Viral infections of the spinal cord have a common name: myelitis. Experts distinguish between primary and secondary myelitis. In the first case, the disease is most often caused by neurotropic viruses . But in the second, much more common case, common infectious diseases are to blame: influenza, typhoid, measles, etc.
The disease begins when infectious agents and their toxic secretions begin to penetrate through the blood and lymphatic vessels into the spinal cord. They cause inflammation and dystrophic changes. Viral infections can affect the spinal membranes, as well as nerve roots and nerve trunks.
Symptoms and signs of spinal cord diseases
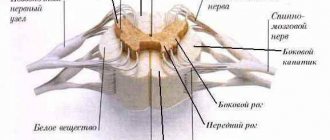
Spinal cord diseases have many symptoms. This organ is divided into specific segments that communicate with a specific pair of nerve endings. Each such pair is fully responsible for the functioning of certain organs. The fibers of the gray matter are crossed, it is for this reason that the pathology on the left side is a direct violation on the right.
Spinal cord tissue consists of two elements: gray matter (nerve cells) and white matter (processes). Its length is approximately 45 cm, it regulates all functions of the body, and its work occurs through the transmission of impulses.
Symptoms may vary in severity. The mildest of these are dizziness and nausea, as well as muscle soreness, which appears periodically. Depending on the intensity of the sensations, the condition may worsen.
Frequent and dangerous signs are considered to be motor disorders, that is, limitations of movement with complete or partial paralysis. This is accompanied by increased tone in muscle tissue. Usually such violations are symmetrical, but in some cases there may be exceptions.
Sensory impairment depends on the location of the disease and its degree. It can be superficial, temperature or painful. Autonomic disorders are accompanied by high fever and severe sweating. At the same time, metabolism is disrupted, the nature of stool and urination changes. When the nerves are pinched, the pain symptoms go to the hands. If the lower back is affected, pain will be felt in the lower extremities.
In addition to the main symptoms that accompany the disease, it can be expressed in:
- uncontrolled bowel movements;
- muscle soreness;
- muscle atrophy.
Selectivity is the main characteristic of viruses
A characteristic biological uniqueness of any viral agent is the inability to reproduce outside the cells of other organisms. The main property of the virus is selectivity. This means that the virus gets inside only a specially selected cell, organizing a factory in it for the production of its own kind.
Any cell is not suitable for the existence of a viral agent - in order to do evil, the virus needs its own specific cell.
For example, the virus that causes hepatitis can live and multiply exclusively in liver cells, the polio virus can do evil only in the cells of the spinal cord, the measles virus - in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract, etc. The selectivity of the virus also means that it is only capable of causing specific diseases in certain species. For example, HIV, the most terrible virus discovered at the end of the 20th century, is deadly for humans, but does not pose any threat to the family’s beloved pet, the dog Barbos. Conversely, the virus that causes Carré's disease (canine distemper) is incredibly dangerous for Barbos, but completely harmless for humans. However, there are exceptions to this rule due to the fact that some cells of different biological species are similar to each other. In such cases, a wide variety of animals can be targeted by the virus. The most striking and terrible example is the rabies virus.
Fortunately, the history of medicine can boast of examples of very successful fights against terrible viral agents. A typical example is the blackpox virus. This terrible disease alone in the 20th century (!) claimed the lives of about 500 million people, which prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to conduct a global campaign to eradicate this terrifying infection. As a result, in 1980, at the official WHO Assembly, the complete elimination of the smallpox virus was announced, and the last case of natural infection was recorded in Somalia back in 1977.
Brain tumors
Absolutely any neoplasms in the spinal cord are dangerous, so greater importance is paid not to malignancy, but to the location of the tumor. Typically, three groups of such formations are distinguished: extradural, intradural and intramedullary.
Extradural ones are the most dangerous and progress faster than others. They appear in the vertebrae or hard tissue of the brain. Intradural occur under the hard tissue of the spinal cord membrane. Intramedullary are located in the brain itself.
Tumors are treated only with surgery, which is not always successful. Restorative therapy is prescribed only after successful surgery, otherwise it will be ineffective.
Cauda equina syndrome
A homogeneous symptom complex is characteristic of damage to the cauda equina of the spinal cord. The disease can develop due to exposure to the following provoking factors:
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Traumatic injuries.
- Growth of neoplasms.
- Spinal deformities.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- Painful sensations in the sacrum and lower back. They often radiate to the groin and lower extremities.
- Increased sensitivity (over time it changes to numbness).
- Paresthesia.
- Muscle weakness.
- Rapid onset of fatigue when walking.
- Anorgasmia.
- Erectile disfunction.
- Loss of feeling of fullness in the rectum and bladder.
Diagnosis of cauda equina syndrome is complicated by the fact that the disease has symptoms similar to those of other spinal cord diseases. To identify pathology, the following studies are prescribed: CT, MRI, lumbar puncture, histological analysis.
Treatment involves the use of both conservative and surgical methods. If urine is retained, catheterization of the bladder is performed. If the cause of the syndrome is a hernia, tumor, or abnormal development of the spine, surgical intervention is indicated.
Intervertebral hernia
The most common of all back diseases are herniated discs. Initially, a protrusion is formed, and only after a while a hernia occurs due to the rupture of the fibrous ring, which performs the fixing function of the disc core.
After the rupture occurs, all the fluid begins to flow out and, most often, it enters the spinal canal. If the disease affects the spinal cord, myelopathy (destruction of the substance of the spine) begins to develop.
There are cases when the disease does not manifest itself in any way, and the patient feels great, but when the spinal cord is involved in the disease, the following symptoms appear:
- pain in the affected area;
- change in sensitivity;
- loss of limb control;
- weakness;
- disruption of internal organs;
- pain extends from the lower back to the kneecap.
These signs appear when the hernia reaches a huge size. For treatment, therapeutic effects are used, using medications and physiotherapy.
Autonomic disorders ↑
These are the following violations:
- increase or decrease in skin temperature;
- increased sweating or dryness of a certain area of the skin;
- increasing or decreasing the formation of sebum in a certain area;
- violation of tissue trophism (because of this, bedsores and trophic ulcers form very quickly);
- stool retention or, conversely, involuntary bowel movement;
- difficulty or, conversely, voluntary urination;
- disturbances in the functioning of the intestines and stomach (decreased production of HCl, decreased production of enzymes).
Pain
As a sign of compression of the spinal cord - it occurs in the midline of the back, pain in the upper extremities - indicates pinching of the cervical nerves, in the lower - as a sign of radicular pain due to osteochondrosis, trauma or tumor of the lumbar region.
To better understand what disorders will result from damage to one or another part of the spinal cord, watch the following video.
Video: structure and functions
Non-compression neoplastic myelopathies
Radiation and paracarcinomatous myelopathy are considered diseases that are difficult to distinguish between. MRI shows severe swelling of the spinal cord, which is treated with radiation therapy.
Necrotizing myelopathy at the time of exacerbation simultaneously affects several parts of the spinal canal. The reason for this is severe cancerous growths, which are accompanied by inflammation. Patients may experience partial or complete paralysis, and possible pelvic organ disorders.
Carcinomatous meningitis arises from carcinoma. In some cases, it does not cause myelopathy, provided that there is no discrepancy along the nerve roots, which causes infiltration of the spinal canal and provokes acute compression.
Thrombosis of the anterior spinal artery
As a rule, this disease is detected in older people. Doctors consider atherosclerosis to be the most likely cause of the disease. Risk factors include: various types of injuries, neoplasms and recent surgical interventions.
Thrombosis of the anterior spinal artery is a pathology characterized by blockage of a vessel with a blood clot. In most cases, the focus of pathology is localized in the lumbar, cervical and thoracic regions.
- Muscle weakness.
- Slight deterioration in sensitivity.
- Loss of the plantar or Achilles reflex.
- Paresthesia.
Diagnosis of the disease involves laboratory tests, duplex scanning, MRI and radionuclide studies.
Treatment of thrombosis is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. Mild disease requires drug therapy. In the presence of a severe form of the disease, the doctor decides to perform surgical intervention. Surgical treatment methods: thrombectomy, bypass surgery, stenting, artery suturing.
Spinal cord infarction
The cause of a heart attack is often a severe disruption of spinal circulatory circulation, which results in a severe malfunction of the spinal cord, since blood flows to it with great difficulty. This can happen in any spinal region. The one that is more severely affected develops a heart attack.
Most often, it is very difficult to determine the true reason why a heart attack occurred. But the most common is the formation of blood clots in small blood vessels. They supply blood to the spinal cord even when damage to the extravertebral arteries occurs.
Most often, people over the age of 50 suffer from this disorder, and in patients under the age of 40, a heart attack occurs due to aortic pathologies and vasculitis.
The development of a heart attack occurs during the formation of thrombosis or at the time of aortic dissection. But it can also appear for other reasons - with arteritis and serum sickness. General ischemic infarction is often caused by impaired spinal circulatory circulation or myeloschaemia. When a heart attack occurs, several parts are affected at once.
The cause of a heart attack can be a minor injury, for example, during sports. In this case, it is caused by a microparticle breaking off from a herniated intervertebral disc.
Symptoms of spinal cord diseases are very diverse. Severe pain occurs in the back area, sensitivity, both pain and temperature, decreases. In some cases, bilateral flaccid paralysis of the limbs occurs. Signs of a spinal infarction are constant pain in the head, nausea and weakness, which are accompanied by fainting.
How is immunity developed?
Of course, the body cannot stay away from the atrocities of the virus and begins to actively fight it.
First, the body begins to produce special proteins - interferons, due to which cells become less susceptible to the virus. At the next stage, antibodies are produced that eliminate the virus and, accordingly, end the disease. Unfortunately, not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. During the time that antibodies are produced, the effects of the virus can be so destructive that severe consequences of the disease are inevitable. It also happens that a virus, having penetrated a cell, does not immediately provoke a disease. He “sits in ambush” and waits for the hour when the immune system weakens.
A virus capable of active reproduction can quite quickly destroy a captured cell. When the cell disintegrates, the virus enters the blood, where it is fully armed with antibodies. Therefore, it turns out that viral diseases last exactly as long as the body needs to form immunity, i.e. antibody production. And the time frame for the production of immunoglobulins is usually clearly defined and does not exceed 5-10 days. In this regard, when making a diagnosis, the doctor in most cases knows how long it will take for his patient to feel better.
Inflammatory myelopathies
Spinal cord diseases can activate the inflammatory process. This syndrome usually develops over several days or weeks. The most common cause is an infectious disease.
If myelitis worsens, the patient complains of pain in the back and severe weakness in the muscle corset, which develops very quickly. In addition, paresthesia may occur in the lower extremities.
When the spinal cord is infected by a virus, specific types of myelitis can occur. Herpes zoster is a common cause of the disease.
Another disease is arachnoiditis - an inflammatory process in the spinal cord and brain. It is he who affects the arachnoid membrane. There are many reasons for its appearance. These are diseases of various types and severity, injuries and inflammatory processes in the nasal sinuses. When prescribing treatment, the infectious source is first eliminated; for this purpose, antibiotics and various therapies are prescribed.
Spinal stenosis
The causes of this spinal cord disease:
- Mucopolysaccharidoses.
- Joint dysplasia.
- Kniest's disease.
- Rickets.
- Down syndrome.
- Various types of spinal injuries.
- Arthrosis.
- Forestier's disease.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Spondylosis.
- Ossification of elements of the ligamentous apparatus.
- Metabolic disease.
- The presence of scars and adhesions after surgical treatment.
- Ankylosing spondylitis.
- Hematomas.
Stenosis is a disease of the spinal cord characterized by the following symptoms:
Diagnosis of spinal cord disease involves radiography, MRI, contrast myelography and CT. Based on the research results, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen, which may include both conservative and surgical methods.
Chronic myelopathies
Chronic diseases can be localized in different areas and manifest themselves in different ways.
One common cause is spondylosis. It is dangerous because it can cause severe changes in the intervertebral discs. These disorders cause compression abnormalities in the spinal cord and nerve roots. It can be localized in the thoracic, cervical and lumbar regions.
Spondylosis causes salt deposition, which significantly narrows the canals of the spinal column and the openings between the vertebrae. Its complication is the formation of hernias between the vertebrae.
The disease itself is the next stage in the development of osteochondrosis and actively progresses with poor nutrition of the spine, injuries and physical activity. This disease spreads among the male population over 40 years of age. The key symptom is pain after exercise, hypothermia and sudden movements. In some cases, the movement of the spinal column may be limited.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the degree and symptoms of the spinal cord disease, but it is always comprehensive and aimed at slowing the course of the disease, relieving pain and symptoms, as well as preventing possible complications. They use massage, physiotherapy and medications.
Another chronic disease is lumbar stenosis. The disease causes a narrowing of the central canal in the spinal column, resulting in compression in the spine and nerve endings. Pathology is divided into two types:
- Congenital stenosis. Appears due to a narrow passage in the spinal canal and certain features of the vertebrae and their anomalies.
- Acquired stenosis. Caused by displacement of the vertebrae or their reduction, which occurred after an injury. The disease can cause tumors, disc protrusions, or hernias.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using MRI. For treatment, a conservative method is used, and in some cases, surgical intervention is possible.
Treatment ↑
Emergency medical care
Consists of the following activities:
- immobilization of the patient after spinal injury;
- providing him with access to air;
- relief from compression of his head, neck, chest or abdomen by clothing or objects.
If the injury occurred (even presumably) in the cervical region, the patient is placed on a backboard, a cushion is placed under the neck, and a cotton-gauze collar of the Shants type is placed on the neck.
Photo: Shants collar
Before laying, you need to put a soft bedding on the shield, but make sure that there are no folds on it, since bedsores occur very quickly in such patients.
Next, before the team arrives, you can give an Analgin tablet or another non-opiate pain reliever.
Drug therapy
In the first few hours after the onset of the disease, the following is administered:
- glucocorticoid hormones (Methylprednisolone, Solu-Medrol);
- diuretics (“Furosemide”);
- neuroprotectors (“Cerebrolysin”).
Further treatment is carried out based on existing disorders.
Surgery
Used when conservative therapy is ineffective or impossible.
Thus, treatment is mandatory in the presence of an operable malignant tumor of the spine or spinal cord.
For benign tumors and injuries, surgery is performed only in the following cases:
- spinal cord compression;
- severe pain syndrome that cannot be controlled with medication;
- blockade of cerebrospinal fluid pathways;
- with vertebral instability, which threatens further deterioration of the condition.
Features of patient care
Patients with spinal cord lesions require special care:
- it is very important to change your body position as often as possible;
- use anti-bedsore pads under the heels, sacrum, bone protrusions;
- massage the skin as often as possible;
- if possible (if the patient is conscious), breathing exercises should be started as early as possible;
- in the absence of contraindications, passive flexion of the limbs in the joints should be performed.
Arachnoiditis
This term refers to inflammation of the membrane surrounding the spinal cord. As a result, the process of formation of adhesions and cysts starts.
The main reasons for the development of arachnoiditis:
- Spinal injuries.
- Complications after surgery.
- Severe forms of stenosis.
- Contact of the body with the contrast agent. Doctors believe that myelography may be a trigger factor for the development of the disease.
- Infectious pathologies.
For quite a long time, the main symptom of the disease has been sensory disturbance. Over time, the following clinical manifestations occur:
- Weakness in the legs.
- Numbness of the limbs.
- Unusual sensations. For example, a person thinks that an insect is crawling on him or water is flowing down his leg.
- Cramps.
- Shooting pain that is most often associated with electric shocks.
Currently, there is no effective treatment for the disease. All measures taken are aimed solely at relieving pain and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Diffuse disseminated sclerosis
This term refers to a demyelinating disease of the spinal cord that poses a serious threat to life. It is characterized by the destruction of nerve fibers.
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- Viruses (influenza, Epstein-Barr, herpes, Coxsackie, etc.).
- Infectious pathologies (measles, rubella, mumps, chicken pox, pneumonia, etc.).
Clinical manifestations of the disease:
- Paralysis of the body on one side.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Slowness of all movements.
- Inability to evaluate the behavior of others.
- Hearing and vision impairment.
Diagnosis of the disease involves CT, MRI, blood and urine tests.
Treatment of the disease consists of administering medications, the active components of which relieve discomfort and help maintain the functionality of the body.
Syringomyelia
This term refers to a nervous and degenerative disease of the spinal cord that has a chronic course. The pathology is currently incurable. As a rule, it develops in young people and accompanies them throughout their lives.
Syringomyelia is a disease in which cavities form in the substance of the spinal cord. The mechanism of development of the disease is based on a congenital defect in glial tissue. After multiplication, pathological cells die, forming cavities. In this case, degenerative changes in the nerve fibers are observed. Over time, the cavities become larger and larger, aggravating the person’s condition.
Symptoms of spinal cord nerve disease:
- Impaired sensitivity.
- Paresthesia.
- Painful sensations of a dull nature. As a rule, they are localized in the neck, arms, chest and between the shoulder blades.
- Cyanosis and thickening of the skin.
- Even small cuts take a long time to heal.
- Deformation of bone structures and joints.
- Osteoporosis.
- Muscle weakness.
- When the cervical spine is affected, the eyeballs sink, the pupils dilate and the eyelids droop.
Diagnosis of pathology consists of the following studies: radiography, myelography, MRI.
At the initial stage of pathology development, irradiation of the lesions and treatment with radioactive phosphorus and iodine are indicated. If the patient has paresis of the limbs, surgical intervention is prescribed. During its implementation, cavities are drained, adhesions are removed and tissue is decompressed.
Myelitis
This is an inflammatory disease of the spinal cord, characterized by damage to its gray and white matter. Pathology can be either primary or secondary.
Depending on the causes, myelitis can be:
- Viral. Caused by the causative agent of influenza, rabies and pathogenic microorganisms belonging to the Coxsackie group.
- Infectious. Most often it develops against the background of purulent meningitis. Also provoking factors for the occurrence of infectious diseases of the spinal cord are the following pathologies: syphilis, measles, typhoid fever, brucellosis.
- Traumatic.
- Toxic. It develops against the background of prolonged contact of the body with harmful chemical compounds.
- Post-vaccination.
- Luchev. Develops during the treatment of malignant neoplasms.
- Acute idiopathic. In this case, it is customary to talk about the autoimmune nature of the disease.
Clinical manifestations of myelitis:
- General weakness.
- Muscle pain.
- Increased body temperature.
- Sensitivity disorder of the lower extremities, turning into paralysis.
- Retention of feces and urine or, on the contrary, their spontaneous release.
- Painful sensations in the back.
- Rapid formation of bedsores.
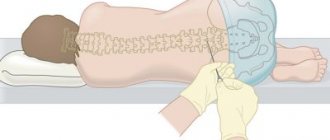
To identify the disease, a cerebrospinal fluid puncture is prescribed. The liquor is examined for the detection of viruses and bacteria.
Treatment of pathology directly depends on the cause that caused it. In any case, conservative therapy is indicated.