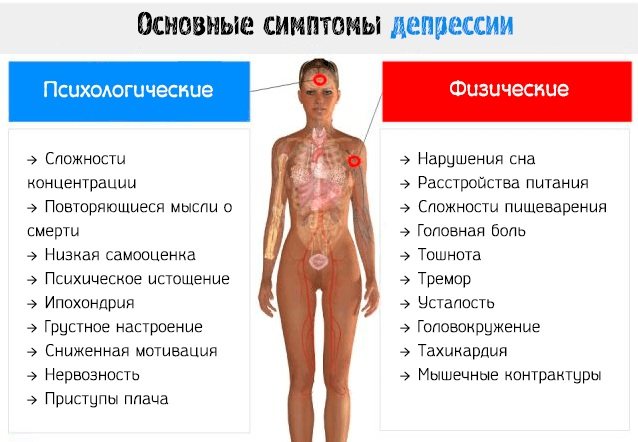
Release forms and composition of the drug
This product is available in the form of tablets or powder for oral use. The active ingredient of the product is the component of the same name, chlorprothixene.
Additional composition:
- corn starch;
- powdered sugar;
- milk sugar;
- calcium stearate;
- opadray 2;
- talc;
- polyvinyl ethanol;
- macrogol;
- titanium dioxide;
- iron oxide – yellow, red and black;
- indigo carmine
Dragees are packed in plastic blisters and packaged in cardboard containers.
Pharmacological properties
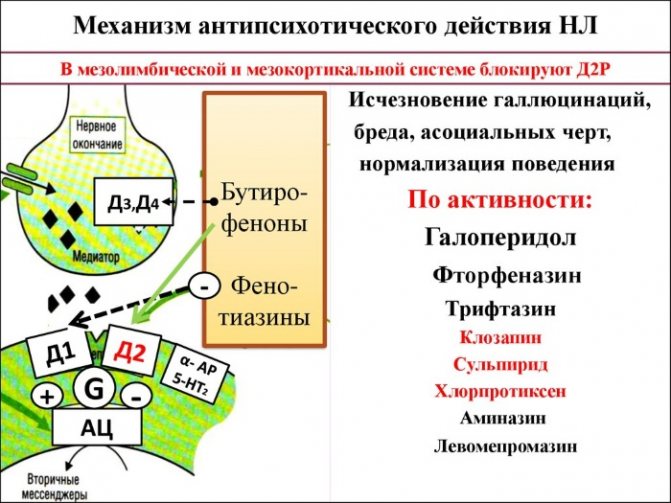
The medication belongs to the category of antipsychotic drugs that have a neuroleptic effect and is a representative of thioxanthene. The drug also exhibits high anticonvulsant, antiemetic and thymoleptic properties.
The action of the drug components is aimed at suppressing the production of serotonin. In this case, a high anticholinergic and adrenolytic effect is noted. The drug has a suppressive effect on dopamine receptors located in the brain.
The medication suppresses the symptoms of psychosis, preventing the development of delusional states and hallucinations. The drug has an inhibitory effect on gag reflexes and also binds to the action of receptors located in the central nervous system.
Medications
For sleep disturbances, patients with dementia are prescribed medications.
Among the frequently used ones are the following:
- antidepressants: Chlorprothixene, Citalopram, Amitriptyline and others;
- sedatives: Afobazol, Novopassit, Diazepam, Fanesipam, etc.;
- neuroleptic drugs: Haloperidol, Cortexin, Olanzapine, Risperidone and others.
There are a number of medications that can be freely purchased at pharmacies (table), but the strongest and most effective medications can only be purchased with a prescription.
Table. Drugs on the market:
| Name | A comment | Analogs |
| Selective anxiolytic, produced in Russia, does not cause drowsiness or addiction. The effect is cumulative, so a lasting effect is observed several weeks after the start of administration. Price – about 750 rubles. | Noofen, Tranquilar, Adaptol |
| This antipsychotic helps older people with melatonin deficiency. It enhances its production, which improves sleep, has a sedative and anticonvulsant effect. Helps reduce hallucinations. You should not drink if you have kidney disease, certain types of cancer, or epilepsy. Approximate cost 600 rub. | Circadin, Sonovan Melarithm |
| A good sleeping pill with a sedative effect. The tablets are divided into strips, making it easy to adjust the dosage. Contraindications: glaucoma, genitourinary pathologies, galactosemia, individual intolerance to the components included in the composition. Price 300–400 rub. | Bromcamphor, Balocordin-Doxylamine, Adonis-Bromine |
Important. Only the attending physician should diagnose and prescribe medications. Self-medication can make the situation worse and cause serious side effects.
Popular prescription medications include:
- Sonapax is a combined remedy that helps quickly combat anxiety, panic attacks and insomnia, and is also useful for coordination disorders. Not prescribed for heart disease, liver disease, hematopoietic disorders, pulmonary failure and others.
- Aminazine is an antipsychotic drug that weakens psychomotor agitation, helps fight fear and anxiety, and removes affective reactions by inhibiting reactions in the central nervous system. If taken before going to bed, it acts as a sleeping pill. Contraindications: chronic diseases of the liver, digestive organs, cardiovascular system and spinal cord lesions. Analogues: Clopixol, Propazin, Haloperidol.
- Andante is a powerful sleeping pill, so it copes well with its functions and is indicated for old people with dementia. It is important that the drug should be used situationally; systematic use is contraindicated, as it can aggravate the patient’s condition. It should not be prescribed for respiratory tract disease, apnea, physical weakness of the patient, or liver dysfunction. Analogs: Relaxon, Hypnogen, Sonovan and others.
- Ivadal is a relatively new drug, has a hypnotic and sedative nature, helps with neuroses, worries, anxiety, lack of coordination, and is not addictive or dependent. Contraindications: see the description of the drug Andante. The price is quite expensive - about three and a half thousand rubles, but you can use analogues: Adolma, Hypnogen and others.
- Phenibut is a nootropic drug that improves the conduction of nerve impulses, helps optimize brain processes, improves cranial blood circulation, which is important for proper gas exchange and trophism in tissues. The therapeutic effect manifests itself in the form of improved sleep and muscle coordination, a reduction in ischemic processes in the brain, relieving fear and nervous tension, and can help improve speech activity in case of speech disorders. The frequency and duration of courses are prescribed individually according to indications. Price no more than 300 rubles, analogues: Tranquesipam, Phenazepam.
- Sanval is another sleeping pill from a new generation of drugs. Indicated to improve the duration and quality of sleep, relieve heightened emotional states. Should not be prescribed for alcohol or drug addiction. Analogs: Zolpidem, Ivadal.
Sleeping pills Andante
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The medicine has good absorption capacity and is quickly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the effect of the active substance appears after 20 minutes.
- The main substance of the tablets undergoes metabolic processes in the liver and intestines.
- The components of the product are able to penetrate the placental barrier and into breast milk.
- The components of the drug are excreted through the renal system in the form of metabolites.
- The half-life of components from the body ranges from 8 to 12 hours.
Benefits and harms
Chlorprothixene (reviews from patients who took the drug are overwhelmingly positive) in addition to its beneficial effects, has some significant disadvantages.
Among the advantages of the drug, patients and specialists note a good therapeutic effect that helps fight various forms of psychosis, as well as the low cost for this group of drugs.
However, in some cases, capsules can harm the human body and psyche. Patient complaints are directed at multiple side effects that can develop while using the drug. In this case, the underlying disease may worsen or lead to additional complications.
Practical use
Review by a doctor and reviews of relatives of elderly patients who were prescribed Akatinol (Memantine).
I have been prescribing Akatinol to my patients for a long time. It has a positive effect in moderate to severe dementia.
During use, an improvement in consciousness is observed, mental clarity appears, and memory is normalized. Basically, it had to be prescribed to old people who had symptoms of insanity.
In these cases, I prescribe the medication according to the following regimen: 5 mg in the first week, 10 mg in the next week, 15 in the 3rd week. It was not necessary to prescribe more than 20 mg.
However, this remedy only helps to maintain the condition of patients, but it does not cure the disease. Therefore, sooner or later, insanity will still overtake the patient, even when taking this drug, and the drug only helps to prolong social existence.
Neurologist
My friend’s grandmother is already old, she is already 89 years old. Of course, as often happens at this age, she developed a state of dementia, she became absent-minded, forgetful, her consciousness was somewhere far from reality. My friend became worried, and I advised her to take her grandmother to the doctor.
After the examination, she was prescribed to take a number of medications, among which was Akatinol. After she started taking the medicine, her condition began to improve. At least the absent-mindedness disappeared and clarity of mind appeared. But it’s a pity that the medicine only helps to maintain a normal state, but does not completely cure the disease.
Anna, 35 years old
My mother is 75 years old and she began to show symptoms of absent-mindedness, forgetfulness, sometimes you talk to her, and it’s as if she is in a different reality. I immediately took her to see a doctor, after the examination the doctor said that she had dementia caused by Alzheimer’s disease, and immediately warned that nothing good should be expected.
For maintenance, he prescribed me to take the medicine Akatinol. After taking it, her condition improved, and now at least I can talk to her normally.
Maria, 48 years old
Indications for use
This medication has a wide range of indications. A neuroleptic can be used as an independent therapy.
Indications:
- various forms of psychoses, including schizophrenic and manic states, accompanied by increased psychomotor excitability, anxiety disorders and psycho-emotional arousal;
- depression that occurs during menopause;
- paroxysmal states provoked by fear and psycho-emotional stress;
- injuries in the head area, trauma, discirculatory form of encephalopathy, development of withdrawal symptoms associated with addiction - alcoholism, drug use;
- hyperactivity syndrome – increased excitability, irritation;
- confusion in the elderly;
- increased anxiety associated with sleep disorders, the period before surgery;
- pain, development of bronchospasms, anxiety in disorders and diseases, itching, vomiting.
In childhood, the drug is prescribed for psychosomatic and neurotic conditions, as well as for the treatment of behavioral disorders in children.
Application area
Memantine is used to treat the following disorders:
- severe and moderate dementia, which is accompanied by Alzheimer's disease;
- dementia with Lewy bodies;
- senile dementia at any stage of development;
- dementia with vascular type in any degree of severity.
In addition, the use of Akatinol is justified in the following cases:
- spastic syndrome of spinal and cerebral type;
- for head injuries, multiple sclerosis, strokes, traumatic brain injuries, paraplegia;
- with a decrease in the level of mental abilities, which are accompanied by a decrease in concentration, memory, and learning ability.
Article on the topic: Hyperpathy as a diagnostic criterion in neurological practice
Contraindications
Chlorprothixene (reviews from patients who took the drug warn of the presence of multiple contraindications) should be used only if there are no restrictions on its use.
Contraindications:
- intolerance to the composition of the product;
- intoxication and poisoning with drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing the central nervous system;
- ethanol poisoning;
- coma;
- vascular collapse;
- damage to organs responsible for hematopoietic functions;
- presence of pheochromocytomas;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- age up to 6 years.

Before using the medicine, you should first familiarize yourself with the list of contraindications.
Behavior of people with dementia
In studies on dementia, much attention is paid to the description of behavioral and mental disorders.
The choice of therapy and features of patient care largely depend on these manifestations of the disease. The patient’s destructive actions can often be aggressive in nature towards others and threaten the lives of both the patient himself and other people.
Therefore, it is important for both relatives and medical personnel to know the features of the development of symptoms and understand how to properly communicate with patients with dementia.
Features of behavior of a patient with dementia
All dementia disorders can be divided into psychotic, behavioral and depressive disorders.
Psychotic disorders
These include hallucinations, delusional and mixed disorders. The first place is taken by delusions arising from progressive dementia. It is usually monotonous and unproductive.
Delusional beliefs
Ideas of damage, robbery, theft are typical, especially after 65 years. Before this period, ideas of persecution, oppression, persecution were more common. Delirium in dementia is transient, weakens as the disease progresses and gradually fades away completely. The main types of delusions in people with dementia:
- simple;
- complex, or combined;
- grandiose;
- associated with neurological defects (for example, during the recovery period after post-traumatic encephalopathy).
Simple delusions look like ordinary, unstructured beliefs. For example, the patient is sure that his spouse is cheating on him, children regularly steal money, and other relatives mix poison into food; hypochondria, erotomania are common. These manifestations are characteristic of vascular dementia and asthma.
Complex delusions in behavior are detected in patients with b. Parkinson's, hepatic encephalopathy. It is more closely connected with real life. The patient is convinced that intrigues are being woven against him, people are discussing him behind his back at work, conspiracies are being woven, etc.
Grandiose delusions are distinguished by the scale of the idea and are rare in dementia patients.
Hallucinatory disorders
The behavior of patients with dementia is characterized by visual and auditory hallucinations. As a rule, they are short-lived, rudimentary, and pass without serious disturbances of consciousness and severe post-amnesia.
Visual hallucinosis is a common manifestation of mental changes in Parkinson's disease. Delirium and confusion appear in the later stages of Alzheimer's senile dementia and are associated with the addition of somatics.
Mixed psychotic disorders have features of hallucinatory and delusional disorders.
Depressive symptoms
Dementia and depression are inextricably linked: it is not without reason that among the cognitive tests carried out when dementia is suspected, there are questionnaires that identify depressive symptoms. Depression often precedes dementia (especially in AD). Dementia is characterized by early onset of corresponding changes in behavior:
- anhedonia;
- sleep and appetite disorders;
- apathy;
- increased anxiety;
- constant feeling of guilt;
- low self-esteem;
- slowness of reaction;
- dysphoria.
The character of a person with dementia also changes: he gives up normal everyday habits, hygiene rules, stops washing his face and brushing his teeth. Obsessive rituals appear: the patient rearranges things, sings, and performs repeated taps.
All this can be manifestations of anxiety, as one of the symptoms of depression. Sleep and appetite disturbances are observed. A person with dementia does not sleep at night, but during the day they can sleep until lunchtime. Taste preferences change.
Violations in the early stages are often manifested in behavior by excessive appetite, gluttony, and in the later stages, on the contrary, complete refusal of food.
Behavioral disorders
These include:
- aggression;
- agitation;
- inappropriate sexual behavior;
- violent screams;
- wandering, etc.
Aggression is observed in approximately one fifth of patients.
It can be physical - attempts to get into a fight, bite, push, and verbal - a person curses the interlocutor, insults, often raises his voice, breaks into a scream.
You should behave carefully with a person with senile dementia in this situation; you should approach him slowly, briefly explaining that no one will harm him.
Important! A calm environment, a familiar routine, and the absence of stimulating factors have a positive effect on the patient’s behavior. Therefore, you should communicate with people with dementia in a peaceful manner: this helps prevent outbursts of aggression.
Often, some behavioral disorders, such as agitation, agitation, occur while taking certain medications and are side effects of therapy. Behavior in dementia is characterized by a decrease in the ability to self-control.
The patient is able to undress naked in a public place, relieve himself not in the restroom, but in the kitchen, and even masturbate in front of relatives.
He misinterprets auditory and visual signals, and may refuse to take medications, perceiving them as poison due to increased suspicion.
Cognitive impairment plays a significant role in behavior: for example, a person suffering from dementia asks the same questions several times and repeatedly expresses his demands. He is unable to clearly express his needs, which makes him feel lonely and afraid. There is a tendency to wander, to search for something or someone.
Violent screams in dementia are monotonous, the patient can draw out one note for a long time, and when asked what happened, he usually answers that it was not he who screamed.
Frequency of mental and behavioral changes (%), not associated with cognitive impairment, in a sample of a total of 255 people * Clinical manifestations / stage of dementia Mild (41 patients) Moderate (119 patients) Severe (95 patients)
| Delusional disorders | 43,9 | 51,3 | 29,5 |
| Depression | 56,1 | 55,5 | 45,3 |
| Hallucination | 14,6 | 21,8 | 20,0 |
| Anxiety | 80,5 | 72,3 | 64,2 |
| Apathy | 14,6 | 30,3 | 34,7 |
| Aggression | 46,3 | 63,0 | 62,1 |
| Appetite disorders | 7,3 | 11,8 | 20,0 |
| Sleep disorders | 12,3 | 34,5 | 28,4 |
*Research data provided by the Mental Health Research Center
Behavior of a dementia patient depending on the stage of the disease
Dementia often manifests with depressive symptoms and mild cognitive impairment. Emotional disorders of a patient with dementia even at the preclinical stage are manifested in behavior by mood lability, sudden, short-term emotional shifts:
- the person becomes less cheerful, more self-centered and passive;
- own character traits become dulled;
- incontinence, disinhibition, laziness come first;
- slight difficulties arise when performing intellectual operations.
At this stage, a patient with dementia sleeps a lot - according to some data, daytime sleepiness, frequent fatigue, and fatigue are the first signals of the onset of pathology.
Important! By consulting a doctor in a timely manner, you can slow down the progression of the disease. Therefore, you should pay close attention to possible signs of dementia.
Soft stage
How does a person with dementia behave in the early stages of pathology? Characterized by forgetfulness, problems with thinking, and decreased professional and social activity. Patients are able to take care of themselves independently; minor problems appear in everyday life, but spatial thinking may be impaired.
Changes in personality are insignificant, often attributed to fatigue and circumstances. Depending on the cause of dementia, cognitive impairment, sharpening of personality traits, or, conversely, a sharp change in character may come to the fore. Depressive symptoms worsen. In some cases, criticism of one's condition persists.
You should behave calmly with a person with dementia.
Causes and prevention of certain behavioral disordersBehavioral disordersCauseWhat to do
| aggression | despair, fear, anger | try to anticipate the patient's needs |
| disproportionate reaction | inadmissibility of criticism towards oneself | make it clear slowly and clearly that there is no criticism |
| repetitive actions | mnestic disorders | calmly answer questions and demonstrate understanding |
| desire to hide things | isolation, loneliness, fear, flashbacks | place markers in the apartment to make it easier for the patient to navigate |
Moderate stage
Cognitive and behavioral disorders and changes in behavior become more pronounced. Criticality towards the perception of the disease decreases. Domestic and social difficulties appear. A person may forget to close the doors, turn off the iron, leave the gas open; unable to cope with professional obligations.
There is no motivation to acquire new knowledge. Help is needed with daily maintenance, cooking, and dressing. Basic information about himself is still preserved, the patient recognizes loved ones, but cannot remember vital events; feels scared and alone.
Insomnia in dementia is not yet severe, but there are difficulties falling asleep and frequent awakenings in the middle of the night.
Severe dementia
Complete disorientation. Characterized by deep decay of memory, intellectual functions, and total amnesia. Mental activity is destroyed, severe neurological and metabolic disorders, reflexes, and violent actions appear.
There are no clear rules on how to behave for the relatives of a person with dementia at this stage, since the latter lies a lot and practically does not speak. All that is required is constant supervision and full care, from changing linen to spoon feeding. Sleep with dementia in this case has its own characteristics.
In the later stages, a patient with dementia sleeps all the time, is apathetic, lethargic, and does not take any action.
Behavior in society
The difference in the behavior of men and women suffering from this pathology is insignificant, and lies mainly in the characteristics of the psyche. Thus, men more quickly experience problems with performing professional duties, while women experience difficulties in everyday life: with cooking, sewing, knitting. In males, unrestrained sexual behavior and erotomania are more often recorded.
How does a person with dementia behave at the initial stage? Changes in character concern behavior both with relatives and with the team at work, however, with loved ones, some restraint is shown. As the pathology of aggression progresses, family members are more often accused of theft, attempts to poison, and unreasonable jealousy; Colleagues are usually suspected of intrigue, gossip, and conspiracies.
You should behave with a person with senile dementia at this stage in an understanding manner; it is advisable to keep him busy with business, physical activity, and try to anticipate his needs.
As memory is lost, foreign, unfamiliar faces are first forgotten. Relatives are the last to disappear from memories.
In later stages, exogenous and endogenous factors: physical pain, difficulty urinating, improper handling - can aggravate changes in behavior, since patients, due to a lack of self-criticism, are unable to adequately deal with others.
A patient with dementia constantly sleeps during the day and is awake at night, which is why it is difficult to adapt to the regime of being in special institutions. For most patients, limitations in their capabilities can provoke a worsening of behavioral disorders.
052
Source: https://demenciya.ru/demenciya/povedenie-bolnyh-dementsiej/
Instructions for use, dosage
The product is intended for oral use. Adult patients with psychosis are prescribed 50-100 mg of the drug per day. In this case, the dosage is divided into several equal parts. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 600 mg.
As a maintenance treatment, 100-200 mg of the drug per day is prescribed. Before taking, the dosage must be divided into several equal parts. For children over 6 years old, the dosage is calculated depending on the child’s weight - 0.5-2 mg per 1 kg of weight. The duration of treatment in both cases is determined by the treating specialist.
Application and dosage regimen
The medication must be taken orally during meals. The optimal dosage regimen is established for each patient individually. You need to start taking the drug with a small dosage.
For dementia in elderly patients, it is recommended to take Akatinol during the first 7 days of therapy at a dosage of 5 mg daily, during the second 7 days at a dosage of 10 mg daily, during the third 7 days at 15-20 mg of the drug daily.
If the need suddenly arises, in subsequent weeks the dose of the medicine should be increased by 10 mg per week, but the maximum dose per day should not be more than 30 mg.
During the treatment of spastic type syndrome, which is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, during the first week of therapeutic treatment with the drug Akatinol, 10 mg daily is recommended, during the 2nd week, 20 mg daily, during the third week, 20-30 mg daily.
If such a need suddenly arises, then you can increase the dosage of the medicine by 10 mg every 7 days, the maximum dose of the medicine should be no more than 60 mg per day.
The dosage level for maintenance therapy should be 10-20 mg per day.
Side effects
If used incorrectly or due to the physiological characteristics of the patient, various negative manifestations may occur.
Side effects:
- disorders of the hematopoietic organs and cardiovascular system: orthostatic form of hypotension, increased heart rate. In extremely rare cases, after 1-2 months of therapy, the following disorders may occur: a decrease in the number of leukocytes, a hemolytic form of anemia.
- Disorders of the central nervous system and sensory organs: development of dizziness, rapid fatigue, lethargy, development of akathisia, dystonic disorders, dyskinia, clouding in the eye area, accompanied by visual disturbances, accommodation paresis. In extremely rare cases, taking the drug can lead to the occurrence of dystonic syndrome (late form), as well as to the development of neuroleptic disorders.
- Problems with the digestive system: constipation, jaundice, dryness of the oral mucosa.
- Genitourinary disorders: urinary retention, development of dysmenorrhea, decreased erectile function or sexual desire.
- Allergic reactions: skin rashes, dermatitis, increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
- Other disorders: withdrawal syndrome, hyperemia, nipple discharge, gynecomastia, disruptions in carbohydrate metabolism, increased appetite, weight gain, hyperhidrosis.
If side effects occur, including those not described in clinical practice, it is recommended to stop using the capsules and consult a specialist.
Cases of overdose and possible side effects
The following side effects may occur while taking the medication:
- the appearance of headaches;
- the occurrence of rapid fatigue;
- constipation;
- fungal infections may occur;
- the appearance of dizziness;
- venous type thrombosis;
- state of drowsiness;
- problems with gait;
- the occurrence of nausea, vomiting;
- state of confusion;
- the appearance of hypertension;
- manifestation of hallucinations;
- thromboembolic condition;
- in rare cases, mental reactions appear;
- state of pancreatitis (rare);
- in rare cases, seizures occur.
If you take an increased dosage of the drug, there may be an increase in the side effects that this drug can cause.
If symptoms of overdose occur, it is necessary to immediately cleanse the gastrointestinal tract; it is recommended to take sorbents. After this, further symptomatic treatment is provided.
Article on the topic: Sulfasalazine - instructions for use, release form, composition, indications, side effects and price
Overdose
If dosing rules are violated, negative symptoms may develop.
Signs of overdose:
- respiratory disorders;

- convulsive state;
- increased heart rate;
- coma;
- increased drowsiness;
- lowering blood pressure;
- overheating of the body.
If symptoms of overdose develop, you should seek medical help for gastric lavage and other symptomatic treatments. It is also recommended to use sorbents or laxatives on your own.
First aid for an overdose of Haloperidol
Haloperidol can be removed from the body if it has already been absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood only in a hospital setting. Therefore, if an overdose is detected, you must immediately call an ambulance. And only then should you try to alleviate the condition of the victim:
- if a person is conscious, it is necessary to cleanse his stomach until the water leaves without any vomit. You should give him an enterosorbent (activated carbon, Polysorb, Smecta, Polyphepan), lay him down, calm him down, cover him with a blanket;
- when the victim has lost consciousness, he must be turned on his side so that he does not choke on the vomit. Then you need to monitor his condition until the ambulance arrives.
The doctor will perform diagnostic procedures, prescribe treatment, or decide whether to hospitalize the patient. Further detoxification will take place in the toxicology department.
special instructions
Chlorprothixene should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional. According to patient reviews, the capsules show their effect after the first days of treatment and can be addictive. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the prescribed rules for taking the drug.
Therapy should be discontinued by gradually reducing the dosage.
When taking capsules, it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol, avoid temperature changes, and also stay in the open rays of the sun for long periods of time.
The drug can have an effect on a person’s psychomotor functions, so it is recommended to refrain from driving or performing potentially dangerous work for the entire period of treatment.
Special patient groups
It is not recommended to take this medicine during pregnancy because the components may have a harmful effect on the development of the fetus.
During breastfeeding, taking the medication is also contraindicated, since the constituent elements end up in the milk.
The medication Akatinol is contraindicated for use by children and adolescents under 18 years of age. There is no information on the safety and effectiveness of treating this group of patients with this drug.
Drug interactions
The medication may enhance the sedative effect caused by alcohol consumption. It can also enhance the effect of drugs belonging to the group of barbiturates and other drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing the central nervous system.
When taking the drug and drugs aimed at lowering blood pressure simultaneously, the effectiveness of the second group of drugs may decrease.
Chlorprothixene
The combined use of capsules and lithium preparations may increase the risk of developing neurotoxic damage. Suppression of the metabolic activity of drugs is observed when combining tablets and tricyclic antidepressants.
The medication may lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of adrenergic drugs and may also cause an increase in anticholinergic drugs. Extrapyramidal disorders may occur much more frequently when the drug is used concomitantly with metoclopramide and piperazine.
The drug is incompatible with alcohol.
Taking the tablets is contraindicated with drugs that prolong the QT interval. It is recommended to avoid the combined use of capsules and thiazide diuretics. The simultaneous use of the drug and drugs that suppress cytochrome CYP 2D6 can lead to an increase in the concentration in the blood of the first drug.
Taking pills and anticholinergic drugs can lead to an enhanced effect of the second group of drugs.
Efficacy of therapy
Haloperidol is known for its severe early and late extrapyramidal side effects.
The risk of developing tardive dyskinesia is about 4% per year in younger patients. Other predisposing factors may include female gender, pre-existing mood disorder, and brain dysfunction. Akathisia often occurs along with anxiety, dysphoria, and an inability to remain still. Other side effects include dry mouth, lethargy, akathisia restlessness, muscle stiffness and spasms, restlessness, tremors, rabbit syndrome, and weight gain; These and other side effects are most likely to occur when the drug is taken in high doses and/or during long-term treatment.
With long-term treatment, depression may occur that is severe enough to lead to suicide. In order to recognize and begin to treat depression on time, you should be especially careful. Switching from haloperidol to a moderately potent antipsychotic (eg, chlorprothixene or chlorpromazine), along with appropriate antidepressant therapy, is sometimes helpful.
Sedative and anticholinergic side effects are more common in older adults. The likelihood of experiencing one or more of these side effects is quite high, regardless of age and gender, especially with long-term use. In the first few days of treatment, susceptible individuals may exhibit symptoms of dystonia, a prolonged abnormal contraction of muscle groups.
Dystonic symptoms include neck muscle spasms, sometimes developing into a tight throat, difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing, and/or tongue protrusion. Although these symptoms may occur at low doses, they occur more frequently and with greater severity with higher doses of highly effective first-generation antipsychotic drugs.
An increased risk of developing acute dystonia is observed in men and people from younger age groups. A significant side effect is the potentially fatal neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS). Haloperidol and fluphenazine are the most common causes of NMS. NMS includes fever and other symptoms.
Allergic and toxic side effects are observed. Skin rash and photosensitivity occur in less than 1% of patients. Children and adolescents are especially sensitive to early and late extrapyramidal side effects of Haloperidol. The drug is not recommended for the treatment of children. Sometimes, in cases of sudden death, prolongation of the QT interval may be seen.
In addition, the development of thromboembolic complications was also observed. Haloperidol may have a negative effect on alertness or reduce the patient's ability to drive, especially initially. Haloperidol does not have the potential to cause psychological dependence. However, due to severe side effects, patients prescribed this drug often violate the dosage regimen.
It is recommended to pay close attention to the patient's experience, and reduce or discontinue use if the patient has a high level of dissatisfaction with treatment, as this may lead to dangerously rapid discontinuation. Haloperidol has been shown to significantly increase dopamine activity, up to 98% in subjects after two weeks of "moderate to high" doses compared to chronic schizophrenia.
In another study, the patient had 90% more dopamine receptors of the D2 subtype than before treatment with Haloperidol. The long-term effect of this phenomenon is unknown, but the first study to conclude this activation is positively associated with severe dyskinesia (the greater the regulation, the higher the risk of dyskinesia).
Some studies have shown that Haloperidol has effects on brain tissue. A 2005 study of six macaques under 27 months of age compared Haloperidol with placebo, showing a significant change in brain volume of approximately 10% and a reduction in weight. In later works (2008
) in retained samples, previously reported changes were associated primarily with the loss of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, with a loss of about 5% of neurons, which was not a statistically significant result. A 2011 study in rats treated with clinical doses of Haloperidol for eight weeks found a 10-12% reduction in cortical volume.
Several studies have examined the possibility that psychosis and/or its pharmacological treatment with antipsychotics such as Haloperidol may increase patients' risk of developing cancer, particularly breast cancer in women, tobacco smoking-related cancer in men, and obesity-related disorders, as well as many other non-mental health disorders, including metabolic, cardiovascular and respiratory disorders, some or all of which may be due to decreased access to health care and treatment and smoking behavior, alcoholism, drug addiction, and eating disorders, and not due to specific pharmacological side effects.
An association has been reported between use of atypical antipsychotics such as risperidone and quetiapine and tumor growth. Before definitive conclusions can be drawn, large, controlled, randomized population-based studies are needed to differentiate drug-induced from behavior-induced morbidity.
The main causes of neurosis are psychological in nature. Therefore, medication, including neuroleptic treatment, has the status of auxiliary therapy. But antipsychotics become a necessity if a person has a pronounced neurosis-like condition. Haloperidol is prescribed during psychotherapy.
Neurosis as a reversible disorder is manifested mainly by non-psychotic disorders of psychological, neurological and somatic origin. The main symptoms of a neurosis-like state are headaches, sleep disturbances, cognitive problems in the form of memory impairment, attention, etc. In complicated cases, the clinical picture of the disease is supplemented by panic attacks, obsessive thoughts and somatic disorders in the form of visual impairment, gastrointestinal problems, etc.
Each of these symptoms negatively affects a person’s quality of life, namely the areas of communication and social activity. Stopping feeling like a full-fledged member of society, he is faced with low self-esteem, apathy, depression, loneliness, etc. By stimulating and suppressing certain areas of the brain, Haloperidol eliminates depressive and negative symptoms.
Not all specialists have a positive view of the prescription of Haloperidol and other antipsychotics in neurology. This is explained by a wide range of side effects when using the medication, which can minimize the positive results of the therapy. So, what are the undesirable reactions that Haloperidol can cause for the central nervous system and the body as a whole:
- Late psychosis - against the background of long-term use of the drug, hypersensitivity of dopamine receptors may occur, which leads to conditions such as delusions, hallucinations, etc.
- Neuroleptic deficiency syndrome is similar in clinical manifestations to schizophrenia. A person experiences inhibition, both physical and cognitive, loss of connections in society, lack of emotions, depersonalization, etc.
- Tardive dyskinesia is involuntary automatic movements uncontrollable by a person, for example, smacking.
- Extrapyramidal disorders.
- Visual disturbances, digestive system functioning, headaches.
Complications can be avoided by following the recommendations of your doctor. Self-adjustment of drug doses, abrupt cessation of treatment, combination of Haloperidol with incompatible components (alcoholic beverages, prohibited substances, certain medications) leads to a more serious condition - intoxication of the body and symptoms of overdose, which threatens irreversible mental disorders and death. This once again emphasizes that self-administration of antipsychotics or interference with a treatment regimen is fraught with unintended consequences.
Analogs
Chlorprothixene (reviews from patients who took the drug report episodes of intolerance to the components of the drug) can be replaced by other medications that belong to the same pharmacological group and have identical indications.
Analogues:
- Haloperidol. This drug is manufactured by a Hungarian manufacturer in the form of a solution for intramuscular or intravenous injection.
The main substance of the drug is haloperidol, a substance that has antipsychotic and neuroleptic effects. Indications for prescribing the solution: manic syndrome, delusional states, hallucinations, psychomotor agitation, psychosomatic disorders, behavioral disorders in children and adolescents, Terette's syndrome and Huntington's disease. The drug can also be used as a maintenance treatment for schizophrenic disorder. Before using the solution, you should definitely consult with a neuropsychiatrist, since the drug has numerous contraindications. The dosage and duration of use of the solution are calculated by a specialist according to the patient’s condition. Conditions for selling the medicine are by prescription. Prices for medications in state pharmacies start from 25 rubles. per package. - Truxal. This drug is produced in Denmark on the basis of chlorprothixene in the form of tablets for oral use. The drug belongs to the category of neuroleptics and antipsychotic drugs. It is used in the development of psychoses and psychotic states, which are accompanied by various neurophysiological reactions. The medicine is also indicated for traumatic brain injuries, psychosomatic disorders and behavioral disorders in adolescents and children. The dosage for adult patients ranges from 10 to 600 mg per day. Children are recommended from 5 to 200 mg per day. The duration of the course is individual and depends on the pathological disorder. Before taking pills, you must consult a neuropsychiatrist, as they have numerous contraindications. Terms of sale of the product - according to a doctor's prescription. You can purchase medicine in Moscow pharmacies from 400 rubles. per package.
- Prosulpin. This medication is produced by a Czech pharmaceutical company in the form of tablets for oral use. The active ingredient of the drug is sulpiride, which belongs to the class of substances that have neuroleptic and antipsychotic effects. The drug is used in combination with other psychostimulant drugs and is used for schizophrenic conditions, depression of various forms and etiologies, as well as for the development of neuroses and behavioral disorders in children, including children with autism syndrome. For psychosis, schizophrenic and depressive conditions, 200-1000 mg per day is prescribed. In this case, the dosage should be divided into several different doses. The duration of treatment is determined by the treating psychoneurologist. The tablets have multiple prescription restrictions, so before taking them you should make sure there are no contraindications. Terms of sale of the product - by prescription. The cost of packaging in pharmacies ranges from 82 to 235 rubles.
Chlorprothixene (reviews from patients who took the drug recommend extremely careful selection of a similar drug) should be replaced with a similar drug only after prior consultation with a neuropsychiatrist.
Chlorprothixene Zentiva
The drug Chlorprothixene Zentiva is produced in the form of tablets, which are intended for oral administration, as well as in the form of a solution used for injections. The kit includes instructions for use. The components of the medication are the following substances:
- hydrochloride;
- lactobiose;
- calcium salt and stearic acid;
- corn starch;
- talc;
- cane sugar;
- hypromellose;
- polyethylene glycol.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Medicine and alcohol incompatibility
The drug is recommended for use for the following health problems:
- withdrawal state;
- mental disorders;
- manic syndrome;
- schizophrenia;
- behavioral disorders;
- sleep disorders;
- excited state;
- increased activity;
- nervousness;
- clouding of consciousness;
- pain.
F.09. Mental disorder;F.10.3. Withdrawal syndrome;F.11. Mental disorders and behavioral disorders due to the use of opioids; F.20. Schizophrenia;F.29. Severe mental disorder; F.30. Manic syndrome; F.32.9. Depression;F.41.9. Increased anxiety; F.45. Psychosomatic disorders; F.48. Other neuroses; F.91.9.
Behavioral disorders;G.93.4. Non-inflammatory diseases of the brain; I.67.9. Damage to cerebral vessels; J.98.8.0. Narrowing of the bronchi; L.29. Itching; R.11. Feeling of nausea and vomiting; R.45.1. Feeling of restlessness and agitation; R.52.9. Pain;R.54. Old age;S.06. Traumatic brain injury;Z.100.0.
Preliminary drug preparation for general anesthesia.
Taking the medication can cause a number of adverse reactions in the body, which are expressed in the following symptomatic signs:
- nervous system: sleep disorders, fatigue, vestibular disorders, psychomotor activity disorders, amyostatic symptom complex, motor functionality disorder, acute dystonia, tardive dyskinesia, NMS, extrapyramidal disorder;
- heart and blood vessels: decreased systolic pressure, painful rapid heartbeat;
- digestive system: dry mouth, difficulty defecating, yellowing of the skin;
- endocrine system: severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation, secretion of milk and colostrum from the mammary glands, diabetes, sexual coldness in men and women, increased appetite, altered carbohydrate metabolism, weight gain, hyperhidrosis;
- sensory organs: keratitis, cataracts, visual disturbances, impaired clarity of the lens;
- hematopoietic system: decreased level of leukocytes, leukocytopenia, shortened life cycle of red blood cells;
- other body reactions: problems with emptying the bladder, skin rashes, inflammatory skin lesions, photosensitivity of the skin, withdrawal symptoms, flushing.
The drug should not be taken if you have the following health problems and a number of factors such as:
- increased susceptibility to the components of the drug;
- CNS depression syndrome;
- coma;
- acute vascular insufficiency;
- blood pathology;
- depression of brain functions;
- tumor with predominant localization in the adrenal medulla;
- intolerance to lactobiose or fruit sugar;
- lack of lactase;
- malabsorption of glucose-galactose;
- sucrase-isomaltase deficiency;
- children under six years of age.
The drug should not be taken by women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The drug Chlorprothixene Zentiva is intended for oral use.
The drug is used for the treatment of mental disorders, schizophrenia, manic syndrome, withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism and drug addiction, depression, neurotic disorders, psychosomatic diseases, and sleep disorders.
The medication can be taken for a long time, as it does not cause addiction or dependence. The instructions contain general recommendations for the use of the medication. Recommendations for the treatment of mental disorders, schizophrenia and manic syndrome:
- the initial dosage is 50 to 100 mg per day;
- then the dosage is increased to 300 mg per day;
- to maintain the body, it is recommended to take from 100 to 200 mg per day;
- the maximum dose is 600 mg;
- the dosage should be divided into three doses;
- Most of the drug should be administered in the evening.
Recommendations for the treatment of withdrawal syndrome:
- daily dosage is 500 mg;
- to maintain the body, it is recommended to take from 15 to 45 mg per day;
- the dosage is divided into three doses;
- The duration of therapy is a week.
Recommendations for the treatment of depression, neurotic disorders, psychosomatic diseases:
- the drug is taken in combination with antidepressants or as a single drug;
- The recommended daily dosage is 90 mg;
- The dosage is divided into three doses.
Recommendations for the treatment of sleep disorders:
- daily dosage varies from 15 to 30 mg.
- The drug should be taken one hour before going to bed.
To relieve painful manifestations, the recommended daily dosage varies from 15 to 300 mg. The medication should not be taken by patients suffering from kidney or liver diseases. Elderly patients need to adjust the dose downward on an individual basis. The daily dose is divided into three doses.
- Parkinson's disease;
- epileptic seizures;
- cardiovascular failure;
- respiratory failure;
- diabetes;
- kidney dysfunction;
- liver dysfunction;
- prostate hypertrophy;
- atherosclerosis.
During the period of drug therapy, you should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages.
The drug Chlorprothixene Zentiva cannot be taken with certain other medications due to possible incompatibility reactions, namely:
- ethanol-containing drugs, painkillers, narcotic analgesics, psycholeptics, hypnotic drugs, antipsychotics can cause excessive effects on the nervous system;
- drugs that block m-cholinergic receptors, antihistamines, antiparkinsonian drugs enhance the anticholinergic effect;
- anticonvulsants, the antiparkinsonian drug Levodopa, partially lose their effectiveness and an increase in dosage is required;
- phenothiazine derivatives, antiemetic Metoclopramide, antipsychotic Haloperidol, sympatholytic Reserpine lead to neuroleptic disorders;
- cardiotonic Dopamine, pacemaker Epinephrine, sympathomimetic Ephedrine affect vasoconstriction;
- antihypertensive drugs have an enhanced effect on the body, so dosage adjustment is necessary;
- the sympatholytic Guanethidine loses its hypotensive effect;
- the cardiac drug Quinidine increases the risk of adverse reactions.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to drink alcohol after an IV?
An overdose of the drug components can lead to the following adverse reactions of the body:
- drowsiness;
- decrease in body temperature;
- increased body temperature;
- changes in muscle tone;
- impairment of motor activity;
- twitching or immobility;
- involuntary muscle contractions;
- state of shock;
- coma.
If signs of overdose appear, the patient is recommended to provide first aid, and then contact the attending physician to receive the necessary symptomatic care. First aid:
- perform gastric lavage;
- give an adsorbent drug.
The following drugs are analogues of the drug:
- Chlorprothixene 15 Leciva;
- Chlorprothixene 50 Leciva;
- Truskal.
The drug is sold in pharmacies as prescribed by the attending physician and with a prescription from a medical institution.
It is recommended to store the drug in a cool room, out of reach of children and away from any light sources, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
The shelf life of the medicine is two years from the date of manufacture. After the expiration date and storage period, the medication cannot be used and should be disposed of in accordance with sanitary standards.
All information can be found in the instructions for use.
Price in pharmacies in Moscow, St. Petersburg, regions
The cost of the drug may vary depending on the region, sales area and sales representative of the company (pharmacy). You can find out the exact price at any pharmacy located at the patient’s place of residence.
| Region, region | Dosage, packaging | Price |
| Moscow, Moscow region | Tablets, 15 mg | 129-447 rub. |
| Saint Petersburg | Tablets, 50 mg | 172-501 rub. |
| St. Petersburg (suburbs) | Tablets, 25 mg | 538-773 rub. |
| Leningrad region | Tablets, 50 mg | 119-630 rub. |
| Novgorod region | Tablets, 15 mg | 80-473 rub. |
Before using Chlorprothixene, you should carefully read the instructions for use of the product and consult with your doctor. As an addition, it is recommended to read the reviews of patients who took the drug in the treatment of psychoneurological pathologies.
Purchasing the product and its analogues
The price of a package of Memantine tablets with a dosage of 10 mg in an amount of 10 pieces is 1,600 rubles. Sets of tablets 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg 7x4 cost from 1800 rubles.
The medicine should be stored in a dark place, out of reach of children, at a temperature of no more than 25 degrees Celsius.
Analogs of Akatinol (products based on Memantine and other active ingredients):
- Marux;
- Memantinol;
- Vitrum Memory;
- Noogeron;
- Intellan;
- Tanakan;
- Memantine Canon.