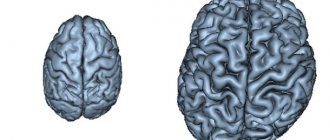
The diagnosis of ventriculomegaly is made when pathological enlargement of the lateral ventricles of the brain is detected. In this condition, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles to the spinal cord is disrupted. Ventriculomegaly in a child can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, neurological problems, and the development of cerebral palsy.
To prevent the disease, pregnancy planning is necessary. This makes it possible to prevent the future impact on the fetus of infections that the parents may have, medications taken, or hereditary factors that could lead to the development of ventriculomegaly; What is dangerous about the lack of medical control during pregnancy is the lack of possibility of early correction of any abnormalities.
Causes, manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus is an enlargement of the lateral ventricles of the brain.
The pathology occurs during fetal development and leads to disruption of the functionality of the central nervous system. Newborns with this diagnosis experience neurological disorders and developmental delays.
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 10th revision, the disease is included in group Q00-Q07 - “Congenital anomalies (malformations) of the nervous system.”
Normative and pathological parameters of BZ
Analysis of fetal brain structures is carried out in the second trimester, between 18 and 27 weeks of pregnancy. In most cases, pathological changes are detected on routine ultrasound. The diagnosis is also made at 30-33 weeks of pregnancy.
Table of the norm of the lateral ventricles (LV) in the fetus
| Age of the fetus / child | BZ width in mm |
| 18 weeks | 4,9 – 7,5 |
| 27 weeks | 5,6 – 8,7 |
| newborn | 23,5 |
| 3 months | 36,2 |
| 6-9 months | 60,8 |
| 12 months | 64,7 |
Discrepancies in parameter measurements of 0.1-0.3 mm are normal.
Degrees of ventricular dilatation (by how many mm do they increase from standard values):
- 1st (mild, insignificant) – an increase in the depth of the bodies of the 1st and 2nd basins from 5 to 8 mm, the lateral curvature is smoothed out, the outlines become more rounded, the 3rd and 4th ventricles remain unchanged;
- 2nd (moderate severity, moderate) - the body expands to 9-10 mm above the norm, the increase is uniform on all sides, the 3rd ventricle increases by 6 mm, 4 - within the anatomical norm;
- 3rd (severe, pronounced) - the depth of the bodies expands by 10-21 mm or more in all ventricles, the subarachnoid cisterns of the brain increase.
The disease is unilateral (left-sided, right-sided) or bilateral (biventriculomegaly).
What is the cause of the pathology
One of the reasons for the development of ventriculomegaly in the fetus is a viral infection in early pregnancy, TORCH syndrome. The disease can be triggered by an infectious lesion of the brain during the perinatal period (prenatal).
Rarely, the cause of the pathology is neonatal sepsis - blood poisoning in an infant during the first 28 days of life.
In many sources you can find information that in most cases the disease is diagnosed in children whose mothers are over 35 years old.
This is argued by the high risk of genetic damage in a woman’s body. There are no clear WHO statistics (percentages) on this issue, and clinical practice refutes this statement.
Children with ventriculomegaly are also born to women aged 20-28 years.
At the Detroit Medical Research Center (USA) from 1992 to 1994. Pregnant women were monitored during the prenatal period.
The scientific data obtained are presented in the publication “Mild Isolated Ventriculomegaly: Associated Anomalies and Observations” Mark W. Tomlinson, Marjorie C. Treadwel, 1997.
Women whose fetuses had enlarged lateral ventricles by 11-15 mm underwent cytogenetic tests. In 10-12% of cases, a positive relationship was found between the disease and chromosomal abnormalities.
Factors leading to the development of pathology:
- multifunctional immaturity of the central nervous system;
- increased reabsorption (reabsorption) of bicarbonates by the kidneys, resulting in metabolic acidosis (blood oxidation);
- disturbance of fetal hemodynamics (blood movement along the vascular bed);
- perinatal hypoxia (intrauterine oxygen deficiency);
- injuries during labor.
The listed factors lead to the disease not only in infants, but also in children and adolescents under 18 years of age. Ventriculomegaly is extremely rare in adults.
The scientific publication “Neurosurgery and Neurology of Children” by L.V. Kuznetsova, 2007, contains data from numerous clinical studies. According to their results, 50-64% of patients have stable ventriculomegaly of unknown etiology (idiopathic).
How does the disease manifest itself?
The disease often occurs without neurological symptoms. There is also no hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. This means that the disease is not characterized by increased intracranial pressure.
At the initial and middle stages, external changes in the anatomy of the head are not observed. If there are no deviations in the child’s behavior or psyche, parents are not able to independently detect the disease. A pediatrician may suspect a pathology during a routine examination in the first months of life.
Severe ventriculomegaly in a small child develops when the disease is advanced. The volume of the head noticeably increases, the frontal parts protrude, and the superficial veins swell.
Subjective symptoms:
- convulsions, epileptic-type seizures;
- headaches of varying intensity;
- sleep disturbance, decreased physical activity;
- retardation in physical development (slow weight gain, stunted growth).
Diagnosis of the disease
Acquired ventriculomegaly in a newborn is diagnosed during a comprehensive examination. Laboratory tests and instrumental studies are performed as part of differential diagnosis. The disease must be distinguished from hydrocephalus.
With ventriculomegaly, the width of the ventricular bodies varies from 0.6 to 1 cm. Signs of neuronal maturation are poorly expressed. The ratio of the width of the germinal and new zones of the cerebral cortex is 1:2.
With internal hydrocephalus, the ventricles expand evenly in all directions by more than 1 cm. The brain parenchyma is atrophied, with a jelly-like consistency. The cortical plate narrows. The germinal layer is much wider than the neocortex, their ratio is 2:1.
Indicators of ultrasound and MRI performed before and after childbirth differ significantly in 57-83% of cases. If ventricular dilatation is detected in the fetus, do not panic.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a repeated ultrasound and tomographic examination of the newborn.
Such arguments are presented in the publication “Frequency and causes of discrepancies in diagnostic images in children with ventriculomegaly” GM Senapati, 2010.
Treatment
In infants, with the expansion of the gastrointestinal tract, the hemodynamics of blood vessels and anterior cerebral arteries are disrupted during the first 2-3 weeks of life, and the pH of the blood shifts to the acidic side. The child's body compensates for these phenomena. If compensatory mechanisms fail by the end of 4 weeks of life, Diacarb is prescribed.
A diuretic belongs to the group of diuretic drugs that are prescribed for epileptic seizures and disruptions in the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid. The drug is prescribed with caution, monitoring kidney function, as it has a nephrotoxic effect. Diacarb can increase blood oxidation.
Infants are prescribed antihypoxants to eliminate oxygen deficiency. Saturation of the brain with O2 improves the functionality of the central nervous system.
B vitamins have a positive effect on the immature nervous system, normalize metabolic processes at the cellular level, and synthesize hemoglobin. If the expansion of the gallbladder is caused by an infection, the woman is prescribed antibiotics.
Neurosurgical treatment is indicated for children if the disease progresses to hydrocephalus, when a large amount of fluid accumulates in the brain. If the condition of the fetus during gestation is extremely serious, there is a high probability of incompatibility with life, it is recommended not to give birth.
Consequences of pathology
Ventriculomegaly with chromosomal consequences in the fetus after birth is manifested by Down syndrome in 70% of children. In 30% of cases, trisomy on the X chromosome is diagnosed - the eyes are set at a great distance from each other, a characteristic type of curvature of the fingers, epicanthal (Mongolian) folds of the upper eyelid hanging over the inner corner of the eye.
Rare consequences associated with chromosomal mosaicism (scientific publication “Prenatal finding in a fetus with mosaicism due to two chromosomal rearrangements” RJ Hastings, SG Watson, LS):
- Klinefelter syndrome - manifests itself only in boys during puberty (erectile dysfunction, infertility, endocrine disorders - diabetes, thyroid disease);
- Edwards syndrome - diagnosed 3 times more often in girls - birth weight does not exceed 2 kg, while pregnancy proceeds normally; there are anomalies in the structure of the skull, narrow palpebral fissures, deformed ears, heart defects;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome – malformations of internal organs, gonads, short stature;
- de la Chapelle syndrome - typical for boys - when they become adults, infertility appears, the absence of secondary sexual characteristics (male pattern hair), mental and physical development remains normal.
In clinical practice, the following consequences of severe progressive ventriculomegaly have been encountered (an increase in cerebral ventricles in the fetus to 27 mm):
- Fanconi anemia - the gradual development of a deficiency of all blood cells;
- aplasia of the radius - a developmental defect, the absence of a section of bone;
- ectopia of the kidneys - incorrect location of the organ.
Moderate isolated ventriculomegaly causes neurological complications in 10% of cases.
90% of children with a similar diagnosis develop in accordance with their age, the indicators of their psychomotor, neurological, and intellectual development are the same as those of peers with normal BD sizes.
An increase in the ventricles by 4 mm, provided there is no progression, is not a pathology. Children with this disorder are not treated; it does not affect the quality of life.
Source: https://vsepromozg.ru/oslozhneniya/ventrikulomegaliya-u-ploda
Lateral ventricles of the fetal brain
The ventricular system is a capacitive structure of the brain. Its purpose is to synthesize and store cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid, called cerebrospinal fluid, is responsible for a number of functions in the body.
It acts as a shock absorber, protecting the thinking organ from external damage, and helps stabilize intracranial pressure.
Without cerebrospinal fluid, metabolic processes between the brain and blood cells would be impossible.
How is the structure responsible for the synthesis of this essential fluid represented in the human body? A table illustrating the normal four-cavity structure of the ventricular system of the brain in humans will help answer the question:
Treatment of ventriculomegaly
The goal of treatment for ventriculomegaly:
- eliminate the causes of the disease;
- prevent negative consequences that may manifest themselves later.
Since the disease is detected in the fetus in the womb, treatment is prescribed to the expectant mother. Mild degrees of the disease generally do not require drug intervention. In such cases, constant monitoring and monitoring of the condition of the mother and fetus is indicated.
Serious pathological phenomena in the fetus require immediate intervention, so expectant mothers are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- antihypoxants;
- diuretics;
- vitamins.
Massage and exercise therapy are indicated.
A pediatrician and neurologist prescribe antihypoxants, diuretics and vitamins as drug therapy.
To treat ventriculomegaly, massage and physical therapy (static exercises with loads on the pelvic muscles and pelvic floor) are prescribed.
As medications intended to prevent the development of neurological disorders in a child, drugs are prescribed that are aimed at retaining potassium in the body.
Normal ventricle sizes
The volume of each ventricle directly determines how much cerebrospinal fluid is synthesized or stored in it. If the size of the structure exceeds normal, there is a risk of overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid or problems with its removal, which cannot but lead to malfunctions in the functioning of the thinking organ.
What is the usual ventricular depth in newborns? According to the observations of neonatologists, normal values will be approximately as follows:
Over time, as the newborn's brain begins to grow, the depth of its internal cavities will gradually increase. If the expansion of the ventricles occurs sharply, and their proportions cease to be linearly consistent with the size of the skull, this, like a congenital deviation from normal values, is a reason to sound the alarm.
What will you need for an ultrasound?
Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics does not require special preparation. The procedure itself is also not a complex manipulation. At this stage, there is no need to fill the bladder, since there is already enough amniotic fluid to examine the structure of the areas of interest. Eating food before the procedure does not in any way affect the results of the ultrasound.
Many clinics do not indicate the need to bring anything with you; otherwise, you will be warned about this in advance. Most often, for the procedure, the patient may need a diaper and napkins. The diaper will need to be placed on the couch, since the ultrasound is performed in the supine position. Wipes are used to wipe away excess gel.
Causes of enlarged ventricles of the brain
Sometimes a slight discrepancy between the size of brain structures and normal values is genetically determined. This feature is detected already during the initial examination of the baby and, as a rule, is not considered pathological. At the same time, noticeable dilatation or asymmetry of the ventricles may be the result of a serious chromosomal abnormality that arose during the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Doctors have also identified a number of non-genetic factors that provoke the expansion of brain cavities. These include:
- infections suffered by the child's mother during pregnancy;
- pathologies of fetal development caused by chronic diseases of the parent;
- sepsis;
- entry of a foreign body into the liquor spaces;
- hydrocephalus of unknown etiology;
- the occurrence of tumors and other neoplasms in the brain;
- birth injuries and complications.
Information content of ultrasound at 19 weeks
With the help of ultrasound diagnostics, at this period it is possible to ascertain the degree of formation and development of the functional systems of the fetal body, and to assess the condition of the woman’s reproductive organs. The baby at the 19th week of pregnancy is already developed so much that an ultrasound will tell about:
- The activity of movements and their purposefulness
- Formation of tooth buds
- Development, first of all, of the nervous, urinary and muscular systems
- Child's field (with body position available for viewing)
- Body proportions, anatomical features
- The size of the fetus - its weight and height
- The number of heartbeats and respiratory acts
- The presence of pathologies such as: hydrocele of the brain, Down syndrome, developmental retardation, malnutrition, abnormal body constitution, fetoplacental insufficiency)
- Condition of the umbilical cord
- Degrees of placenta maturity
- Condition of the uterus
- Quantity and quality of amniotic fluid
An addition to the standard ultrasound procedure is vascular Doppler. This study is carried out in the same way as ultrasound. Doppler ultrasound allows you to evaluate blood circulation in the functional system “uterus-placenta-fetus”: the direction of blood movement through the vessels, its speed.
Consequences of pathology in children
Depending on the severity and location of the problem, the consequences of enlarged cerebral ventricles for the child also vary. As a rule, the pathology in question is completely harmless.
The prospects for its development are unpleasant, but not fatal. Enlargement of the ventricles leads to an increased concentration of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain spaces, which increases the pressure on local nerve endings.
As a result, complications arise such as:
- defecation disorders;
- problems with urination;
- periodic failure of the senses (temporary blindness or deafness);
- impaired coordination of movements;
- delays in mental and physical development.
The resulting hemorrhage can lead to:
- epilepsy;
- permanent loss of hearing or vision;
- paralysis or coma;
- instant death.
Fetal cerebellum by week: table (normal, pathological)
Each pregnant woman undergoes at least 3 ultrasound screening examinations as planned. During its implementation, specialists monitor the condition of the fetus, the dynamics of its growth and the absence of congenital developmental pathologies. The obtained data are compared with tabulated values of normal fetometry values for each gestation period.
Cerebellum table by week
The most informative, from the point of view of detecting pathologies of brain development, is screening 2. It is performed around the 20th week of pregnancy. At this time, the fetus is already fully formed, so having the examination results in hand, specialists can determine whether there are any deviations or pathologies in development.
Particular attention is paid to the condition of the cerebellum of the brain. Normally, it consists of 3 parts: 2 hemispheres and a worm. It is this part of the central nervous system that is responsible for coordinating movements.
Hypoplasia (delayed development) of this rudiment of the brain can lead to serious consequences: the child will not be able to maintain balance, perform coordinated actions, and will have problems with gait and smooth movements. With this pathology, speech problems often arise.
When identifying hypoplasia, specialists pay attention to the value of the interhemispheric size of the cerebellum. It is determined based on data obtained using ultrasound of the fetal brain in a transcerebellar section. Normally, the interhemispheric size (IH) in the 2nd trimester should be equal to the gestational age.
Fetal cerebellum by week (table), MRM norm, in cm.
To enlarge, click on the table.
Normal indicators
Measuring the interhemispheric space of the fetal cerebellum using ultrasound equipment is most informative before the 20th week of pregnancy, due to the fact that later it will be difficult to do this - the child becomes larger, the bones of his skull become thicker.
MRM is determined by horizontal scanning of the fetal head with an ultrasound probe at the level of the 4th ventricle at the maximum distance of the extreme lateral boundaries of the opposite hemispheres of the “small brain”. If this cannot be done, then this value is measured in another section.
In the vast majority of cases, the interhemispheric size of the cerebellum corresponds to the gestational age of pregnancy, this makes it possible to clarify the presence of central nervous system pathologies - developmental delays.
According to the table values, the size of the fetal cerebellum at 36 weeks of pregnancy is less than 5.2 cm, at 37 - already 5.2 cm, at 40 - more than 5.8 cm. It has been noted that newborns with an interhemispheric cerebellar size of more than 5.3 cm after birth are mature. Thus, it follows that for a functionally mature newborn child, the MRM value should be greater than or equal to 5.3 cm.
Identification of pathology and its causes
Deviations in the values of the MRM and its structure during ultrasound imaging indicate the presence of pathologies. It could be:
- Violation of morphogenesis (formation). Anomalies of the structure of the cerebellum and posterior cranial fossa: Gendry-Walker malformation (hypoplasia of the vermis, its low location; dilatation of the 4th ventricle, increase in the size of the posterior cranial fossa), aplasia, hypoplasia. Anomalies in the development of the rhombencephalon - rhombencephalosynapsis, in which the cerebellar hemispheres merge with the dentate nuclei uniting along the midline, tectomerbellar dysraphism - the “small brain” is located inside the 4th ventricle.
- Hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis.
- Disorders of cortical organization. Defects in the structure of the cerebellar cortex are a fairly common pathology of the central nervous system. Due to the fact that its influence on the organization of the central nervous system is not great, it is rarely diagnosed. Usually this is degeneration (destruction) of the granular layer of the rudimentary cortex, hypertrophy (increase in volume) of the granular layer.
- Cysts, neoplasms.
A large number of factors can cause the development of pathologies of the cerebellar structure, including:
- Heredity. It plays an important role, for the reason that any physiological abnormalities in parents in the future can affect the development of the child. Before planning a pregnancy, a woman and a man must undergo a series of examinations and tests to identify the risk of developing pathologies in their offspring.
- Unfavorable environment. Pollution of nature by products of the petrochemical industry, exhaust gases, high content of carcinogens and pesticides in food affects the health of future parents. Therefore, the risk group for developing various pathologies of the central nervous system includes children whose parents work in hazardous industries, interact with toxic substances, or live near large industrial plants or in areas with high background radiation.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. Smoking, alcoholism, and drug use by parents affect the health of future children.
- Infection. The penetration of dangerous viruses and pathogenic bacteria into the body of the expectant mother can result in dangerous pathologies for the baby. Pregnancy can end badly if infection occurs before 12 weeks of pregnancy. Over long periods of time, pathogens can cause various pathologies in the fetus. For example:
- toxoplasmosis provokes the development of microcephaly, meningoencephalitis, hydrocephalus, and central nervous system damage in a child.
- rubella causes deafness, blindness, glaucoma and damage to the fetal skeletal system;
- hepatitis B is dangerous due to the high probability of the virus penetrating the fetus through the placenta, in which case approximately 40% of children do not live to see 2 years of age;
- cytomegaly, can cause blindness, deafness, liver cirrhosis, gastrointestinal damage, encephalopathy;
- Treponema pallidum – damage to the skeletal system, liver, kidneys, central nervous system, congenital syphilis;
- gonococcus - eye diseases, sepsis, conjunctivitis, in a pregnant woman - inflammation of the fetal placenta.
Prevention of the development of various pathologies of the central nervous system consists of preventing exposure to the above risk factors. Expectant parents are advised to take care of their health long before conception and monitor their diet and lifestyle. During pregnancy, a woman needs to undergo routine screening (especially at 20 weeks of pregnancy) and monitor her condition.
Fetal cerebellum by week: table (norm, pathology) Link to main publication
Source: https://GolovaiMozg.ru/deti/mozzhechok-ploda-po-nedelyam-tablitsa-norma-patologiya
Ventriculomegaly of the fetal brain | Women's magazine online - EVA.RU | Pregnancy
- Dear mothers, good afternoon! I have a DISASTER!!! My pregnancy is 32-33 weeks. The entire pregnancy proceeds without problems: no illnesses, no swelling, everything is easy and good, tests, ultrasounds and screenings are completely normal! And suddenly: the day before yesterday, at the next ultrasound, my baby was diagnosed with RIGHT VENTRICULOMEGALY of the lateral ventricle of the brain. The left ventricle is normal. And the right one is enlarged by almost 2 times! And they immediately said: don’t do anything yet, don’t panic. An accurate diagnosis is made over time. In 1.5 weeks, another ultrasound and if it’s the same or worse, then measures (I don’t know what) I’ve been living in a nightmare for two days now! Please, be so kind! Please tell us who knows what about this? Who came across!? What they were doing? How did you deal with this? I'm WORRIED: what if we need to start therapy now - to help the baby reduce swelling or whatever is wrong with the ventricle? I will very, very, very much wait for your answer! Write, please, either by email or just in case, my mob: 8-916 -424-25-27 Best regards, Elena
- Yeah. 11.5 so far. Studying in 4th grade. The awesome guy is growing up. Lover of blondes. There are persistent problems (speech, balance), but they do not interfere with life. I mean, they don't interfere with him.
- This is not treated in utero. My son was diagnosed with fetal ventriculomegaly (in 2004). It is important to carry out a diagnosis after the birth of the child, do an MRI of the brain and determine what kind of abnormality there is. My son had ventriculomegaly as a sign of Dandy-Walker malformation, but this is only a particular happening.
- Thank you!!! I’m really looking forward to the ultrasound, which will be with another doctor at the beginning of next week. I will study your articles. Thanks again!
- Please excuse me! Did I understand correctly: your son had this diagnosis? Inside the womb? Oh, how I would like to chat with you! Is this possible?
- Was your son diagnosed in utero? Were both ventricles large? Don't remember the measurements? And are you convinced that they are not treated before birth? Tell me, do you know of cases where they return to normal even before birth? What is the reason for the enlargement of the ventricles if the pregnancy is ideal?
- Yes, of course, write to me by email, I’ll send you a personal email.
- In utero, yes. Both, yes. But I don’t remember the measurements. We need to look, but here’s where... I personally haven’t encountered a return to normal, I’m not a doctor. The point is, what is behind the expansion of the ventricles, what exactly will be the diagnosis after birth. If it was an expansion as a result of swelling, then it may return to normal. But swelling does not happen without a reason. The reasons for the increase are varied. Well-being during b. not an indicator. This could be a hereditary cause, a virus in the early stages, some undiagnosed diseases in the mother, or intrauterine infection. There are a lot of reasons.
- Thank you for your detailed answer! I am waiting for the ultrasound trace with incredible hope and praying that everything will be fine! Fine!
- How are you doing? I found information on Eva, hurray, it was there after all. The dimensions of the lateral ventricles of the brain - at 24 weeks it was 9.5 mm, at 27 - 10.4 mm - that is, again a borderline value. Bottom line: this is not was a chromosomal abnormality. Due to obstetric and gynecological problems, fetal development was impaired. One option: the effect of the virus on a weakened body. During that pregnancy there were: 3 pyelonephritis (including in the early stages), there was sugar in the urine. 17-OP increased. Increased blood clotting, asterisks **** (highest degree). And all this was in one pregnant carcass ((For some reason, TSH was not controlled at all. It is likely that there were inflated values there too.
- To my great regret, a second ultrasound from a more competent specialist confirmed everything. In addition, the ventricles seem to have grown. One up to 20mm and they also added some kind of diagnosis... I’m worried - I can’t. Tomorrow I’m going to get an MRI. We will build on it further in our steps... Dynamics trace. ultrasound 8.02. The most important thing for us is that the ventricles do not grow beyond what they are now!!!!! Otherwise, we may even need early delivery... Lord, help us! I’m already exhausted, I’m so worried... Tomorrow is an MRI, which should give us a clearer picture. But I still have a hard time understanding what exactly. I only know that it is more accurate than ultrasound. And then I will rush to neurosurgeons!!!!!!!!!!
- Is it possible to have an MRI during pregnancy? I didn’t understand anything about your MRI at all
- I didn't expect it myself!!! It turns out that it is possible - according to the indications: according to it, the whole picture is more accurately visible, and it is also possible to begin planning further treatment immediately after childbirth, because everything is clear. And today they told me (but I’m not sure) that it is possible to determine the cause of the disease. I’m only going tomorrow, so I’ll take a day or two to decipher it and only then will I go to the specialist who interprets it and we’ll consult and ask questions!
- You can have an MRI, yes. During the second pregnancy, the geneticist immediately prepared a strategy: if the ultrasound showed abnormalities in the brain, then an MRI would be prescribed. MRI is indeed a very informative type of study. It was only thanks to him that Vanya received an accurate diagnosis. Good luck! Don't get lost, write your news. (I read your topic on the family).
- Thank you! If you don’t mind, tell me about the MRI: there will be a machine on the outside of my head (I have claustrophobia) and for how long? Thank you!
- And it depends on what kind of MRI machine, they are different. If there is a pipe, then most likely the head is outside. On average, an MRI takes about 20 minutes, they look at different sections. It’s not scary, but it’s noisy. It probably won’t be very comfortable to lie on your back. Well, remove all the chains, remove everything metal. They will ask if you have a pacemaker or artificial metal inserts in your body.
- I'm so worried…. Most of all, of course, what information we learn….
- After the study, will they be able to at least look right away? Approximately: what is there?
- Nowadays there are open devices almost everywhere. many are afraid of closed ones - we should have clarified in advance.
- Not likely right away. Because there is a series of pictures from different positions, sections, etc. All this needs to be analyzed wholesale and retail and takes quite a lot of time. Sometimes the conclusion needs to wait several hours, and sometimes days. But you can ask the specialist who does the MRI, and suddenly he will say something. I would ask, even if I was sure of a negative answer. It’s better to hear with confidence that there won’t be any information right now, than to be tormented later that you didn’t ask anything.
- Whatever the information, everything is for the better - the unknown is much harder. Mom’s brain doesn’t even have anything to work with. It suffers at idle, like an internal combustion engine without lubricating oil.
- after an MRI of the spine, the results were given within 20 minutes
- Only the open ones definitely have much less
- The result of the MRI of the GM (mine) was also given quickly. And the MRI data of the son’s brain was analyzed for 24 hours. In one center...Everything can happen, of course. Maybe they’ll describe it quickly.
- Lena, I have a question. You write that up to 7.5 months there was an ideal pregnancy. That is. were the screenings (both the first and the second) both for ultrasound and biochemistry ideal? Are these all PAPP-A, beta-hCG, ACE, estriol and inhibin A?
- Before pregnancy, we prepared for six months. A bunch of tests, etc. All this before and during the treatment was carried out by the doctors at the Center for Surveillance and Rehabilitation. Everything is normal. They approved it and did it and are doing it now. All tests, screenings, everything everything was normal. And at 33 weeks at the next ultrasound - boom!!!! I did an MRI of the fetal head (for me the procedure was a test because I have claustrophobia) on Thursday. On Friday (yesterday) I took it and went straight to the neurosurgeon. While I was driving I almost died (what was it?)… He essentially confirmed everything. I believe that these two diagnoses are still hanging over us (ventriculomegaly of both ventricles is significant, agenesis of the corpus callosum). Everything else is normal, THANK GOD!!! But these diagnoses also torment me. It is UNknown how they will behave further..... And forecasts And it is also important to me: where did they come from!????? If the Lord has mercy...... then they will change in a favorable direction or at least stabilize! I can’t breathe and live! So hard!!!!
- What do your doctors say when asked “where did it come from?” Where did it come from - this is the most tormenting question at first... The ultrasounds of the 1st and 2nd screening were done according to the standards for sure? Biparietal size of the head, parts of the brain should have been examined specifically - the lateral ventricles, 4th ventricle, corpus callosum visible from 12-13 weeks (according to CTR). And at 20 weeks they look even more closely... I understand you very much, I sympathize with you very much.
- Elena, good afternoon, please tell me how are you doing now? What's wrong with the child? How did you give birth and at what week? We just have the same situation, 30 weeks, the left ventricle is 19 mm, I’m in despair, I don’t know what to do, should I continue the pregnancy or not?
- What does it mean to leave a pregnancy? At 30 weeks, this is already a full-fledged child who can easily survive (if the conditions exist and his defect allows). No one will give you an abortion at this time. At most, they will arrange a premature birth, but doctors will have to fight for the child’s life because period 30 weeks... And what will this give? What if it was a misdiagnosis? Won't you regret it later? Wait until your due date and give birth. Write a refusal, suddenly the child will not be what you need...
- I was also surprised by the wording... should I leave it at 30 weeks.....
Source: https://eva.ru/pregnancy/messages-3408518.htm
How to treat ventriculomegaly
If significant ventriculomegaly is detected in the fetus, the question of artificial termination of pregnancy may arise. Sometimes this is necessary, because children born with such a pathology can be doomed to lifelong suffering or early death. With moderate severity of ventriculomegaly, the symptoms of which do not progress, therapy is prescribed in the prenatal period.
When ventriculomegaly is detected in a fetus, first of all they try to identify the causes. It is important to check if the mother has any infectious diseases that need treatment. Next, tendencies to hereditary ventriculomegaly are examined. It is known that with chromosomal abnormalities, other developmental defects can be added to the disease - Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.
If the conditions described above are not found, but there is only a pathology in itself, isolated ventriculomegaly, treatment includes taking diuretics, such as Diacarb, designed to remove excess fluid from the body. At the same time, additional potassium intake is prescribed to compensate for its loss. For ventriculomegaly in the fetus, antihypoxants are also indicated to help saturate tissues with oxygen. Massage sessions and therapeutic physical exercises are also necessary to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
The pediatrician and neurologist decide how to treat ventriculomegaly. In serious cases, the help of a neurosurgeon is necessary. It may be needed in cases of concomitant genetic pathologies or the presence of increased cranial pressure. The diagnosis of ventriculomegaly requires careful attention and constant medical supervision.
All of the above measures are taken to reduce the tendency towards more severe ventriculomegaly and help prevent the development of neurological disorders. Sometimes treatment for ventriculomegaly can be surgical. With significant enlargement of the ventricles, when the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is very difficult, an operation may be necessary to install a shunt through which excess fluid will be removed. Surgery for ventriculomegaly in an infant can be performed soon after birth. The very absence of excess fluid, and therefore pressure in the brain, usually immediately has a positive effect on the general well-being of children. After this treatment of ventriculomegaly, the child’s sleep improves and there are no headaches.
Norm and pathology on ultrasound of the fetal head during pregnancy at 1st, 2nd and 3rd screening
Ultrasound for pregnant women is a screening method of examination. The medical term “ultrasound screening” is an examination of absolutely all pregnant women within a specified period of time in order to identify intrauterine malformations of the fetus.
A screening test is carried out three times during pregnancy:
- I screening – at 11-14 weeks;
- II screening – at 18-22 weeks;
- III screening - at 32-34 weeks.
Ultrasound of the fetal head at 1st screening
At the end of the first trimester, the expectant mother is prescribed the first ultrasound screening in utero in order to exclude such gross malformations of the fetal head as pathology of the brain, skull bones and facial skeleton.
The doctor evaluates the following fetal structures:
- contours of the bones of the cranial vault for their integrity;
- brain structures that normally look like a “butterfly”;
- measures the length of the fetal nasal bone (at 11 weeks its presence or absence is indicated, and at 12-14 weeks the norm is from 2 to 4 mm);
- biparietal size (BDS) of the head - measured between the most prominent points of the parietal bones of the fetus. The average normative value of BPR in the period of 11-14 weeks is from 17 to 27 mm. The doctor will look at these indicators in a special table.
If everything is fine with your fetus, the doctor will write down the following in the ultrasound report:
- bones of the cranial vault – integrity preserved;
- BPR -21 mm;
- the choroid plexuses are symmetrical, in the shape of a “butterfly”;
- the length of the nasal bone is 3 mm.
What head pathology occurs during the first ultrasound screening?
Particular attention is paid to assessing the length of the fetal nasal bone. This is an informative criterion for early diagnosis of Down syndrome.
Examination of the skull bones already at the end of the first trimester makes it possible to identify such severe developmental abnormalities as:
- acrania;
- exencephaly;
- anencephaly;
- cranial hernia.
Anencephaly
– the most common defect of the central nervous system, in which brain tissue and skull bones are completely absent.
Exencephaly - the skull bones are also absent, but there is a fragment of brain tissue.
Acrania is a developmental defect in which the fetal brain is not surrounded by the bones of the skull.
It is important to know! With these three defects, the death of the child occurs. Therefore, if they are detected at any stage of pregnancy, it is proposed to terminate it for medical reasons. In the future, the woman needs genetic counseling.
A cranial hernia is a protrusion of the meninges and brain tissue through a defect in the bones of the skull. In this case, a consultation with a neurosurgeon is required to find out whether it is possible to correct this defect with surgery after the birth of the child.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the fetal head at 2nd screening
During the second screening, close attention is also paid to the brain and facial skeleton. Identifying pathologies of fetal development makes it possible to warn future parents about possible consequences and obtain information about the long-term prognosis.
Important indicators during examination are biparietal size (BPR), fronto-occipital size (FOR) and fetal head circumference. All these important measurements are carried out in a strictly cross-section at the level of certain anatomical structures.
The doctor evaluates the shape of the fetal head using the cephalic index (BPR/LZR ratio). Variants of the norm are:
- dolichocephalic shape (oval or oblong);
- brachycephalic form (when the skull has a rounded shape).
Important! If the fetus is found to have a lemon- or strawberry-shaped head, this is bad. It is necessary to exclude genetic diseases and concomitant malformations.
A decrease in these indicators ( a small head in the fetus ) is an unfavorable sign in which it is necessary to exclude microcephaly (a disease characterized by a decrease in brain mass and mental retardation).
But a small head circumference does not always indicate pathology.
So, for example, if all other dimensions (abdominal circumference, thigh length) are also less than normal, this will indicate intrauterine growth retardation, and not a malformation.
With an increase in the BPR and head circumference ( large fetal head ), they may indicate hydrocele of the brain or the presence of a cerebral hernia. If during fetometry (measurement of the fetus) all other indicators are also higher than normal, then an increase in the BPR indicates a large size of the fetus.
By the time of the second screening, all the anatomical structures of the brain have already formed and they are well visualized. Measuring the lateral ventricles of the brain is of great importance. Normally, their dimensions should not exceed 10 mm (on average 6 mm).
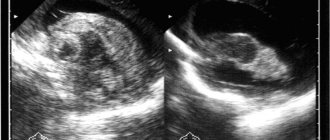
Note! If the lateral ventricles of the fetal brain are dilated from 10 to 15 mm on ultrasound, but the size of the head is not enlarged, this condition is called ventriculomegaly .
Chromosomal abnormalities, infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, and intrauterine fetal hypoxia can lead to expansion of the lateral ventricles and ventriculomegaly.
Ventriculomegaly can be:
- symmetrical (when the lateral ventricles of both hemispheres of the brain are expanded);
- asymmetric (enlargement of one of the ventricles or its horn, for example, left-sided ventriculomegaly);
- can exist in isolation from developmental defects;
- or combined with other vices.
In mild to moderate cases, careful dynamic monitoring of the size of the ventricles of the brain is necessary. In severe cases, this pathology can develop into fetal hydrocephalus (or hydrocephalus). The earlier and faster the transition from ventriculomegaly to hydrocephalus occurs, the worse the prognosis.
It can be very difficult to answer parents’ questions about how pronounced the neurological manifestations of their unborn baby will be with such a deviation and what his psychomotor development will be like. And if there is a question about terminating a pregnancy after the discovery of this pathology, you should follow the recommendations of doctors.
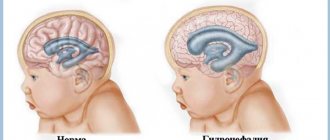
Hydrocephalus –
another brain pathology that is detected on ultrasound.
This is a condition when there is an increase in the size of the ventricles of the brain by more than 15 mm due to the accumulation of fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) in their cavities with a simultaneous increase in intracranial pressure and leading to compression or atrophy of the brain. As a rule, this pathology is characterized by an increase in the size of the fetal head.
It should be said that the most unfavorable prognosis will be when ventriculomegaly/hydrocephalus is combined with other developmental defects, chromosomal abnormalities, as well as with isolated hydrocephalus.
At the second screening, special importance is given to assessing the anatomy of the cerebellum (it consists of two hemispheres that are connected to each other by the so-called cerebellar vermis). The cerebellum – translated as “small brain”, is responsible for the coordination of movements.
Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the cerebellar vermis can lead to disastrous consequences:
- the ability to maintain balance is lost;
- lack of muscle coordination;
- smoothness in movements is lost;
- problems appear with gait (it becomes staggering, like a drunk);
- tremors appear in the child’s limbs and head, and slow speech.
Very important for identifying this pathology is the measurement of the interhemispheric size of the cerebellum.
By making a “cut” through the cerebellum, the doctor assesses the size of the cerebellum and determines the cerebellar vermis. Normally, the interhemispheric size of the cerebellum (IMD) in the 2nd trimester is equal to the gestational age.
Size of the fetal cerebellum by week of pregnancy: table
| Gestation period, weeks | 95% | 50% | 5% |
| 14 | 1,4 | 1,2 | 1 |
| 15 | 1,5 | 1,3 | 1,1 |
| 16 | 1,6 | 1,4 | 1,2 |
| 17 | 1,8 | 1,6 | 1,4 |
| 18 | 1,9 | 1,7 | 1,5 |
| 19 | 2 | 1,8 | 1,6 |
| 20 | 2,2 | 2 | 1,8 |
| 21 | 2,3 | 2,1 | 1,9 |
| 22 | 2,6 | 2,3 | 2 |
| 23 | 2,7 | 2,4 | 2,1 |
| 24 | 2,9 | 2,6 | 2,3 |
| 25 | 3 | 2,7 | 2,4 |
| 26 | 3,2 | 2,9 | 2,6 |
| 27 | 3,3 | 3 | 2,7 |
| 28 | 3,5 | 3,2 | 2,9 |
| 29 | 3,6 | 3,3 | 3 |
| 30 | 3,8 | 3,5 | 3,2 |
| 31 | 3,9 | 3,6 | 3,3 |
| 32 | 4,1 | 3,8 | 3,5 |
| 33 | 4,3 | 4 | 3,7 |
| 34 | 4,5 | 4,2 | 3,9 |
| 35 | 4,7 | 4,4 | 4,1 |
| 36 | 4,9 | 4,6 | 4,3 |
| 37 | 5,2 | 4,8 | 4,4 |
| 38 | 5,4 | 5 | 4,6 |
| 39 | 5,6 | 5,2 | 4,8 |
| 40 | 5,9 | 5,5 | 5,1 |
The following are subject to careful study:
- reflection of the ultrasound signal from the median interhemispheric fissure (M-echo);
- cavity of the transparent septum;
- visual hillocks;
- the shape of the horns of the lateral ventricles;
- corpus callosum.
The second screening may reveal abnormalities in a brain structure such as the corpus callosum. It is a plexus of nerve fibers connecting the right and left hemispheres.
If the corpus callosum is not clearly visualized on a midline section of the brain, then one can think of dysplasia, hypoplasia, or agenesis of the corpus callosum.
The cause of this deviation may be hereditary, infectious factors and chromosomal diseases.
The doctor compares all obtained digital indicators with the average statistical norms indicated in special tables.
Examination of the facial skeleton in the second trimester
The fetal face is another important area of examination during ultrasound screening.
When studying the fetal face and nasolabial triangle using ultrasound, you can see the lips, nose, eye sockets and even pupils. With certain skills, the doctor will see movements of the lips, including protruding the tongue, chewing movements, and opening the mouth.
You can diagnose defects such as cleft lip and hard palate :
- A cleft on both sides of the upper lip is popularly called a “cleft lip.”
- The splitting of the tissues of the hard and soft palate, in which there is communication between the oral and nasal cavities, is called the “cleft palate.”
It is not difficult to imagine the confusion of the expectant mother when she is informed about such tricks of nature. Of course, the pathology is complex and unpleasant. But modern medicine is able to perform surgical correction and help such babies.
Ventriculomegaly symptoms
For the first time, ventriculomegaly may be detected in the fetus. It is diagnosed during routine ultrasound examinations from the 17th week of pregnancy. If there is a tendency to ventriculomegaly, the size of the lateral ventricles of the brain is more than 10 mm in the posterior horn.
There are three degrees of severity of the disorder, which depend on the severity of the signs of ventriculomegaly. Depending on this, the tactics for further patient management are determined. Ventriculomegaly in a newborn can manifest itself in excessive tearfulness, an excited state, or, conversely, too calm behavior. Such conditions in any case require consultation with a doctor to clarify their causes.
With a high degree of ventriculomegaly, the consequences can be expressed in an increase in the size of the head, protruding veins, and convulsions. The listed symptoms cannot go unnoticed by any neonatologist, neurologist and pediatrician, who will then decide how to treat ventriculomegaly in each specific case.
Sometimes ventriculomegaly is detected in an infant during a routine examination. Typically, ultrasound of the brain is performed at the age of 1-2 months, and is prescribed to almost all babies, even those who do not have any pronounced complaints or a tendency to ventriculomegaly.
To confirm ventriculomegaly in a newborn and to clarify the location of increased fluid accumulation, sonography and MRI of the brain can be performed. If there are minor deviations, doctors order monitoring of the dynamics - repeat the studies at certain intervals.
It is possible to detect mild ventriculomegaly in adults, for example, during an MRI of the brain or an ultrasound scan prescribed for some other reason. In such cases of mild ventriculomegaly, treatment is not required. If before this it did not manifest itself in any way and did not have a negative impact on lifestyle, a moderate increase in the cerebral ventricles is considered a variant of the norm, an individual developmental feature. If ventriculomegaly in adults is the result of injury or infection, treatment consists of eliminating the causes of the condition. .