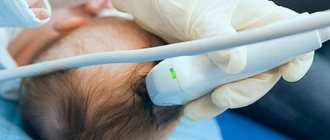
Stages and degrees
The birth of a child is a rather unpredictable process and often the baby’s health suffers as a result.
Brain damage resulting from fetal asphyxia and hypoxia during pregnancy poses a particular danger to the baby’s health. Oxygen starvation of the brain can lead to intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in newborns. The risk of such a complication lies mainly in children who were born prematurely. This is due to the immaturity of blood vessels and structural features of the brain in this group of newborns.
Premature babies have a special structure in the brain - the germinal matrix, the cells of which subsequently create the framework of the brain, migrating to the cortex. Intraventricular hemorrhage in newborns occurs as a result of rupture of the vessels of the germinal matrix and the flow of blood into the lateral ventricles.
As a result of IVH, the migration of germinal matrix cells occurs with disturbances, which has a detrimental effect on the development of the child, causing delays.
Degrees of residential housing complex
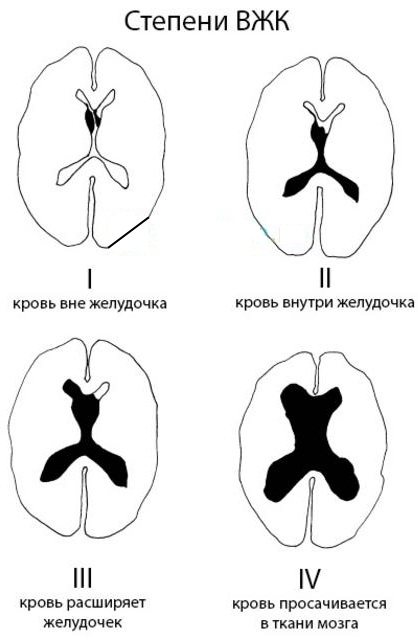
- IVH stage 1 - hemorrhage is limited to the wall of the ventricles, without spreading to their cavity.
- IVH stage 2 – hemorrhage penetrates into the ventricular cavity.
- IVH stage 3 – disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid occur, causing hydrocephalus.
- IVH stage 4 – hemorrhage spreads to the brain tissue.
IVH of grade 1 and 2 in newborns are usually characterized by an asymptomatic course, and they can only be detected through examination with additional methods (computed tomography, neurosonography).
Consequences of IVH
The consequences of IVH for the health of a newborn depend on many factors, in particular the severity of hemorrhage, the gestational age of the baby, the presence of developmental pathologies and concomitant diseases.
IVH of the 1st and 2nd degrees in newborns in 90% of cases resolves without a trace, without causing serious harm to the health of the child. IVH grades 3 and 4 cause motor disorders and neuropsychological problems.
Copying information is permitted only with a direct and indexed link to the source
the best materials from WomanAdvice
Subscribe to receive the best articles in
According to statistics, the lower the infant's gestational age and body weight, the higher the risk of IVH.
The data is not reassuring:
- with a body weight of 1500 g, the probability of IVH of the 1st and 2nd degrees in newborns is 45%;
- with a mass of 1000 g - 80%.
IVH classification is based on computed tomography scan data. The degree of damage depends on the location of the hemorrhage and the size of the ventricle. Today, classification according to the Papile method is used.
Degrees of IVH in newborns
| Degree | Description |
| 1st degree | Subependymal one or two-sided effusion of blood. Spreads into the germinal matrix. |
| 2nd degree | Hemorrhages cover the walls of the ventricles and can spread into the ventricular cavity without their expansion. |
| 3rd degree | Effusion of blood to the walls and cavity of the ventricles, their expansion is noted. |
| 4th degree | The ventricles and periventricular parenchyma are filled with blood. |

IVH of the 1st degree in newborns is characterized by the passage of blood only to the walls of the ventricles, without filling the space of the ventricles themselves. The greater the degree of damage, the more extensive the hemorrhages and the worse the condition of the newborn.
Severity of IVH
Depending on the location of the spread of hemorrhage, IVH is divided into 4 degrees of severity.
In grade I, the blood affects only the walls of the ventricles;
In stage II, blood enters the cavity;
In grade III, extensive hemorrhage occurs, leading to dilation of the lateral ventricles. This process can lead to hydrocephalus.
In degree IV, blood enters the brain tissue, affecting it.
Symptoms of IVH in newborns
IVH of degrees I and II can be asymptomatic. The development of IVH of degrees III and IV is much more dangerous. In such cases, fluid may accumulate in the ventricles of the brain, which can cause the development of dropsy, hydrocephalus, and brain atrophy.
The main signs indicating the possible presence of IVH:
- swelling of the fontanelles in the upper part of the head;
- weak sucking reflex;
- breathing problems;
- lethargy, apathy;
- increased muscle tone;
- muscle spasms.
Diagnosis of IVH
You cannot make this diagnosis on your own. There are many diseases that have similar symptoms to IVH, so it is better to leave the diagnosis to a specialist. While still in the maternity hospital, the baby will be examined by a neonatologist. If there are no visible signs, the child will still remain under observation for several days.
Many maternity hospitals today practice ultrasound scanning of all newborns. Do not refuse this procedure, even if you were not referred to it. Using an ultrasound, the doctor will check the abdominal organs and the baby's head. The slightest deviations from the norm will help you gain time and avoid starting treatment for diseases that are not visible visually.
If the doctor sent the child for an ultrasound, there is a risk of rupture of blood vessels. In this case, diagnosis should be immediate.
At the same time, tests may be prescribed to detect anemia and infections. Developmentchild.ru
Classification
Newborn brain cysts are classified according to certain parameters. Some of them have a congenital etiology, appearing during fetal development, or as a result of childbirth, aggravated by suffocation and oxygen starvation of the child.
Other cysts appear after injury or inflammation as a complication. A vulnerable period when multicystic brain disease with multiple necrotic areas can occur, in which the prognosis is unfavorable, is the period between the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy and the first week after birth.
Depending on the location where these hollow structures are located, several varieties are distinguished. Cysts located in the pituitary gland, which controls growth and metabolism, most often cause developmental disorders in the corresponding area.
Cystic cavities are also found in the cerebellum, also known as lacunar cavities. They are quite rare and usually affect male children, causing motor dysfunction.
In the pineal gland, which is responsible for endocrine processes, pineal formations are formed due to improper movement of the cerebrospinal fluid. This also includes a pineal gland cyst.
In the arachnoid mater, due to mechanical damage, intracranial bleeding, and infection, a newborn may develop an arachnoid cyst of the brain, which is prone to enlargement, to which boys are also more susceptible.
An intermediate velum cyst may often occur. Its location is the fold of the inner lining of the brain, where its third ventricle is located. Detected primarily on MRI.
A tumor in the subarachnoid space can appear as a consequence of injury, inflammation, or as a postoperative complication. This appearance is not typical for infants.
Cystic formations also form in the lateral ventricles of the brain; as they grow, they cause an increase in intracranial pressure.
Most often found in infants are subependymal cysts filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which occur after intracranial bleeding due to vascular damage.
It can be a consequence of injuries received by the child while passing through the birth canal. SECs can be of different sizes and have a negative impact on the baby’s health.
Retrocerebellar formations occur in the tissues of the gray matter of the brain when its cells die, provoked by infections, bleeding, and wounds. These cysts can be severe and require treatment.
Such a type of cyst as porencephalic is almost never detected in childhood.
In this case, several cavities in the brain replace necrotic areas of the brain.
Periventricular damage to the white matter is caused by disturbances in intrauterine development or exposure to infection, which can result in paralysis of the baby.
According to the cellular structure, the cyst can be:
- colloidal. It appears during fetal development and increases as the baby grows, causing fluid accumulation in the brain. Requires removal;
- dermoid. A rare formation located in the corners of the eyes, behind the ears, in the back of the head, on the lips or on the nose. It consists of cells of dental, bone, glandular tissues, and hair follicles. It needs to be disposed of promptly;
- an epidermoid cavity filled with flat epithelium and keratinized particles, which should also be removed;
- a choroid plexus cyst, also called a pseudocyst, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It is diagnosed in the fetus by ultrasound examination and usually disappears by 28 weeks on its own, but may persist after birth. Manifestations are directly related to the place where it originated.
Reasons for education
As we have already noted, children with a small gestational age are at risk of intraventricular hemorrhage; full-term infants who have had intrauterine growth retardation are also at risk.
The main and main cause is chronic fetal hypoxia in the third trimester of pregnancy. During this period, with insufficient oxygen, hemorrhage forms, and under the influence of mechanical pressure during delivery, the situation worsens, leading to IVH of the 1st or 2nd degree.
Other factors also contribute to the development of IVH in newborns:
- deficiency of vitamin K and K-dependent factors;
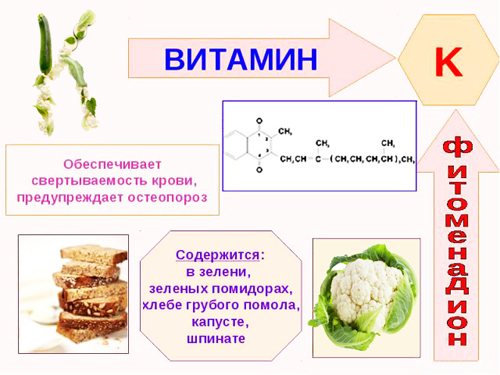
- problems with blood coagulation (clotting);
- pathological conditions that appear against the background of hypoxia: acidosis, low blood pressure, high activation of fat peroxidation;
- intrauterine development of viral infections and mycoplasmas;
- maternal history of diabetes diagnosis;
- bad habits of a pregnant woman (smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction);
- mechanical injuries during childbirth due to the mother’s narrow pelvis or the baby’s large head, also during rapid delivery or caesarean section;
- use of obstetric forceps or vacuum extraction during childbirth;
- obstetrician mistakes.
Many circumstances can lead to the formation of a brain cyst in an infant. The exact causes of its appearance, as well as other brain pathologies, are still being studied and established.
It is known that with necrosis of brain tissue, cystic cavities are formed in its place, containing fluid inside. Thus, a pathology arises, leading to neurological disorders that prevent the babies from fully developing.
The most obvious causes of brain cysts in newborns include:
- diseases and abnormalities of fetal development;
- complications during childbirth with large fetuses or multiple pregnancies;
- infections and inflammatory processes that occur in the mother during pregnancy;
- cerebrovascular accidents, hypoxic brain damage;
- intracranial bleeding due to injuries, falls, blows.
Particular attention is always paid to checking the functions and condition of those babies whose mothers:
- there was an exacerbation of herpes during pregnancy;
- pregnancy proceeded with pathologies (oligohydramnios, large fetus);
- the birth took place with complications.
Causes and symptoms
For the most part, doctors diagnose cerebral hemorrhage in underdeveloped children - according to statistics, in newborns born weighing up to 1.5 kg, such a pathology is diagnosed in 50%.
If the child is full-term, normally developed and formed, then, according to medical statistics, pathology manifests itself only in one case for every thousand newborns. Quite encouraging statistics.
Speaking about the root causes themselves, which can lead to hemorrhage in the brain and gray matter, for the most part doctors identify the following among them:
- severe prematurity in the womb or, on the contrary, postmaturity of the fetus, prolonged intrauterine development;
- if the pregnancy proceeded with a certain pathology - there was intrauterine infection or hypoxia or another reason;
- the fetal head is large in size, which does not correspond to the size of the birth canal and during the birth process the skull bones were displaced and thus injured the vessels of the head;
- labor that is too rapid in time or, on the contrary, a prolonged delivery, when the fetus may experience oxygen starvation and increased intracranial pressure, leading to rupture of blood vessels;
- incorrect, unqualified actions of a doctor - gynecologist, obstetrician during childbirth, when doctors could strongly pull the fetus when leaving the birth canal or otherwise damage the head;
In any case, whatever the root cause, the main thing is to promptly diagnose a cerebral hemorrhage and begin a course of effective and adequate treatment. In terms of signs, the symptoms of the pathology will be discussed below and depend on the location of the hemorrhage.
Symptoms of a brain cyst in a child
The severity and variety of symptoms depends on the location of the brain cyst in the newborn. Education may not be the only one; this creates more difficulties in finding it and determining its type.
Manifestations also depend on the size of the brain cyst and the rate of its increase. With a diameter of about 4 centimeters, it already affects the surrounding structures, causing various disorders in the baby.
The growth of cystic formations may accelerate due to the following circumstances:
- increasing the effect of liquid on the walls of the cavity;
- exacerbation of inflammatory and infectious processes in the baby;
- concussions, blows, injuries in babies who already have a cyst.
Small growths that do not grow often do not cause symptoms during childhood. But they still need to be observed and controlled. During puberty, with its rapid puberty and other changes, cystic formations may begin to show the first signs and increase in size.
Large formations put significant pressure on brain tissue and lead to symptoms considered signs of a cyst:
- cephalgia of various types - from unbearable spasmodic to constant aching;
- visual, auditory, olfactory dysfunction;
- sleep disturbance and lethargy, apathy, loss of appetite;
- loss of ability to control your body;
- excessive or insufficient muscle tone;
- the appearance of noise, rhythmic pulsation in the head, increased intracranial pressure;
- convulsive attacks and fainting;
- involuntary tremors in the limbs; deformation and enlargement of the skull;
- gagging
- a convex pulsating fontanel on the head;
- epilepsy;
- delayed neuropsychic development;
- hormonal imbalance and delayed sexual development;
- partial transient immobilization of the limbs, sensory disturbances.
Symptoms may appear separately or in combination. In nine out of ten cases, the cyst resolves without additional intervention. However, some of its varieties should definitely be removed. This is especially true if the tumor:
- formed in the fetus in the womb and is rapidly increasing;
- appeared in the baby after he was born;
- significant in volume, compresses important areas of the brain.
Sometimes the manifestations can be similar to some symptoms of meningitis in children, so it is important to carry out a careful differential diagnosis.
Symptoms and signs
Pathology can be detected immediately after birth, within a few hours or even days. The diagnosis is made by characteristic symptoms in children, laboratory and hardware examinations.
Important information: Why does it bleed after inserting and removing the IUD?
Signs of cerebral hemorrhages depend on the type of hemorrhage:
- With an epidural, breathing is heavy, the pulse is rare, the pupil on the injured side is dilated.
- Subdural causes muscle weakness, unconditioned reflexes are absent, and infants experience convulsions that are repeated cyclically. It is difficult to stop without the use of pharmaceuticals.
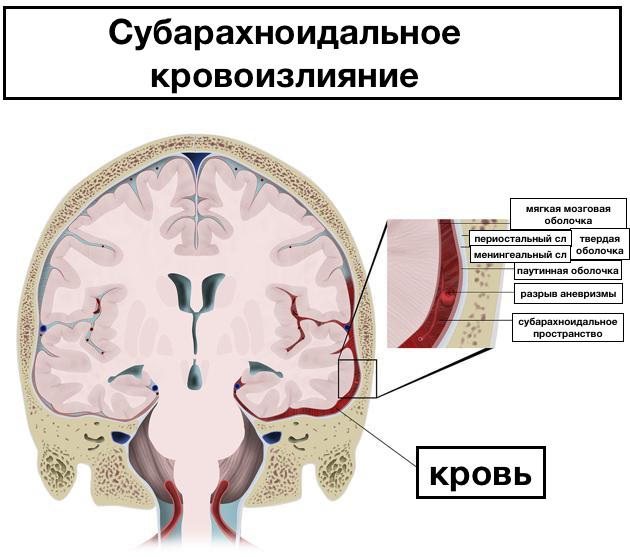
- Subarachnoid is accompanied by hyperactivity, increased excitability, difficulty falling asleep, and frequent monotonous crying. Possible squint.
- Ventricular and interventricular can lead to apnea - cessation of breathing.
Common symptoms that may indicate the presence of pathology in infants are frequent regurgitation, weakness or hyperexcitability, developmental delays, headaches, which are indicated by moaning on one note and attempts to reach the forehead with hands.
One should be alert to periodic holding of breath, numbness with increasing pallor of the skin, a sharp drop in temperature, absence of a sucking reflex, and loss of appetite. Accumulation of blood in the brain tissue is indicated by paresis of the limbs and stiffness of the neck muscles.
Diagnosis of a newborn is carried out in the maternity hospital. To assess the condition, general and specific blood tests are done - necessarily a coagulogram, puncture - to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid and cerebral fluid for the presence of blood fragments. X-rays of the skull, neurosonography, MRI or CT may be required.
When to see a doctor
Given that premature infants are at risk for IVH, their condition is monitored in the intensive care unit immediately after birth and during the first few days.
Due to the low weight and weakness of the body of such children, all medical procedures are carried out at the same time, so as not to touch the baby once again, because even ordinary weight control for such children is a lot of stress, as a result of which IVH can appear. Medical staff treats premature newborns carefully and with care.
Before discharging a mother and baby home, doctors are required to make sure that there is no IVH by conducting a series of diagnostic measures and assessing the child’s condition. If a pathological condition is detected, treatment is prescribed depending on the diagnostic results.
It is very important to monitor head circumference in premature babies. If its volume increases by more than 10 mm in 7 days, there is a need to monitor the volume of the ventricles of the brain using neurosonography.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent premature birth or premature rupture of membranes, as well as to eliminate the risk of choriamnionitis, will help reduce the incidence of IVH.
The development of a pathological condition can be prevented both postnatally and prenatally. In the first case, if there is a risk of a problem, hemostatic agents, pancuronium, vitamin K, phenobarbital, and indomethacin are prescribed.
Prenatal prevention includes taking glucocorticoids. According to medical research, taking these dosage forms greatly reduces the likelihood of IVH in newborns.
Treatment methods
Treatment of newborns diagnosed with IVH is carried out by neurosurgeons and neonatologists. Therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating the consequences of the problem, as well as restoring vital functions, quality and blood counts.
In case of insufficient coagulation and the presence of platelets, transfusion of plasma components is performed. If the baby has clear signs of respiratory distress, the child in the intensive care unit is placed under a ventilator.
Conservative treatment of IVH of the 1st or 2nd degree includes:
- control and normalization of blood pressure (premature infants are prescribed intravenous or intramuscular administration of sulfuric acid, full-term infants are prescribed Diacarb, Veroshpiron, Furosemide);
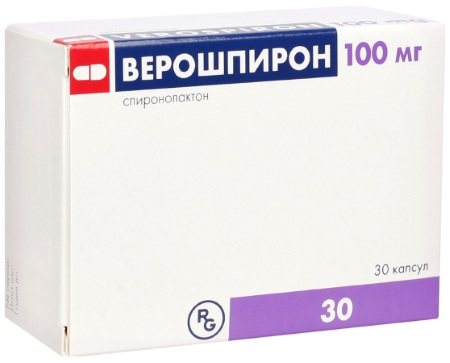
- taking anticonvulsant medications (Diazepam, Valproic acid preparations);
- taking oxygen;
- control and normalization of blood clotting;
- elimination of signs of intoxication (infusion therapy);
- prevention of acidosis (intravenous administration of Sodium Bicarbonate solution).
Drug treatment is effective only for grade 1 or 2 intraventricular hemorrhage. In frequent cases, the problem goes away without a trace, without causing complications. If stage 3 or 4 IVH is detected, treatment requires surgical intervention.
All medications and their dosage are prescribed by a doctor; a problem such as intracranial hemorrhage is highly life-threatening.
Traditional methods
IVH of the 1st degree in newborns is not a disease as such, it is a pathological condition caused by certain factors (intracranial pressure, premature birth, improper delivery, use of obstetric forceps, etc.). In this case, it is impossible to talk about traditional methods of treatment, since the pathology requires special attention from neurosurgeons and neonatologists.
As a preventative measure, the expectant mother can be advised to take herbal soothing infusions during pregnancy. They are prepared on the basis of mint, lemon balm, chamomile, and rose hips. Such decoctions will not help solve the problem, but a calm and balanced state of the pregnant woman can prevent the risk of premature birth.
Other methods
Stage 3 IVH in newborns often becomes irreversible, and if there is no result of conservative therapy, neurosurgeons determine the need for surgical treatment.
- Shunting with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity. A silicone tube is installed, passing under the scalp and towards the abdominal cavity. The shunt is removed when the child’s health condition has stabilized and IVH has not progressed.
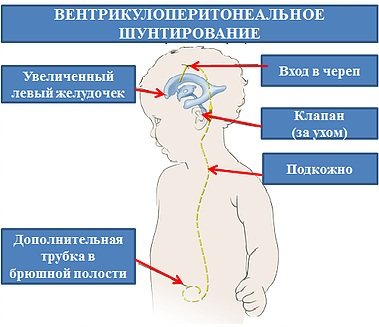
- Endoscopic ventriculostomy. It is carried out by installing anastomoses passing between the ventricle and the interpeduncular cistern. The goal is to ensure free flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt. This method allows you to administer medications and control the rate of outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. One edge of the drainage is installed in the ventricular cavity, and the other is placed in a container where cerebrospinal fluid accumulates. This method takes a long time and does not interfere with child care.
Some specialists also use a method such as spinal puncture. But the effectiveness of this method has not been proven.
Only a specialist can choose a method for treating a cyst, based on the size of the cyst in the brain, its location, and the severity of symptoms. Some types of formations can resolve on their own and do not require intervention.
Many cysts of vascular and subependymal nature decrease and disappear on their own. But if the doctor discovers an infection, it is imperative to take action and deal with it, and then conduct a repeat ultrasound examination.
In any case, if a child is diagnosed with this pathology, he needs to be observed and undergo periodic examinations, which will help begin treatment if the formation increases or changes in health.
Cystic formations of significant volume, not inclined to shrink and resolve, need to be removed by various methods. Surgery should be performed immediately when:
- education is growing rapidly;
- the growth process affects important areas of the brain and the patient’s condition;
- The baby was diagnosed with hydrocephalus;
- the child suffers significantly above normal;
- a blood vessel burst due to frequent convulsive seizures;
- intracranial pressure, intracranial bleeding began.
If the patient can only be helped by surgery, the specialist selects the best option appropriate to the situation from the following:
- resection with a scalpel with trepanation of the desired area of the skull. An effective, but quite traumatic method that requires a long recovery;
- bypass surgery, in which the doctor opens the cyst through a hole in the skull, drains fluid from it, after which the empty chamber resolves on its own. The weak point of this type of manipulation is the likelihood of infection in the wound;
- minimally invasive endoscopic surgery through a puncture in the skull. Cystic tissue is removed using an endoscope through an opening, with little or no damage to healthy tissue.
Rehabilitation after this optimal type of intervention is faster and more effective. But this method is allowed only if the affected areas are located close to the surface of the skull.
The essence of conservative treatment is to take medications that alleviate symptoms. With high intracranial pressure, these will be diuretics and vascular drugs that stimulate the movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
If the cystic formation appears as a result of inflammation of the meninges of a bacterial nature, antibiotics are used. After the infection goes away, the cyst often resolves. It is useful to support a weak immune system with immunostimulants and vitamins.
Agents that restore blood supply, promote the dissolution of adhesive structures, antiviral, antifungal drugs, and nootropic drugs are also used.
Whatever method is preferred by the treating specialist, you need to listen to all his recommendations and follow the instructions. Then the recovery and recovery period will pass quickly, without compromising the health and development of the baby.
Possible complications
The success of treatment in the case of a brain cyst in a newborn is influenced by its correct and accurate diagnosis. Low volume and no increase in size usually means a good prognosis.
If a cystic formation in a newborn child’s head rapidly increases in size, compresses neighboring areas of the brain, increasing intracranial pressure, there is a threat of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Everything will be decided by the professionalism of the operating doctor, quick and accurate intervention. Late detection and growth of the cyst can cause necrosis of brain tissue, deafness, blindness, paralysis, abnormal growth and development of the child, accumulation of fluid in the brain, dangerous bleeding and death.
Complications of IVH depend on the severity of the pathological condition. With the timeliness and adequacy of medical actions for the 1st and 2nd severity of IVH, the consequences may bypass the newborn.
Complications of intraventricular hemorrhage may be the following:
- IVH of the 1st and 2nd degrees sometimes does not require any therapy, however, such children need constant monitoring during the first month of their life. The likelihood of neurological disorders is still present. Deaths at these stages of the pathological condition do occur, but are extremely rare.
- With stage 3 IVH in newborns, when blood fills more than 50% of the ventricular cavity, there is a high risk of developing hydrocephalus (55% of all cases). The occurrence of neurological abnormalities (35% of cases) and death (5% of cases) cannot be ruled out. As a rule, in such situations, doctors determine the need for surgical intervention. Favorable prognosis is made if IVH is distributed only to one frontal lobe.
- IVH of the 4th degree is the most dangerous; the prognosis in this case is disappointing. Without surgical intervention, the problem cannot be eliminated, and the risk of mortality is quite high. Death occurs in 50% of cases, hydrocephalus develops in 80% of cases, and serious neurological disorders develop in 90% of cases.
Stage 3 IVH in newborns without appropriate treatment can lead to the most unpredictable and serious consequences - coma and even death.
It is difficult to predict the final outcome of the pathology, since it depends on the severity and timeliness of treatment. The prognosis is also influenced by the baby's gestational age and weight.
The difficulty of predicting the future condition of a newborn lies in the fact that even after adequate treatment for IVH of the 3rd degree, it is not possible to identify neurological abnormalities. This is due to the fact that in the first year of life there are no special requirements regarding the psychomotor development of the baby.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Possibilities of modern medicine
If a child is found to have hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain, he should be under the vigilant supervision of medical staff. The baby's condition is monitored to ensure his stability.
Basically, therapy for IVH is aimed at eliminating complications and consequences. If any diseases arise as a result of hemorrhage, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Sometimes (if too much fluid accumulates in the brain), the following measures are applied:
- Ventricular (through the fontanel) or lumbar (through the lower back) puncture .
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt , when a special drainage tube is inserted into the ventricles. It is pulled under the skin into the patient's abdomen, where excess cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed. The drainage system must remain in the body at all times, and the tube must be replaced if necessary.
It should be noted that for the majority of patients (with degrees 1 and 2 IVH) no therapy is required at all; one can count on a favorable outcome.
Cerebral hemorrhage in a newborn
Brain hemorrhage in newborns is a serious pathology that develops as a result of damage to the vessels of the dura mater or rupture of a cerebral vessel. This often happens with birth injuries.
According to statistics, intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) occurs in 1 in 1000 cases in full-term infants.
However, very premature babies born with a body weight of less than 1.5 kg suffer much more often - hemorrhagic cerebral bleeding occurs in 20-45%.
The consequences of cerebral hemorrhage in newborns are always unfavorable, as they are fraught with complications such as neurological pathologies, hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy, cerebral edema, impaired vision, motor activity, speech apparatus, and even death. It all depends on the degree of hemorrhage, its location, the general condition of the baby and the compensatory abilities of the brain.
Causes
As we have already found out, very premature infants or full-term infants who have a history of intrauterine growth retardation are most at risk of developing pathology.
One of the first reasons can be considered chronic fetal hypoxia at 26-34 weeks of pregnancy.
The fact is that during this period the periventricular space is literally penetrated by a large number of vessels, which play an important role at this stage, but over time cease to be functional.
If complications arise and there is a lack of oxygen during these weeks, hemorrhages may form, which will worsen during childbirth under the influence of mechanical pressure.
Other causes of cerebral hemorrhage are:
- lack of vitamin K and K-dependent factors, other anomalies associated with the coagulation process (blood clotting);
- pathologies due to severe hypoxia: acidosis, too strong activation of fat peroxidation, low blood pressure;
- intrauterine infections with viruses, mycoplasmas that contribute to the destruction of vascular walls;
- chronic maternal diseases (for example, diabetes);
- the influence of a woman’s harmful habits (tobacco smoking, alcoholism);
- injuries during childbirth due to the narrow birth canal and large fetal head, during rapid labor, caesarean section;
- use of obstetric aids (vacuum extraction of the fetus, obstetric forceps).
The brain, like our other organs, has an impressive network of blood and lymphatic vessels, small and large, that deliver oxygen to it and protect the brain center from germs and viruses.
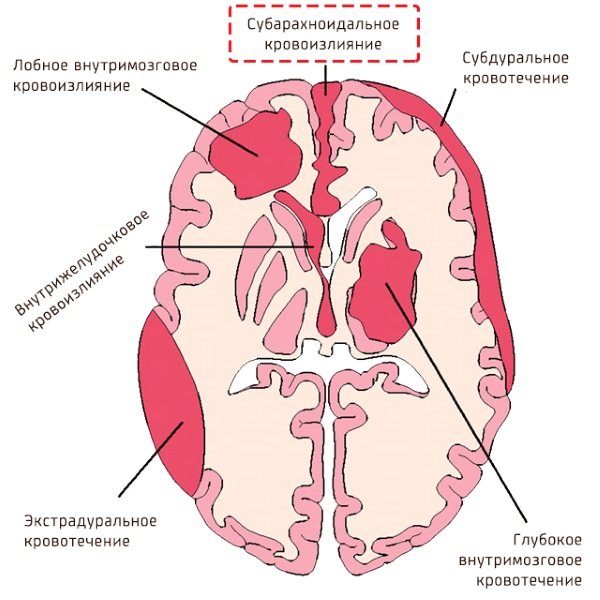
The skull is covered on top with a hard shell, called “dura mater” in Latin. If the hemorrhage occurs under this membrane, it is called subdural, if between the membrane and the skull, it is called epidural.
This is followed by the arachnoid (in medicine, arachnoid) and pia mater. Between them there is a subarachnoid space filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The cavities that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid are called ventricles.
The degree of severity is judged depending on which part of the brain or its membrane is damaged and how extensive its damage is:
- 1st degree of severity - subependymal hemorrhage (hereinafter abbreviated as SEC);
- 2nd degree - blood partially or completely penetrates the lateral ventricle, but does not change its size;
- 3rd degree - the ventricle, filling with blood, increases in size;
- 4th degree - blood fills the ventricles, expanding them, and goes beyond their limits, entering the substance of the brain in newborns.
According to the ICD-10 classification, hemorrhages are divided as follows:
- subependymal;
- IVH without penetration into the brain parenchyma (tissue);
- IVH with penetration into the brain parenchyma.
Various diagnostic formulations sometimes confuse the correct diagnosis, so when deciding on a treatment regimen, the doctor is guided by the results of an ultrasound, MRI or X-ray examination.
Signs of a brain hemorrhage do not always appear immediately. The pathology may be asymptomatic for the first day
Symptoms
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) is a pathology in which small vessels burst and bleed into the ventricles of the brain of a newborn child.
The ventricles are cavities in the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). A person has several of them and they are all connected to each other.
The diagnosis of IVH is quite often made in premature infants, which is due to their physiological characteristics. The shorter the gestational age, the higher the likelihood of hemorrhage.
Hemorrhage does not appear just like that; there must be reasons for this disorder.
Who is at risk?
Brain hemorrhage in newborns can be associated both with damage to the skull itself and with a lack of oxygen.
Prerequisites for DRC:
- Post-maturity or, conversely, under-maturity. Premature babies are especially susceptible to intracranial hemorrhages, since their immature vessels do not yet have sufficient support in the tissues. In babies born late, the bones harden and the head is unable to adjust during birth. According to statistics, IVH occurs in every fifth premature baby and every tenth post-term baby.
- The size of the fetal head does not correspond to the size of the birth canal. In this case, natural delivery is contraindicated, because it is fraught with injury and hypoxia for the newborn baby.
- Difficult pregnancy (fetal hypoxia, intrauterine infection with various infections).
- Difficult (protracted or rapid) labor, breech presentation.
- Incorrect actions of obstetricians during childbirth.

Based on the above, several risk groups can be identified.
The risk of cerebral hemorrhage in a child increases with:
- prematurity;
- low birth weight (less than 1.5 kg);
- oxygen deficiency (hypoxia);
- child's head injury during childbirth;
- breathing complications during childbirth;
- infections leading to blood clotting disorders.