The exact order of what follows what cannot be described.
First, the person’s heart and breathing stop, but this is not death and the person can be brought back to life. It is generally accepted that the brain dies within minutes after cardiovascular activity stops. Only in my practice was there a case when a person was resuscitated within 40 minutes and the brain was completely fine. Man has not turned into a vegetable. True, this is the only case in 20 years of work, and the patient had to learn all over again to talk, hold a spoon, walk and do everything else.
Often after resuscitation the brain dies, but the person’s body is connected to a ventilator. So a person can exist for a long time while the heart is working.
I remembered one patient who was kept on the device for about three months. It was quite a hot summer. Over these couple of months, it swelled so much that it doubled in size. All the employees had a dream during this time. And who, one wonders, needs such humanity?
The heart can be a donor organ and continue to live in another body for many years after the death of its original owner.
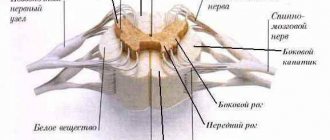
Cardiovascular activity and respiration are controlled by the corresponding centers (nuclei of the medulla oblongata). During the first 5-6 minutes of hypoxia, the cerebral cortex dies, and a little later the deeper structures of the brain and subcortical formations. This is evidenced by the results of resuscitation, the person is in a coma. Breathing is maintained, the cardiovascular system is working, the cortex is turned off. Plant Man. All primary resuscitation measures are considered appropriate within 5-10 minutes to maintain blood circulation in the brain, in the hope of starting the function of the heartbeat and breathing. The heart, to some extent, has the ability to operate autonomously, due to its unique nervous system: nerve ganglia, sinus pacemaker, pathways. Electrical stimulation can support short-term autonomous work of the heart when the brain is turned off. Heart tissue is more resistant to hypoxia, lack of oxygen. The principles of heart transplantation are based on this. Irreversible changes in the myocardium, without appropriate preservation and created preservation conditions, occur within the first two hours after brain death.
I will answer as a doctor who has been to intensive care and the morgue many times (where everyone ends up one way or another). So what is Death? It’s like a transition from one state to another, much like a chrysalis turns into a butterfly. Is such a simple idea really incomprehensible? There is a concept of “clinical death” - this is when the heart stops for 2 minutes at room temperature and blood (oxygen for stupid people) simply does not enter the brain; by the way, the human brain during life resembles mucus. And for stupid people it also stinks. What happens during brain death? Nothing special - it just begins to decompose from its own cells, like the rest of the body. It's destined to be so. As a doctor, I will say that your question is interesting, because it happens that first the brain stops “living” and only then the motor “heart”, and it happens that first the heart sends signals to the brain (by the way, the heart muscle - the myocardium - is the only muscle that contracts under the influence of impulses generated within itself!) This is called the atrioventricular node. For example, almost any muscle in the body is controlled by the brain, and the heart muscle is controlled by the myocardium - don’t care about your brain! The hand was strained, but the heart seemed to be separate. In other words, it’s difficult to say what comes first (for example, the chicken or the egg). But one thing I can say for sure is that there is no Death as it is understood. There is parting with loved ones or with THIS WORLD, but where the Soul is is not yet very clear. I would stupidly explain the concept of the Human Soul as a “flash drive” on which all the information about the life of any person is recorded - his visions, his emotions, his character, etc. For some, 1 MB is enough to “record” his life, while for others, 20,000,000 GB is not enough! Those who have 1 byte are in the trash, but those who have at least a couple of gigabytes will not die. But the brain and the heart are the same thing - they need blood. By the way, I brought people back “from the other world” several times and I assure you that they didn’t have any corridors or other bullshit. It’s just that the brain, during hypoxia for more than 3 minutes, works as if it were heroine - visions and other bullshit! Again, when any person dies, the brain, like a security structure, begins to work chaotically - some see one thing, others see another. Death in general is a mystery, just like Birth. For a Cosmos where there is emptiness, any person or thinking being is a unique one, and why do you think this Huge Cosmos needs you to be born and then just bury you? This is absurd!
If the brain dies, this means the onset of biological death. The death of the tissues that make it up is irreversible. Without neuron signals, the body will not be able to maintain heartbeat and breathing.
In the world, it is customary to distinguish several types of death - biological, clinical, brain death.
Clinical death is considered reversible. Degenerative processes begin to occur, from which a person can die, but there is still a chance to restore the vital functions of the body. If the outcome is favorable, you can fully regain your health and continue to live a full life. In this case, necrosis of tissues and organs does not occur.
Causes
Brain death can be caused by different reasons, but they trigger the development of the same pathological processes. Blood circulation is impaired, and this dysfunction is persistent. This provokes acute oxygen starvation, which causes metabolic products to stagnate in the tissues. Irreversible brain damage develops.
The main reasons are as follows:
- diseases, including inflammatory processes in brain tissue;
- injuries;
- circulatory disorders (hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke);
- multiple organ failure;
- poisoning (alcohol, lithium, drugs);
- tumor (cancer causes numerous tissue destructions);
- heart diseases, etc.
The phenomenon of vascular occlusion is extremely dangerous. At the same time, their patency is impaired, and oxygen starvation of the tissues occurs. Occlusion of arteries and veins that lead to the brain is especially dangerous. Often, pathological anatomy of the deceased reveals complete blockage of blood vessels. This can be a consequence of injury, disease and causes damage to neurons.
The brain stem may be damaged primarily or secondary. With a primary lesion, direct damage occurs (if there is a fracture of the base of the skull, the functions of the trunk itself are impaired). In case of secondary damage, the trunk suffers due to the resulting edema and dislocation syndrome. With swelling, the tissue begins to protrude strongly through the opening of the back of the head, due to which the trunk is excessively compressed, blood circulation stops and necrosis begins. This is why protecting the brain from swelling is so important.
All of the above reasons are considered extreme; they have an extremely negative effect on neurons. The brain stem and its cortex are primarily affected. The task of the trunk area is to maintain cardiac activity, breathing, control blood pressure, and the cortex is responsible for thought processes, consciousness, etc.
Cardiac arrest does not immediately lead to brain death, but everything happens very quickly. A person without blood circulation can live only a few minutes. 3 minutes without blood supply can lead to irreversible death of neurons, resulting in coma. If the cerebral cortex has died, vital functions will be lost and death can occur almost immediately.
The time that the body can survive without cardiac activity is influenced by a whole range of factors:
- age;
- general condition of the body;
- presence of diseases;
- the reason that caused this condition;
- ambient temperature, etc.
After just three minutes of oxygen starvation, neurons begin to die. This is an irreversible process, since dead tissue is not restored. In a healthy young person, brain death may slow down slightly. If the ambient temperature is low, the brain will die more slowly. If resuscitation is performed correctly at this time, the person can be brought back to life.
The consequences of circulatory arrest can be unpredictable. Sometimes a person wakes up from a coma, blood supply to the brain is restored, but it turns out that a significant part of the neurons have already died. If the brain dies, but the heart works, it will no longer be possible to return the victim to normal life. He can only exist, and is not even able to breathe on his own.
Inflammatory diseases
The consequences of meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain) include epilepsy, fluid accumulation in the brain, hormonal dysfunction, mental disorders, persistent dysfunction of the central nervous system and paralysis. How to recognize the symptoms of meningitis in adults? Symptoms are usually acute. A very severe headache, abnormal bowel movements, nausea, general weakness appear, the legs involuntarily bend at the knee and hip joints when the head is tilted to the chest in a supine position. Treatment should be carried out only in a hospital and under the supervision of specialists. Lack of therapy or attempts at self-medication can lead to a deterioration in the patient's condition.
How to recognize the symptoms of meningitis in adults? The first signs will allow you to identify the pathology in the early stages and begin adequate treatment in time. Usually there is a sharp change in body temperature, headache, numbness in the neck and difficulty turning or tilting the head, lack of appetite, and frequent vomiting without relief. Sometimes a pink or red rash appears, which disappears with pressure. How to recognize the symptoms of meningitis in children? The main signs are the same fever, headache, apathy and lack of appetite. The lymph nodes become inflamed, increased sensitivity to light, diarrhea, and pressure in the eye area appear.
How to recognize meningitis in children? The symptoms of a dangerous disease can be confused with a common cold or flu. In children under one year of age, meningitis can be caused by Haemophilus influenzae; the disease can appear after pneumonia or sinusitis. In young patients, pathology in most cases begins with fever. Therefore, it is imperative to show your baby to the doctor at the first alarming symptoms. The risk group includes children under five years of age.
Symptoms
The following symptoms indicate brain death:
- there is no consciousness, and this process is persistent;
- there are no reactions to tingling, stroking, handling, no tactile sensitivity;
- no movement of the eyeballs;
- the heart has stopped, as evidenced by a straight line on the ECG;
- there is urinary and fecal incontinence;
- breathing is impaired, the chest does not rise.
Determining whether a patient has died is an extremely important task. Doctors do not immediately diagnose death. Even if all of the listed signs are detected, the person is monitored in the hospital for up to 12 hours. Sometimes, although rarely, signs of brain activity may appear. If during this time the patient does not react in any way, there are no trunk reflexes, then biological death can be stated.
It is important how the brain dies, what triggered the death of neurons. If poisoning has led to such serious consequences, the patient should be monitored for at least a day. If the cause is TBI, the observation time is reduced to 6 hours. The specific decision must be made by the neurosurgeon. It is important that the doctor monitors the patient from the onset of this condition, then he will have a complete picture of events that will allow him to make the right decision.
The onset of biological death is determined exclusively by a neurologist. It is based on subjective and objective criteria. If signs of brain death are clearly identified, the person must be disconnected from life support. This difficult decision is especially difficult to make if the disaster happened suddenly. Often relatives are literally horrified by such a message. If a person is sick for a long time, his loved ones eventually become at least a little accustomed to the idea that their loved one will be gone. In any case, this decision is very difficult.
Additional examination
It is allowed to perform angiography and EEG if it is difficult to determine reflexes - in case of head injury, rupture of the eardrum. The final stage of diagnosis is panangiography, which confirms the stoppage of brain function.
Please note that it is quite difficult to diagnose the clinical death of a patient; he needs to be constantly monitored. Some doctors want to declare death as quickly as possible in order to transplant vital organs to donors. It is very important here that the doctor observes medical ethics and also does not make a mistake in his diagnosis. As a rule, the diagnosis is made by a neurologist or resuscitator with sufficient experience.
Read also: How to make it bad
Diagnostics
When diagnosing, the doctor must collect anamnesis. He must find out how long ago the patient fell into such a dangerous state, under what conditions he lost consciousness, and whether he had speech or motor activity. It is important to know what event preceded the loss of consciousness. An examination is carried out by a neurologist, he necessarily assesses the patient’s level of consciousness and checks his reflexes.
It is extremely important that the doctor excludes all those factors that can cause simulated brain death. It is sometimes caused by severe poisoning, including drugs. For this reason, a toxicological analysis is prescribed. It will help detect toxins or drugs that mimic the appearance of death.
Body temperature must be measured. If the temperature is below 32.2°C, it may distort the picture and show a false death. In this case, the person may be alive, but tests will show the opposite, since physiological processes literally freeze from the cold.
A blood test is prescribed that will help determine whether the metabolism is disturbed, whether there is hormonal dysfunction, and at what level the glucose levels are.
To correctly diagnose brain death, inpatients resort to instrumental research:
- encephalogram (EEG);
- contrast study of cerebral vessels;
- test with irritation of the eardrums (ice water is dripped onto them through the ear canal);
- apneic oxygenation test.
Oxygen starvation is extremely destructive for neurons, even if it is not long-term. Literally after a few minutes of complete lack of oxygen supply, tissues begin to die. The electroencephalogram in this case will show a zero line. This means that there is no brain activity at all.
Encephalography examines brain activity. In this case, the device registers biocurrents, their work is reproduced on paper in the form of curves.
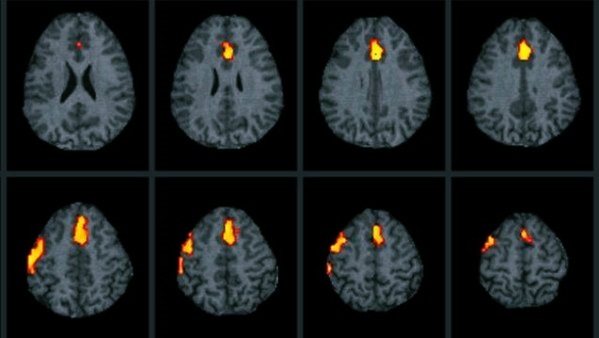
The diagnostic protocol also includes the study of cerebral vessels using a contrast agent. It cannot always be accomplished, as there may be financial restrictions, and sometimes there is simply no equipment. The essence of the test is that a contrast agent is injected, which enters the brain vessels through the bloodstream and identifies possible areas of necrosis. If the brain is dead, the substance does not enter its vessels. This is one hundred percent confirmation of death.
Apneic oxygenation involves temporarily removing the patient from a ventilator. The goal is to observe whether spontaneous respiratory movements have appeared. The monitor monitors the level of carbon dioxide in the blood. It is carbon dioxide that stimulates the body to produce breathing movements. If after 8-10 minutes breathing does not appear, and the level of CO2 in the blood jumps by 20 mm Hg. Art. higher than the original, we can definitely talk about death.
Light at the end of the tunnel
This experience is also often mentioned when describing near-death experiences. Living people experience similar sensations. During overload, pilots' blood pressure drops significantly and hypotensive syncope may occur, which is accompanied by temporary depression of peripheral vision. For 5 to 8 seconds, pilots observe the same dark tunnel that humans experience during an NDE.
There is an assumption that the tunnel occurs due to impaired blood supply to the retina. This state is characteristic of extreme fear and hypoxia, which, in principle, is close to dying.
If the body is accidentally discovered
If an ambulance team finds a victim without signs of life, doctors have no information how long he remains in this condition. In the absence of cadaveric spots, doctors cannot confirm in the field that biological death has occurred. In this case, resuscitation is mandatory.
Resuscitation measures include artificial ventilation of the lungs and closed heart massage. If there is bleeding, it is important to stop it so the victim does not bleed out. Damage to a large artery or head is extremely dangerous. If resuscitation measures are carried out correctly, a person can be brought back to life.
Meeting with the Dead
Many scientists believe that a person's near-death experience takes place in an intermediate state between sleep and wakefulness, and that the REM sleep phase is responsible for all mystical images and hallucinations.
To test this hypothesis, scientists studied 55 people who had had near-death experiences. It turned out that these people were more susceptible to sleep paralysis and associated visual and auditory hallucinations. Scientists have suggested that when in danger, such people are more likely to enter REM sleep, which is why they have vivid memories of their near-death experiences.
In addition, hallucinations are common in some brain injuries. For example, patients with Alzheimer's disease or advanced Parkinson's disease sometimes report ghosts or monsters, and after brain surgery, some patients see dead relatives.
How to tell your family
Recently, it has become common to resort to the help of a psychologist in such cases. It will help family members come to terms with their loss.
Making a decision to disconnect a patient from life support is extremely difficult even for experienced doctors. Relatives are always unprepared for such a tragic development of events, so they literally lose their minds. Relatives tend to believe that they can still try to do something. They are often asked to wait at least a few days. If there is accurate evidence of brain death, the doctor must find the right words to explain the current situation to the relatives.
According to the rules of bioethics, if brain death is definitely established, the patient should be disconnected from devices that support life processes. There is no point in expecting him to come back to life if all tests have confirmed the absence of neuronal activity. This will be a humane decision.
Relatives should definitely ask what diagnostic research methods were used. The doctor must show a document confirming the established brain death. Only relatives have the right to decide to disconnect the victim from life-sustaining devices. The doctor’s task is not to succumb to emotions, but to make the right decision based on the specific results of the patient’s examination.
It is important to exclude the human factor and rely only on test results.
How long to keep the victim on life support is decided individually in each case. After a person is disconnected from the devices, Lazarus syndrome may occur. It consists in the fact that the deceased experiences individual muscle twitches. The head may turn involuntarily, the person may bend an arm or leg. It even happens that an already dead person arches. This is the result of contraction of the back muscles. It is important that the doctor warns the patient’s relatives in advance that such manifestations are possible. This does not mean that the victim comes to life.
Awareness of one's own death
One of the most common experiences is the awareness of one's own death. However, this feeling has also been experienced by living people with Cotard's syndrome (walking corpse syndrome).
A striking example is the case of a 24-year-old female patient in a London hospital. She believed that she had died of a cold and was in heaven. After a few days, the mania began to subside and then disappeared completely.
This syndrome is associated with dysfunction of the parietal lobe and prefrontal cortex of the brain. It is observed after head injuries, during the advanced stages of typhus and multiple sclerosis.
Consequences
Brain death does not always lead to biological death. Sometimes medical intervention can save a life, if such a condition can be called that. In fact, after brain death, only certain vital functions can be maintained. The consequences of total neuronal death are terrible, this is complete dementia. Any vital indicator is so low that the body cannot cope without the support of devices. Such people are no longer able to continue living a full life. They live like plants and can die at any moment.
Death of brain cells (atrophic changes) - what is it?
The death of nerve and other brain cells with the breakdown of connections between neurons is called brain atrophy. The process is detected in the cortex, subcortical and other areas. The patient’s personality disintegrates completely, a phenomenon that leads to the impossibility of rehabilitation.
Serious pathology is accompanied by irreversible damage to the nervous system - this is the cerebral form of the disease. With this disease, there is a decrease in the thinking organ, which loses the ability to perform all necessary functions.
Brain atrophy conditions are most often found in older patients, especially women.
What is brain atrophy
An irreversible disease in which cells consistently die and neural connections are disrupted is brain atrophy. The initial stage of the disease has only subtle symptoms, visible only to loved ones.
This is the appearance of apathy, lack of goals in the sick person, instability of emotional states, lethargy. Some experience immorality or increased sexual activity.
The gradual death of cells in the brain leads to the decline of mental abilities.
Atrophic changes may be similar to senile changes in behavior, but the latter do not lead to dementia. The death of cells and nerve endings is pathological. This leads to changes in the structure of the frontal lobes, hemispheres and other parts of the main thinking organ of a person. The convolutions are smoothed out, its volume and weight are reduced.
The stages of the disease, as well as its types, differ depending on the location of the pathology. So subatrophy leads to global death of neurons.
After all, this term refers to partial local lesions that predetermine such degradation.
The cortical and subcortical varieties also require timely action, as they can develop into serious disorders of speech and thinking abilities.
Degrees of the disease
The international classification distinguishes different degrees of brain atrophy. Symptoms vary depending on the stage of the disease.
The first degree is observed with minimal changes: memory impairment, difficulty performing complex mental tasks. Sometimes there are complaints of dizziness, and emotional instability is observed.
Symptoms are mistaken for overwork, the effects of stress, or age-related factors. With grade 1, the patient is able to work, but the brain atrophies, and the condition progresses rapidly. Timely diagnosis is very important. After all, the development of the disease can be stopped.
Sometimes life expectancy depends on it.
The second stage is characterized by aggravation of the symptoms of the first. When solving mental problems, hints are required.
Commutative properties deteriorate: a person develops irritability, lack of restraint, and speech intonations change.
Neurology manifests itself in the form of movement disorders, lack of coordination, and lack of self-control. An example is generalized cerebral atrophy of the brain, degree 2.
The third stage is uncontrollability with manifestations of psychosis. Unmotivated actions appear, morality is lost. These are moderate atrophic changes in the diseased brain - the beginning of a decrease in working capacity, the appearance of difficulties in social adaptation.
The fourth stage - severe atrophy is characterized by loss of response to external stimuli, the central nervous system is affected. Disorders are observed in gait, speech, and the ability to perform simple actions is lost. The psyche is unstable: changes in states of excitement, apathy.
Subsequently, the personality is completely destroyed. Systems and vital functions fail: urinary incontinence, swallowing reflex disorder. The ability to work, self-service, and contacts is absent. The patient needs systematic monitoring; he is placed in a psychiatric institution.
Types of brain atrophy
Brain atrophy also varies with respect to the places of its manifestation and with lesions of specific areas of the nervous system. Let us consider cases of localized pathology and associated disorders of mental abilities, behavior, and personality.
Reanimation
The consequences of brain death are irreversible. Just because a person is unconscious does not mean that he needs to perform resuscitation measures (ventilation, cardiac massage).
Cardiac massage is strictly contraindicated if the victim’s heart is beating, even abnormally. In this case, massage can, on the contrary, interfere with the correct contraction of the heart muscles.
Mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose breathing, as well as chest compressions, are performed only if there is no heartbeat. Such events can save a person's life. If you ensure the supply of oxygen to the body and improve blood circulation, irreversible necrotic changes will not occur. Body functions can be completely restored.

If a pregnant woman is injured, it is important to monitor not only her vital signs, but also the condition of the fetus. The patient must be taken to the hospital as quickly as possible, since the child may die due to injury and stress.
It is extremely important to thoroughly master resuscitation techniques. Any of us can master them and, if necessary, save a person’s life.
Why is oxygen so important?
Of the total body weight, gray matter occupies only 2%, but at the same time, for full-fledged work, it consumes 20% of all gas entering the body.
Without oxygen, the brain will not be able to do its job. Glucose is needed to perform any activity, such as the neurons that control all body functions. Without oxygen, cells will not be able to produce this substance and subsequently convert it into the necessary energy.
If you deprive the brain of oxygen, the cause of its death will be the inability to nourish the cells, because there simply will not be energy (glucose) for this.
Controversies and theories
Numerous studies have been carried out, the results of which were the statement that the human brain continues to function for 4-6 minutes after the death of the body. Many scientists have argued about how a person sees and relates to his own death and still cannot come to a common conclusion.
Some doctors believe that the individual’s mind dies immediately, while others believe that it continues to work indefinitely. Recent testing has shown that after death, the work of the central nervous system does not stop. Therefore, in a state of clinical death, a person can be aware of what happened to him, because consciousness continues to function.
Modern medicine has reached a high level of development. New devices can keep the body in working condition (pumping blood and oxygen) for years. Therefore, a reasonable question arose: how long does the brain live after death, and what can be considered death in general? Its main symptom is the death of neurons, which leads to the loss of the individual’s personality.