Medical center of the highest category AILAZ
To paraphrase a well-known expression, alas, all organs are submissive to old age - this is true, and the eyes are no exception. Over the years, the eyes can be affected by age-related cataracts or retinal dystrophy... To avoid loss of vision or other possible threats, you need to be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist - this is the only way to protect your eyes.
There are vision diseases, such as, for example, an acute attack of glaucoma - when the clock counts: the sooner you see a doctor, the greater the chance of preserving your vision. So, what are the most dangerous signs of visual impairment?
1. Sharp deterioration of vision in one eye
If you have already passed the 60th birthday and if you have at least one of the listed diseases: myopia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, there is a high risk that vision loss is caused by vascular disorders. In this case, emergency medical care is necessary - consult a doctor as soon as possible!
2. The feeling of a black curtain in front of the eyes that covers some part of the field of vision
This is a serious symptom that is often observed with retinal detachment. Here, as in the previous case, the sooner you start treatment, the greater the chance of keeping your eyes healthy.
3. Sharp pain in the eye, redness, blurred vision, possibly nausea, vomiting
This is how an attack of angle-closure glaucoma can occur. Intraocular pressure rises sharply, and this can damage the optic nerve. There is an urgent need to reduce intraocular pressure, including surgical treatment. This will not go away on its own; you need to see a doctor.
4. Gradual or sudden narrowing of the field of view
If your field of vision gradually narrows, over time you will only be able to see what is directly in front of you. This is called “tubular” vision and may indicate glaucoma: a narrowing of the visual field due to damage to the optic nerve is one of its main signs. Treatment is also necessary here, otherwise vision will deteriorate.
Glaucoma is an insidious disease and often patients are not aware of its existence. the AILAZ medical center you will find a questionnaire for self-diagnosis of glaucoma .
5. Gradual deterioration of central vision, blurred, unclear image (straight lines look wavy, curved)
This may indicate a disease in the central region of the retina - the macula, which is essentially responsible for normal vision. This disease is age-related - older people are often susceptible to it. Glasses do not help; without treatment, vision steadily declines. Today, there are many treatment options depending on the form of macular degeneration.
Another reason for a sudden decrease in vision is a retinal tear in the central zone. If you do not immediately contact an ophthalmologist and begin treatment, your vision is unlikely to be restored.
6. When everything in front of your eyes is as if in a fog, the brightness and contrast of vision decreases
Thus, cataracts can develop, causing clouding of the lens. In this case, vision decreases gradually, down to the ability to only distinguish light. Here we are talking about planned surgical intervention - removal of cataracts followed by implantation of an artificial lens. At the same time, it is worth seeing an ophthalmologist, since sometimes cataracts cause intraocular pressure, and this is an indication for urgent surgical treatment. In addition, cataracts cause the lens to enlarge and harden, which can make it difficult to remove—another reason to visit your eye doctor regularly: to avoid wasting time.
Modern technologies make it possible to remove a cataract and replace it with a transparent artificial lens painlessly and in a matter of minutes. You don't have to endure the discomfort of blurred vision. Decide to undergo examination and surgery.
7. Dark spots, partial opacities, feeling of fog or haze before the eyes
If a patient suffers from diabetes, the likelihood of eye damage is quite high, and the longer the diabetes period, the more likely changes in the eye are. Regular visits to an ophthalmologist are mandatory. If necessary, the ophthalmologist will prescribe complex treatment: not only appropriate medications, but often laser treatment. Timely treatment will allow you to preserve your vision.
8. A burning sensation, sand in the eyes, a sensation of a foreign body, lacrimation or, conversely, a feeling of dryness
This is a typical description of dry eye syndrome, the symptoms of which can worsen with age. As a rule, this disease does not cause any particular danger to vision, but severe dry eye syndrome can cause some pathological conditions. An experienced ophthalmologist will conduct the necessary examination and prescribe moisturizing drops.
the AILAZ medical center you will find a questionnaire for self-diagnosis of dry eye syndrome .
9. When the image appears double
When you see double, there can be several reasons, and it is not necessarily a “visual” problem. The reason for this may be intoxication, vascular disorders, diseases of the nervous system, pathology of the endocrine system. If double vision appears, it is better to immediately be examined by several doctors: a therapist, an ophthalmologist, a neurologist and an endocrinologist.
10. Floaters before the eyes
As a rule, floating spots, threads, “spiders” before the eyes are caused by destruction of the vitreous body. This is due to age-related changes in its structure and does not cause danger. With age, the vitreous body loses its density, liquefies and does not fit as tightly to the retina as before. When its fibers stick together and lose transparency, they cast a shadow on the retina and are perceived as defects in the visual field. This is clearly visible on a white background: snow, a sheet of paper. Destruction of the vitreous body can be caused by arterial hypertension, cervical osteochondrosis, diabetes mellitus, injuries to the head, eyes and nose.
At the same time, a spot that suddenly appears before the eyes, a “curtain,” may be the result of a serious pathology that requires surgical treatment, for example, hemorrhage in the retina or vitreous body. If symptoms appear suddenly, within one day, immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
In any case, it is important to remember: if unknown visual symptoms occur, it is better to immediately consult an ophthalmologist. If your vision has deteriorated sharply - over a few days or even hours, or pain bothers you, do not waste time. Even if you cannot consult your doctor, you can go to an emergency eye care office, which is located in every city. As a last resort, many optician stores have competent ophthalmologists who will conduct an initial diagnosis and advise further actions.
ophthalmologist
Address: 02140, Ukraine, Kiev, Bazhana Ave., 12a, right wing, 5th floor. Telephone: Free hotline from a landline phone in Ukraine: 0.
Source: tv.ua
Is headache one of the symptoms of decreased vision?
Headache and decreased vision are often interrelated and occur simultaneously.
At the same time, it is sometimes difficult to determine what is the cause and what is the effect. So can a headache be considered a symptom of visual impairment and what should be done in such cases? Deterioration of vision is indeed often accompanied by pain in the center of the forehead and above the eyebrows.
This is due to the fact that with myopia, especially progressive one, a person has to constantly strain the eye muscles in order to properly see the surrounding objects.
Constant overload causes discomfort. The pain in this case is aching, most often it is uniform, does not intensify or weaken.
There is another possible reason for a headache due to deteriorating vision: simple fatigue when working at a computer for a long time or reading text in very small print, especially in poor lighting. Such a load can lead to a noticeable, but short-term drop in visual acuity, and also causes painful sensations similar to those described in the first case.
Why does my head hurt and put pressure on my eyes?
Doctors give an impressive list of reasons. In most cases, timely initiation of treatment allows you to quickly and completely get rid of the unpleasant syndrome. The main thing is not to delay going to the doctor, not to try to solve the problem with the help of painkillers and not to get carried away with traditional medicine without the permission of a specialist.
Pain in the eyes always indicates possible ophthalmological disorders.
But it is impossible to make a diagnosis solely on the basis of the very fact of having headaches.
A complete examination of the visual organs and identification of additional specific symptoms that develop with eye pain are required.
One of these symptoms is dizziness, which can indicate either overwork or occur with more serious problems.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a person’s condition is carried out in several stages:
- Anamnesis collection. This is information obtained from the words of the patient or his close relatives. Based on it, the doctor may prescribe additional research methods.
- Examination of the superficial tissues of the eyes, measuring blood pressure, studying the general condition of the patient.
- Examination of the fundus after instillation of a solution that disrupts pupil accommodation. The doctor diagnoses the condition of the lens, eye chambers, and retina.
- Laboratory tests, including general blood and urine analysis, blood biochemistry. Next, specific research methods are prescribed if any abnormalities are detected in general clinical tests, for example, testing for tumor markers.
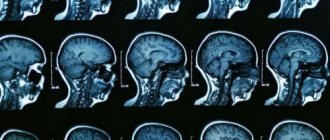
- MRI, . Prescribed if any disease is suspected. By viewing the internal structures of the body, you can confirm the diagnosis proposed by the doctor.
Based on diagnostic procedures, the doctor prescribes the treatment most suitable for the patient.
Causes of sudden vision loss
In medical language this phenomenon is called amaurosis. Vision loss may be a consequence of retinal detachment or ischemia and other eye diseases (for example, glaucoma or uveitis), damage to the optic nerves, or bilateral damage to the visual cortex.
Patients with acutely developed visual impairment should be urgently hospitalized. At the same time, the information that the emergency doctor is able to collect about the development of vision loss is important and helps to quickly establish a diagnosis at the hospital stage.
In this article we will look at what it is and what are the causes of this disease.
Pain in the eye and head area has many causes. These may include inflammatory and infectious diseases, migraines and many others. The success of treatment depends on the quality of the diagnostic measures performed.
Therefore, for pain in the head that puts pressure on the eyes, it is especially important for the doctor to conduct a differential examination. This will allow you to avoid errors in diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
It must be said right away that a sharp decrease in vision is almost always a symptom of some disease.
The causes of eye problems can be both direct eye pathologies: diseases of the cornea, lens, retina, and general diseases.
Among the eye diseases that most often lead to a sharp decrease in vision are retinal detachment and rupture, macular degeneration, inflammation or ischemia of the optic nerve, rupture or blockage of a vessel.
Also, a common cause of the development of this symptom is diabetic retinopathy, a complication of diabetes mellitus in which damage to the vessels of the retina occurs.
With this disease, vision loss is usually irreversible.
In addition, a sharp deterioration in vision can occur with retrobulbar neuritis, intracranial hypertension, intoxication of the body and other pathological conditions.
Causes
During myopia, the work of the ciliary muscles of the eye is disrupted, the lens takes on an irregular shape, so a person has difficulty seeing surrounding objects.
Trying to concentrate on them, he involuntarily tenses the muscles located around the eyeball and lens.
Constant overvoltage leads to continuous transmission of nerve impulses to the brain, and a spasm of accommodation is formed.
During spasm, blood circulation through the vessels to the eyeballs is disrupted. This results in a reduced amount of oxygen supplied. This causes a headache. If a person puts on glasses or contacts, he stops straining his eye muscles. Therefore, blood circulation is normalized and headaches are eliminated.
Source: https://neuro-orto.ru/bolezni/mozg/bolit-golova-i-uhudshaetsya-zrenie.html
Diagnostics
You can determine the reasons why everything is blurry in your eyes using an MRI or CT scan of the brain, X-ray examination of the spine, and laboratory tests. Additionally, the patient visits an ophthalmologist. This specialist undergoes a standard examination: they alternately close the left and right eyes, and recognize the letters that the doctor points to. Other types of diagnostics depend on the characteristics of the clinical case.
Headaches and decreased vision
With the onset of myopia and the progression of this process, headaches often appear, especially if the person does not use optical devices to improve the quality of vision.
To diagnose the cause of headaches, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist. He will examine the patient’s fundus, make an accurate diagnosis, and prescribe treatment that eliminates this effect.
Risk group
The risk group includes the following categories of patients:
- people whose parents suffer from visual impairment;
- persons with disorders of the internal structures of the eyes, various diseases (glaucoma, cataracts, retinal detachment, dysfunction of the optic nerve);
- persons who work at a computer for a long time;
- patients who selected optical devices without a doctor’s recommendation (there may be a risk of incorrect selection of lenses for glasses, incorrect diopter).
Symptoms
Symptoms of the condition depend on the underlying cause that caused decreased visual acuity and headache.
The most common signs are:
- poor health, loss of strength;
- double vision;
- increased blood or intraocular pressure;
- the eyes become tense, dry mucous membranes and overwork of the eyeballs may develop;
- migraine occurs.
A person may have only a headache or be accompanied by the above symptoms.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are based on the cause that caused the disorder:
- prescription of glasses and lenses that correct decreased visual acuity;
- drugs against glaucoma, cataracts, prescribed in the form of drops;
- medications that lower blood pressure;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- surgical methods to restore damaged tissues;
- surgical removal of malignant and benign tumors.
If any serious systemic disease is detected, specific therapy is prescribed. After complete healing, the headaches will go away on their own.
Complications
When visual acuity decreases, accompanied by headache, various complications are possible, which depend on the cause of the condition:
- internal bleeding in the eye or brain;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity up to complete blindness;
- spread of metastases from a malignant neoplasm;
- compression of neighboring tissues by a benign tumor;
- progression of cataracts, glaucoma, which sharply reduces vision to complete blindness;
- spread of the infectious process to adjacent tissues and into the blood.
To avoid complications, it is recommended to start therapeutic measures prescribed by your doctor on time.
Forecast
If the cause of the condition is identified early, the prognosis is positive. A complete cure is possible. In the absence of therapy, a person’s condition can be complicated by complete loss of vision and death.
Prevention
It is recommended to use the following prevention rules to avoid decreased visual acuity and headaches:
- examination by an ophthalmologist once a year, especially if a person has impaired functionality of the visual organs;
- timely treatment of all systemic and ophthalmological diseases;
- selection of lenses and glasses together with an ophthalmologist;
- Carrying out daily eye exercises, especially if a person works at a computer for a long time.
When visual acuity decreases, headaches appear frequently. If this condition occurs, the root cause should be identified. It may be due to a serious systemic disease, which, by treating the patient, will completely eliminate the headache.
Poor vision significantly worsens the quality of life and makes it impossible to see the world as it is.
Not to mention the progression of pathologies and complete blindness.
MNTK "Eye Microsurgery" published an article on non-surgical restoration of vision up to 90%, this became possible thanks to...
Read more Was this article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 5.00
Source: https://proglazki.ru/simptomy/golovnye-boli-i-padenie-zreniya/
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is an ametropic visual impairment caused by changes in the shape of the lens, cornea and eye. As a result of these changes, a difference in quality occurs vertically and horizontally, causing a decrease in the clarity of vision. In a healthy eye, the convergence of light rays occurs on the retina, at one point, while with astigmatism, the focus is concentrated at two points, forming a picture similar to a segment, a blurred ellipse or a “figure eight”.
Astigmatism, as a rule, develops from childhood - in some cases it accompanies myopia and farsightedness. In addition to “blurred” vision of objects, astigmatism is characterized by double vision and increased eye fatigue.
Diffuse vision and headache
Modern life with a huge amount of stress, spending many hours at the computer, contributes to weakness, dizziness, and visual pathologies. But we must not forget that prolonged pressing pain in the eyes and headaches are also caused by serious illnesses. And the correct diagnosis is established by a specialist.
The above symptoms have many causes.
Itching in the eyes can also be caused by glasses that are chosen incorrectly, which overstrains the optic nerve. Trust the selection of optics only to a specialist.
Ophthalmological disorders. False myopia or accommodation spasm is a spasm of the eye muscle when vision deteriorates and a person does not react to changes in focal length. This causes pain in the eyes.
To get rid of negative symptoms, you need to relax the muscle using eye drops or laser therapy.
Glaucoma, leading to blindness, is considered a serious problem. When sick, a person suffers from eye pain, headache, dizziness and nausea.
The pupil dilates and the eye swells.
How to remove pain
The most common cause of discomfort in the eye sockets and head is fatigue. You can get rid of it using simple relaxation techniques:
- if you are at home, lie down, turn off the lights, close the curtains;
- try to get enough sleep;
- do not turn on the TV and computer for a day or two;
- massage your head from the back of the head to the temples and neck;
- pain caused by spasms is eliminated by spasmalgon. But if the symptoms recur, rush to the doctor.
Traditional medicine methods
Eye pain and headaches are relieved with traditional medicine.
- Mint decoction. Pour boiling water (1 cup) over peppermint (1 tablespoon). After straining, drink 50 g before meals.
- Garlic elixir. Add 9 - 10 cloves of garlic to half a glass of milk, boil and cook for 4 - 6 minutes. Cool, strain. Place a few drops (5 - 7) of the decoction into the ear. After a couple of minutes, remove by tilting your head.
- Valerian decoction. Pour boiling water over the chopped rhizome (1 tablespoon). Steam for 25 - 27 minutes in a water bath. Consume before meals.
- Honey cocktail. Mix 1 part agave juice, 2 parts each honey and wine (red). Drink a cocktail before meals.
- Therapeutic compresses. To prevent headaches, compresses made from cabbage leaves and raw potato gruel are applied to the temples and forehead. A cold, damp towel also relieves pain.
Myopia (nearsightedness)
Very often, vision deteriorates due to developing myopia. With myopia, the image is not projected on the retina, but is focused in front of it, thereby causing impairment of distance vision.
Myopia can be either congenital or acquired.
- In the first case, it may be caused by a genetic predisposition (passed on by inheritance; according to statistics, half of the parents suffering from this disease give birth to children with the same disorder). Congenital myopia can also occur due to the irregular shape of the lens - its elongation in conditions of weak oculomotor and ciliary muscles.
- Acquired myopia is usually associated with prolonged stress on the eye apparatus. There are also a number of pathologies that provoke the development of the disease: subluxation and sclerosis of the lens (especially in older people), spasms of the accommodative apparatus, increased thickness of the cornea, vascular diseases.
Diplopia (split picture)
Diplopia also causes blurred vision and can even lead to strabismus. With such an anomaly, the object in question doubles vertically, horizontally, diagonally, and can also rotate relative to the original picture. This usually happens due to a malfunction in the coordinated functioning of the oculomotor muscles, which disrupts the concentration of both eyes on one object.
Diplopia can be binocular, monocular, temporary and volitional. At the same time, volitional diplopia does not affect the health of vision and is a kind of gymnastics.
Diseases
- Optic nerve atrophy is a phenomenon in which the central part of the visual zone “falls out” (very often associated with age-related changes).
- Retinal detachment - a characteristic feature is a “curtain” effect in the peripheral area of the visual field. Also, when peeling, the image may float and the outlines of objects may be distorted. Often the cause is a degenerative condition of the retinal membrane, previous injuries and a high degree of myopia.
- Bilateral loss of the outer part of the field in most cases appears with a pituitary adenoma, which provokes an interruption of the optic tract at the intersection point.
- Glaucoma - this disease is characterized by loss of half of the fields located close to the nose. Signs include a hazy effect in the eyes, as well as a rainbow effect when the patient looks at a bright light. A similar disorder accompanies an aneurysm of the internal carotid arteries.
- With hematoma, tumors and inflammation in the central nervous system, there is a possibility of cross-impairment of visual fields. In addition, quarter and half loss is also possible - the so-called quadrant hemianopsia.
- The effect of curtains making it difficult to see clearly on the eyes signals changes occurring in the vitreous body, cornea and lens.
- Tube vision or concentric narrowing of the visual area explains PDS (retinal pigment degeneration). In this case, high acuity is characteristic of the central region, while in the peripheral part it is almost absent. If the development of concentric vision is balanced, then such a defect is caused by a failure of blood circulation in the brain or glaucoma. Narrowing also occurs with inflammation of the posterior parts of the retina - peripheral chorioretinitis.
Visual field distortion
The field of vision is the reality around us, which the fixed eye sees. Using the example of a spatial relationship, this can be called rather a 3D mountain, at the top of which there is the highest quality vision, which deteriorates closer to the foot (near the nose) and is least expressed in the temporal region. The limiters of visibility from an anatomical position are the facial bones of the skull, while optical limitations are placed on the retina.
Normal field of vision in the right eye
The norm of white color in the visual fields is as follows:
- outside - ninety degrees;
- below - sixty-five;
- from above - fifty degrees;
- inside - fifty-five degrees.
The viewing area for each eye is divided into four parts: two vertical and two horizontal. Changes in these areas are similar to a dark spot - a scotoma, as well as concentric narrowing.
Scotoma is a spot in which a person does not see anything, if it is absolute and partially (blurred) - if relative (sometimes of a mixed type). A distinctive feature is absolute blackness and blurry peripheral vision. A positive scotoma is observed as a symptom, while a negative one can be detected by examination by a specialist.
Keratitis
In addition to the above diseases, infectious corneal diseases can also cause a sharp deterioration in vision. Inflammation of the cornea occurs as a result of a complication of an advanced form of conjunctivitis. In addition, harmful bacteria enter the eye during operations performed on it.
The most dangerous causative agent of keratitis is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which appears as a result of unsanitary conditions and lack of antiseptics and asepsis.
Symptoms:
- redness in the affected eye;
- the occurrence of pain;
- corneal clouding.
- fear of light;
- increased lacrimation.
Fifty percent of keratins are arborescent, which occurs due to herpes. In this situation, a damaged nerve trunk, similar to a tree branch, may appear in the eyeball.
A herpetic corneal lesion or chronic injury caused by a foreign body is called a creeping corneal ulcer. Most often, the formation of such ulcers occurs due to amoebic keratitis, which develops due to non-compliance with the rules of wearing contact lenses or their poor quality.
- Keratitis can be not only ulcerative, but also non-ulcerative.
- The disease can occur from sunburn or from welding - this form is called photokeratitis.
- The disease can be deep, or may affect only the superficial corneal layer.
- Dystrophy and inflammation provoke opacities of the cornea; in this case, the thorn is a scar, the presence of which sometimes limits visibility to the level of light perception. The spots can also cause astigmatism.
As a sign of disease
However, mydriasis is not always a dangerous sign. It can be noted as one of the symptoms in a number of diseases, for example:
- tumors inside the skull;
- aortic aneurysm;
- meningitis;
- hemorrhage inside the skull due to head trauma;
- injuries to the organs of vision;
- glaucoma;
- encephalitis;
- tumors of a number of lymph nodes.
This is what the tick-borne encephalitis virus looks like
Mydriasis is also often observed in chronic migraines.
On a note! During anesthesia, the doctor may note a certain state of the pupils. For example, with deep anesthesia they tend to expand, but with light anesthesia they can narrow. If the pupillary openings become small while the patient is under heavy anesthesia, then this is one of the signals for the doctor that the operation needs to be canceled - something is wrong in the body.
There are many causes of mydriasis
Visual impairment in children
In children, vision most often deteriorates as a result of weakening of the eye muscle. Today, more and more schoolchildren have low vision. Violations are observed even in preschool age. Two thirds of children leave school with vision loss.
Today there are many ways to correct vision. Laser vision correction opens up enormous prospects for children. But the operation is contraindicated before the age of 16. But besides surgical correction methods, there are many methods of maintenance and restoration.
It is also important to observe good visual hygiene. The child should study only at the desk and must maintain the correct distance between the eyes and the book or notebook. Timely correction is very important for the child, since the development of vision pathology in childhood entails serious mental problems.
It is also important to eat right, follow a work and rest schedule. The diet should include the required amount of nutrients, vitamins and microelements.
Why does dizziness occur during pregnancy?
A consultation with an ophthalmologist is one of the mandatory consultations for a pregnant woman. If a problem is detected, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment. It is especially dangerous if degenerative processes occur in the eye, the retina is damaged, or there are tears or detachments.
Consultations are carried out due to the fact that pregnancy is often accompanied by the appearance of spots, circles, light, blurred vision occurs, silhouettes are distorted, and become blurry. Strabismus is often observed.
Ophthalmologists advise resorting to a cesarean section for myopia of more than 6 diopters. Below this threshold, natural delivery is completely acceptable. However, the indications for cesarean section include pathological processes that occur with myopia.
Types of miosis
Depending on the cause of miosis, the following types are distinguished:
- Functional. Constriction of the pupil is caused by natural causes and is normal.
- Drug-induced (reactive) miosis is caused by taking medications that, in addition to their main effect, have a stimulating effect on the sphincter or suppress the functioning of the dilator.
- Paralytic. It occurs due to dilator paralysis caused by pathological processes localized near the carotid plexus (located around the carotid artery), the ciliospinal center (the sympathetic cervical nerve originates from it) or the cervical sympathetic trunk.
- Spastic or miosis of irritation (usually bilateral). It is caused by a spasm of the sphincter caused by stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system. It can develop in the presence of tumors in the brain, meningitis and encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, uremia, the formation of cavities in the spinal cord (syringomyelia), during the tonic phase that occurs during an epileptic attack.
- Syphilitic. Develops as a result of penetration of the causative agent of syphilis into the central nervous system. Treponema pallidum, which has penetrated the nervous system, leads to the appearance of symptoms of meningitis, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, meningomyelitis, which are characterized by miosis. It can develop at any stage of the disease, but with timely treatment it is rare.
Miosis, in which constriction of the pupil occurs as a consequence of taking medications, is caused by:
- adrenergic blockers - block receptors that respond to the mediators adrenaline and norepinephrine. Used to treat arrhythmia, hypertension, urological diseases, etc.;
- cholinergic stimulants (acetylcholine and its derivatives). Used to treat glaucoma, mydriasis caused by the use of atropine, to eliminate adhesions between the lens and the iris, as well as to treat certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder;
- M-cholinomimetics - pilocarpine, used for the treatment of glaucoma and intraocular hypertension, and gliatin, used for traumatic brain injury in the acute period, for cerebral circulatory disorders and for multi-infarct dementia. It is also used in the presence of psychoorganic syndromes characterized by memory impairment, disorientation, etc. Miosis after the use of gliatin occurs as a result of the breakdown of the drug into glycerophosphate and choline, which is involved in the biosynthesis of acetylcholine.