Medical statistics say that at least once during their lifetime, every third inhabitant of the planet “fainted.” Most of these attacks are spontaneous and one-time in nature, sometimes they can be a symptom of a specific disease. Fainting can bother a person in childhood or in old age; in women, as a rule, they occur while bearing a child. In what situations does this attack of loss of consciousness pose no danger to human health, and when should it not be ignored?
What is fainting?
In simple terms, fainting is a sudden loss of consciousness. The causes of this condition are unexpected disorders of brain metabolism. A decrease in metabolic rate occurs due to a decrease in cerebral blood flow. This pathological condition most often overtakes a person unexpectedly, but in rare cases, there are some kind of precursors: the person becomes weak, feels clouded in consciousness, and “spots” may flash before the eyes. As soon as the reduced muscle tone reaches very low levels, after which the person falls sharply, this condition can be characterized as “legs giving way.”
Symptoms of fainting:
• Increased sweating in humans
• His heart is beating fast
• Nausea may occur both before and after an attack.
• Severe dizziness, loss of orientation in space
• The skin becomes pale, marbled
• Vision deteriorates, causing objects to blur before the eyes
• After consciousness returns, a broken and depressed state may appear, the patient would rather lie down.
Causes of fainting
What causes a person to lose consciousness? First of all, with severe restriction of cerebral circulation, that is, fainting is a consequence of a decrease in blood flow to the brain. The reasons for this decrease may be various:
• Decreased or sharply increased vascular tone. This occurs when the body rises very sharply from a horizontal to a vertical position, the arteries of the legs are unable to quickly react and become toned, the blood stagnates in the lower extremities, and the brain is “starving” at this time. This phenomenon can be caused by the use of certain groups of drugs, in case of weakening of the body after protracted illnesses. Rarely, this condition can appear in a completely healthy person.
Fainting: 8 signs of a serious problem
Fainting is caused by a temporary loss of blood supply to the brain and may be a sign of a more serious condition...
Temporary loss of consciousness - fainting
Fainting is a temporary loss of consciousness.
Fainting is caused by a temporary loss of blood supply to the brain and may be a sign of a more serious condition.
People of any age can faint, but older people may have more serious causes.
The most common causes of fainting are vasovagal (a sharp decrease in heart rate and blood pressure) and heart disease.
In most cases, the cause of fainting is unknown.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
Fainting can have many different causes:
Vasovagal syncope is also known as "general weakness." This is the most common cause of syncope and is caused by an abnormal vascular reflex.
The heart pumps more intensely, the blood vessels relax, but the heart rate does not compensate quickly enough to maintain blood flow to the brain.
Causes of vasovagal syncope:
1) environmental factors (happens more often when it’s hot);
2) emotional factors (stress);
3) physical factors (loads);
4) illness (fatigue, dehydration, etc.).
Situational syncope only occurs in certain situations.
Causes of situational fainting:
1) cough (some people faint when coughing too hard);
2) when swallowing (in some people, loss of consciousness is associated with illness in the throat or esophagus);
3) when urinating (when a susceptible person loses consciousness with a full bladder);
4) hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus (in some people when turning the neck, shaving or wearing a tight collar);
5) Postprandial syncope can occur in older people when their blood pressure drops about an hour after eating.
Orthostatic syncope occurs when a person feels fine while lying down, but may suddenly faint when standing up. Blood flow to the brain decreases when a person stands due to a temporary decrease in blood pressure.
This fainting sometimes occurs in people who have recently started taking (or have been changed to) certain heart medications.
Orthostatic syncope can be due to the following reasons:
1) low circulating blood volume caused by blood loss (external or internal blood loss), dehydration or heat exhaustion;
2) impaired circulatory reflexes caused by medications, diseases of the nervous system, or congenital problems. Cardiac syncope occurs when a person loses consciousness due to cardiovascular disease.
Cardiac causes of fainting are usually life-threatening and include the following:
1) abnormal heart rhythm - arrhythmia. Electrical problems in the heart impair its pumping function. This leads to decreased blood flow. Your heart rate may be too fast or too slow. This condition usually causes fainting without any warning.
2) cardiac obstructions. Blood flow may be obstructed in the blood vessels in the chest. Cardiac obstruction can cause loss of consciousness during exercise. Various diseases can lead to obstruction (heart attacks, diseased heart valves due to pulmonary embolism, cardiomyopathy, pulmonary hypertension, cardiac and aortic tamponade).
3) heart failure: the pumping ability of the heart is impaired. This reduces the force with which blood circulates through the body, which can reduce blood flow to the brain.
Neurological syncope may be associated with neurological conditions.
Its reasons are:
1) a stroke (bleeding in the brain) can cause fainting associated with headache;
2) a transient ischemic attack (or mini-stroke) can cause loss of consciousness. In this case, fainting is usually preceded by double vision, loss of balance, slurred speech, or dizziness;
3) in rare cases, migraine can cause fainting. Psychogenic fainting. Hyperventilation due to anxiety can lead to fainting. The diagnosis of psychogenic syncope should be considered only after all other causes have been excluded.
Symptoms of fainting
Losing consciousness is an obvious sign of fainting.
Vasovagal syncope. Before fainting, a person may feel light-headed; blurred vision will be noted. A person may see “spots before the eyes.”
The patient experiences pallor, dilated pupils, and sweating.
While unconscious, a person may have a low heart rate (less than 60 beats per minute).
The person must quickly regain consciousness. Many people do not have any warning signs before fainting.
Situational fainting. Consciousness returns very quickly when the situation passes.
Orthostatic syncope. Before an episode of fainting, a person may notice blood loss (black stools, heavy periods) or fluid loss (vomiting, diarrhea, fever). The person may also experience delusions. Observers may also note paleness, sweating, or signs of dehydration (dry lips and tongue).
Cardiac syncope. The person may report palpitations, chest pain, or shortness of breath. Observers may note the patient's weakness, irregular pulse, pallor, or sweating. Fainting often occurs without warning or after exertion.
Neurological syncope. The person may have a headache, loss of balance, slurred speech, double vision, or dizziness (the feeling that the room is spinning). Observers note a strong pulse during the unconscious period and normal skin color.
When to seek medical help?
Because fainting can be caused by a serious condition, all episodes of loss of consciousness should be taken seriously .
Anyone, even after the first episode of loss of consciousness, should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Depending on what the physical examination reveals, your doctor may require tests.
These tests may include: blood tests; ECG, 24-hour monitoring, echocardiography, functional stress test. Table tilt test. This test checks how your body reacts to changes in position. Tests to detect nervous system problems (head CT scan, brain MRI or EEG).
If the person next to you faints, help him.
- Place it on the ground to minimize the chance of injury.
- Encourage the person actively and call an ambulance immediately if the person is unresponsive.
- Check your pulse and begin CPR if necessary.
- If the person is recovering, let him lie down until the ambulance arrives.
- Even if the cause of fainting is not dangerous, have the person lie down for 15-20 minutes before getting up.
- Ask him about any symptoms such as headache, back pain, chest pain, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, weakness or loss of function, because these may indicate life-threatening causes of fainting.
Treatment of fainting
Treatment for fainting depends on the diagnosis.
Vasovagal syncope. Drink plenty of water, increase your salt intake (under medical supervision), and avoid standing for long periods of time.
Orthostatic syncope. Change your lifestyle: Sit down and flex your calf muscles for a few minutes before getting out of bed. Stay hydrated.
Older adults with low blood pressure after meals should avoid large meals or plan to lie down for several hours after eating. In most cases, you should stop taking the medications that cause fainting (or change them).
Cardiac fainting. To treat cardiac syncope, the underlying condition must be treated.
Valvular heart disease often requires surgery, while arrhythmia can be treated with medications.
Medications and lifestyle changes.
These procedures are designed to optimize heart performance and control high blood pressure; in some cases, antiarrhythmic drugs may be prescribed.
Surgery: Bypass surgery or angioplasty is used to treat coronary artery disease; in some cases the valves may need to be replaced.
A pacemaker may be implanted to normalize the heart rate (slows the heart for fast arrhythmias or speeds up the heart for slow arrhythmias).
Implanted defibrillators are used to manage life-threatening rapid arrhythmias.
Preventing fainting
Preventive measures depend on the cause and severity of the fainting problem.
Fainting can sometimes be prevented by taking simple precautions.
- If you are weak due to the heat, cool down your body.
- If you faint while standing (after lying down), move slowly while standing. Slowly move to a sitting position and rest for a few minutes. When you are ready, stand up using slow and fluid movements.
In other cases, the causes of fainting may be subtle. Therefore, consult a doctor to determine the causes of fainting.
Once the cause is determined, treatment for the underlying disease should begin.
Cardiac syncope: Because of the high risk of death from cardiac syncope, people who experience it should be treated for their underlying illness.
Periodic fainting. Consult a doctor to determine the reasons for frequent loss of consciousness.
Prognosis due to fainting
The prognosis for a person who has fainted depends largely on the cause, the patient's age, and available treatments.
- Cardiac syncope has the greatest risk of sudden death, especially in older people.
- Fainting, which is not associated with cardiac or neurological disease, represents a more limited risk than in the general population.
Checking the pulse in the neck area. The pulse can be clearly felt only near the throat (trachea).
If the pulse is felt, notice whether it is regular and count the number of beats in 15 seconds.
To determine your heart rate (beats per minute), multiply this number by 4.
The normal heart rate for adults is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
If fainting happened just once, then you don’t have to worry about it.
It is important to see a doctor because fainting can have serious causes.
Diagnosis of fainting conditions
Fainting usually occurs very suddenly and is difficult to prevent, but can still be diagnosed in the following ways:
• First of all, the doctor must interview the patient, listen to his complaints and clarify how often and why fainting occurs
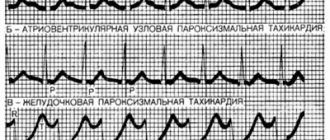
• An examination by a neurologist should be carried out, and it is difficult to detect symptoms in the intervals between fainting spells. The study during an attack is significant, it allows you to determine why the attack occurred, how much consciousness is depressed, the role of skin moisture, blood pressure and heart rate plays a role.
• A clinical blood test is also required, the levels of glucose, hemoglobin and red blood cells are assessed
• If fainting occurs frequently, but the cause has not yet been determined, then an electrocardiogram of the heart is prescribed
• Dopplerography of cervical vessels is sometimes used
• In rare cases, consultation with a cardiologist is indicated.
If you have a headache after fainting
Good afternoon, 2 weeks ago I drank coffee and smoked a cigarette, after which I became suddenly ill and fainted. After which my head still hurts. Is this normal? Patient age: 24 years
Headache after fainting - medical consultation with a doctor on the topic
First, you need to see a therapist to measure your blood pressure; if your blood pressure is high, the doctor will prescribe you appropriate treatment.
Then you contact a neurologist to examine your neurological status and examination (MRI of the brain, ultrasound of cerebral vessels, determination of fundus pressure, which also corresponds to intracranial pressure, and so on).
Based on examinations, the doctor will be able to determine the diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Please ask a clarifying question in the special form below if you think the answer is incomplete. We will answer your question as soon as possible.
- 1
Write a question to the doctor - 2 Click ask a question
- 3 Wait for a response by email
Get your consultation. To do this, simply ask your question in the box below and we will try to help you.
We need to know your opinion. Leave a review about our service
Sources used: puzkarapuz.ru
SEE ALSO: Copper wire for the treatment of headaches Headaches for men after 50 years Headaches go away only after coffee Headache in the temples after wisdom tooth removal
Headaches and fainting
12 reasons why you can suddenly collapse without feelings
1. You fainted due to pain while drawing blood from a vein or while sitting in the dentist's chair. Before this, you feel ringing in your ears, weakness, darkening and “floaters” in your eyes.
This is the most common type of fainting in healthy people. The reason is that during a stressful situation, the release of hormones and active substances into the blood increases. After fainting there is weakness, pallor, the skin is moist and warm. Ammonia or tart perfume will help you come to your senses.
2. Fainting in the same situation - in the morning or at night after you suddenly got out of bed. Fainting occurs without “preceding” symptoms, that is, suddenly (you immediately stand up and faint).
You have orthostatic hypotension (that is, a sharp decrease in blood pressure when standing up). Normally, when a person gets up, his blood pressure first decreases and then recovers. With orthostatic hypotension, the pressure recovery mechanism is triggered later. Therefore, such people need to get up slowly, gradually.
3. Fainting after a blow, head injury, with severe headache.
This is a very common symptom of concussions and vascular diseases of the brain. It also happens with migraine and epilepsy. You definitely need to check with a neurologist.
4. Fainting occurs during heart rhythm disturbances. The heart is pounding, jumping out of the chest, or, conversely, “on a thread.” Pale face, sweating, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing.
With some arrhythmias, the blood supply to all organs, including the brain, deteriorates. This leads to the development of fainting. You need to put nitroglycerin under your tongue. Then be sure to check with a cardiologist.
5. Fainting occurs on a sea cruise, in the mountains, or on a long bus ride. Before losing consciousness, you feel dizzy, there may be a loss of balance and a fall, always in the same direction.
This often indicates that you have a weak vestibular system. Such people feel sick and sick in transport. If, in addition to these symptoms, you have tinnitus or abdominal pain, consult an ENT doctor: you need to find a medicine for seasickness.
6. Fainting occurs exclusively in front of a “grateful” public, and occurs mainly in young women. People around them often note their certain mannerisms.
This is a typical hysterical fainting spell. It continues for quite a long time, and the patient, even after being put to bed, does not immediately come to her senses. (This is the difference between hysterical fainting and ordinary fainting.) The diagnosis of a hysterical attack is most often clear immediately, but it can be officially made only by excluding other causes of fainting. The best way to stop a hysterical faint is to pat your cheeks.
7. Fainting occurs mainly in men when turning their heads sharply, for example, while shaving, or playing sports, or when wearing shirts with a tight collar.
In the vessels of the neck there is an active zone - the carotid sinus, when irritated, the pressure sharply decreases by 40 mm Hg. Art. With a sharp turn of the head or a tight “noose” of the tie, the vessels of the neck are compressed and the carotid sinus is irritated. The result is a sharp drop in blood pressure and fainting. This condition is called carotid sinus syndrome. Conclusion: make appointments without a tie.
8. You have had rheumatism or a severe cold in the past. When listening, the doctor determines the heart murmur. Rhythm disturbances and pressure changes may be of concern.
You definitely need to do an ECHO-cardiography. You may have an acquired heart defect, which most often occurs against the background of rheumatism. With almost any heart defect, fainting occurs from time to time.
Source: //indosti.ru/esli-posle-obmoroka-bolit-golova/
Treatment
Since fainting is not a specific disease, but rather a symptom of a disease, it is almost impossible to choose a treatment program for it. But if such attacks do not happen just once, but haunt a person constantly, it is worth knowing the basic rules of behavior. If someone next to you has lost consciousness, then even before finding out the reasons for this phenomenon, it is necessary to provide first aid to the person. The algorithm of actions looks like this:
• If you notice that a person’s legs begin to give way, he loses his balance and risks falling to the ground, then you need to catch him. This is not so easy to do, because fainting, as a rule, comes suddenly, taking the patient and the people around him by surprise. If the person's weight is heavy and you feel that you cannot hold him or save him from falling, try to put your hands under your head to avoid a concussion
• Even if you catch a falling citizen, and he does not have time to hit, now it is necessary that his head is below the level of his legs, so you will stimulate the restoration of cerebral blood flow. When a pregnant woman faints, it is worth ensuring a safe position that eliminates pressure on the fetus. If a woman falls on her stomach, then you should call an ambulance as quickly as possible.
• At the first opportunity, provide access to air from the street, open the nearest window. It is also worth freeing the victim’s neck from tight clothing.
• Then you can wet his face with cool water, and, if possible, let him inhale the vapor of ammonia applied to cotton wool. A sharp unpleasant smell will awaken the sleeping consciousness
• In order to restore brain nutrition in a short period of time, you can give a person candy or a piece of sugar. If he still does not regain consciousness, it is worth administering a glucose solution intravenously.
If you have experienced fainting several times already, you should consult a doctor. Between attacks, you will be prescribed the following general restorative treatment regimen, which will enhance brain nutrition:
• It is worth taking medications from time to time that help the body adapt to sudden changes in the environment
• A course of vetonics is also recommended - medications that help normalize venous tone
• The patient is prescribed vitamins C, as well as A and B
• It is worth excluding extreme environmental conditions.
Headache, dizziness and loss of consciousness diagnosis
Attacks of dizziness with loss of consciousness are an alarming symptom that may indicate serious illness.
Dizziness, accompanied by short-term fainting (as well as nausea, vomiting, weakness, darkening of the eyes and other signs of deterioration in health) should not be ignored - it is imperative to find out the cause of these manifestations in the clinic.
Let's consider what reasons can cause sudden dizziness and temporary loss of consciousness, and how to provide primary care to patients who faint.
Causes
Sudden dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness and a feeling of weakness - all these signs sometimes appear in healthy people in situations associated with severe fatigue, hunger, overheating or poisoning.
In such cases, the symptoms go away on their own as soon as the external exposure factor is eliminated. Dizziness, episodes of vomiting, blackouts and fainting stop as soon as the physical condition stabilizes.
If sudden fainting, nausea, vomiting, a feeling of weakness and other symptoms are repeated many times over a long period, then it is not a matter of external influences: the cause must be sought in the body itself. Most likely there are systemic disorders, then it is necessary to undergo a full examination.
There are neurogenic cases of loss of consciousness, when painful symptoms are caused by lesions of the nervous system, and somatogenic cases - in such cases, attacks of vomiting and loss of consciousness are associated with cardiac disorders, endocrine pathologies, and hypoglycemia.
We list the main causes of dizziness with subsequent loss of consciousness:
- Neurogenic fainting caused by pathologies of the nervous system;
- Epilepsy;
- Intracerebral hemorrhages;
- Consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- Thrombosis and progressive atherosclerosis;
- Jumps in blood pressure (fainting can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure);
- Pathologies of metabolic processes: hypoglycemia (sharp drop in plasma glucose levels), uremia;
- Exogenous intoxication;
- Psychogenic seizures;
- Taking certain medications;
- Long-term alcoholism and drug use;
- Infectious diseases;
- Heart disease (ischemia, heart failure);
- Tumors of brain localization;
- Hydrocephalus (accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the brain);
- Anemia (anemia).
Fainting, vomiting, weakness, tinnitus and darkening of the eyes often appear in women during pregnancy and menopause. Often similar symptoms develop in older people as a result of natural age-related changes.
Associated symptoms
The most common form of sudden loss of consciousness is fainting. Against the background of dizziness, darkening of the eyes and weakness, the patient falls and loses consciousness for a short period of time (measured in seconds).
Prolonged fainting is recorded much less frequently. There are different types of fainting - vasomotor, hyperventilation, nocturic, hypoglycemic .
Almost all types of loss of consciousness are accompanied by a presyncope, which includes the following symptoms:
Useful information: Nausea, dry mouth and weakness are signs of illness in the body
Nocturic night fainting is associated with prostate diseases in men: loss of consciousness in this case occurs immediately after urination. Epileptic seizures can develop against the background of organic disorders, sometimes their occurrence is provoked by regular use of alcohol or drugs.
Most often, vasodepressor syncope (simple syncope) is diagnosed, caused by various stressful influences: anticipation or sensation of pain, the sight of blood, fear, stuffy room. Hyperventilation fainting is also common; such attacks are usually accompanied by feelings of nausea and visual symptoms (“floaters” and flashes of light). Vomiting often occurs after or before attacks.
Another specific cause of fainting is increased sensitivity of the carotenoid sinus. People with this diagnosis do not tolerate ties and narrow collars well: they may experience attacks of dizziness and fainting even with slight pressure on the neck area.
What to do if you lose consciousness
If you experience a feeling of dizziness, weakness, and a feeling of impending loss of consciousness, you should quickly sit down and lower your head as low as possible . In this case, the fall will not cause much harm.
If someone in your presence loses consciousness, you should lay the victim on his back, raising his legs up and turning his head to the side (to prevent vomit from entering the lungs in case of vomiting). If vomiting has already begun, support the patient's head in a safe position.
If attacks of dizziness and short-term loss of consciousness are repeated more than 2 times in a short period, you need to visit a neurologist or therapist and get a referral for diagnostics. Therapy will depend on the results of the examination: in any case, the primary cause of loss of consciousness is eliminated.
Helpful information
Source: https://novosibmemorial.ru/golovnaja-bol-golovokruzhenie-i-poterja-soznanija-diagnoz/
Prevention of fainting attacks
A person who often collapses from loss of consciousness should eat a dense and balanced diet. Fiber must be present in his diet; it is found in abundance in vegetables and fruits. The patient is advised not to eat spicy, fried or very salty foods. Such a person should eat often, but in small portions. You should not put too much strain on your body physically; heavy lifting and extreme sports are contraindicated. But at the same time, you should not lead a sedentary lifestyle; the optimal sport for them is swimming. It is also necessary to completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages, as well as smoking, and increase the time of daily walks to two hours.
Source:
Lekar.ru
I feel like I'm losing consciousness
Symptoms such as cloudiness, dizziness, heaviness, a feeling as if the head is in a fog, can accompany a person constantly or appear several times a week.
This condition does not always mean that a person has any disease. Often these signs arise due to the influence of certain factors: changes in weather conditions, excessive physical exertion, lack of sleep, mental work, etc.
The main feature of the brain fog symptom is its sudden appearance. So, a person who felt good a minute ago, almost in an instant feels discomfort, fogginess, dizziness, blurred vision, dullness of consciousness.
The problem is that these symptoms can appear in the workplace or while performing an important task. Due to this, a person is deprived of the opportunity to carry out usual activities.
Brain fog is often accompanied by various symptoms:
- increased or decreased blood pressure;
- drowsiness during the day and sleep disturbance at night;
- weakness;
- headache;
- strong heartbeat;
- excessive sweating, etc.
Often this picture is accompanied by a feeling of unreasonable fear, a feeling of lack of air, and the appearance of a ringing in the head. There are many reasons for this condition.
Causes of the symptom
As stated earlier, the causes of brain fog may not always be due to health problems. Thus, when there are disruptions in the hormonal system, fog in the head is almost always observed. During pregnancy, a woman is often accompanied by this condition, as well as irritability and forgetfulness. The same symptoms may occur during menopause.
If there is no clarity in your head, then most likely we are talking about astheno-neurotic syndrome. This pathology, in addition to brain fog, is accompanied by other symptoms:
- shallow sleep;
- problems falling asleep;
- irritability, suspiciousness, hot temper;
- unreasonable anxiety;
- rapid fatigue;
- drowsiness during the day;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- decreased ability to work;
- stiffness of movements;
- memory problems;
- pressing headaches;
- dizziness;
- tremor of the limbs.
The syndrome mainly affects people whose work involves mental activity and increased responsibility. In addition, pathology often affects those who have an unstable psyche.
The main causes of astheno-neurotic syndrome are prolonged stress, prolonged nervous tension, anxiety, chronic lack of sleep, and overwork. In addition, the pathology occurs in people with:
- chronic diseases;
- hypertension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- acute viral infections;
- poisoning;
- vitamin deficiency;
- bad habits;
- head injuries.
The syndrome develops gradually. At the initial stage of neurosis, a person feels weak in the morning, mild irritability, and anxiety.
Then, in the absence of medical assistance, other symptoms appear in the form of loss of strength, sleep disturbances, memory problems, a feeling of “vatness,” heaviness in the head, fog in the eyes, decreased ability to work, etc.
Then pain in the heart occurs, severe irritability gives way to weakness, appetite disappears, libido (sexual desire) and mood decrease, apathy appears, the patient constantly thinks about his health, and fear of death appears. Subsequent ignoring of these symptoms leads to mental disorders.
VSD is the most common cause of brain fog. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a separate disease, but a combination of many symptoms that arise against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the functioning of all internal organs and systems.
VSD is characterized by the following symptoms:
- fog, heaviness in the head;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- anxiety;
- unreasonable fears;
- nausea, stomach pain;
- tachycardia;
- lack of air;
- tremor of the limbs;
- unsteadiness when walking;
- sleep disorders - insomnia, shallow sleep;
- changes in blood pressure;
- irritability;
- “midges” before the eyes;
- ringing in the ears, etc.
The list of symptoms for VSD can be endless. The main feature of the disease is frequent relapses, manifested in the form of panic attacks.
If you do not take any action - do not take medications, do not strive for changes in lifestyle, do not seek help from doctors (psychotherapist, neurologist) - this can result in the appearance of various phobias and fears.
If the brain lacks oxygen, this leads to a feeling of brain fog. The process of hypoxia develops due to compression of the vessels through which the blood carries oxygen and all the substances necessary to nourish the organ.
At the same time, in addition to fogginess and “vatness” in the head, a person experiences:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- severe heaviness in the head;
- decreased ability to work;
- memory problems;
- confusion of consciousness;
- problems with perception of information;
- inhibition of reactions;
- severe weakness, fatigue.
With severe oxygen starvation, a person may lose consciousness.
The causes of this condition may be:
- the presence of cervical osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spine;
- use of drugs and alcoholic beverages;
- hypertension, hypotension;
- previous traumatic brain injuries;
- smoking;
- lack of fresh air;
- limited physical activity;
- runny nose.
If this pathology is not treated, then oxygen-starved brain cells gradually lose their functionality, which ultimately leads to serious complications.
Fog in the head is the main symptom that accompanies cervical osteochondrosis. The disease is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical vertebrae.
This process is almost always accompanied by compression of arteries and other vessels in the specified area. This leads to poor circulation and insufficient nutrition of brain cells.
In this regard, a person begins to feel all of the above symptoms, which are accompanied by:
- pain in the neck when bending or turning the head;
- severe heaviness in the head;
- pain in the shoulders, arms;
- a feeling of “dull pain in the head”;
- weakness in the neck;
- stiffness of movement in the shoulder joints.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops due to poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, and staying in the same position for a long time.
In advanced cases, the neck and shoulders can be completely immobilized.
Not only diseases of the spine, neurosis and VSD can cause a feeling of fog, heaviness and “cottoniness” in the head, but also the consumption of foods containing gluten. An allergy to this component causes the production of substances that have a negative effect on the brain.
If people with a gluten allergy eat a lot of buns, bread, semolina, and pasta made with wheat flour, they will gradually develop the following symptoms:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract - bloating, constipation followed by diarrhea, pain in the stomach and intestines;
- weakness, fatigue, apathy, lethargy;
- brain fog;
- slow reaction;
- mental confusion;
- depression;
- psychological confusion;
- fog.
To find out if you really have a gluten allergy, you should see a doctor and take an allergy test.
Treatment
If the cloudy head appears due to lack of sleep, and the symptom is temporary, then just rest and get enough sleep. If this symptom occurs regularly, measures should be taken to avoid complications.
First of all, you need to see a doctor and find out the cause of the feeling of fog in your head.
If the source is astheno-neurotic syndrome, then it can be cured using psychotherapeutic methods. But first, you should exclude all provoking factors - stress, lack of sleep, excessive physical and mental stress.
If the influence of these factors is not reduced, then psychotherapy and drug treatment will not have the desired effect and will not eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Medicines are used in severe cases. General restoratives, sleeping pills, antidepressants, antipsychotics and tranquilizers are considered effective.
If you have symptoms of VSD, you should consult a specialist. The therapist deals with this issue. To relieve symptoms, various medications are used - sedatives, sleeping pills, drugs for dizziness, to normalize blood pressure, etc. In addition to drug therapy, it is recommended to adjust your lifestyle:
- engage in light, non-competitive sports;
- learn to eat right;
- travel outside the city more often or simply go outside, taking long walks;
- eliminate stress factors;
- learn to go to bed and wake up at the same time;
- give up bad habits.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, and massage will help get rid of the fog in the head with VSD.
The symptoms of neurosis will be eliminated by drugs that normalize the activity of the autonomic nervous system, as well as drugs with a sedative effect.
In case of poor blood circulation in the brain, accompanied by fog in the head, medications with vasodilating and nootropic effects are prescribed. Pathology at the initial stage can be treated without drugs - with the help of massage and manual therapy.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is aimed at relieving the inflammatory process and eliminating pain. For this purpose, NSAIDs, nerve blockade, and medications that normalize blood circulation are prescribed.
In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage, and manual therapy are recommended for people with cervical osteochondrosis.
Diagnostics
If fogginess in the head appears constantly, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Therapists, neurologists, and psychotherapists deal with this issue.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must interview the patient and find out what additional symptoms he has, as well as conduct a diagnosis. Here is a list of mandatory tests needed to find out why fuzzy head syndrome occurs:
- General analysis of urine and blood. Exclude the presence of inflammatory reactions and infectious processes.
- Ultrasound of blood vessels in the cervical spine.
- CT or MRI of the spine and brain. An MRI and CT scan will allow you to exclude malignant processes, determine the condition of blood vessels, identify the presence of chronic diseases of the nervous system, etc.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
The patient may also need to consult other specialists.
Preventive measures
A cloudy head will no longer bother you if you follow preventive measures. It is easy to guess that this symptom primarily appears due to an incorrect lifestyle.
If a person eats poorly, walks little in the fresh air, smokes, drinks alcohol, does not want to exercise, takes drugs, sleeps poorly or is constantly stressed, then there is no need to talk about good health.
Therefore, to improve the condition it is recommended:
- normalize sleep and rest patterns - sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- avoid stressful situations;
- increase physical activity, play sports. The best option is cycling, swimming, jogging;
- Healthy food;
- get rid of bad habits.
By completely changing your life, you can not only get rid of the feeling of fog in your head, but also strengthen your immune system and improve your health.
Source: https://koms24.ru/oshchushchenie-budto-teryayu-soznanie/