Minimal brain dysfunction (MMD) is a concept that combines almost any disorder of childhood behavior in combination with minimal neurological manifestations:
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- speech delay
- delayed motor development
- delayed psychomotor development
- childhood psychoses
- and others…
Minimal brain dysfunction occurs in approximately 20% of preschool children and 5% of children attending primary school.
What are the causes of MMD?
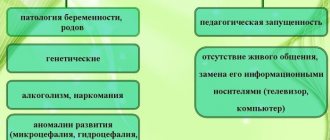
The causes of neurological disorders that cause minimal brain dysfunction include various factors - for example, experts note that the child is affected even before birth by:
- hereditary predisposition,
- pathology of pregnancy (prematurity, threatened miscarriage, anemia, illness and poor nutrition of the expectant mother, fetal hypoxia, etc.),
- pathology of childbirth (quick birth, weak labor, asphyxia of the newborn).
In addition to these factors, the appearance of dysfunction in children can be provoked by:
- poor nutrition and even malnutrition,
- various diseases associated with oxygen deficiency (for example, with bronchial asthma, the lungs poorly enrich the blood with oxygen).
Reasons for violations
Among the most common causes of the onset of the disease, experts cite trauma to the brain stem area, resulting from concussions, bruises, as well as exposure to pathogenic microflora. In children, a separate group includes dysfunctions of brain stem structures resulting from severe pregnancy, caused by prolonged consumption of alcohol, maternal smoking, or as a result of birth trauma.
If there are suspicious signs, the cause of the pathology is determined. After describing the symptoms of the disease to the patient, the doctor prescribes a computed tomography scan, in which deviations from the normal functioning of the brainstem trunk are detected as a result of layer-by-layer scanning. Magnetic resonance or computed tomography will identify and evaluate the size of pathological neoplasms and detect displacement or deformation of the organ.
Note! Computed tomography is not recommended in the absence of signs indicating organ trauma.
An electroencephalogram is also prescribed, the essence of which is to record the electrical signals of the brain and their subsequent evaluation. The goal of the test is to find the source that is causing the brain stem irritation. Depending on the location of the area of deformation or damage to the organ structure, experts identify the following types of deviations of the brain stem.
Attention deficit
Parents raising preschool children must be attentive to the child’s behavioral and mental reactions in order to recognize neurological disorders in time.
It is worth considering that outwardly minimal brain dysfunction can manifest itself in different ways - it depends on the severity of the disorder and the characteristics of the child’s psyche. It is important not to confuse the disorder with normal manifestations of childhood activity or common speech disorders.
And yet, determining the presence of this syndrome is not so difficult. Experts have classified the symptoms that occur with minimal brain dysfunction. Their main symptoms include attention deficit, impulsivity and hyperactivity in children.
The essence of attention deficit is manifested in pronounced inattention and has the following characteristics:
- the baby does not respond to the call, although he hears it,
- cannot concentrate for a long time even on an interesting activity (game, reading a fairy tale, film),
- the older preschooler willingly begins to complete the task, but does not finish it,
- in preparation for learning and during the learning itself, the child experiences difficulties mainly associated with organizing activities (games, completing tasks),
- at any age, cannot concentrate on activities that require attentiveness and certain mental efforts, rejects such activities,
- They are characterized by frequent loss of things,
- Children have difficulty remembering even the simplest texts or rhymes.
Organic brain dysfunction
It includes not one symptom, but a grouped complex of diseases, the common feature of which is dystrophic changes. A distinctive feature of this group is that the pathological process can occur hidden, and a person may not even be aware of such a pathology. Many of the symptoms that indicate brain dysfunction are very similar to those of normal fatigue. In general, it means that there are functional changes in the brain and it is not able to function fully.
There can be many reasons. Conventionally, they are all divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital diseases include various infectious diseases that have been transferred, exposure to teratogenic factors, and nicotine on the fetus. Fetal hypoxia has a negative impact during prolonged and pathological labor. The cause may be exposure to stress factors, vitamin deficiency, poor nutrition and any factors that affect a pregnant woman.
Acquired causes are, first of all, bruises, diseases, especially atherosclerosis, intoxication, taking certain medications, exposure to endogenous and exogenous factors. Many concomitant diseases, especially those related to the heart and vascular system, can contribute to the development of a pathological condition of the brain.
Symptoms can vary greatly. A characteristic feature is that they are manifested by any reactions and somatic signs. Dysfunction may be indicated by attacks, fears, most often unfounded. A person, as a rule, has impaired conscious and unconscious processes, associative connections, and lacks initiative.
Night sleep is disturbed, incorrect perception is detected, and the analysis of visual and auditory images becomes difficult. But in order to finally make a diagnosis, a comprehensive diagnosis is required: an examination and questioning is carried out, additional methods are prescribed, such as an electroencephalogram, rheoencephalogram, and ultrasound.
The danger of brain damage lies in the fact that it is the coordinator of basic human functions and controls the functioning of all organs and systems of the body. If its function is impaired, the functioning of all other organs accordingly occurs. The risk of developing pathologies and diseases increases significantly, the activity of the immune and endocrine systems and blood circulation are disrupted, the likelihood of tumors and the transformation of existing benign processes into malignant ones increases. Numerous complications of existing diseases develop, relapses and exacerbations of chronic diseases are observed.
Hyperactivity as a symptom of dysfunction
Increased motor activity or hyperactivity with minimal brain dysfunction is manifested already from infancy by the following actions:
- the baby sleeps restlessly or very little,
- from an early age, a preschooler becomes restless, is in constant motion,
- even in a calm state, he makes aimless movements with his arms and legs,
- there is instability when walking, frequent falls are possible,
- the child constantly touches objects, hits corners,
- is characterized by the manifestation of anxiety in various situations, especially disturbing ones,
- the baby may often break things, toys,
- fine motor skills are poorly developed, which may later manifest itself in poor handwriting, rapid hand fatigue when writing,
- although there are minimal disturbances in speech, the child is often very talkative, interrupts, interferes in the conversations of adults,
- If they have problems articulating speech, it is difficult for them to construct long sentences, so they have difficulty retelling the text.
Possible complications
All patients with severe and moderate brain damage require hospital treatment. Children with mild impairments are discharged from the maternity hospital under outpatient supervision by a neurologist. Let us dwell in more detail on the clinical manifestations of individual PEP syndromes, which are most often encountered in outpatient settings.
The syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability is manifested by increased spontaneous motor activity, restless shallow sleep, prolongation of the period of active wakefulness, difficulty falling asleep, frequent unmotivated crying, revival of unconditioned innate reflexes, variable muscle tone, tremor (twitching) of the limbs and chin.
In premature infants, this syndrome in most cases reflects a lowering of the threshold for convulsive readiness, that is, it indicates that the baby can easily develop convulsions, for example, when the temperature rises or when exposed to other irritants. With a favorable course, the severity of symptoms gradually decreases and disappears within a period of 4-6 months to 1 year.
If the course of the disease is unfavorable and there is no timely treatment, epileptic syndrome may develop. Convulsive (epileptic) syndrome can manifest itself at any age. In infancy it is characterized by a variety of forms. An imitation of unconditioned motor reflexes is often observed in the form of paroxysmal bending and tilting of the head with tension in the arms and legs, turning the head to the side and straightening the arms and legs of the same name; episodes of shuddering, paroxysmal twitching of limbs, imitations of sucking movements, etc.
Sometimes it is difficult even for a specialist to determine the nature of the convulsive conditions that arise without additional research methods. Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is characterized by excess fluid in the spaces of the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which leads to increased intracranial pressure.
Doctors often call this disorder to parents exactly that - they say that the baby has increased intracranial pressure. The mechanism of occurrence of this syndrome can be different: excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid, impaired absorption of excess cerebrospinal fluid into the bloodstream, or a combination of both. The main symptoms of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, which doctors focus on and which parents can control, are the rate of increase in the child’s head circumference and the size and condition of the large fontanel.
Impulsivity syndrome
Minimal brain dysfunction in impulsivity syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
- emotional lability manifests itself very sharply (changes in mood from elated to depressed),
- children may experience unreasonable outbursts of anger not only towards others, but also towards themselves,
- the preschooler quickly answers questions without thinking, without listening to the instructions,
- allows destructive behavior during classes,
- the child does not know how to lose, during a loss he can be aggressive and get into fights with other children,
- cannot wait for distant reward, demanding immediate delivery,
- does not obey the rules (of behavior, games),
- commits actions that are dangerous to himself and others, although he does not understand this,
- While performing tasks, the child’s unstable behavior easily changes from calm to aggressive (gets angry if the task does not work out).
What are the diagnostic criteria for MMD syndrome? The diagnosis is made by the presence of at least six symptoms that have been observed over the past six months. Parents need to take into account that children experience great difficulties when studying at school, but remember that it is not the level of development of intellectual abilities that plays a significant role, but the inability to realize them.
Advantages of treatment at the Neonatus Sanus Osteopathy and Neurology Center
Our clinic of osteopathy and neurology on Vasilyevsky Island “Neonatus Sanus” - health from birth, has extensive practical experience in the prevention and treatment of newborns, infants and children.
We know how and love to work with children!
Our clinic employs experienced osteopathic doctors and neurologists. A lot of attention is paid to each child in order to understand the child, accurately assess his condition, give recommendations to parents and, if necessary, carry out effective osteopathic treatment.
In our center you can get the best examination, treatment and recommendations from leading specialists in St. Petersburg.
Treatment of children with MMD syndrome
Parents of children with MMD syndrome do not need to despair or expect that everything will go away as the child grows up. As a rule, those of them who are actively involved with their children, fulfill all the instructions of specialists, get good results. The main thing is that timely diagnosis is carried out and correct treatment is prescribed. According to experts, 70% of children, as a result of actively carried out therapeutic measures, catch up with their peers in development and do not differ from them in their behavior.
When treating MMD, it is necessary to understand that it must take place in the interaction of a specialist, the child and the people around him in order to create a positive atmosphere around him. The main directions in treatment are psychological and pedagogical correction, drug treatment, patience and consistency of parents.
A corrective treatment program can be structured as follows:
- Medications are prescribed only by a specialist. Medicines, course, doses - everything should be under the supervision of a doctor.
- Psychological and pedagogical correction should include classes, games, and psycho-gymnastic exercises that take into account all the problems of children with MMD. The correction system is compiled by specialists (speech therapist, psychologist, teacher) and carried out under their supervision. Tasks should be aimed at concentration, development of thinking, memory, fine motor skills, have clear instructions with repeated repetition, because it is difficult for a child to focus on verbal explanations. At first, it is better to use clarity - for example, when doing graphic dictations with a pencil, show the beginning of the work. It is also necessary to take into account that it is difficult for preschoolers to immediately absorb educational material, so repetitions and a return to what has been covered are needed.
- Children with MMD must follow a clear daily routine , which is organized and supported by the adults around them. They simply have to make sure that the baby wakes up, gets proper nutrition, goes for walks, plays games, and goes to bed at the same time. This implementation of the regime makes the work of the nervous system synchronous, while deviations undermine the nervous processes.
- correct the child’s motor activity , which recommends feasible exercises, sports games, swimming, cycling, and skating.
Dysfunction of midline structures
This variant of pathology manifests itself in the form of sleep disturbances, emotional disorders and deviations in the functioning of the nervous system. Signs of dysfunction of the mid-stem structures of the brain are expressed as follows:
- Deviations of the endocrine system, which, depending on the location of the damage, make themselves felt by an increase or decrease in the patient’s pressure and body temperature.
- A decrease in sensitivity, especially clearly manifested in the area of the patient’s face and torso.
- Pathologies in the epiphyseal region of the brain, leading to early onset of sexual activity.
- Unnatural character of the patient's laughter or crying.
- Impaired fine motor skills and involuntary trembling of the limbs.
- Lowering the pain threshold, increasing sensitivity to discomfort.
Note! Dysfunction of the mid-stem structures occurs as a result of TBI in the brain stem associated with the consequences of an accident, falls, or bruises.
Raising a child with MMD in a family
- In a family setting, parents should remember that their frequent mood swings and family quarrels have a bad effect on the child’s emotional well-being and can aggravate the course of a brain disorder, so unity of demands between parents, adequacy and clarity of actions, and slow and friendly speech are necessary. Parents should be careful when their child communicates with his peers. It is necessary to encourage friendship with a slow child in order to reduce emotional outbursts.
- For the same purpose, children should not be among large crowds of people, for example, at mass city events.
- Experts also advise that instead of traveling abroad to hot countries, organize a summer vacation in a familiar place, for example, at a dacha. Include outdoor games, swimming in a pond, and walks in the forest in children's leisure time, as this calms the nervous system.
- To correct fine motor skills, develop attentiveness, and memory, it is recommended to engage in creative activities with the child at home: draw, sculpt, cut, glue. It is useful to read fairy tales, memorize poems in a playful way, listen to music, children's songs.
- Psychologists do not recommend attending sections or clubs at this time until the treatment is completed. When a preschooler begins to study, the teacher must be told about the diagnosis in order to provide him with an individual approach.
When raising a child with MMD, parents should remember that comprehensive treatment will help to cope with the problems in a short time. According to the famous doctor Komarovsky, children with minimal brain dysfunction can be influenced by their own example, patience and proper upbringing. This way, parents will quickly find an approach to their child.
Pediatrician of the 2nd category, allergist-immunologist, graduated from the Belarusian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development. Read more », Rate this article: (1 rated 4.00 out of 5) Loading...Share with friends!
Forecast
In a third of cases, minimal cerebral dysfunction goes away on its own: the central nervous system of such people matures later, but without consequences.
The second third is compensated: external signs may disappear from a person’s behavior, even in the absence of changes in the neurophysiological picture. For example, a person with dyslexia will learn to read; but when he is assigned to read during an EEG study, a characteristic slowdown in brain activity occurs. Compensation may fail due to stress.
The prognosis of the last third of patients is worse: they do not “outgrow” and are not compensated. This group usually has social problems.
Source