Symptoms
Tick-borne encephalitis can easily be confused with other diseases. At the same time, you should not hesitate when becoming infected, because... The course of the disease is very rapid. According to scientific data, the incubation period of this virus can last up to 14 days. During this period, a person may not even realize that such a dangerous and insidious virus has entered the body. After this period, the first symptoms appear:
- Muscle fatigue
- Headache
- Slight increase in temperature
- Mild feeling
These symptoms can be symptoms of almost any disease. Moreover, encephalitis is clearly not the first thing a person will think about. Most often, an infected person begins to be treated for a common cold, because... the symptoms are quite similar. Sometimes a person feels better, but after a short time the symptoms begin to recur and intensify.
By the way, according to statistics, some people overcome encephalitis precisely thanks to high-quality treatment for colds. This is explained by the fact that during treatment a person’s immunity is strengthened, which allows him to get rid of the insidious virus.
Unfortunately, about half of infected people cannot overcome encephalitis on their own, and 2-3 weeks after infection, the symptoms become stronger. Also, a person begins to experience disturbances in the nervous system, and the body temperature rises sharply.
What are the consequences and dangers of the disease?
Mild encephalitis can be cured in approximately three months. As for severe forms, this process can drag on for many years. Typically, in severe cases of the disease, death occurs in approximately 70% of cases .
In this case, complications may occur, overcoming which will be a significant part of working with the patient’s health during rehabilitation.
If the inflammatory process is in full swing
The consequences of encephalitis present can be so serious that they will lead not only to health problems in general, but also to disability.
Thus, in the acute period, danger may lie in wait from the endocrine system associated with damage to the hypothalamic region.
This, in turn, can affect a pathological decrease or, conversely, increase in appetite, respectively, sudden weight loss or excessive weight gain, constant thirst may be present, and cases of dystrophy are frequent.
But that’s not all: women experience menstrual cycle disorders. Often the disease causes damage to internal organs.
In the case of epidemic encephalitis, with its endocrine form, symptoms of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system may appear: drooling, excessive sweating, greasiness of the face.
Changes in the neurons of the substantia nigra in the chronic stage are overwhelmingly an irreversible process. Significant changes also occur in the cerebral vessels.
Damage to the subcutaneous region can provoke the development of tachycardia, asymmetry of blood pressure: its increase or decrease.
If you miss the moment and do not start treatment, the dangers of encephalitis present, such as damage to the subcortical nuclei, can lead to a disorder of the vestibular apparatus and impaired coordination of movements.
A person with the consequences of the disease can lie exceptionally straight, without looking away from one point. The slightest turn of the head, and in some cases the eyes, can lead to severe dizziness, often vomiting.
The most common consequences are mental disorders: they rarely manifest themselves as psychomotor agitation, in most cases, on the contrary, it is indifference to the environment, detachment, isolation, patients lead a sedentary lifestyle. In rare cases, hypersexuality manifests itself.
The most dangerous is the fulminant form of encephalitis: all symptoms develop extremely quickly: a sharp rise in body temperature, severe headache, almost instantaneous loss of consciousness and coma.
In this case, death occurs from bulbar disorders or heart failure in just a few hours, or at most in a few days.
Consequences of tick-borne encephalitis:
When it seems everything is over
After suffering from encephalitis, you should not think that everything is already over; the consequences of the disease can manifest themselves for a long time in the form of:
- impairment of vision and hearing;
- meningitis, headaches;
- enuresis;
- respiratory arrest;
- mental retardation;
- weak memory;
- mental disorders;
- general weakness;
- paralysis;
- violations of motor coordination.
Complications, in principle, can be avoided if you fully follow the recommendations of your doctor. The positive course of treatment can be aggravated by:
- alcoholism;
- incorrect treatment;
- pregnancy;
- physical and mental fatigue.
Why is this dangerous?
If immediate action is not taken, encephalitis can lead to impaired consciousness, paralysis and even death. It all depends on the area of the brain that was affected by the virus. The severity of the consequences is also influenced by a person’s age and health status: the elderly and people with weak immune systems are at risk. As for the fatal outcome, it all depends on the type of virus. According to statistics, some types of encephalitis lead to death in 20% of cases of infection. The virus that lives in central Europe is weaker and its mortality rate is about 5%.
It is important to understand that encephalitis can significantly worsen your health and make you disabled for the rest of your life. Neurological damage from this virus is not always reversible. Moreover, the range of such disorders is extremely wide and the development of each of them is different for all people. Therefore, you cannot hesitate and take risks with this virus; it is best to immediately consult a doctor.
Viral encephalitis
The therapy is complex and consists of etiotropic, pathogenetic, symptomatic and rehabilitation treatment. The etiotropic component involves the prescription of antiviral pharmaceuticals: for herpetic encephalitis acyclovir and ganciclovir, for arboviruses - ribavirin. In parallel, therapy with interferon and its analogues is carried out. It is possible to use specific immunoglobulin.
The pathogenetic component consists of the correction of vital functions (according to indications - cardiac glycosides, vasoactive drugs, oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation), the use of decongestants (mannitol, furosemide, acetazolamide), antihypoxants (ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, meldonium), neuroprotectors (hydroxymethylethylpyridine succinate, piracetam, glycine , scopolamine). Often there is a need to prescribe glucocorticoids, which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect. Symptomatic therapy involves the use of anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, valproate, diazepam), antiemetics (metoclopramide), and psychotropic drugs (neuroleptics, tranquilizers) as needed.
Restorative treatment involves vascular and neuroprotective therapy with the goal of the fastest and most complete restoration of cerebral structures and their functions. In the presence of paresis, massage and exercise therapy are mandatory components of rehabilitation; It is possible to use physiotherapy - electrophoresis, electromyostimulation, reflexology. In case of mental disorders, consultation with a psychiatrist is necessary with the implementation of correctional therapy, psychotherapy, and social adaptation.
Prognosis and prevention of viral encephalitis
Viral encephalitis can have a number of serious complications. First of all, this is cerebral edema and the occurrence of dislocation syndrome with compression of the brain in the brain stem, which can cause death. The development of cerebral coma threatens the formation of a vegetative state in the patient. The death of the patient may be associated with the addition of an intercurrent infection, the development of cardiac or respiratory failure. Against the background of encephalitis, the formation of epilepsy, persistent neurological deficit, intracranial hypertension, hearing loss, and mental disorders is possible.
In general, the prognosis of encephalitis depends on its type, severity, and the patient’s condition (Glasgow scale) at the time of initiation of therapy. With tick-borne, herpetic and lethargic encephalitis, the mortality rate reaches 30%, with St. Louis encephalitis - less than 7%. Japanese encephalitis is characterized by a high mortality rate and a large percentage of residual effects in survivors. Post-vaccination encephalitis usually has a favorable course. The exception is viral encephalitis, which develops after rabies vaccination according to the type of Landry's ascending paralysis and is accompanied by a risk of death due to bulbar disorders.
Measures to prevent transmissible encephalitis include protection from insect vectors, specific vaccination of the population of endemic foci and people planning to visit them. Prevention of the development of secondary encephalitis against the background of a viral disease is timely and adequate treatment of the infection, maintaining a high level of functioning of the immune system. Prevention of post-vaccination encephalitis consists of adequate selection of persons for vaccination, correct dosing and administration of vaccines.
What to do?
First you need to calm down and choose a method of action for a specific case.
You found a tick on your body
Doctors do not recommend removing a tick yourself if you do not know the appropriate technique. In such cases, it is recommended to go to the hospital immediately. After this, the doctor will remove the tick and send it for examination. You will also be asked to take tests. If the examination confirms the infection (the tick can carry various diseases), you will be given a referral to an infectious disease doctor who will prescribe individual treatment.
If you know how to remove a tick, then do not rush to throw it away. Doctors recommend taking the seized tick to the hospital for examination. Further steps are the same: if the tick was encephalitic, you will be referred to an infectious disease doctor.
You suspect encephalitis
In this case, you need to go to an appointment with a therapist, where you need to talk about your suspicions and symptoms. An experienced doctor will conduct an examination and determine whether encephalitis is truly suspected. If suspected, you will be asked to undergo tests and given a referral to an infectious disease specialist.
Concept of disease
The term encephalitis refers to the process of inflammation of the nerve cells of the brain. The development of this disease can be caused by various reasons, namely infectious, allergic, infectious-allergic, toxic.
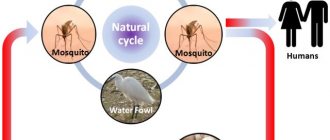
The most common source of the disease is a variety of viral infections. So, it is caused by herpes, viruses carried by mosquitoes and ticks, measles and a number of others. This disease is divided into primary and secondary encephalitis.
Speaking about the primary, which is also called independent, it can be noted that it includes enteroviral, herpetic, mosquito, tick-borne and epidemic encephalitis. All of these viruses attack directly the spinal cord and brain.
Secondary is a consequence of various types of diseases. These, among others, include: influenza virus, measles, osteomyelitis, toxoplasmosis, etc. Unlike the primary one, here the virus invades some other part of the body and affects it. Then it moves through the body, gradually reaching the brain and affecting it.
Also distinguished:
- polioencephalitis - affects the gray matter of the brain;
- leukoencephalitis - it affects the white matter of the brain;
- panencephalitis - it affects both white and gray matter.
In addition, this disease is classified according to the speed of its progression. So, it is divided into chronic, subacute and acute.
It should be noted that encephalitis and meningitis are two different diseases. But both of these infections can appear at the same time. Encephalitis viruses themselves rarely live for a long time, but they are quite capable of threatening human life.
Viral encephalitis is an acute form of the disease, which can be of either primary or secondary type. It affects the meninges of the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system.
It should be noted that encephalitis is more common in children than in adults. Moreover, it is characterized by greater symptomatic polymorphism. A fragile child's body is often more susceptible to a variety of viruses. In addition, secondary encephalitis is more common in children.
How to protect yourself from tick-borne encephalitis?
There is a certain set of recommendations for protection against tick-borne encephalitis.
- When going into the forest, try to wear a hat, high boots, long pants and a jacket. Tuck T-shirts, sweaters and shirts into your pants. In turn, tuck your pants into your shoes.
- Periodically inspect the clothing of both your own and those around you.
- Try to avoid tall thickets of grass and bushes. This is where ticks most often live, including infected ones.
- Use repellents. You can find many products against ticks and other parasites on sale.
- When you return home, take a shower and carefully examine your body. Pay special attention to the scalp and the areas behind the knees.
- After your walk, remove all clothes and wash them. The fact is that tick larvae can remain on clothing.
- Be sure to get vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis. There are many vaccines, both domestic and foreign produced.
These recommendations minimize the chance of contracting tick-borne encephalitis.
Prevention
For each type of disease, preventive measures are different. In order not to become infected with encephalitis from mosquitoes and ticks, you need to protect the surface of your baby’s skin while going for a walk with him in the park or outside the city. If there is a danger of epidemic encephalitis, it is necessary to disinfect the home and avoid crowded places.
After each visit to the forest, park or cottage, check the child’s body and clothes for ticks. Only female ticks attach and feed on blood. Males, having inflicted a bite, fall off and do not stick to the skin. An unpleasant sensation, itching, remains at the site of the bite and this cannot be ignored. The child needs to be shown to a doctor. It is possible to prevent secondary encephalitis through vaccinations. This can be vaccination directly against encephalitis, but also against measles, rubella, and chickenpox. Complications of these dangerous diseases occur more often than complications after immunization against them.
Prevention includes measures to strengthen the immune system. This is facilitated by proper nutrition, hardening, adherence to a daily routine, physical activity, and fresh air.
Privileged body
The brain is an organ that is remarkable in many ways [1]. The infinite complexity of the device, its functionality and the connection between our lives and its state attract the attention of researchers to the brain. The relationship between the brain and the immune system of our body is also special: the brain is an immune-privileged organ. Immune reactions that easily develop in other tissues (liver cells, muscles, fatty tissue) rarely occur in the brain. Along with the brain, the thyroid gland, testicles and some eye tissues, in particular the cornea, found themselves in such a special relationship with the immune system.
It has long been believed that the basis of the immune privilege of the brain is the presence of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The BBB is a complex of cellular and extracellular structures that separate the blood flowing in the capillaries from the neurons of the brain parenchyma. The cells of the vascular walls, the basement membrane on which they lie, and astrocytes participate in the formation of the BBB. The immune privilege of parts of the central nervous system was in good agreement with the extent of the BBB within it. The brain parenchyma is reliably protected by the BBB, and inflammatory processes (encephalitis) rarely occur in it. The choroid plexus, which produces cerebrospinal fluid, and the membranes of the brain do not have such cover, and their inflammation (choroiditis, meningitis) is much more common (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Structure of the central nervous system. The parts that are well protected by the BBB include the gray and white matter. Other components do not have this protection.
The brain has difficulty delivering activated immune cells to the cervical lymph nodes. Dendritic cells are responsible for working with antigens in the brain. In other organs, they recognize the antigen and then provide information about it to T and B lymphocytes in the lymph nodes. During inflammation in the brain, this process does not occur: dendritic cells do not migrate to the lymph nodes and do not present antigen. The immune response becomes localized and is regulated by dendritic cells in the brain parenchyma. If in other organs the cellular elements of immunity, after the presentation of the antigen, rush to the site of bacterial penetration [6], then with the development of inflammation in the brain parenchyma this does not happen. The brain has to rely on itself. A similar locality of the immune response is observed in the parenchyma, but not in the choroid plexuses and meninges.
Treatment Options
Rasmussen's encephalitis is a serious pathology that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. For any form of autoimmune encephalitis, an electroencephalogram, magnetic resonance imaging and tests are prescribed. The acute stage does not require such an approach, since a diagnosis can be made based on pronounced symptoms. After identifying the problem, immunostimulating drugs are used. They help slow down the development of dementia and severe speech impairment.
Advanced stages are not treated, and it becomes difficult for the body to tolerate antiepileptic medications. Degraded areas of the brain can be surgically removed.
At the beginning of the development of pathology, a combination of drugs against epilepsy with proper nutrition can alleviate the condition. The patient should focus on fatty acids and reduce the intake of proteins and carbohydrates. There are many essential substances in unrefined vegetable oils.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is considered a new treatment method. With its help, epilepsy is eliminated. They also resort to plasmapheresis and blood filtration. To alleviate the condition, people turn to hormonal and immunomodulating drugs.
04 September 2018
- 2983
- 2,7
- 4
The image shows changes in the metabolism of the basal ganglia and medial temporal regions in a type of autoimmune encephalitis
Currently, more and more attention is being paid to how immunity affects various processes in our body. Disturbed immune responses discovered in new studies become the missing link in pathogenesis. This stimulates the search for new drugs and other preventive and therapeutic effects. In this text we will discuss the special immune status of the brain - its isolation from systemic immune processes. In addition, let's talk about disorders that violate the immune sovereignty of the central nervous system - autoimmune encephalitis.