to taking medications, therapy for mixed type VSD requires the creation of favorable conditions for rehabilitation and normal functioning of all systems in the patient’s body.
Depending on the prevailing clinical manifestations, the patient may be prescribed the following drugs:
- sedatives (tranquilizers, antidepressants);
- in case of high blood pressure, drugs that lower it, and vice versa;
- means to improve brain activity (nootropics);
- for constant heaviness and pain in the head, indicating venous insufficiency, use venotonics;
Non-drug treatment options for neurocircular dystonia of mixed type include:
- optimizing the work-rest ratio, eliminating the causes of overload;
- giving up bad habits, as well as unhealthy and heavy foods;
- regular exercise;
- elimination of stress factors, psychological consultations in order to increase stress resistance (we recommend psychologist Nikita Baturin);
- physiotherapy;
- massage, acupuncture, manual therapy.
Due to the direct relationship between the occurrence of the disorder and the psychological health of the patient, an active lifestyle and the formation of healthy habits that improve the overall physical and emotional background of a person are an excellent means of not only therapy, but also prevention of mixed type VSD.
Consequences of the disease
With timely detection and treatment of dysfunction of the autonomic system, complications usually do not arise. However, with prolonged presence, functional disorders can transform into organic ones, provoking arterial hypertension, stomach ulcers, heart disease, and neuralgia.
Interesting to know! Vegetative vascular dystonia is not included in the list of reasons for declaring a conscript unfit for military duty. If the clinical picture includes constant heart pain, fainting, blood pressure surges, as well as poor progress in treatment, a note is placed on the conscript’s military ID about his temporary unsuitability for military service.
Source: https://ProPanika.ru/raznoe/vegeto-sosudistaya-distoniya-po-smeshannomu-tipu/
Diagnostics
Diagnosis can take a lot of time and effort. A patient with numerous complaints is referred for a full examination of the body to exclude the presence of somatic diseases. To identify any pathologies, a wide range of studies may be required - from blood and urine tests to computed tomography.
If no disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems are detected, the patient is recommended to visit a psychoneurologist, who prescribes subsequent treatment.
Under no circumstances should you ignore visiting a neuropsychiatrist. If the examination does not reveal any disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs, only this doctor will be able to determine the reasons that led to this condition.
After all, the main cause of mixed type VSD is:
- Emotional turmoil.
- Neuroses.
- Anxiety disorders.
Therapy must be comprehensive and can last up to six months. Taking medications is combined with physical therapy, proper nutrition and giving up bad habits. All drugs for mixed type VSD are strictly prescribed by a doctor, because this disease does not have an organic basis, and all organs and systems are healthy.
Treatment and symptoms of mixed type dystonia
VSD is a symptomatic manifestation of disturbances in the balance of the autonomic nervous system, accompanied by unpleasant sensations and problems with certain organs. Mixed type dystonia is the most common type of disease. It is not difficult to cure it, but not all people know exactly how it manifests itself.
Peculiarities
In the ICD, the mixed type of VSD is not classified as a separate category. Doctors use a code for diagnosis that corresponds to the cause of problems with the nervous system. Most often the disease is classified as R45.8.
VSD is sometimes called SVD (vegetative dystonia syndrome), RVNS (nervous system disorder) and NCD (neurocirculatory dystonia). It concerns the autonomic part of the nervous system, called the autonomic one, which is divided into sections: sympathetic and parasympathetic.
Both of them can be affected by a number of pathologies, which will cause unpleasant symptoms indicating the development of VSD.
This is due to the failure of the main functions, the task of which is to ensure breathing, blood circulation and digestion, as well as the work of all receptors responsible for the cardiovascular system.
VSD is divided into types:
- Cardiac;
- Cerebral;
- Vascular;
- Vagotonic;
- Hypertensive;
- Hypotonic;
- Mixed.
VSD of mixed type has two varieties in form: primary and secondary. There are also three phases of the course of the disease: intense adaptation, relative compensation and decompensation. Additionally, the nature of its course is distinguished: latent, permanent, paroxysmal.
In most cases, VSD has a primary form, i.e. occurs without the presence of other diseases that could cause its occurrence.
Causes
The exact genesis of the disease has not yet been determined. The average age of manifestation of mixed type SVD is 30 years. Most often, women encounter it, which is why they should pay special attention to their health. However, young children and adolescents are also at risk because... their fragile nervous system is especially susceptible to the environment.
The main causes of VSD:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, puberty);
- Excessive mental and psycho-emotional stress;
- Poor sleep quality;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Traumatic brain or birth injuries;
- Diseases of the central nervous system, its instability;
- Bad habits;
- Endocrine pathologies;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Unfavorable living conditions.
The more points there are in a person’s life, the higher the risk of encountering an unpleasant illness, the origin of which will be even more difficult to determine.
Symptoms
With VSD of a mixed type, the patient may experience a lot of unpleasant symptoms. Often they can be mistaken for the development of another disease, which prompts constant visits to the doctor who will look for a non-existent disease.
Main features:
- Pressure failures;
- Cephalgia and dizziness;
- Heartbeat instability;
- Heart pain;
- Neurotic disorders (nerve problems, anxiety, fear);
- Feeling of lack of air;
- Redness of the skin;
- The appearance of spots before the eyes;
- Intestinal disorders;
- Unreasonable changes in body temperature;
- Increased sweating;
- Asthenic syndrome (apathy, high fatigue, weakness, poor sleep);
- Erectile dysfunction, anorgasmia;
- Decreased tone of veins, arteries, arterioles, capillaries;
- Angiocerebral dystonia of cerebral vessels (tinnitus, memory impairment, depression);
- Angiodystonic syndrome (pale fingers, cold skin, weakness).
With RVNS of the mixed type, a complication may occur in the form of a vagoinsular crisis, due to which the state of health suddenly worsens. This is accompanied by problems with speech, hand tremors, decreased hearing and vision, nausea, slow heart rate, severe weakness and shortness of breath.
With persistent symptoms caused by VSD, men may not be accepted into the army. This applies only to serious symptomatic disorders for which the effectiveness of treatment is too low or completely absent.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to identify VSD of the mixed type. Before making a final diagnosis, the doctor must send the patient for various examinations to rule out the possibility of a serious disease causing such symptoms.
Diagnosis begins with a conversation with a neurologist. He will create a medical history chart detailing the symptoms that occur, asking the patient about his feelings. After this, he will schedule an examination, which will help ensure that there are no other diseases. If necessary, the neurologist can give a referral to another specialist if necessary.
Examinations include:
- Blood and urine tests;
- Chest X-ray;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- ECG;
- ECG with physical activity;
- Daily blood pressure measurement;
- Holter heart rate monitoring;
- Hormone tests.
If you suspect VSD in children, you should visit a children's clinic. Pediatrics does not deal with this disease, which is why you should immediately contact a pediatric neurologist or cardiologist.
The child must undergo the prescribed examination in order to be prescribed treatment.
A child's body, unlike an adult's, can suffer from complications in the form of hypertension, asthma or ulcers if left untreated.
Principles of treatment
In most cases, it is possible to achieve a positive result in the fight against VSD even without drug treatment. However, this is not a reason to refuse to visit a doctor. After a mixed type VSD diagnosis is made, the patient will be prescribed therapy, which will include an important list of recommendations to help speed up recovery.
The fastest way to get rid of VSD without taking medications is for those whose disease is mild. To do this, just follow the classic recommendations:
- Elimination of all sources of stress;
- Normalization of the daily routine, quality sleep;
- Proper nutrition taking into account dietary requirements;
- Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Limiting the amount of mental stress;
- Increasing the level of physical activity, playing sports.
In more severe cases, it will be necessary to expand the treatment regimen with physiotherapeutic procedures and medications. However, the recommendations listed above are always the main treatment, because Without their implementation, it will not be possible to achieve a positive result even with enhanced therapy using other means.
With irreversible damage to organs caused by VSD, patients may receive disability of the second or third group.
Drug treatment
With pronounced VSD of a mixed type, the patient may be prescribed special medications. Most of them come in tablets, but some drugs require injection into the body. Drug treatment involves taking medications for the following purposes:
- Reducing nervous tension, getting rid of anxiety. They prescribe Novo-Passit, Gerbion, Corvalol, Valocordin.
- Normalization of the nervous system, strengthening sleep, improving mood. A doctor can prescribe drugs from several groups at once, each of which has a different effect. “Sonopax”, “Seduxen”, “Sonnat”, “Azafen” are the most popular products.
- Normalization of heart rate. “Panangin” and “Asparkam” have the maximum effect.
- Improving blood circulation in the brain and vascular tone. Vinpocetine and Detralex are best suited.
- Relieving symptoms of dizziness, getting rid of hearing problems. As a rule, Betaserc is prescribed.
Some medications can be combined, i.e. have a double effect on different systems of the body.
All medications prescribed for the treatment of mixed-type VSD must be taken in strict accordance with the doctor’s instructions. If any medication has not been prescribed, you cannot purchase or take it. Such actions can cause irreparable harm to your health.
Non-drug treatment
Almost always, patients for the treatment of VSD are prescribed special procedures that help quickly and effectively get rid of all symptoms and disorders. They are applicable for both mild and severe dystonia. It is allowed to use them in practice without a doctor’s prescription, but it is important to know all the contraindications so as not to harm your body.
The following procedures are popular:
- Massage therapy. Doctors advise visiting a specialist, but if you wish, you can do the massage yourself. Before doing this, you should familiarize yourself with various techniques to achieve maximum effect. Massage can be done on all parts of the body.
- Breathing exercises. Exercises aimed at saturating the body with oxygen and calming the nervous system help achieve results after just a couple of procedures. They are also good for the heart.
- Water procedures. Taking a warm bath has a relaxing effect, and a contrast shower tones muscle tissue and calms the nervous system.
- Aromatherapy. Special aromatherapy procedures improve mood and have a restorative effect on the human nervous system.
Such methods can be used for prevention, so that the nervous system and the entire body are in good shape and receive the necessary amount of rest.
Diet
The most important factor in the effectiveness of mixed type VSD treatment is the patient’s nutrition. You need to train yourself to eat on a strict schedule so that you eat at the same time every day. You should also set serving size limits. But what exactly the patient eats is much more important.
Diet correction is a prerequisite for recovery in mixed type autonomic dysfunction syndrome. You should give preference to fresh and light foods, eliminating everything harmful from food. This diet will also be useful for healthy people, but it is not recommended to abuse it.
The diet should include:
- Fresh fruits;
- Nuts;
- Beans;
- Buckwheat;
- Oatmeal;
- Honey.
It can be supplemented at your discretion, but subject to restrictions. It is prohibited to use:
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Energetic drinks;
- Spicy dishes;
- Pickles;
- Fast food products.
Coffee should be excluded from the diet for the period of treatment only when taking medications that are incompatible with caffeine. In other cases, it is allowed to drink, but the amount should be limited to one cup per day.
Traditional methods
People who want to achieve results without taking medications have the opportunity to be treated using traditional methods. To do this, you will need to prepare special herbal remedies according to the recipes presented. It should be borne in mind that they are not a guarantee of getting rid of VSD, even with regular use.
Effective recipes:
- Mix the juice of carrots, beets, radishes and lemon (200 ml each), add honey (200 ml), squeeze garlic (3-4 heads) into the mixture, pour in red wine (200 ml) and mix thoroughly. Take the drink half an hour before meals in the morning, afternoon and evening. The course of admission is 1 month.
- Prepare mint and elecampane root (10 g), add a mixture of horsetail, meadowsweet herb and nettle (20 g), sprinkle dandelion roots with birch buds (40 g), then add rose hips (60 g). All this needs to be cut into small pieces, mixed and stored in a suitable container. To prepare, you need to pour hot water (1 liter) into part of the mixture (2 tablespoons), let it brew, and then take 50 ml three times a day. The course of admission is 3 months.
Mixed type vegetative-vascular dystonia can be treated only with regular use of these medications. With each omission, the effectiveness of the impact on the disease will decrease.