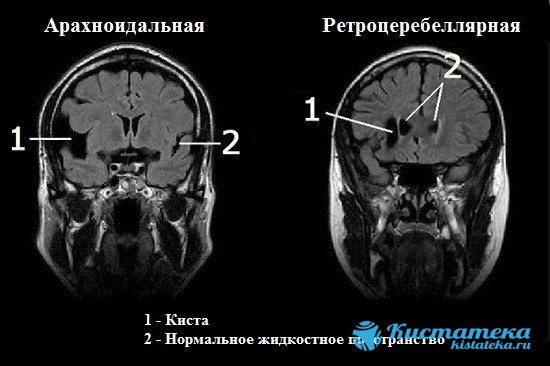
An arachnoid cyst (cerebrospinal fluid) is a benign cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid. A bubble is formed in the membranes of the brain from the cells of the arachnoid tissue. Sometimes such a formation does not manifest itself, it is not subject to growth, and does not affect the patient’s condition.
Sometimes an arachnoid formation does not manifest itself, it is not subject to growth, and does not affect the patient’s condition.
But as the pathology progresses, there is an impact on the membranes of the brain. Gradually, the cerebrospinal fluid cyst compresses the tissue, which leads to symptoms from the nervous system.
What is a retrocerebellar cyst of the brain?
With a disappointing doctor's conclusion, patients often wonder about the diagnosis of a head tumor. It is a cavity containing a capsule with liquid exudate. The pathology forms at the site of necrotic nerve cells in any part of the brain. In most cases, MRI shows the location of the tumor in the posterior fossa behind the cerebellum.
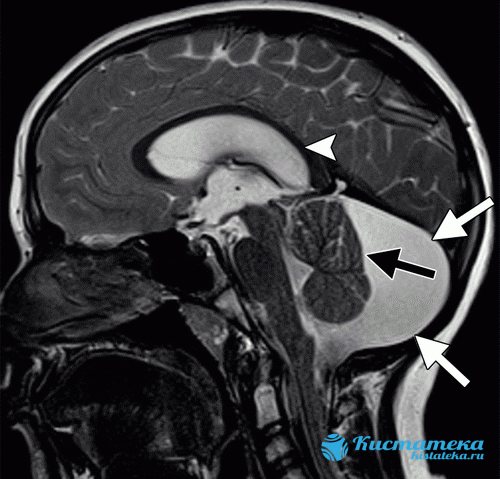
The image shows a retrocebellar arachnoid cyst with obvious enlargement of the posterior fossa (white arrows).
Retrocerebellar cysts are asymptomatic for a long time, but over time the pathology progresses, compressing neighboring organs - parts of the brain, which is often dangerous with serious complications - symptoms of neurological deficit.
Help
If you have problems with the call and you don’t know how to solve them, ask our specialists questions. Lawyers working on the site provide legal assistance, provide valuable recommendations and clear answers on any topic related to the army.
The development of neoplasms in tissues always causes internal concern, since there is a high probability that it is of an oncogenic nature. Even if doctors have determined that a benign cyst appears in the form of a tumor, everything possible must be done to stop its development, get rid of it, or maintain it at its current stage.
Along with its apparent harmlessness, a cyst can cause irreversible functional changes in the body. As it develops and increases in size, a bubble of fluid can interfere with the normal blood supply to neighboring organs, which often leads to necrosis or hemorrhage. Therefore, young men with a similar diagnosis try to protect themselves from provoking environmental influences.
In particular, the question arises: “Do they enlist in the army with a cyst?” It is known that military service takes place in a slightly different mode, which cannot but affect the condition of the body as a whole. It is not uncommon for physical activity to cause a relapse of a latent disease. Today, much attention is paid to the health of conscripts. If the disease is diagnosed in advance, then all deferments provided for by law will be provided to the young man.
But we should not forget that members of the expert commission must attest to the diagnosis already made, but are not required to find and define the disease. Consequently, the ranks of the Armed Forces are still filled with conscripts who are not even aware of the hidden and asymptomatic illness.
Classification of neoplasms
Tumors, which are usually benign, are classified based on location:
- Liquor retrocerebellar cyst - located deep in the brain, containing liquid exudate. It often appears as a result of damage to the skull and intracranial formations, operations, and cerebral hemorrhage.
- Arachnoid retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst - forms more often, in contrast to cerebrospinal fluid cyst. It is formed on the surface of the hemispheres of the main organ of the central nervous system and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Most often diagnosed in childhood due to intracranial pressure, inflammation, brain and cranial injuries.
Treatment options depend on the location of the retrocerebellar cysts. Moreover, the following subtypes of cystic formations are distinguished:
- Congenital (primary) - appears in the fetus during embryogenesis.
- Acquired (secondary) - occurs as a result of damage to brain structures, traumatic brain injury.
A retrocerebellar tumor forms in affected areas of the brain. To determine the type and parameters of the anomaly, the patient needs to undergo an examination.
Kidney pathology
Whether someone with a kidney cyst will be accepted into the army depends on the functioning of the organ. If he is not injured, then the cyst and the service are compatible in this case. Single formations with a diameter of up to 60 mm do not pose a threat and are considered benign. Filled with serous fluid, less often with blood or renal exudate.
If you had to deal with polycystic disease (numerous formations), the situation may turn out in favor of the conscript and you will not have to serve. The fact is that this is a more dangerous disease, characterized by damage to the liver by watery formations in several areas at once.
At first it is also asymptomatic, but later it provokes pain in the lower back, heaviness in the side, nausea, headache, dry mouth. Leads to disruption of excretory function. Serious disorders of excretory function and renal failure are a good reason for receiving category “D”, and the usual course of the disease obliges the commission to assign category “B”.
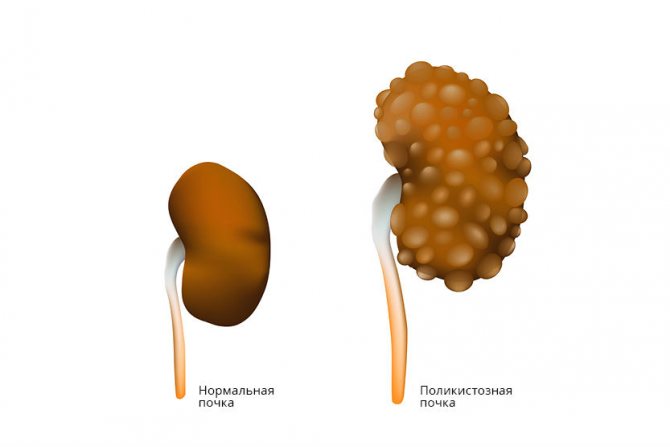
Polycystic kidney disease is dangerous due to the development of renal failure. A diagnosis may be a reason for complete exemption from military service or enlistment in the reserves.
A single education can also be considered as a reason for exemption from the army if a serious renal disorder is detected. In any case, the conscript is sent for a number of additional examinations:
- MRI;
- CT;
- Ultrasound;
- emergency urography;
- angiography.
A number of other procedures are possible, which will be notified by the urologist or nephrologist, taking into account the individual situation of the patient. After entering the military with a kidney cyst, a recruit can request a commission. But while in the army, this is difficult to achieve, so it is recommended to confirm diseases during a medical examination.
Symptoms
Symptoms are determined by the location, size and type of retrocerebellar cyst. Progressive cystic formations make themselves felt with characteristic signs, but tumors that have stopped growing are asymptomatic and are discovered by chance, for example, during a routine examination.
The growth of retrocerebellar formation is caused by autoimmune factors - hemocirculatory dysfunctions (hemodynamic problems), infection, neuroinfections, inflammation, problems with metabolic processes.
The following symptoms indicate a pathological process in the brain. The faster the retrocerebellar tumor progresses, the more severe the symptoms. Sometimes more than two signs are present:
- severe headaches;
- pressure on the skull;
- painless pulsation in the head, tinnitus;
- intracranial hypertension (high blood pressure);
- weakness, fainting;
- hearing loss, decreased visual acuity;
- hand tremors;
- numbness of the limbs;
- motor activity disorders;
- convulsions, epileptic seizures;
- ataxia - impaired coordination of movements (with retrocerebellar cyst of the cerebellum).
In case of persistent dysfunctions and the presence of multiple signs, it is necessary to urgently visit the neurosurgery department in order to avoid danger that threatens health and life.
Symptoms
A mandibular cyst may not manifest clinical symptoms for a long time. Signs of pathology become noticeable with increasing formation, development of the inflammatory process, and deterioration of the condition. The main signs of a cyst are:
- the appearance of pain;
- redness of the gums;
- the occurrence of swelling in soft tissues;
- formation of purulent accumulations;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of general symptoms of malaise - weakness, fatigue, headache, drowsiness;
- deformation of the jaw bones;
- swelling of the jaw;
- the appearance of sinusitis, exacerbation of its symptoms.
Symptoms of a mandibular cyst should not go unnoticed.
Causes of the disease
Most often, a retrocerebellar tumor is formed due to disturbances in intrauterine development or appears as a result of difficult childbirth. With a congenital anomaly (as well as with an acquired one), instead of healthy tissue, a cavity is formed, filled with cerebrospinal fluid or protein fluid from the serous membranes.
Most often, a retrocerebellar tumor is formed due to disturbances in intrauterine development or appears as a result of difficult childbirth.
Secondary retrocerebellar neoplasm is diagnosed as a result of the following pathologies:
- hemodynamic disturbance;
- damage to the skull and brain structures;
- brain surgery;
- infections, inflammations.
Scientists hypothesize that the presence of a retrocerebellar cyst is often due to a hereditary factor—close relatives are diagnosed with the same disease. In this case, the primary cystic formation rarely progresses and does not interfere with normal life activities. An exception is if, in addition to the retrocerebellar formation, organic damage to the central nervous system is noticed.
Provoking factors
A neoplasm of this type can appear without obvious reasons, which significantly complicates its diagnosis. The factors that provoke its development are quite diverse. These include:
- circulatory disorders;
- concussions, head injuries;
- inflammatory processes caused by infectious influence;
- serious adverse changes in the brain;
- surgical interventions performed on the brain;
- previous stroke;
- genetic predisposition;
- birth injuries, negative effects on the fetus of medications taken by the mother during pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalances in the body.
People with the above pathological conditions are at risk. The high probability of cyst formation requires regular monitoring by a specialist. It is necessary to visit him at least once a year to minimize the risk of unexpected development of this disease.
Diagnostic methods
For an accurate diagnosis of retrocerebellar formation, you should consult a neurologist. When diagnosing, the doctor relies on the patient’s anamnesis and complaints. However, symptoms are not absolute proof of a retrocerebellar cyst, so specialists examine the patient using the following methods:
- MRI of the brain with contrast - determines the location, parameters, structure, differentiates between benign and malignant formations.
MRI of the brain.
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the head and neck excludes cerebral circulation disorders.
- Ultrasound of the heart - detects disturbances in heart rhythm, determines the presence or absence of heart failure.
- Blood clotting test.
- Determination of cholesterol concentration in the blood.
- Study of markers of autoimmune diseases.
- Puncture of cerebrospinal fluid - to identify neuroinfections.
Psychological problems
It is also important to remember that the premature loss of a large number of teeth can provoke the patient to develop not only physiological, but also psychological problems. That is why one should not ignore the formation that has arisen and its minimal manifestations.

Features of therapy
When diagnosing a retrocerebellar cyst, the patient is registered at a dispensary and the progression and severity of symptoms are monitored. If the tumor parameters do not change, there are no characteristic symptoms, there is no need for surgical intervention - only observations and conservative methods are sufficient.
Drug therapy
Therapeutic measures will only help at the beginning of the disease if there is no progress. Non-surgical therapy is based on the following areas:
- Treatment of arterial hypertension - drugs Berlipril, Captopril.
- Normalization of blood clotting with anticoagulants - Aspirin, Pentoxifylline.
- Reducing blood cholesterol levels.
- Improved blood circulation.
Homeopathy is effective only as a complement to the main treatment of the cyst. Alternative medicine also does not contribute to cystic resorption, but is used as a symptomatic aid.
In case of infection, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and immunomodulators are prescribed to increase the body's protective functions.
Surgery
If it is not possible to stop the cystic growth with therapeutic methods, surgery is prescribed. Before surgery, specialists assess the extent of the lesion and choose the most appropriate method, taking into account the location and parameters:
- Endoscopy - a special device is used to excise the formation and pump out liquid exudate.
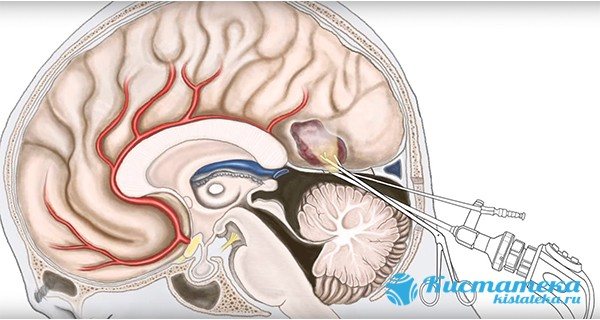
An operation to excise the formation and pump out liquid exudate from the brain.
- Creation of drainage - selected when there is a constant flow of fluid into the cavity.
- Craniotomy is a radical method that involves removing the cyst and adjacent tissues.
Attention! After surgery, patients need to rehabilitate - to normalize the functioning of the brain.
Prognosis, possible complications
In the absence of therapy, the patient's condition, if the tumor progresses, will worsen. As a rule, this leads to severe pain, which most often ends in rupture of brain tissue. The patient will begin to bleed, which is accompanied by inflammation, which ultimately causes death. This is the main danger of retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain.
However, even with proper treatment and surgery, the patient may experience complications. The prognosis of the disease is usually positive if the patient fulfills all the requirements of specialists. Complications may be the following:
Preventive actions
There are no special measures to prevent retrocerebellar cysts. To prevent the intrauterine formation of a neoplasm, the expectant mother should refrain from bad habits and take medications with caution.
To prevent acquired tumors, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- avoid damage to the skull, face and intracranial formations;
- treat infections promptly;
- maintain cholesterol levels;
- diagnose cerebral blood flow disorders in a timely manner.
Despite the fact that a retrocerebellar tumor is a benign formation, when the pathology develops, complications for the health and life of the patient are possible. The appearance of painful symptoms requires a visit to a specialist. The doctor will carry out diagnostic measures and prescribe effective treatment, thanks to which it will be possible to prevent negative consequences and completely recover.